Biology Lab Exam 2
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
205 Terms
What is an ecological niche?
An ecological niche encompasses the full range of physical and biological conditions under which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions. This includes habitat, diet, reproductive strategy, interactions (both abiotic and biotic), and the role in energy flow and nutrient cycling.
Fundamental niche vs. Realized niche
The fundamental niche is the full potential range of conditions and resources a species could theoretically use, without competitors. The realized niche is the portion actually used when competition, predation, and other biotic factors are present.
What is the competitive exclusion principle?
This principle states that two species competing for the same limiting resource cannot coexist indefinitely. Eventually, one species will outcompete and exclude the other.
What is a limiting resource?
A resource that is in shortest supply relative to demand, thus constraining the growth, abundance, or distribution of an organism or population.
What is an ethogram?
A catalog or inventory of all of the behaviors exhibited by an animal used in observational research.
What is focal sampling?
Observing one individual for a specified amount of time and recording all behaviors seen.
What is agonistic behavior?
Social behaviors related to fighting, including threats, displays, retreats, placation, and physical aggression.
What are dominance hierarchies?
Structured rankings among individuals within a group that determine access to resources or mates.
Exponential growth vs. Logistic growth
Exponential growth occurs when resources are unlimited, and population grows at a constant rate (J-shaped curve). Logistic growth includes a carrying capacity (K), where growth slows as resources become limited (S-shaped curve).
Intrinsic growth rate (r)
The rate of population growth under ideal conditions, with no limiting resources.
What is carrying capacity (K)?
The maximum population size that an environment can support sustainably over time.
What happens to population growth as K is approached?
Growth slows due to limited resources, increasing competition, and other density-dependent factors.
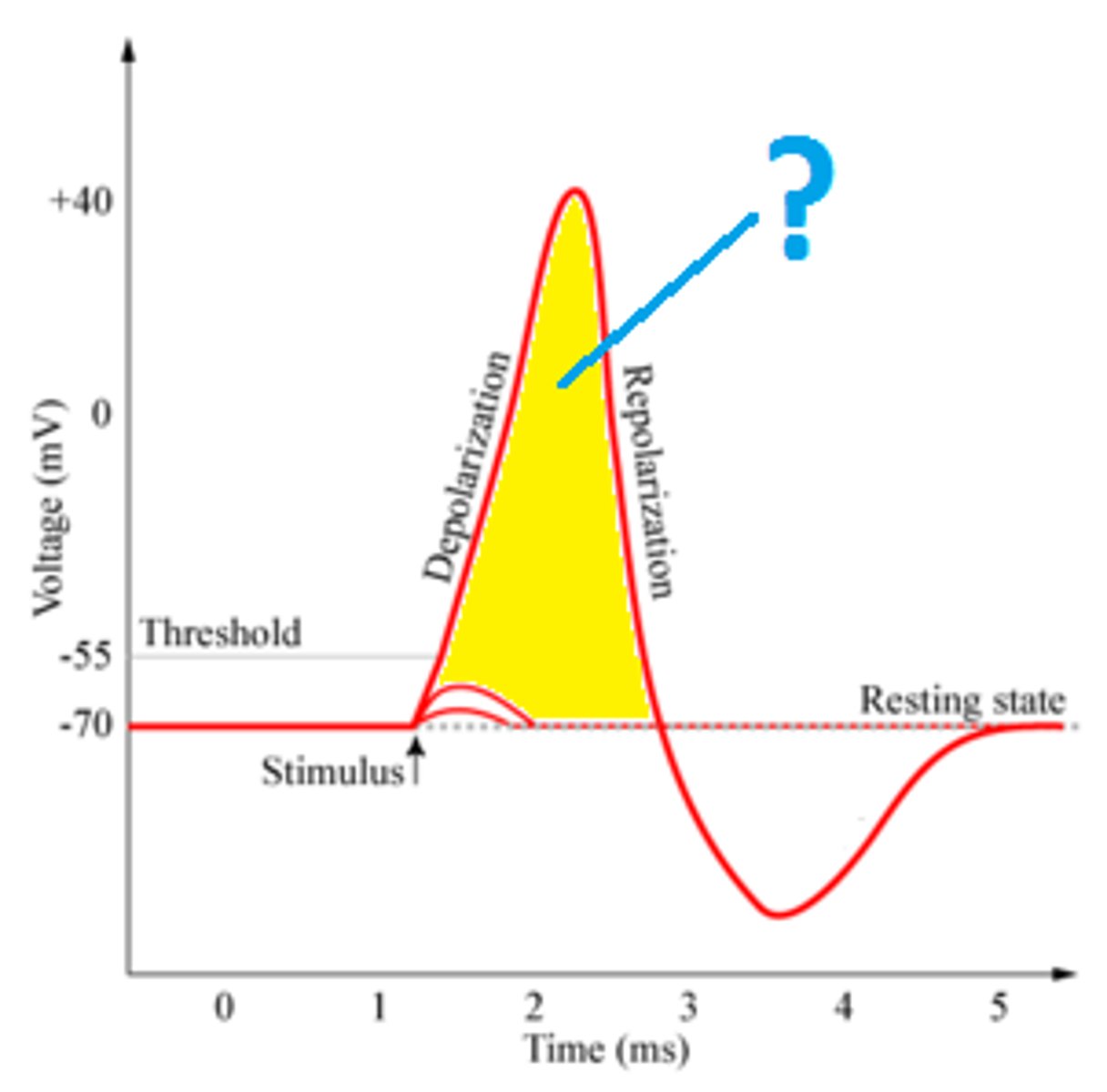
What initiates an action potential?
A stimulus must depolarize the membrane to reach the threshold potential, triggering Na⁺ channels to open.
Depolarization vs. Hyperpolarization
Depolarization: Na⁺ channels open → Na⁺ enters → inside becomes more positive.
Hyperpolarization: K⁺ channels remain open longer → more K⁺ exits → inside becomes more negative.
What is the function of the Na⁺/K⁺ pump?
Maintains resting potential by pumping 3 Na⁺ out and 2 K⁺ in against their concentration gradients (active transport).
What is the effect of lidocaine on neurons?
Lidocaine blocks Na⁺ channels, preventing action potentials and thus pain transmission.
What is population cycling?
Regular oscillation in population sizes of predators and prey due to their interdependent dynamics.
What is the paradox of enrichment?
Increasing food availability can destabilize predator-prey dynamics, sometimes leading to population crashes.
What's the difference between null and alternative hypotheses in a t-test?
Null hypothesis: No significant difference between groups.
Alternative hypothesis: There is a significant difference.
What is a keystone species?
A species with a disproportionately large impact on its ecosystem relative to its abundance, often maintaining community structure.
What is a trophic cascade?
Indirect interactions caused by predators that affect lower trophic levels.
What is a food web?
A network of interlinked food chains showing complex feeding relationships in a community.
What is eutrophication?
Enrichment of water by nutrients (mainly nitrogen and phosphorus), leading to algal blooms and oxygen depletion.
What are cyanobacteria and why are they problematic?
Photosynthetic bacteria that fix nitrogen and can produce harmful toxins (e.g., microcystins).
