Stabilising the Economy - The Role of the Fed
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Fed Watch
Analysts attempt to forecast Fed decisions about monetary policy
Greenspan briefcase indicator
Fed decisions have significant effects on financial markets and the macro economy
Is Monetary Policy a major Stabilisation tool?
yes, its quickly decided and implemented and more flexible and responsive than fiscal policy
What is the Primary task of the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee)?
controlling the money supply
money supply and demand determine the interest rate
the fed manipulates supply to achieve its desired interest rate
Portfolio Allocation Decisions
allocate a persons wealth among alternative forms
Diversification
owning a variety of different assets to manage risk
Demand for Money (Liquidity Preference)
the amount of wealth held in the form of money
What does Demand for Money depend on?
Nominal interest rate (i)
The higher the interest rate, the lower the quantity of money demanded
Real income or output (Y)
The higher the level of income, the greater the quantity of money demanded
The price level (P)
The higher the price level, the greater the quantity of money demanded
What determines the Nominal Interest Rate?
interaction of the aggregate demand for money and the supply of money
Money Demand Curve
Shows the relationship between the aggregate quantity of money demanded, M, and the nominal interest rate
An increase in the nominal interest rate increases the opportunity cost of holding money
Negative slope
Changes in factors other than the nominal interest rate cause a shift in the curve
A change in demand for money can result from anything that affects the cost or benefit of holding it
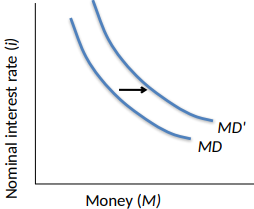
What can affect the Cost/Benefit of Holding Money?
An increase in output
Higher price levels
Technological advances
Financial advances
Foreign demand for dollars
Supply of Money
The Fed primarily controls it with open-market operations
An open-market purchase of bonds by the Fed increases it
An open-market sale of bonds by the Fed decreases it
The line is vertical
Equilibrium is at E
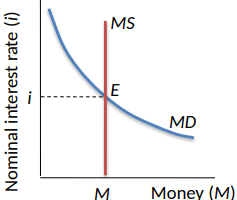
What are Bond Prices Inversely related to?
The interest rate
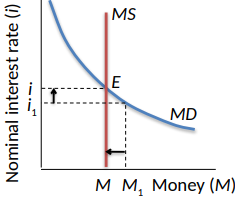
Suppose the interest rate is at i1, below equilibrium
Quantity of money demanded is M1, more than the money available
To get more money, people sell bonds
Bond prices go down, interest rates rise
Quantity of money demanded decreases from M1 to M
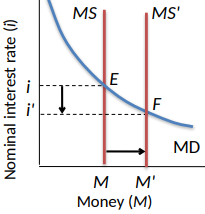
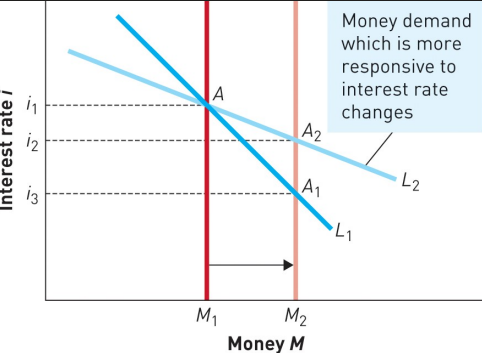
Fed Controls the Nominal Interest Rate
Fed policy is stated in terms of target interest rates
The tool they use is the supply of money
Initial equilibrium at E
Fed increases the money supply to MS'
New equilibrium at F
Interest rated decrease to i' to convince the market to hold the new, larger amount of money
To Decrease the Money Supply
fed sells bonds to the public
supply of bonds increases
price of bonds decreases
interest rate increase
To Increase the Money Supply
fed buys bonds from the public
demand for bonds increase
price of bonds increase
interest rate decreases
Why is Fed Policy announced in terms of Interest Rates?
Public is not familiar with the size of the money supply
Main effects of monetary policy on the economy work through interest rates
Interest rates are easier to monitor than the money supply
Role of the Federal Funds Rate (FFR)
The rate commercial banks charge each other on short-term (usually overnight) loans
Banks borrow from each other if they have insufficient funds
Market determined rate – supply and demand
Targeted by the Fed
Decreasing the FFR
The Fed conducts open market purchases
For example, when the Federal Reserve buys Treasury securities on the open market, it injects reserves into the banking system and lowers the FFR
Reserves increase; excess reserves can be loaned to other banks in the federal funds market
Banks holding excess reserves are incentivized to lend to other banks to avoid holding idle reserves, leading to a downward pressure on interest rates as they compete to offer lower rates
Interest rates tend to move together; consumer, mortgage, prime rates fall
Can the Fed Control the Real Interest Rate?
