N209 - Head, Face, and Neck
1/71
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Normocephalic
term that denotes a round, symmetrical skull that is appropriately related to body size
a,b,d
Which of the following would require you to further evaluate the pt. head, neck or face?
a. “any time I cough or sneeze, I get a headache.”
b. “I can’t turn my neck to the left side.”
c. “I don’t ever experience dizziness.”
d. “I had a concussion about a month ago.”
Normal = round, symmetric skull; appropriate size in relation to the body
Abnormal = large, fixed masses; inflammation of hair follicles (folliculitis); sebaceous cysts; pain, ulcers, indentations, old scars
Which of the following findings on the skull are abnormal and which are normal?
round, symmetric skull
large, fixed masses
inflammation of hair follicles (folliculitis)
appropriate size in relation to the body
sebaceous cysts
pain, ulcers, indentations, old scars
microcephaly
abnormally small head
macrocephaly
abnormally large head
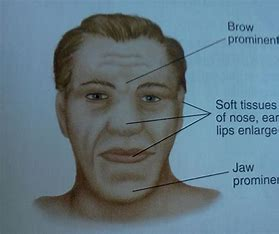
Acromegaly
= large, elongated bones, jaw, forehead, nose, & lips
possibly caused by a pituitary tumor bc of excessive secretion of GH
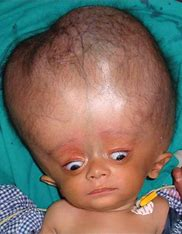
Hydrocephaly
= cerebrospinal fluid accumulation around the brain, causing the head to enlarge in babies
Causes downcast or “sunsetting” eyes