What is biomagnification?
Increase in toxin concentration at higher trophic levels in a food chain.
Two species of barnacles settle on the same rocky intertidal zone. One outcompetes the other at the lower levels but not the upper levels due to desiccation stress. Which niche does the excluded species occupy at the upper level?
→ Realized niche
If an invasive species is introduced and shares the exact niche as a native species, what likely outcome would occur according to the principle of competitive exclusion?
→ One species would be driven to local extinction.
In a study, researchers record every instance of aggression between animals in a troop regardless of which individual is involved. What sampling method is used?
→ All occurrences sampling
A researcher observes a group of primates and records which individuals are eating at fixed 5-minute intervals. What sampling method is this?
→ Scan sampling
If the birth rate is 0.10 and death rate is 0.05, what is the intrinsic growth rate?
→ r = 0.05
A graph shows a population plateauing over time after rapid growth. What growth model is shown?
→ Logistic growth
If a toxin prevents K⁺ channels from opening, what part of the action potential is disrupted?
→ Repolarization
Why does increasing stimulus intensity not increase action potential amplitude?
→ Action potentials are all-or-none; increased intensity affects frequency, not amplitude.
A t-test on moose populations with and without wolves returns p = 0.01. What does this indicate?
→ Statistically significant difference; reject null hypothesis.
If a new prey species is introduced, what may happen to predator population?
→ It may increase due to greater food availability, altering cycling dynamics.
Sea stars eat mussels, which outcompete other species. What happens if sea stars are removed?
→ Mussels dominate → biodiversity declines (example of keystone species effect).
In a tidepool, which is likely a filter feeder: mussel or sea star?
→ Mussel
A lake experiences a fish kill after a bloom of algae dies. What process caused this?
→ Eutrophication → algae die → decomposers consume oxygen → hypoxia
Graphs show increased algal biomass with phosphorus addition, but not with nitrogen. What is the limiting nutrient?
Phosphorus
Ecological Niche
the sum of a species' use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment
Abiotic interactions
interactions between organisms and their nonliving environment
Biotic interactions
interactions among living things
Competitive exclusion
Ecological rule that states that no two species can occupy the same exact niche in the same habitat at the same time
Limiting resource
a resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in quantities lower than the population would require to increase in size
Fundamental niche
The niche species could potentially occupy.
