Bio - Structure and Functions in living organisms
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
nucleus
contains DNA
cytoplasm
site of reactions
cell membrane
selectively permeable membrane
controls what goes in and out of cell
cell wall
provides structural support and maintains cell shape
mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration
prduces atp
chloroplasts
site of photosynthesis
light energy to chrmical
ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
vacuole
stores water, nutrients and waste
maintains pressure in plants
cell differenciation
process in which a cell changes to become specialised for its job
cells can develop different organelles and turn into different types of cells to allow them to carry out specific functions.
elements in carbohydrates
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
elements in lipids
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
elements in proteins
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
nitrogen
what are carbohydrates made up of
starch and glycogen
what are lipids made up of
fatty acids and glycerol
what are proteins made up of
amino acids
enzymes
biological catalysts in metabolic reactions (useful to organism)
increases speed of reaction without being used up
photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
how do light levels affect photosynthesis
chlorophyll uses light energy
if light intensity increases, rate increases steadily
then limiting factors temp and CO2 slow it down
how do CO2 levels affect photosynthesis
one of the raw materials
increasing concentration increases rate up to a point
then graph flattens out, showing that CO2 is no longer limiting factor
how does temp affect photosynthesis
affects enzymes
it increases with rate but up to a point
if temp too high, enzymes denature so rate rapidly decreases
structure of leaf

adaptations of a leaf
flat, broad leaves - larger SA:V
epidermis and mesophyll cell walls very thin - short diffusion distance
many stomata - a lot of entry and exit for gasses
air spaces - gasses can quickly reach places for photosynthesis and respiration
ability to open and close stomata - open when sunny and close to prevent water loss
why do plants need mineral ions
for growth
why are magnesium ions needed in plants
for chlorophyll
why are nitrate ions needed in plants
for amino acids
what does a balanced diet include
carbohydrates
proteins
lipids
vitamins
minerals
water
dietary fibre
why are carbohydrates needed in humans
glucose is used in respiration
(sugars)
why are proteins needed in humans
growth and repair of tissues
production of enzymes
antibodies
examples of proteins
meat / eggs / dairy / nuts + seeds
why are lipids needed in humans
concentrated energy source
part of cell membrane
examples of lipids
dairy / oils / nuts
why is vitamin A needed in humans
vision
immune system
healthy skin
(retinol)
why is vitamin C needed in humans
wound healing
immune system
prevent scurvy
why is vitamin D needed in humans
calcium absorption
why is calcium needed in humans
strong bones/teeth
why is iron needed in humans
needed to make haemoglobin for healthy blood
why do energy requirements vary in humans
due to activity levels, age and pregnancy
peristalsis
movement of food down the alimentary canal
circular muscles contract and make tube narrow
longitudinal muscles contract to make tube wide and short
human alimentary canal
mouth
salivary glands
oesophagus
stomach