use shunts to drain fluid down brain to abdomen
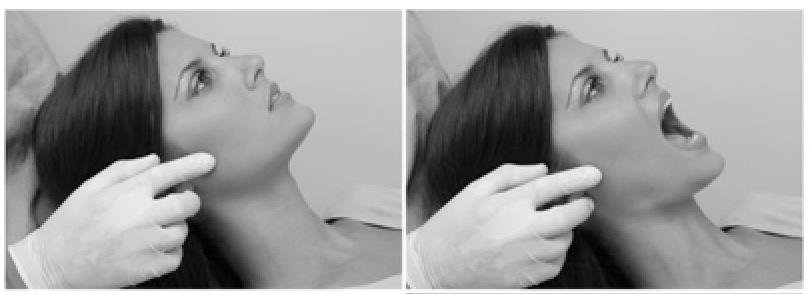
temporomandibular joint
normal findings = smooth movement with no limitations and tenderness
abnormal findings = crepitation (crackling), tenderness, limited ROM
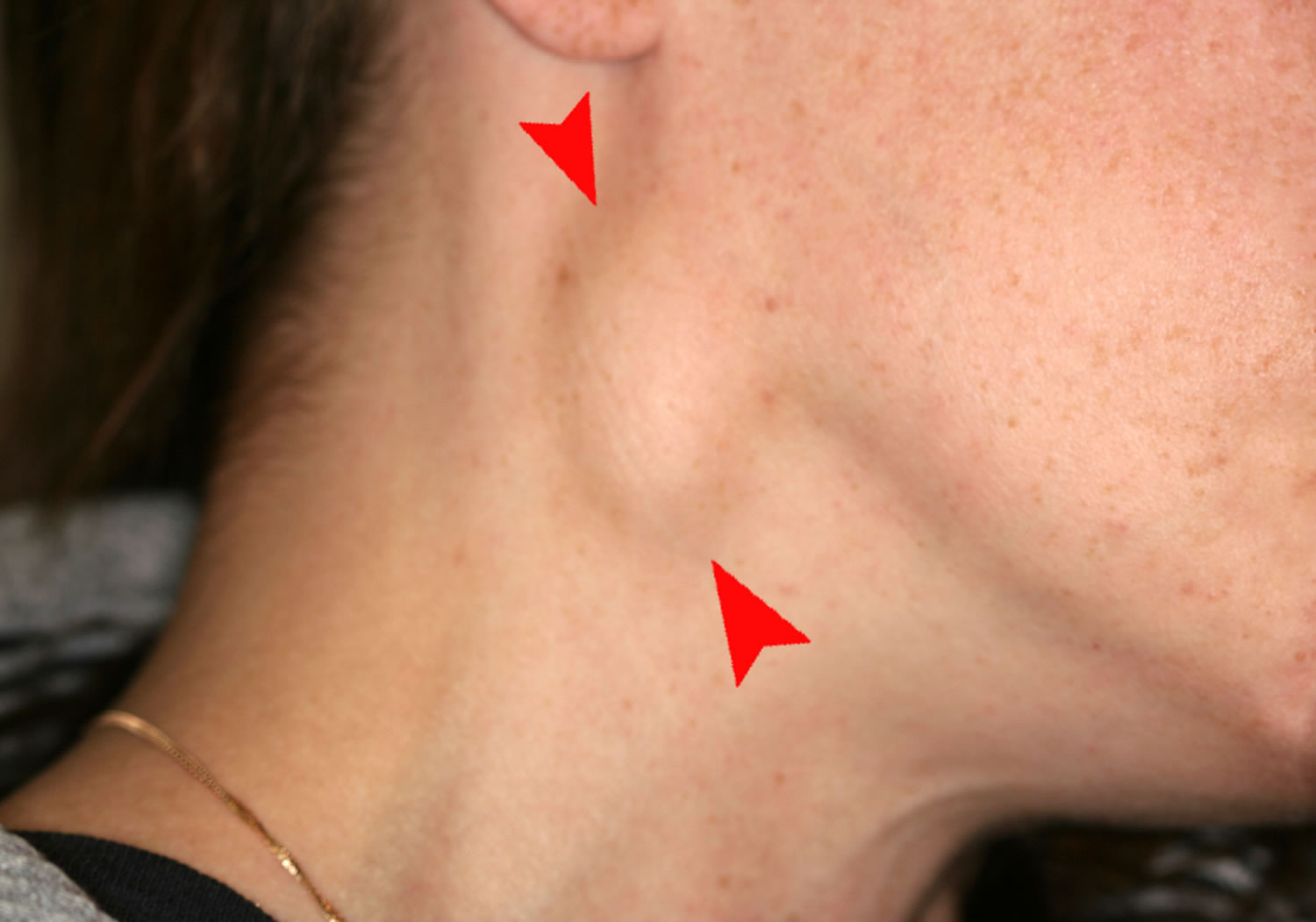
What is being palpated in the image? What is a normal finding? What is abnormal?
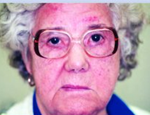
No, the face is asymmetrical.
Is this face a normal finding? why or why not?

Flat Facial Expression
fixed, nonmobile expression, shows no emotion
Labile
shifts rapidly b/t moods and facial expressions.
depressed or sad
withdrawn, turned down mouth, no eye contact
Eyebrows, palpebral fissures, nasolabial folds, sides of mouth
Where should you expect symmetry in the face?
Parkinsons Syndrome
= deficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine and degeneration of the substantia nigra
Immobility of features produces a face that is flat and expressionless
Fixed/staring gaze, elevated eyebrows
Cachexia
= a wasting syndrome associated with complex disease processes such as cancer, heart failure, AIDS, and COPD
Signs:
Severe weight loss
Loss of muscle
sunken eyes
Hollow cheeks
Fatigue
Muscle weakness
anorexia
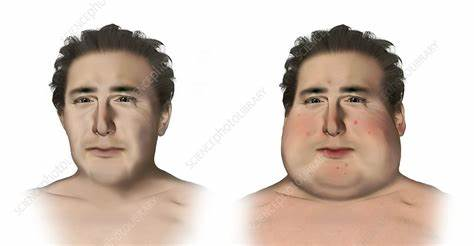
Cushing Syndrome
Caused by excessive secretions of ACTH and chronic steroid use.