Realized niche
The niche species actually occupies.
Ethogram
a table used to record observations of animal behavior
Focal Sampling
used to select a particular member who will be observed at any given time
Scan sampling
a sampling technique in which the observer rapidly scans each member of a group at preselected times, so that the entire group is observed within a relatively short period
All occurrences sampling
Recording every instance of specific behaviors.
Agonistic behavior
A type of behavior involving a contest of some kind that determines which competitor gains access to some resource, such as food or mates. - aggressive
Foraging behavior
The set of behavior through which animals obtain food.
Mating behavior
Behavior surrounding propagation of a species through reproduction. Natural selection plays a role in this.
Mate choice
the intersexual selection of a mate based on attraction and traits
Ad libitum
allowing animals to eat all they want at all times
Behavioral event
any observable action or change in activity of an organism in response to a stimulus
Dominance hierarchies
a social structure within a group of animals (or sometimes humans) where individuals are ranked according to their dominance status
Birth rate
the number of births in a population in a certain amount of time
Carrying capacity
The largest population that an area can support
Death rate
The number of deaths in a population in a certain amount of time
Environment
The sum of your surroundings
Exponential growth
Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate
Fertility
The production of offspring within a population
Instantaneous rate of change
The rate of change at a particular moment
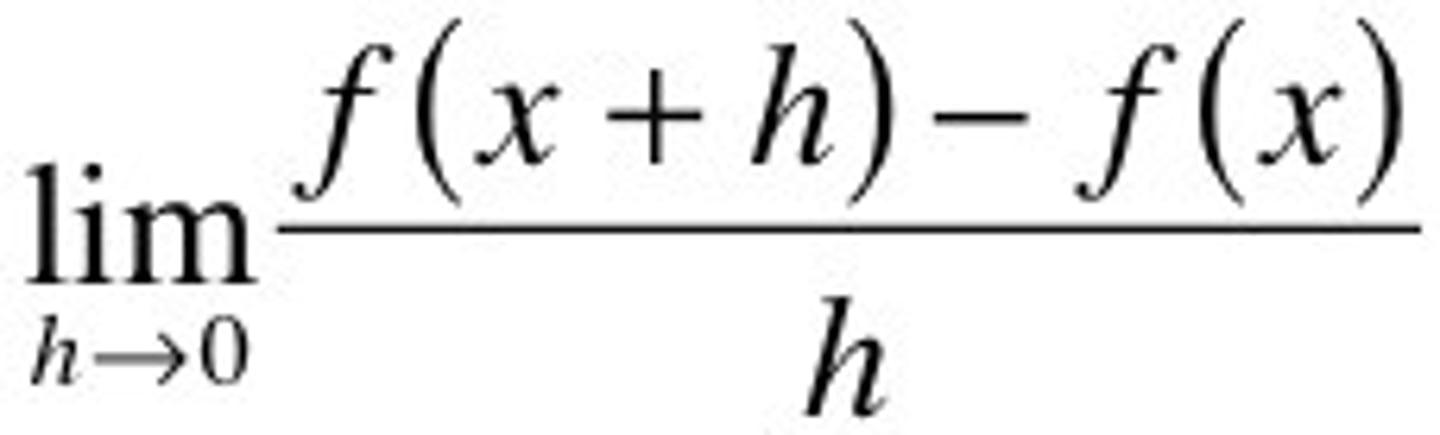
Intrinsic growth rate
under ideal conditions, with unlimited resources, the maximum potential for growth
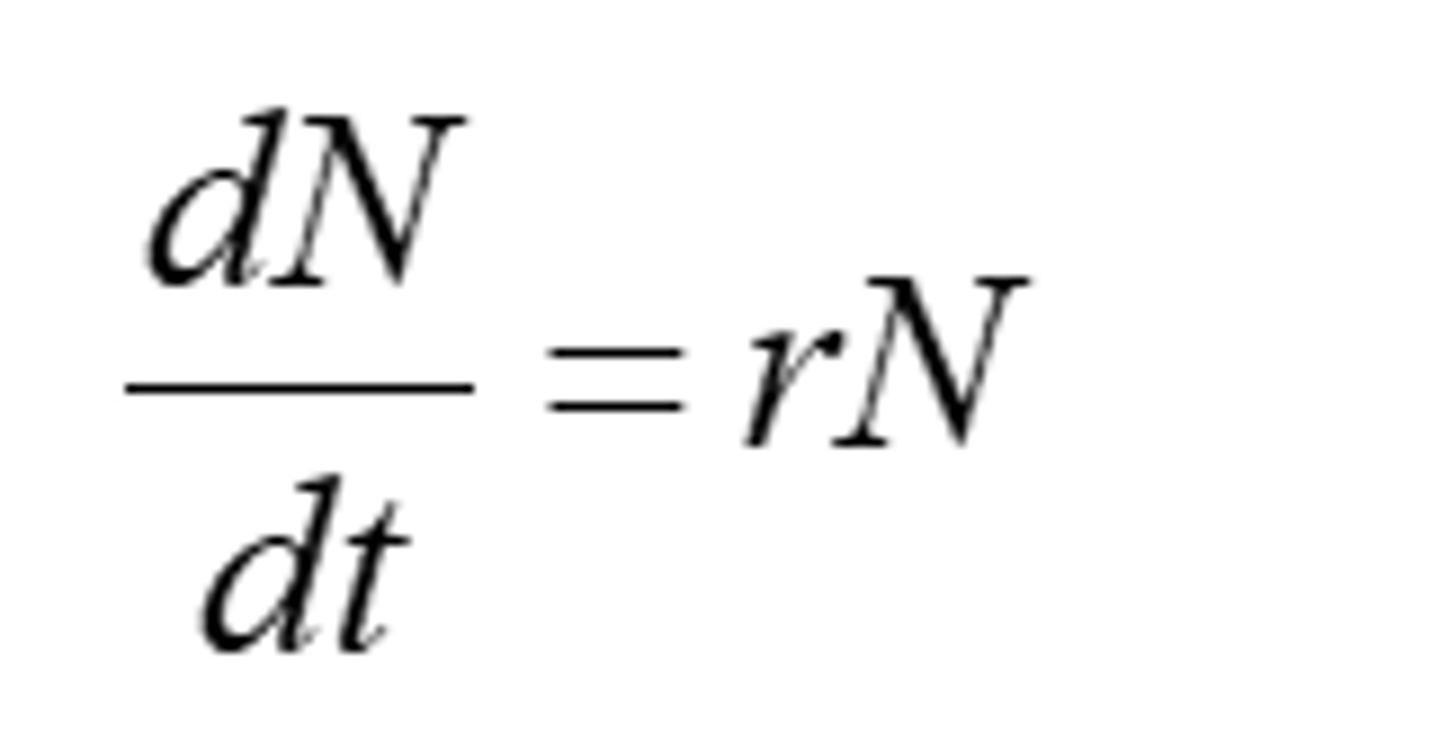
Logistic growth
Population growth that is controlled by limited resources
Per capita growth rate
birth - death / total population
Population
group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area
Population growth rate
explains how fast a given population grows
Population model
a type of mathematical model that is applied to the study of population dynamics
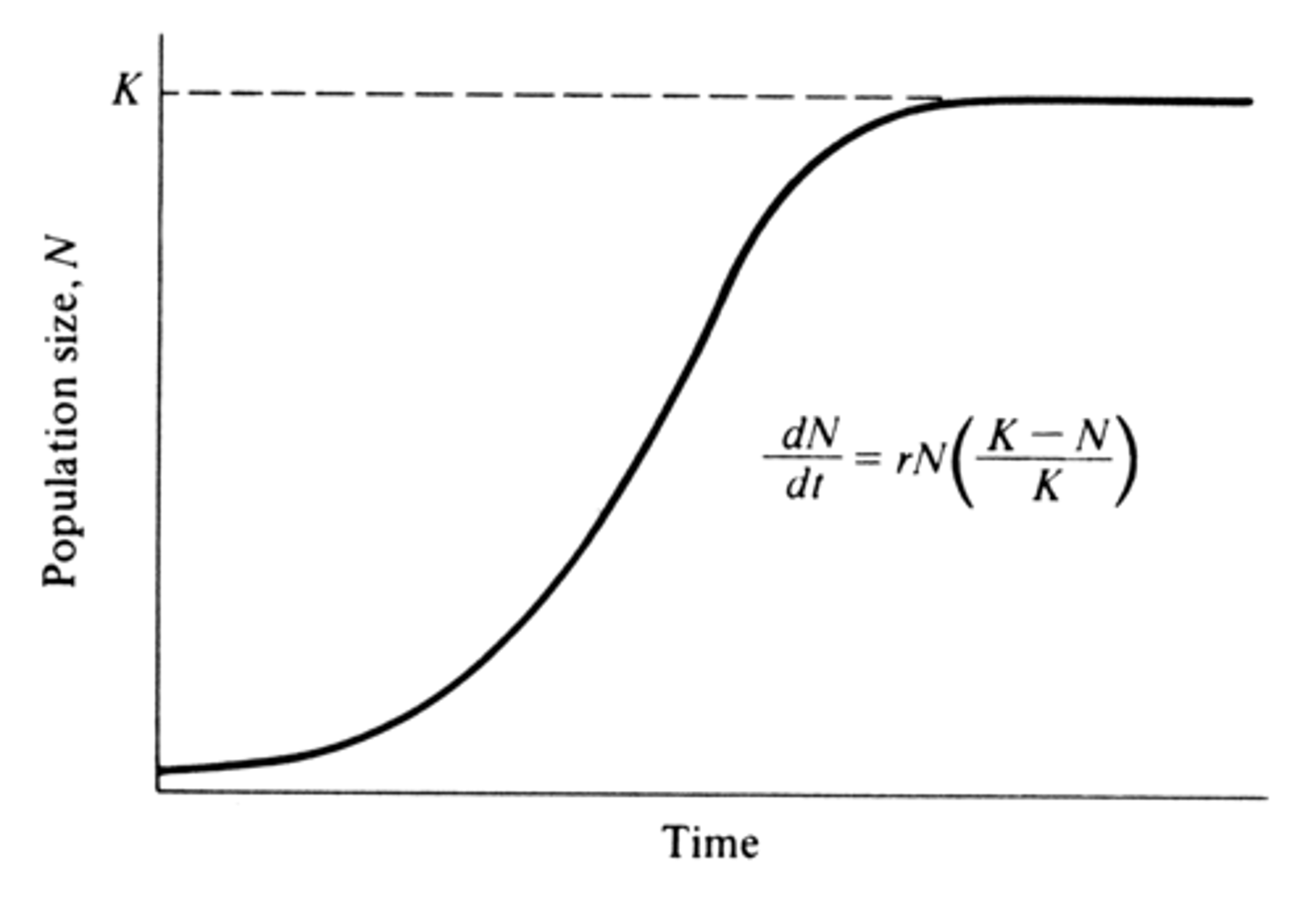
Resource
any necessity of life, such as water, nutrients, light, food, or space
Species
a group of living organisms consisting of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes or interbreeding.
Stable population size
a species whose population size fluctuates slightly above and below its carrying capacity.
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Action Potential
the change in electrical potential associated with the passage of an impulse along the membrane of a muscle cell or nerve cell.
