Genetic Diversity and Natural Selection
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is genetic diverisity
total number of different alleles of genes in a population
more genetic diversity within species - more phenotypes so more able to adapt to environmental change and evolve
A new allele for a gene -
The gene has mutated → new base sequence = new allele
The allele produces a different amino acid sequence
This could change the protein’s shape or function
That could lead to a new phenotype
What is evolution
the change in allele frequency over many generations in a population
Natural Selection
theory created by Charles Darwin
can only occur if there is genetic diversity
results in species becoming better adapted for their environment e.g. antibiotic resistance in bacteria
What kind of adaptations can occur
Anatomical (structural features)
Physiological (chemical reactions in the body)
Behavioural
Explain the process of natural selection
population of species there is a gene pool - contain wide variety of alleles
new alleles of a gene are created by random mutations - results in new allele of gene
Survival Advantage - new allele increases the chances (provides an advantage) of survival in the environment - more likely to survive and reproduce
Reproduction those who reproduce successfully will pass on their alleles to next generation - new individuals have the new advantages allele and more likely to survive and reproduce
Change in Allele Frequency - Over many generations those with advantageous allele increase at the expense of the individuals with less advantages alleles
over time - new allele increases in frequency in population
What are the two types of natural selection
Stabilizing selection
Directional selection
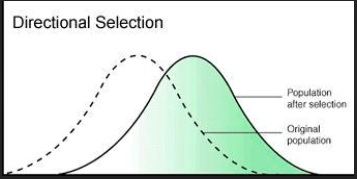
Directional selection
Directional Selection - one of the extreme traits are more likely to survive and reproduce (phenotype at one end of a range of variation is selected - population changes in direction of favoured characteristic)
over time leads to a shift in the mean of the populations trait
occurs when there is a change in the environment
can be a new allele that has appeared and it is advantageous
Before selection:
Normal distribution (bell-shaped curve)
Mean trait value is in the middle
After selection:
The curve shifts towards one extreme phenotype
Mean trait value changes
Selection is against the other extreme and the average
Give an example of directional selection
A few bacteria have alleles for antibiotic resistance (extreme phenotype)
After antibiotic exposure, resistant bacteria survive
They reproduce and pass on the resistance allele
Over time, the population shifts towards greater resistance
🎓 Exam Tip:
They may ask you to interpret a graph OR describe the process using an example. Make sure to:
Mention survival and reproduction
Talk about alleles being passed on
Explain that the mean shifts over time
Stabilising Selection
individuals with alleles for the average phenotype are more likely to survive and reproduce. (modal phenotype is best adapted and selected for)
reduces the range of phenotypes and maintains the status
occurs when there is no change in the environment
over generations - more individuals will have the modal trait
Example of stabilizing selection
Very low birth weight: Higher risk of health issues/death
Very high birth weight: Complicated birth, also higher risk
Average birth weight: More likely to survive
So, alleles for average birth weight are passed on
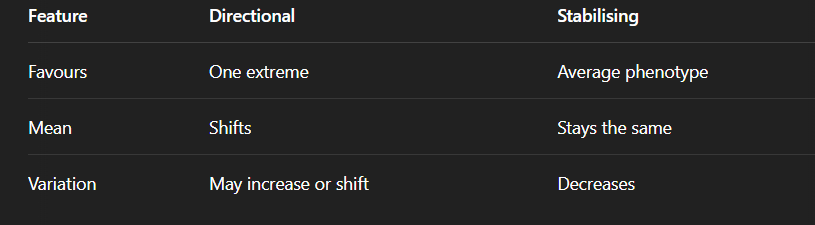
Compare directional selection to stabilizing selection
What is genetic variation
there is small difference in DNA base sequence between individual organism
genetic variation is passed down - leads to genetic diversity
What causes genetic variation
mutations - these alleles can be advantages, disadvantages or no effect on the phenotype
sexual reproduction - during meiosis and fertilization
What are selection pressures
environmental factors that affect chance of survival e.g. predators
increases the chance of survival with those with the specific phenotype compared to others
What is fitness
Those who have the ability to survive and pass on its alleles e.g. those who have the desired phenotype
Variation can be
Interspecific - between different species
Intraspecific - within one species (could be due to genetic factors, environmental factors or combination of both)
Definition of species
a group of organisms capable of interbreeding to produce fertile offspring
What are the key stages in natural selection
Mutation
Variation
Adaptation
Survival of the fittest
Reproduction
What does the advantages allele depend on
the environmental conditions at any one time
You need to say certain traits and selected FOR and AGAINST depending on the selection pressures