Signs:
a rounded, “moonlike” face
prominent jowls (lower portion of cheek)
red cheeks
hirsutism of upper lip
lower cheeks & chin
acneiform rash on chest
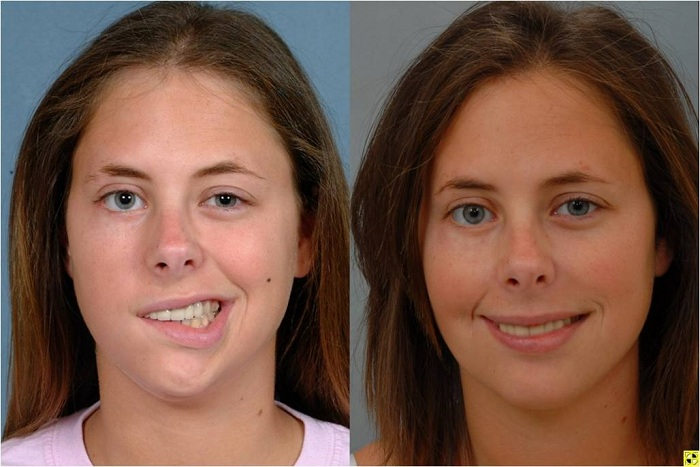
Bell’s Palsy
= a lower motor neuron lesion, producing rapid onset of cranial nerve VII paralysis of facial muscles
almost always unilateral
Most common cause of facial paralysis
Risk factors include:
Being exposed to herpes simplex virus type 1
Having diabetes
Being pregnant
Having had a previous episode of Bell's palsy

Stroke
= an upper motor neuron lesion; caused by a blood clot of a cerebral vessel
lower face paralysis (can still move forehead and close eyes)
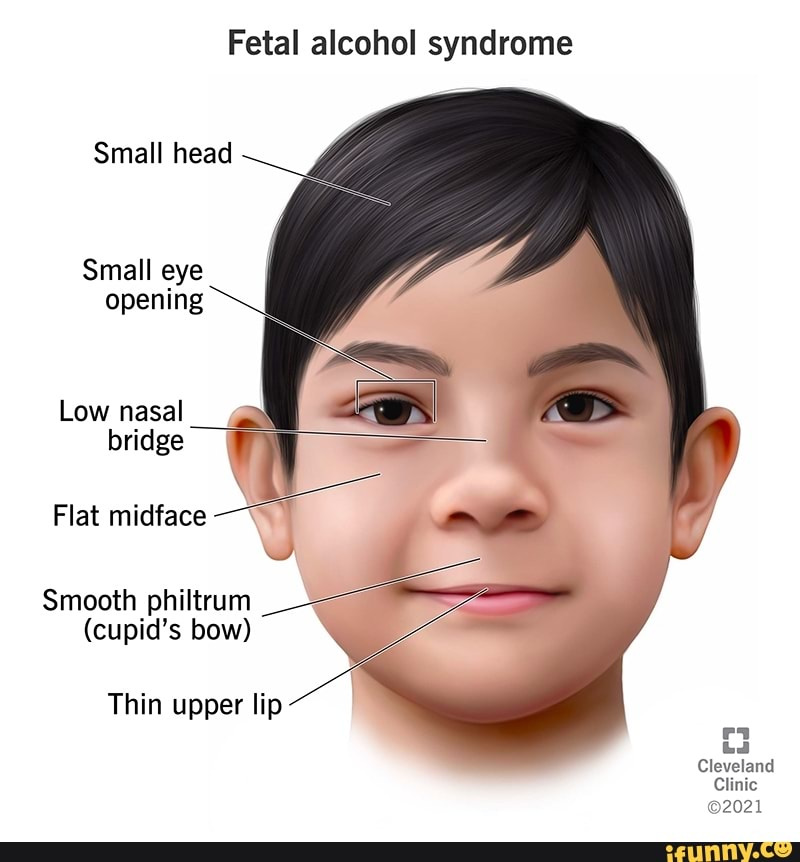
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD)
alcohol = a teratogenic to the developing fetus
can cause intellectual disabilities, birth defects, & changes in face and brain structures
Signs:
small, wide-set eyes
wide flat area between eyes
thin upper lip
upturned nose
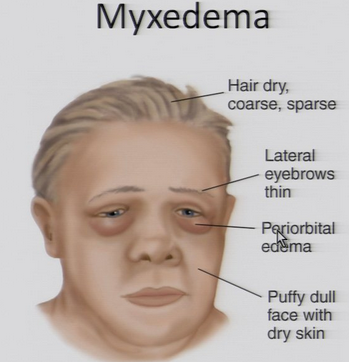
Myxedema
= a deficiency of thyroid hormone, meaning metabolic rate is reduced
caused by hypothyroidism
Signs:
dull skin
round, swollen face and eyes
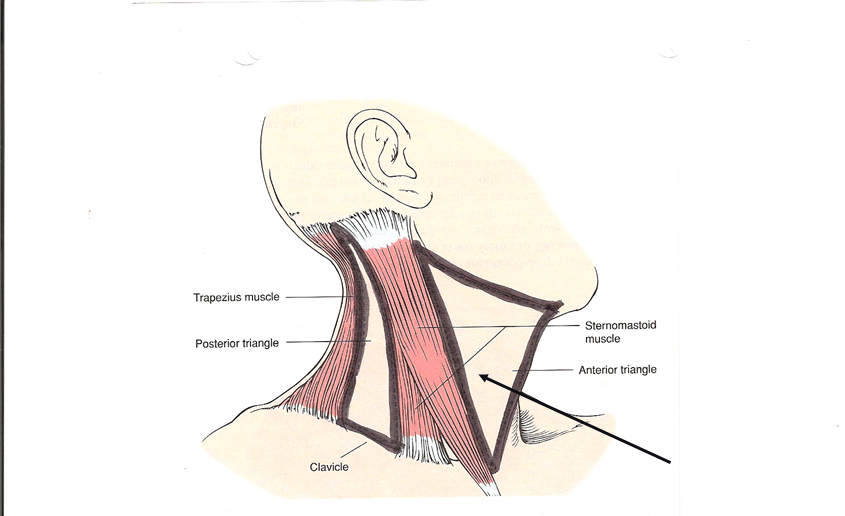
anterior triangle
Which triangle of the neck is this?
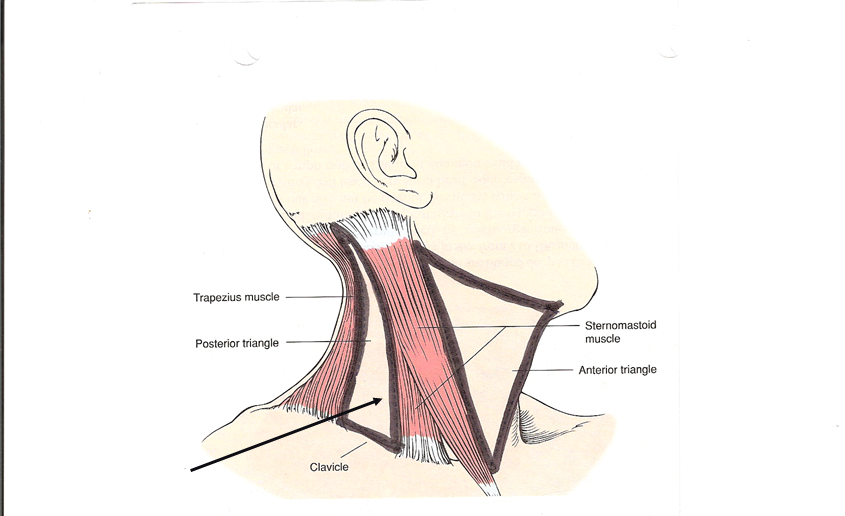
posterior triangle