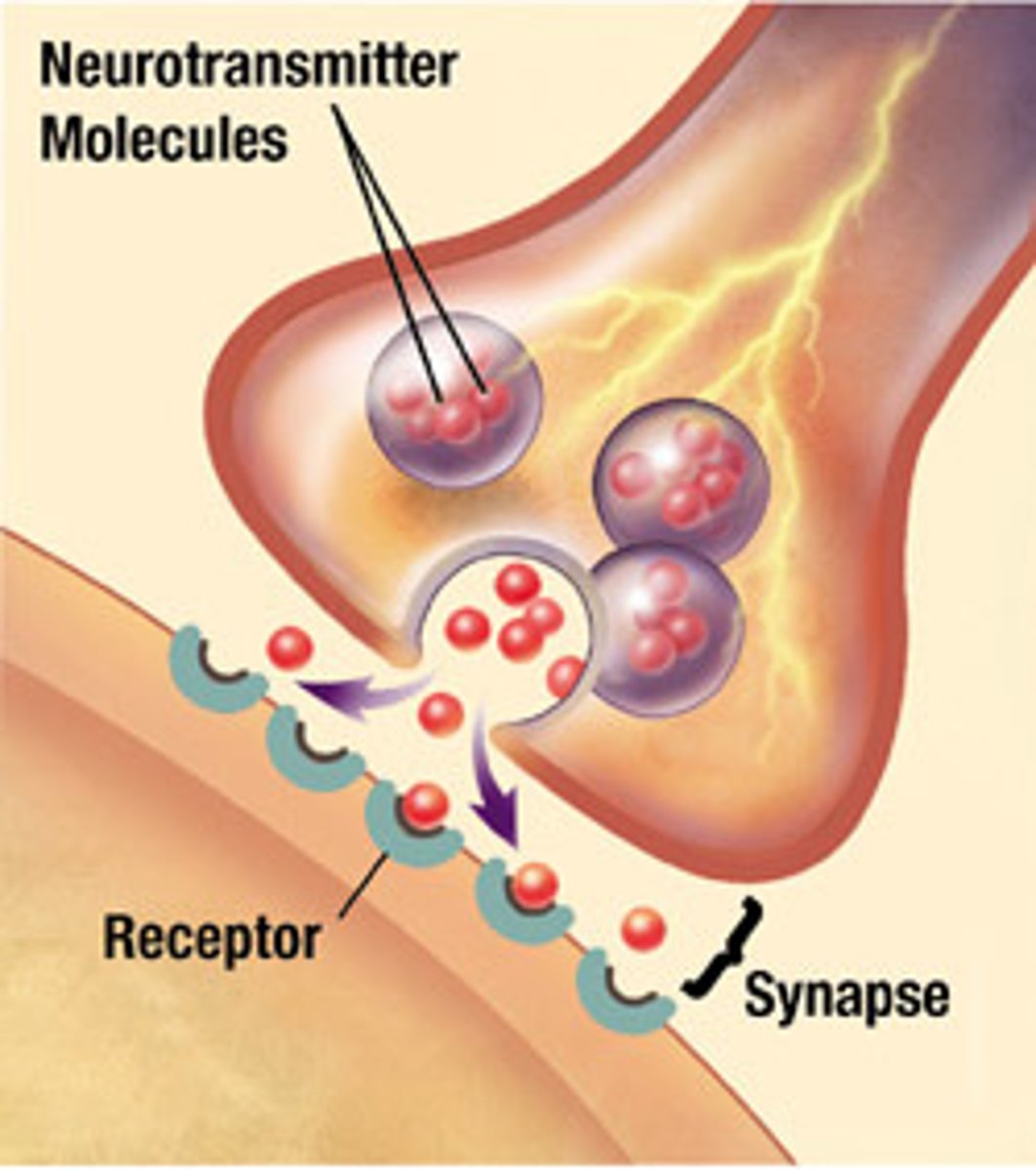
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
Senses
sight, taste, touch, smell, and hearing
Stimulus
a signal to which an organism responds
Nociceptors
pain receptors
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
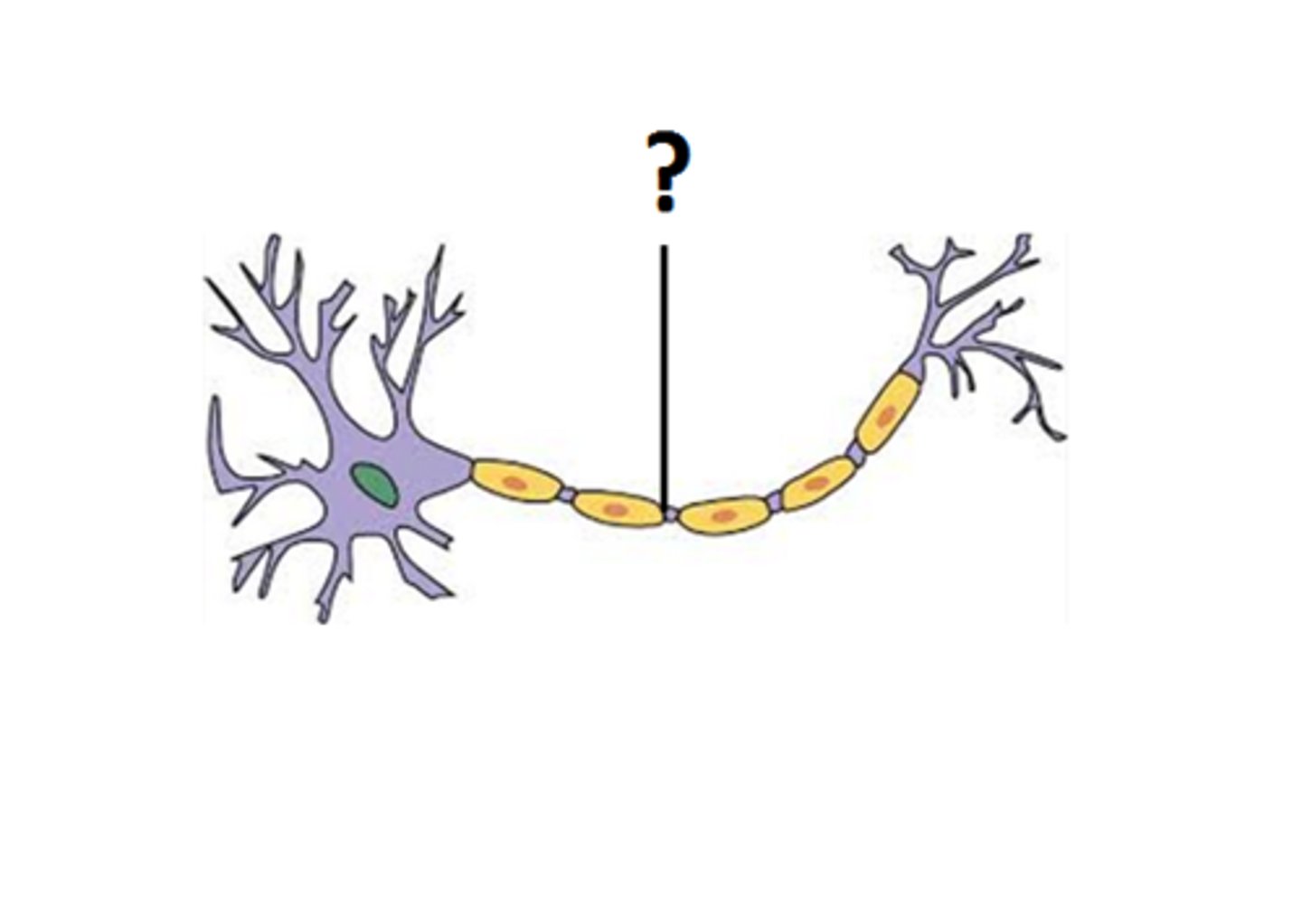