small intestine (duodenum, ileum)
large intestine/colon
rectum
anus
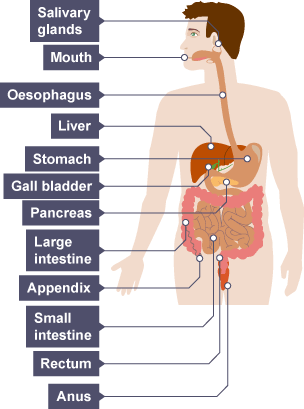
what does the pancreas do
produces digestive enzymes to break down food
lipase, protease, amylase
breaking down of starch
starch → maltose → glucose
by amylase(produced in salivary glands and pancreas) then maltase(produced in small intestine)
breaking down of proteins and lipids
proteins → amino acids
by protease
lipids → fatty acids + glycerol
by lipase
bile production and storage
produced in liver and stored in gall bladder
role of bile
emulsifies fats/lipids (so that lipase can work more effectively)
neutralises stomach acids
adaptations of small intestine
very long allowing for sufficient time for complete digestion
folded inner surface to increase SA available for absorption
villi - millions of tiny projections on walls which dramatically increase SA and increase rate of absorption of nutrients
respiration
produces energy in living organisms
aerobic respiration equation
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + ATP
C6H1206 + O2 → CO2 + H2O + ATP
anaerobic respiration equations
humans:
glucose → lactic acid + ATP
plants:
glucose → ethanol + CO2 + ATP
aerobic vs anaerobic respiration
requires oxygen - does not
occurs in mitochondria - in cytoplasm
complete breakdown of glucose - incomplete
efficient, much energy produced - small amount
slower - faster
— fermentation in plants + yeast
gas exchange in plants
CO2 required for photosynthesis (to make glucose) (waste product of respiration)
O2 required for respiration (to release energy from glucose) (waste product of photosynthesis)
respiration vs photosynthesis in day
light intensity high, stomata open so CO2 can enter for photosynthesis (hydrogen carbonate indicator is purple)
respiration vs photosynthesis in night
light intensity low, no photosynthesis, no CO2 entering, stomata closed (hydrogen carbonate indicator is yellow)
hydrogencarbonate indicator
yellow → orange → red → pink → purple
yellow: highest conc of CO2 (more respiration than photosynthesis)
purple: lowest conc of CO2 (more photosynthesis then respiration)
structure of thorax
ribs
intercostal muscles
diaphragm
trachea
bronchi
bronchioles
alveoli
pleural membranes
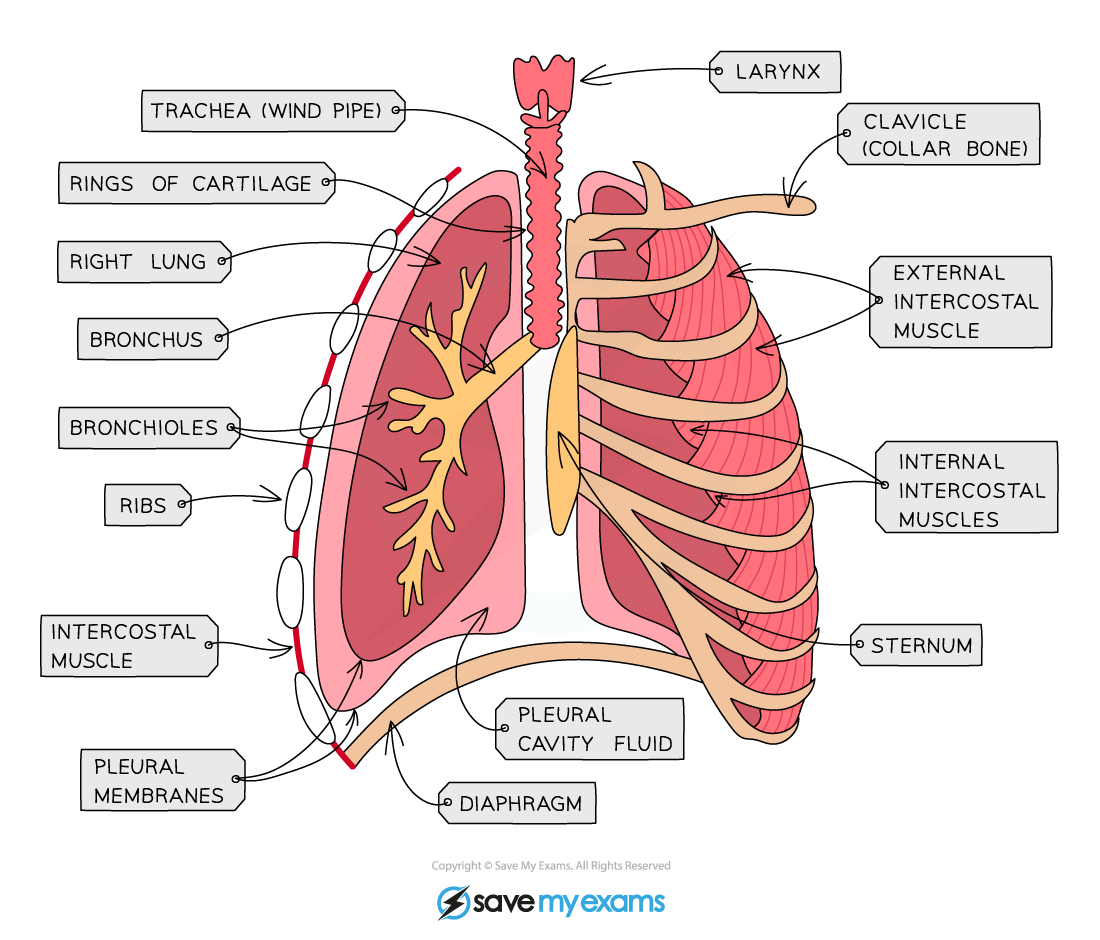
Breathing in
diaphragm contracts and moves downwards
volume of lungs increases and air is sucked in through the nose and mouth
intercostal muscles contract
ribs move up and out
breathing out
diaphragm releases and moves upwards
volume of lungs decreases and air is breathed out of nose and mouth
intercostal muscles relax
ribs move down and in
adaptations of alveloi
700 million alveoli with folded walls to increase SA
alveoli and capillary walls 1 cell thick for short diffusion distance
constant ventilation and good blood supply to maintain sleep concentration gradient
coronary heart disease
Nicotine increases blood pressure
this damages arteries
more fatty deposits into artery walls
blood more likely to clot
increased risk of heart attack and stroke
effects of smoking on respiratory system
carcinogens and tar can lead to uncontrolled cell division → tumours (lung cancer)
cilia damaged, can’t sweep mucus, dust and pathogens out, build up of mucus in air ways (smokers cough)
this can lead to infection and inflammation of bronchi (bronchitis)
smoke chemicals can cause walls of alveoli to break down and merge into larger, irregular spaces, significantly reduce SA for gas exchange (emphysema)