Which triangle of the neck is this?
the nurse is in danger of cutting off both carotid arteries’ circulation to the brain
A nurse is palpating the neck on both sides at the same time. Why is this incorrect?
Torticollis
= a condition causing asymmetrical head or neck position (stiff neck, lateral flexion contracture)
Caused by:
neck injury
inflamed lymph glands
sinus, ear, and throat infections
tumors
drug abuse (i.e., acetaminophens & cocaine)

Cranial Nerve XI (Accessory Nerve)
supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
Holding hand on the side of the pt.’s face and have them push against your hand.
note the sternocleidomastoid muscle contraction and any lymph/gland swelling.
Have the pt. shoulder shrug against resistance of your hand.
How would you test muscle strength and the status of cranial nerve XI?
lymph nodes
size, shape, borders, tenderness/pain, consistency should all be noted when palpating _________ _______.
b.
Which Size/shape indicates a normal lymph node?
a. large, irregular
b. <1 cm or nonpalpable, round
a.
Which delineation indicates an abnormal lymph node?
a. confluent
b. discrete
a
Which mobility indicates a normal lymph node?
a. mobile
b. fixed
b
Which consistency indicates a normal lymph node?
a. hard
b. soft
No, normal lymph nodes are non-tender
Would a tender node be a normal finding?
Preauricular
#1?