Dendrites
a neuron's bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body
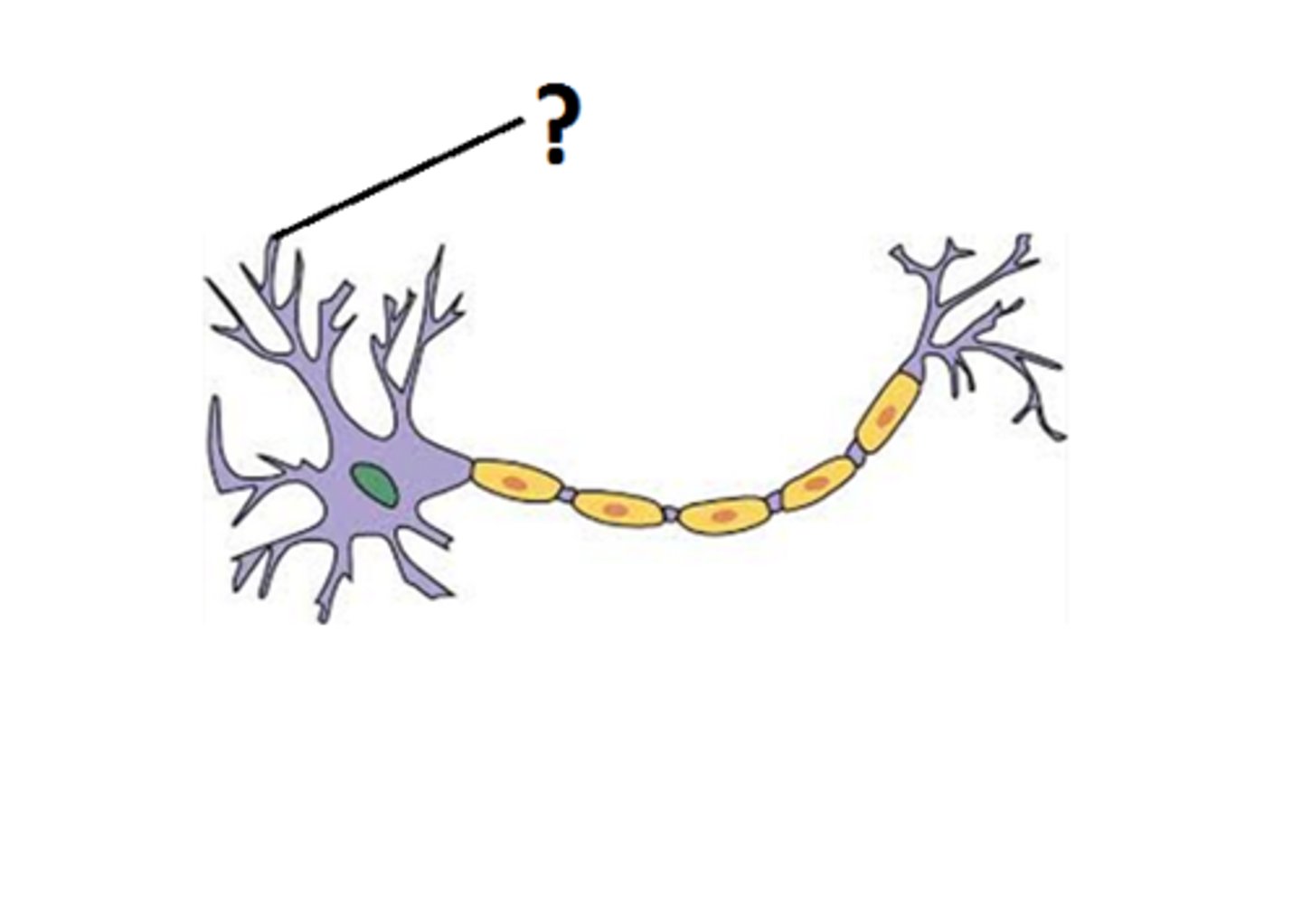
Soma
cell body of a neuron
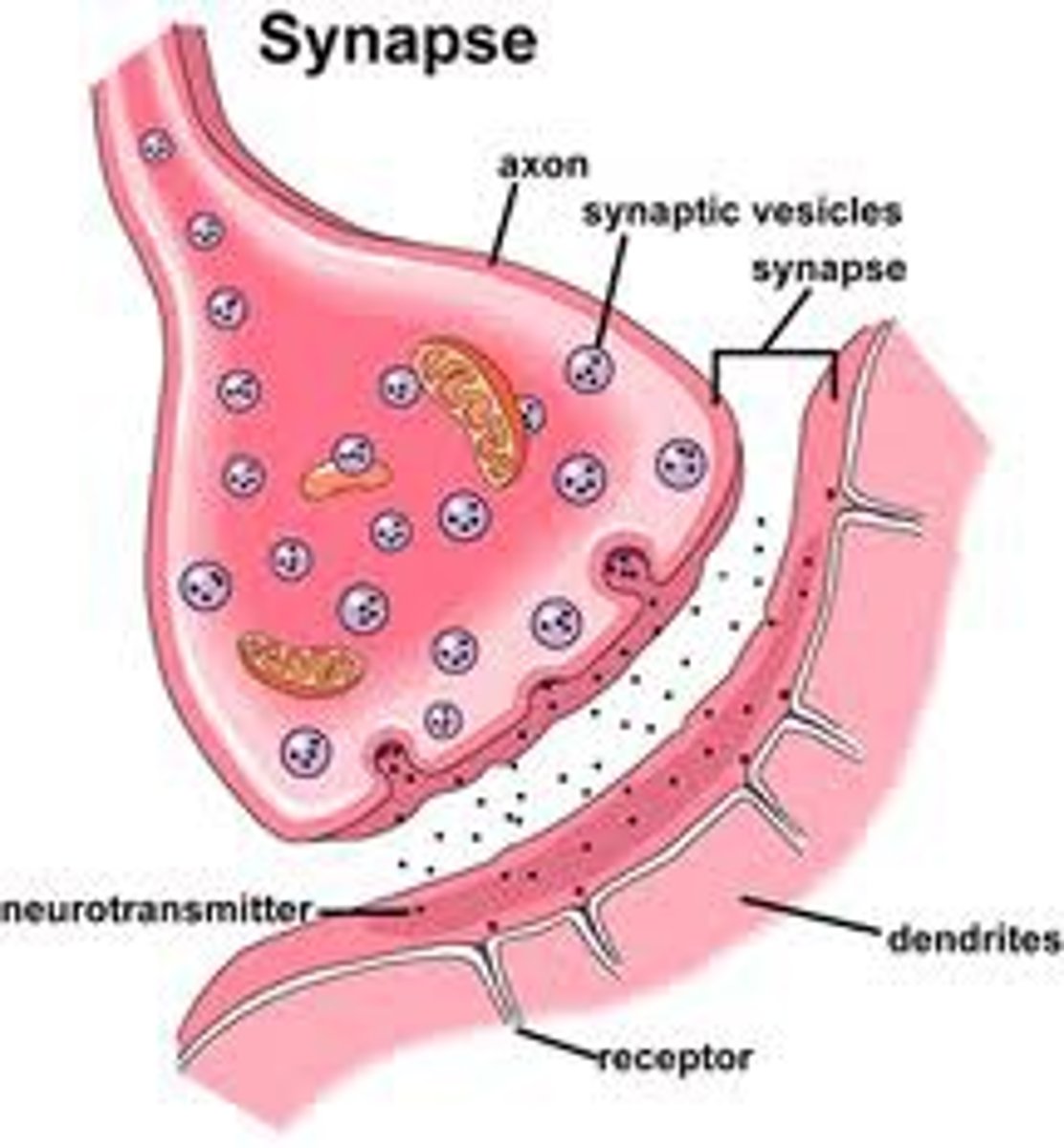
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
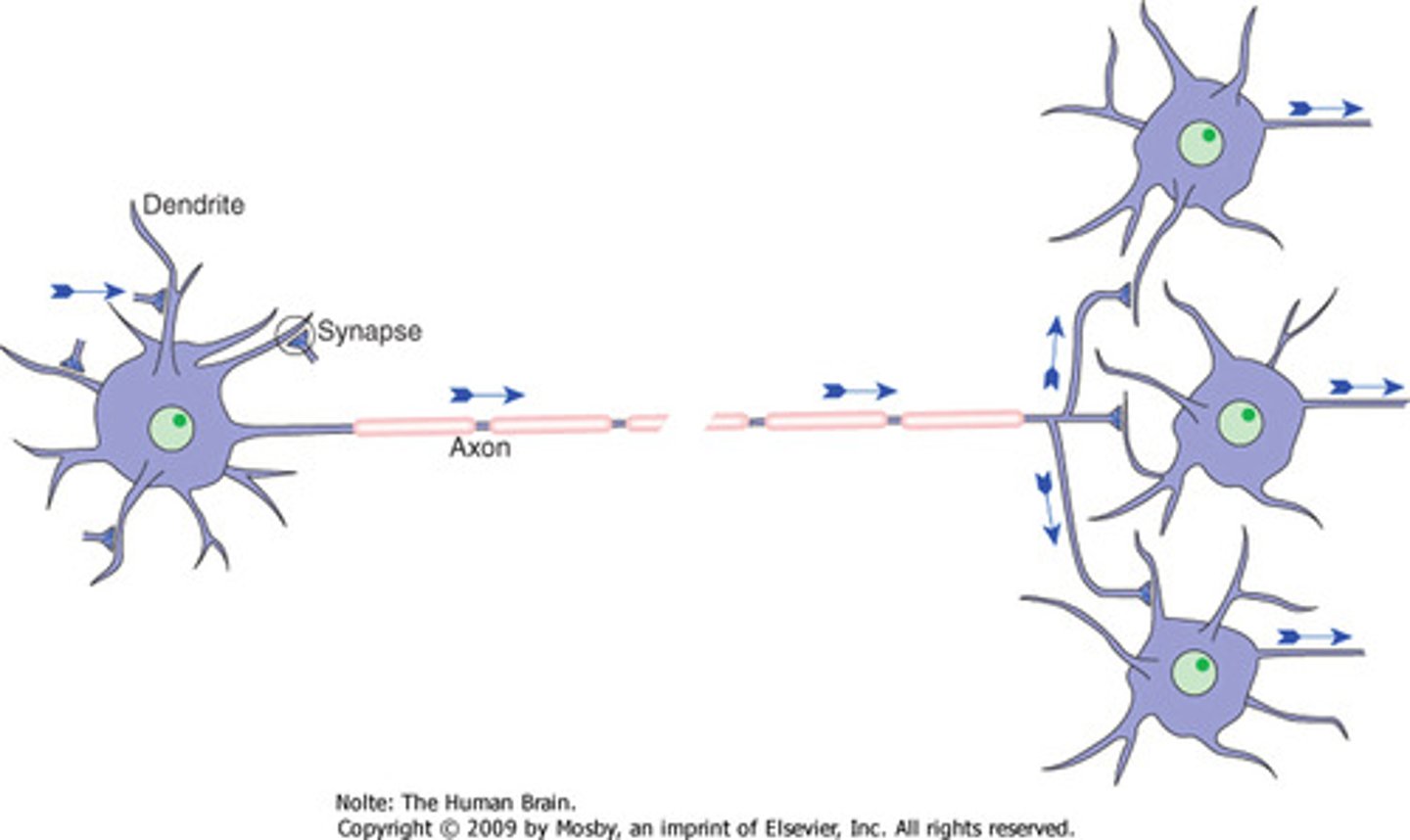