Yes, in the short run, by changing the nominal interest rate (i), since inflation (π) doesn't respond immediately
Open Market Operations
The main tool of money supply
Fed offers lending facility to banks, called discount window lending
If a bank needs reserves, it can borrow from the Fed at the discount rate
Lending increases reserves and ultimately increases the money supply
Source of liquidity in times of distress or financial stability
Changes in the discount rate signal tightening or loosening of the money supply
The Discount Rate
the rate the Fed charges banks to borrow reserves
typically higher than the FFR
penalty rate that encourages banks to lend and borrow from each other instead
commercial banks can only use it if they meet certain eligibility criteria and pay the rate
What is the Money Supply Determined by?
public currency + (bank reserves / reserve-deposit ratio)
How can the Fed affect the Money Supply?
by affecting any of these three things:
Currency held by the public
Bank reserves
The desired reserve-deposit ratio
Reserve Requirements
The minimum values of the ratio of bank deposits that must be held in reserves
It is rarely changed
Can the Fed change Reserve Requirements?
yes
Quantitative Easing (QE)
The Fed buys financial assets, lowering the yield or return of those assets while injecting liquidity.
Used to stimulate the economy by purchasing assets of longer maturity thereby raising their price and lowering longer-term interest rates
Lower long-term interest rates incentivize households and businesses to borrow and invest more, which stimulates economic activity and job creation
Forward Guidance
the Fed gives indications of its future policies so that markets will react
Interest on Reserves
even at an interest rate of 0, the fed can offer this to give banks a reason the keep money at the Fed
Excess Reserves
Bank reserves in excess of the reserve requirements set by the central bank
As a result, the money supply may not change even if the fed changes the supply of reserves
Risk aversion and low interest rates made commercial banks hold onto their reserves instead of lending them
What is the Zero Lower Bound (ZLB)?
a level, close to 0, below which the central bank can’t further reduce short-term interest rates
can’t go far below 0 - would you pay someone to lend them - would you pay someone to lend them money?
What tools can the Fed use at ZLB?
quantitative easing
forward guidance
negative rates on excess reserves
What happens to Money and Bonds at ZLB?
agents are indifferent between holding them, resulting in a liquidity trap
people and businesses hold onto it instead of spending/investing
What is the Economic effect of a Liquidity Trap?
despite ample liquidity, demand remains low, and the economy can get stuck in a low-growth or no-growth phase
How does the ZLB affect Traditional Monetary Policy?
limits the effectiveness of tools, such as the federal funds rate or the discount rate, in stimulating the economy
What components of PAE or affected by r?
Saving decisions of households
More saving at higher real interest rates
Higher saving means less consumption
Investment by firms
Higher interest rates mean less investment
Investments are made if the cost of borrowing is less than the return on the investment
Both consumption and planned investment decrease when the interest rate increases
The Fed Fights a Recession
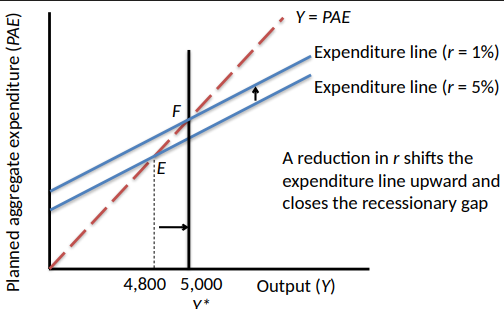
How Effective is Monetary Policy? Money Supply to Interest Rates
How can Expansionary Gaps lead to Inflation?
Planned spending is greater than normal output levels at the established prices
Short-run unplanned decreases in inventories
If gap persists, prices will increase
How does the Fed attempt to close Expansionary Gaps?
Raise interest rates
Decrease consumption and planned investment
Decrease planned aggregate expenditure
Decrease equilibrium output
Why does the Fed have limited ability to manage the Stock Market?
The Fed doesn't know the “right” prices
It has no private information - data is publicly available
Why is Monetary Policy not well suited for addressing Asset Bubbles?
It can raise rates to slow growth
But doing so risks a recession and rising unemployment
What is Forward Guidance in Monetary Policy?
the Fed providing information about how it expects to adjust the FFR in the future, based on the current economic outlook
helps the public and investors better understand the Fed’s views and future policy intentions
What should Central Banks and Regulators do in response to Financial Crises?
Anticipate, defuse threats, and mitigate the effects when crises occur
What conditions help Macroeconomic Policy work best?
Accurate knowledge of current economic conditions
Understanding the economy's path without policy
Precise estimate of potential output
Good control of fiscal and monetary tools
Knowledge of timing and effects of policy changes