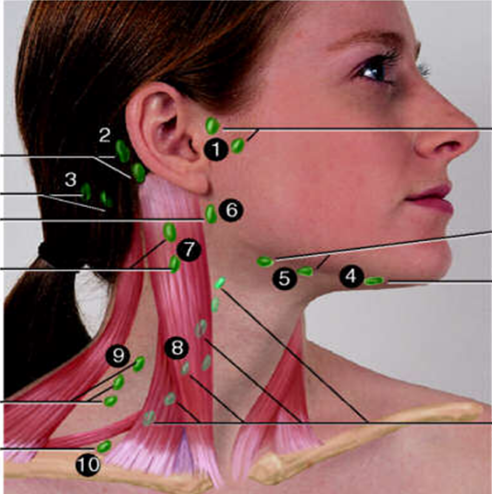
Posterior Auricular
#2?
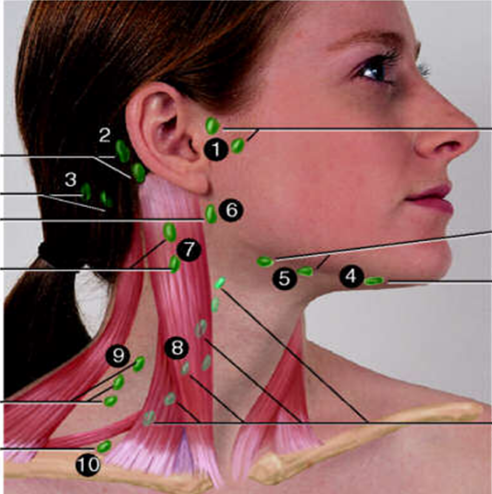
Occipital
#3?
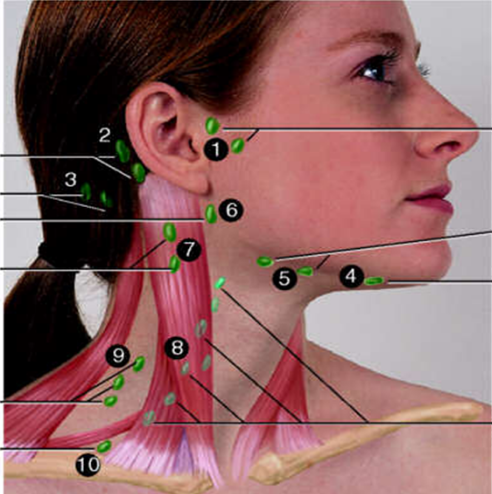
Submental
#4?
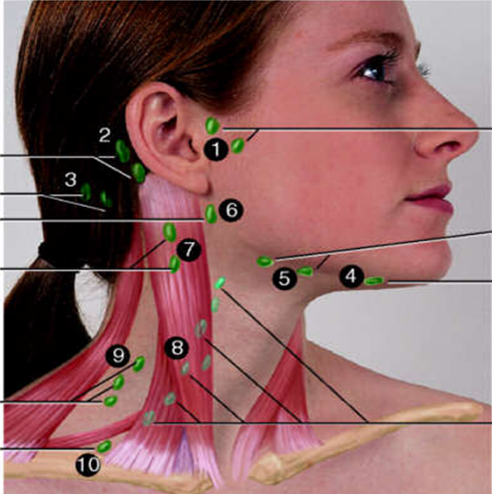
Submandibular
#5?
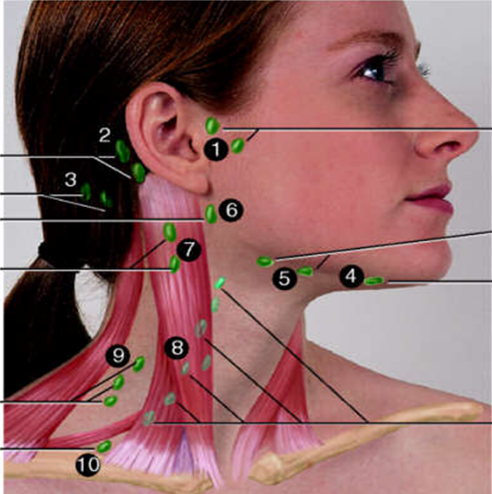
Jugulodigastric
#6?