Synaptic connections
Links between neurons facilitating communication.
Receptive field
the stimulus region and features that affect the activity of a cell in a sensory system

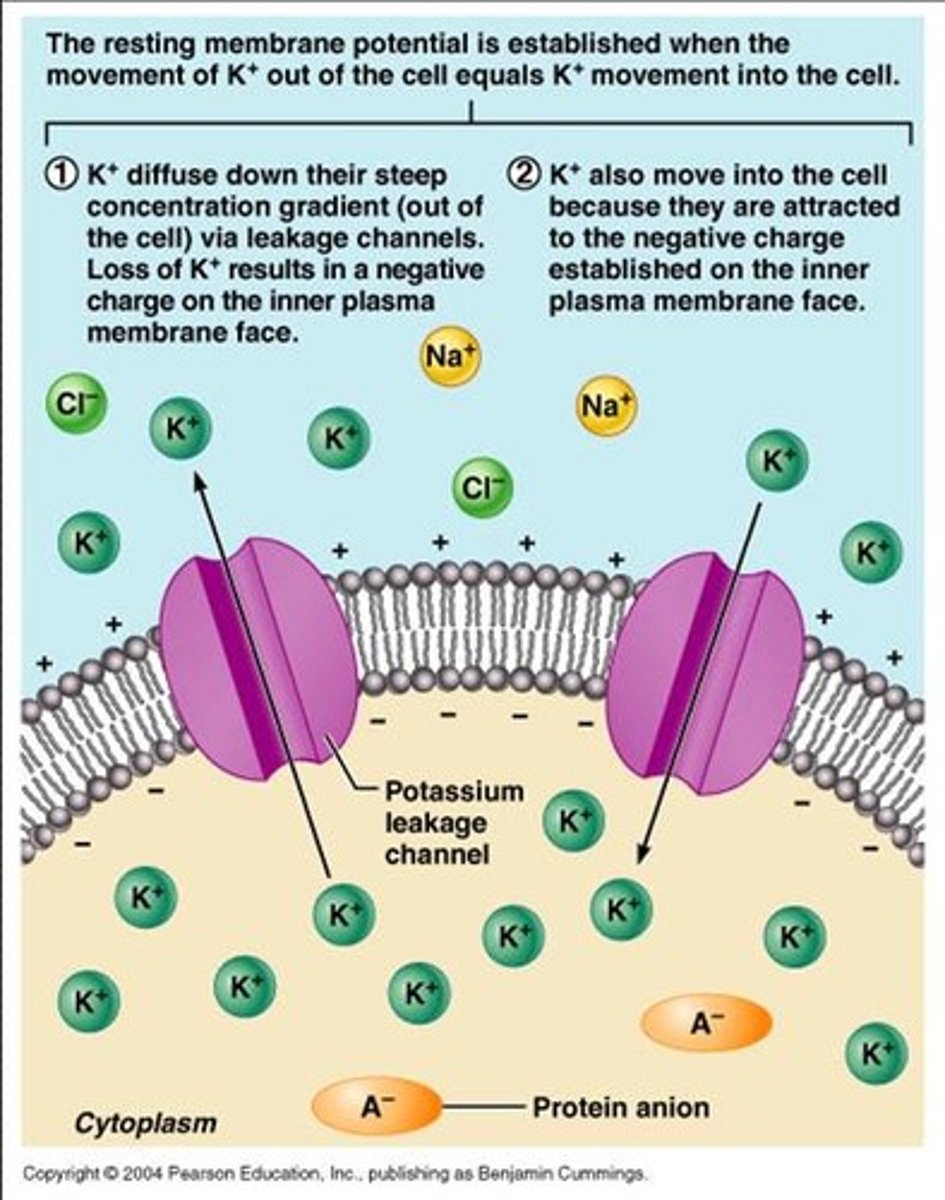
Membrane potential
The voltage across a cell's plasma membrane.