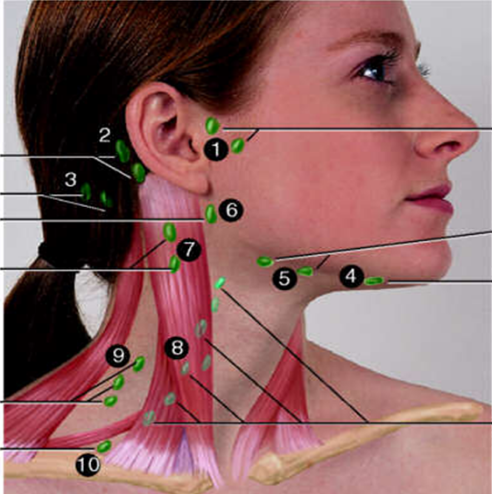
Superficial Cervical
#7?
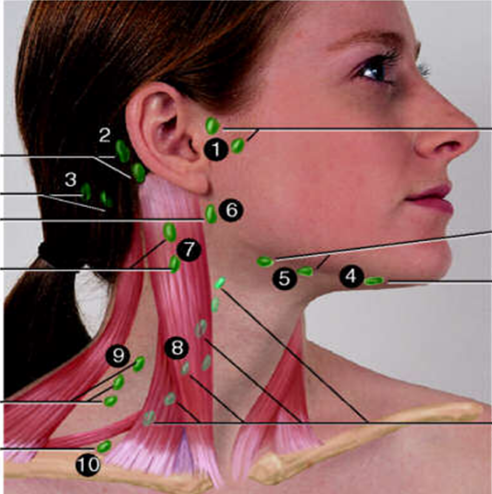
Deep Cervical Chain
#8?
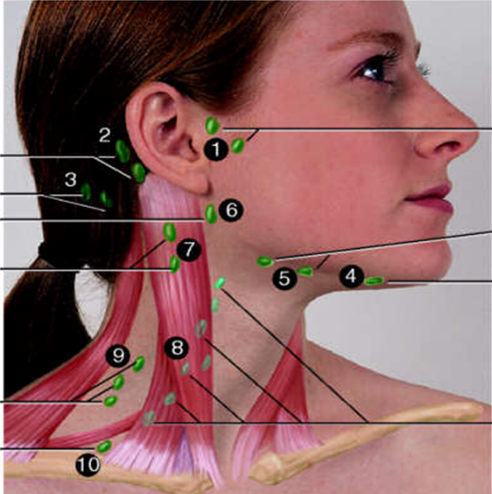
Posterior Cervical
#9?
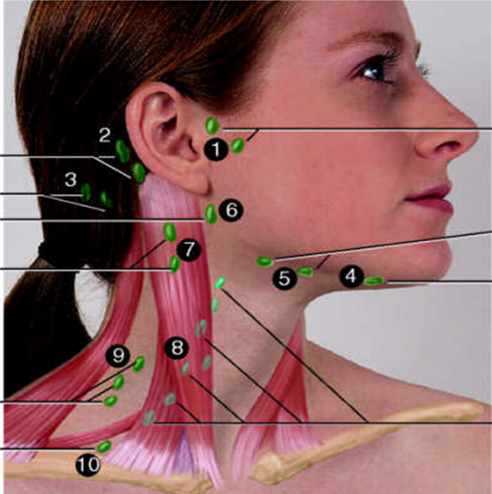
Supraclavicular
#10?
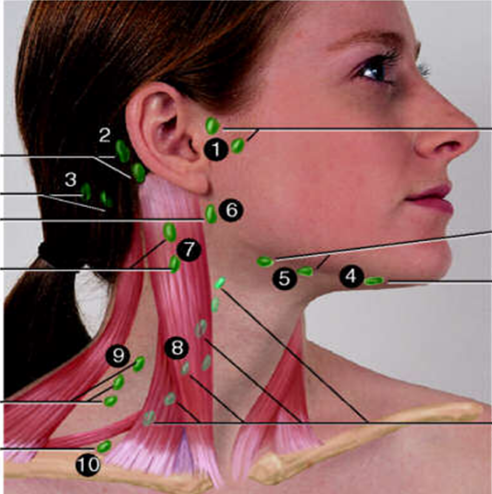
Lymphadenopathy
= enlargement of the lymph nodes (>1cm) from infection, allergy or neoplasm
The pt. has an acute infection
Lymph nodes are bilateral, enlarged, warm, tender, and firm, but are still freely moveable. What can this mean?