Vm
the voltage across the plasma membrane, arises because of the presence of different ion channels/transporters with specific ion selectivity and permeability (measure)
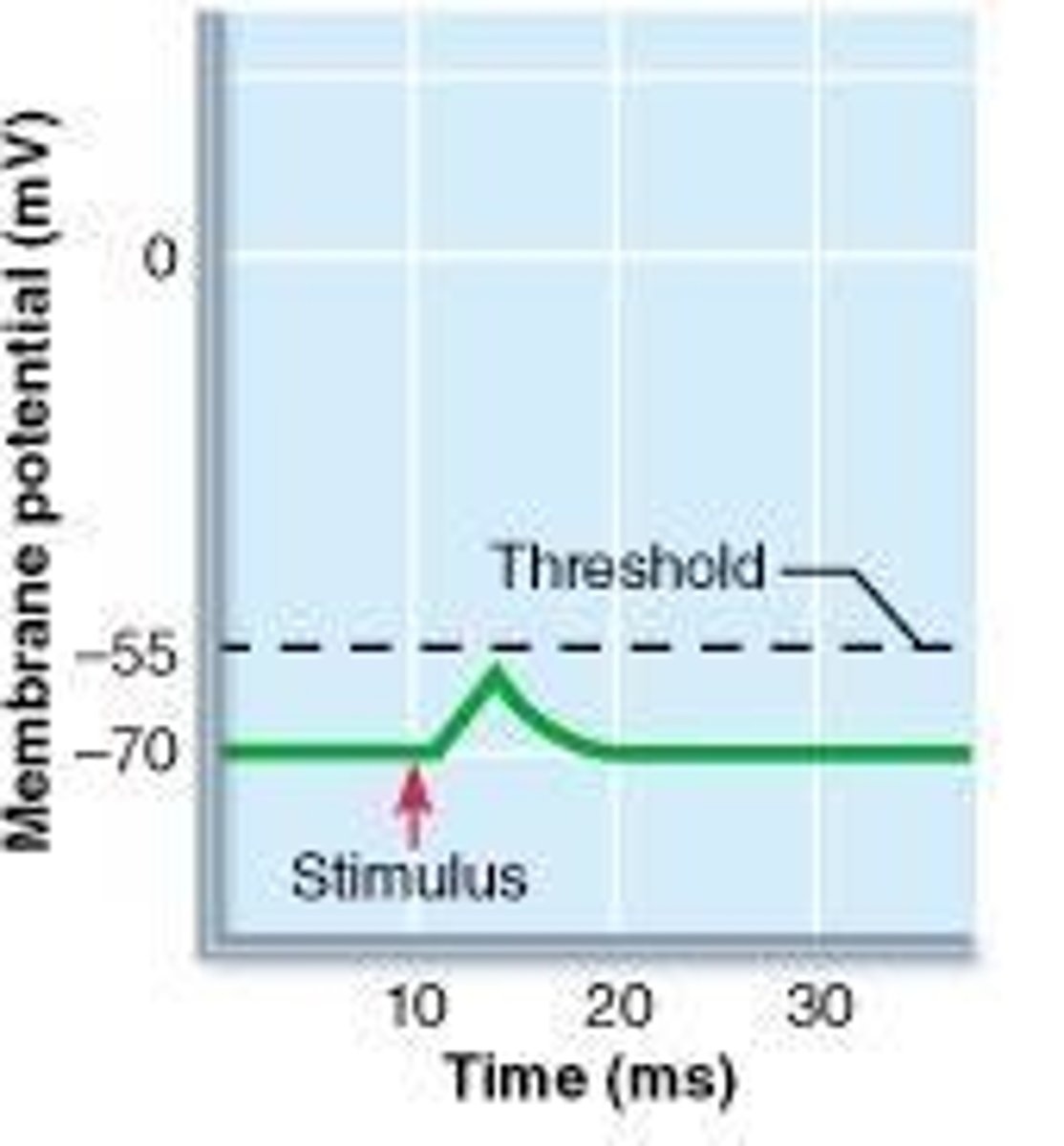
Resting Potential
the state of the neuron when not firing a neural impulse -70
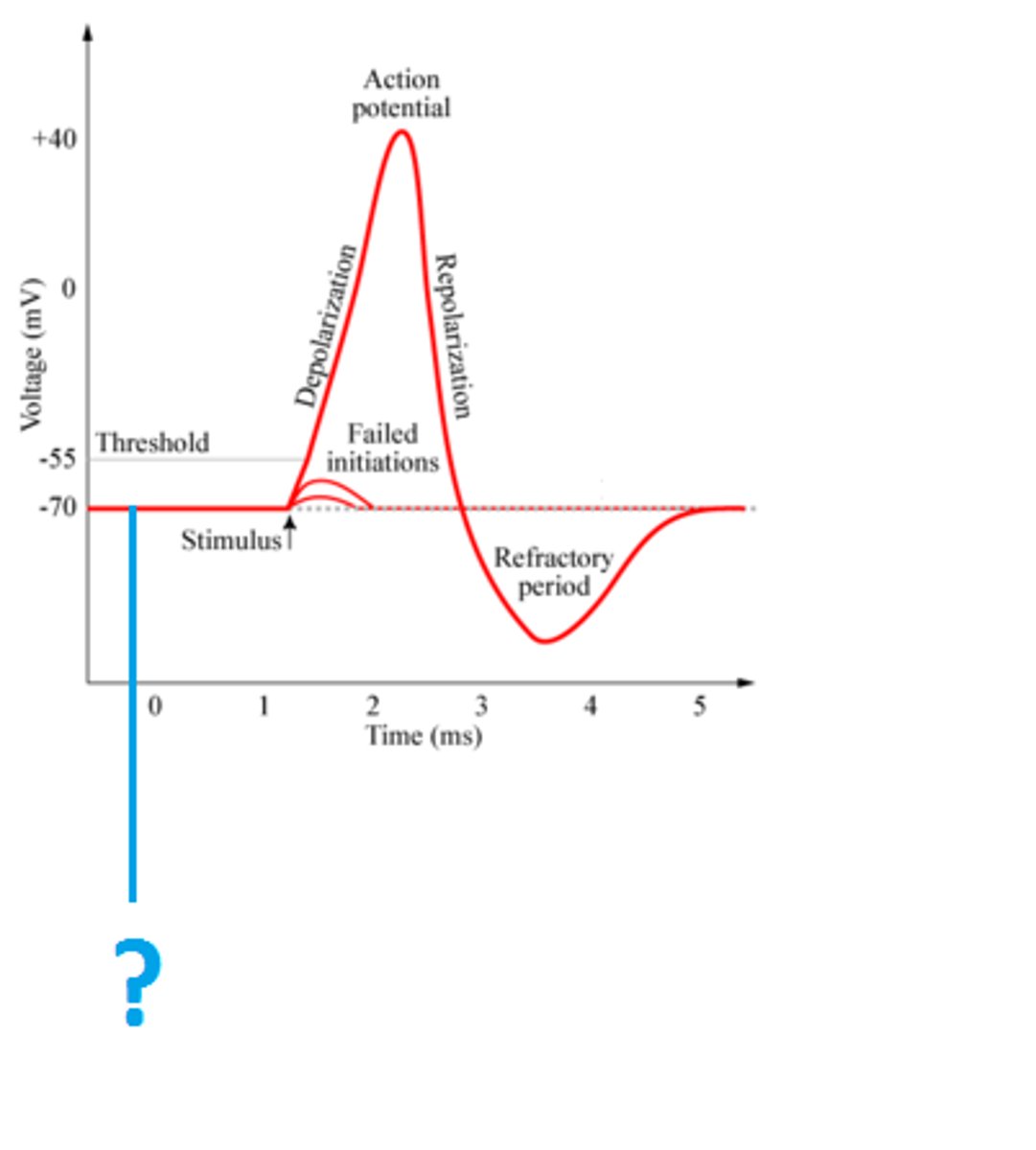
Threshold potential
-55mV, results in an action potential
Botulinum toxin
a neurotoxin produced by bacteria that inhibits acetylcholine release from a neuron, and suppresses muscle contraction for approximate 2-6 months
Lidocaine
role as a local anaesthetic, an anti-arrhythmia drug, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and a drug allergen
Ions
positively and negatively charged atoms
Membranes
a thin, selective barrier that separates the interior of a cell from its external environment, or internal compartments within the cell
Neurotoxins
substances that disrupt or damage the nervous system, either in the brain or peripheral nerves
Ion channels
channel proteins that transport ions
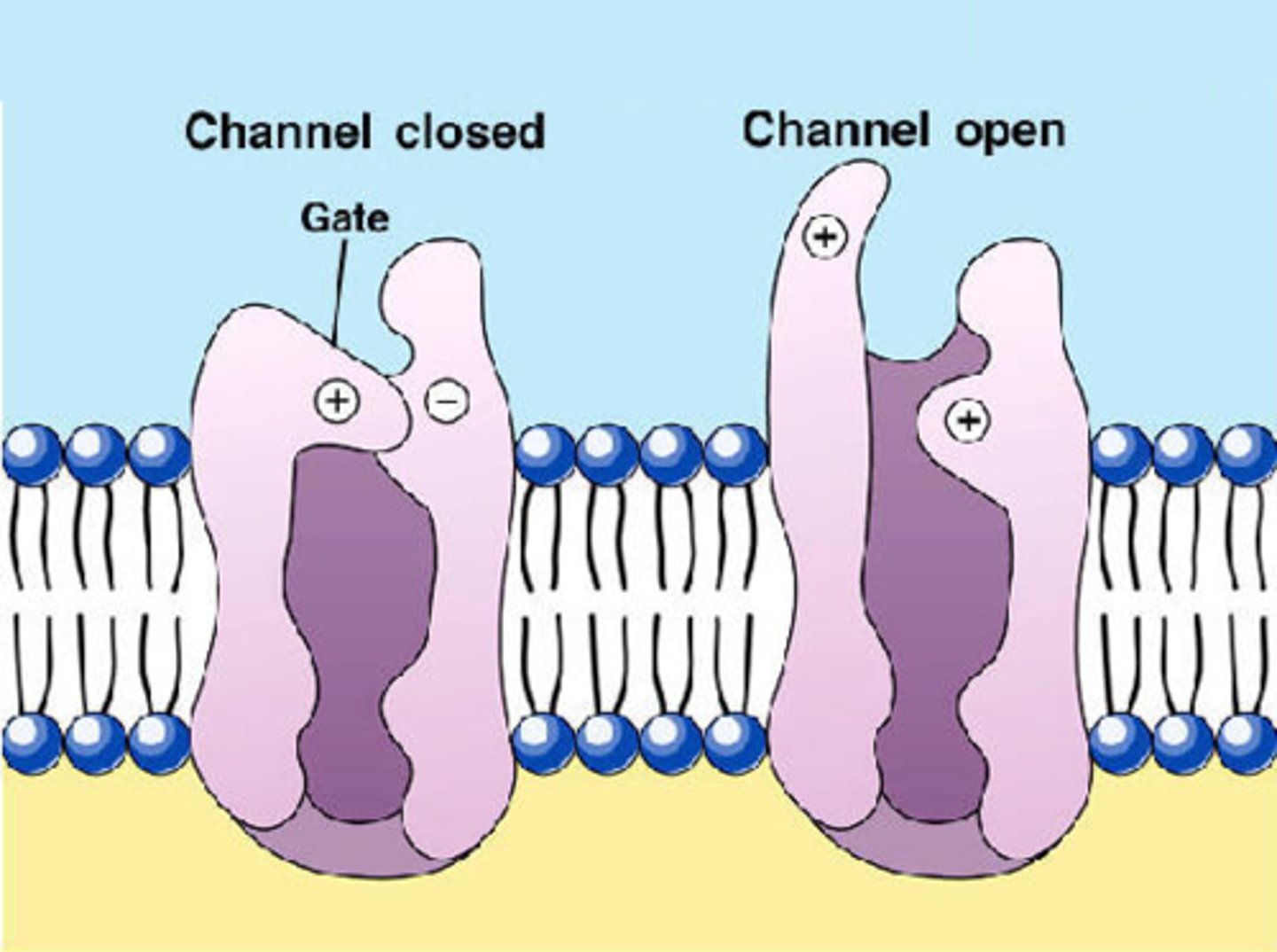
Na+ channels
Open during depolarization, allowing Na+ influx.
K+ channels
Open during repolarization, allowing K+ efflux.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Depolarized
a condition in which the inside of a cell membrane is more positively charged than the outside
Hyperpolarized
when the membrane potential is more negative