There is chronic inflammation (such as TB)
what does it mean if the lymph nodes are clumped together? What illness can cause this?
Cancer (CA)
If the lymph nodes are hard (like rocks), >3 cm, unilateral, nontender, and fixed, what can this indicate?
CA of the thorax or abdomen
What does a single, non-tender, hard, left supraclavicular node indicate?
Hodgkin Lymphoma (CA that affects the lymphatic system)
What do painless, rubbery, discrete nodes in the cervical region indicate?
HIV
What might the pt. have if their lymph nodes are enlarged, firm, non-tender, and mobile?
Occipital
Which nodes are common with HIV when abnormal?
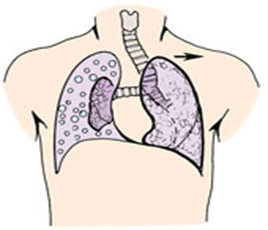
with lung tumors, pneumothorax, or thyroid masses
When might the trachea be pushed to the unaffected/normal side?
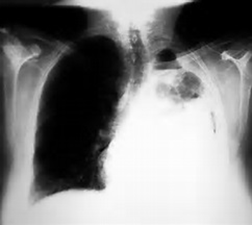
lung diseases such as atelectasis (partial collapse of lung), plural adhesion, or fibrosis (thick lung tissue)
When might the trachea be pulled to the abnormal side?
pulled to the abnormal side
Is the trachea being pushed or pulled in the image?
pushed to the normal side
Is the trachea being pushed or pulled in the image?
tumor
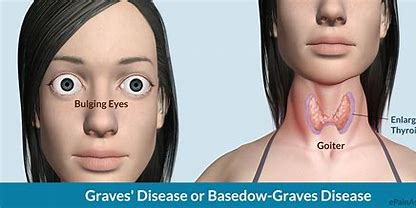
What might unilateral bulging of the thyroid gland indicate?
Grave’s Disease (Hyperthyroidism)
= an autoimmune disease with increased production of TH and increased metabolic rate
manifested by:
goiter
bulging eyes
eyelid retraction
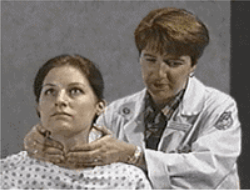
posterior approach to assessing the thyroid gland
What does this photo depict?
nothing, the bell
What would you normally hear when listening to the thyroid gland? What part of the stethoscope is used?
Bruits
Soft, pulsatile, whooshing, blowing sound heard when there is accelerated or turbulent blood flow to the thyroid.
Pediatric variations
unstable neck
discrete, palpable nodes in children
misshapen skulls from birth trauma
measuring head circumference
Caput Succedaneum
swelling & ecchymosis from the presenting part of the head (resolves w/o treatment)
cephalhematoma
subperiosteal (beneath periosteum) hemorrhage (resolves w/o treatment)
craniosynostosis
premature closure of cranial sutures
Results in malformed head & cosmetic deformity
From genetic mutations
OA Variations
Temporal artery may look prominent & twisted
Isolated head tremors are benign (includes head nodding and tongue protrusion)
Slower ROM head/neck
May experience dizziness
Kyphosis (“hump back”)
Thyroid often nodular and may be lower in the neck
Nearly impossible to palpate
Presyncope
= light-headed, swimming sensation from decreased blood flow to brain or decrease cardiac output
Vertigo
= room is spinning
Disequilibrium
= shakiness or instability when walking (r/t musculoskeletal disorder or multisensory deficits)
vagal stimulation or stimulation of carotid sinuses
palpation that can cause the heart rate to drop =
Thyroid Gland
usually nonpalpable, right side is 25% larger than left, sometimes felt in thin necks, and always felt in pregnancy.
migraine headache
character: throbbing, pulsation
severity: moderate-to-severe
duration: rapid onset, peaks 1-2 hours, last 4-72 hours
location: behind the eyes, temples, or forehead
sensitive to light
cluster headache
character: continuous, sharp, burning, piercing, excruciating
duration: abrupt onset, peaks in minutes, lasts 15-180 min
location: always one-sided, behind or around the eye, temple
severity: can occur multiple times a day, very severe pain
tension headache
character: tightness, nonthrobbing, nonpulsatile
duration: gradual onset, lasts 30 minutes-7 days
location: frontal, temporal, occipital
severity: mild-to-moderate pain