L13 Growth (Imported from Quizlet)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Cell growth is differentially regulated to maintain what?
The correct proportions and to drive morphogenesis
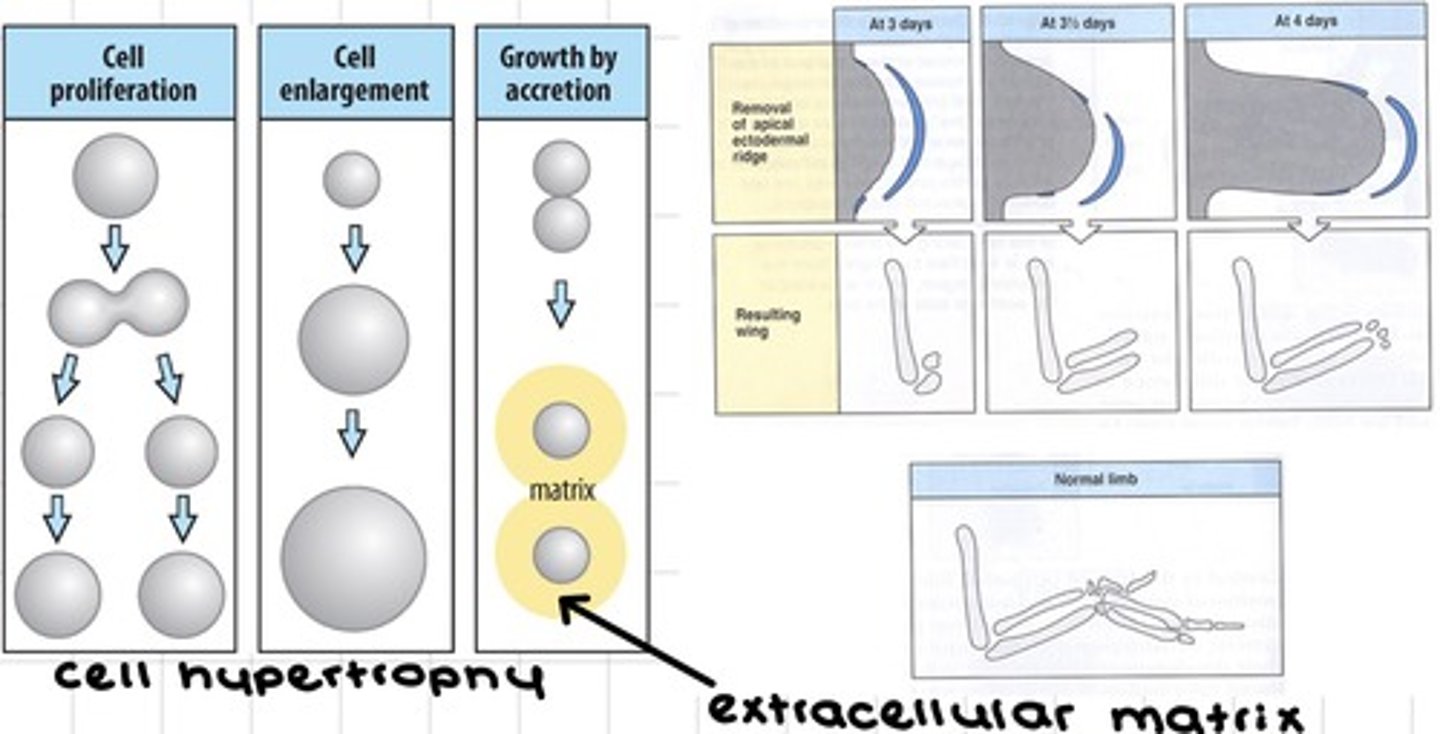
What is meant by hypertrophy?
Getting larger
Rates of division must be carefully regulated to maintain what?
Cell numbers in a given tissue
After early development, division is ______ -> typically one division every 24 hours in proliferating mammalian cells
Slower
Other cells do not divide once they are _____ and last for many years
Born
During DNA replication, each chromosome (maternal and paternal) is _________ to give rise to ________ __________
Duplicated, sister chromatids
Sister chromatids must be distributed (segregated) into ...?
Daughter cells
Cell cycle has how many stages?
Four
G phase is the ______ phase
Gap
G1 can be very ______ or even _________
Long, permanent
Most cells are in which phase?
G1
S phase is ...?
Replication
M phase is ...?
Dividing cells and chromosomes
Cell cycle has different checkpoints (yellow boxes) to ensure what?
That a cell does not enter mitosis unless needed
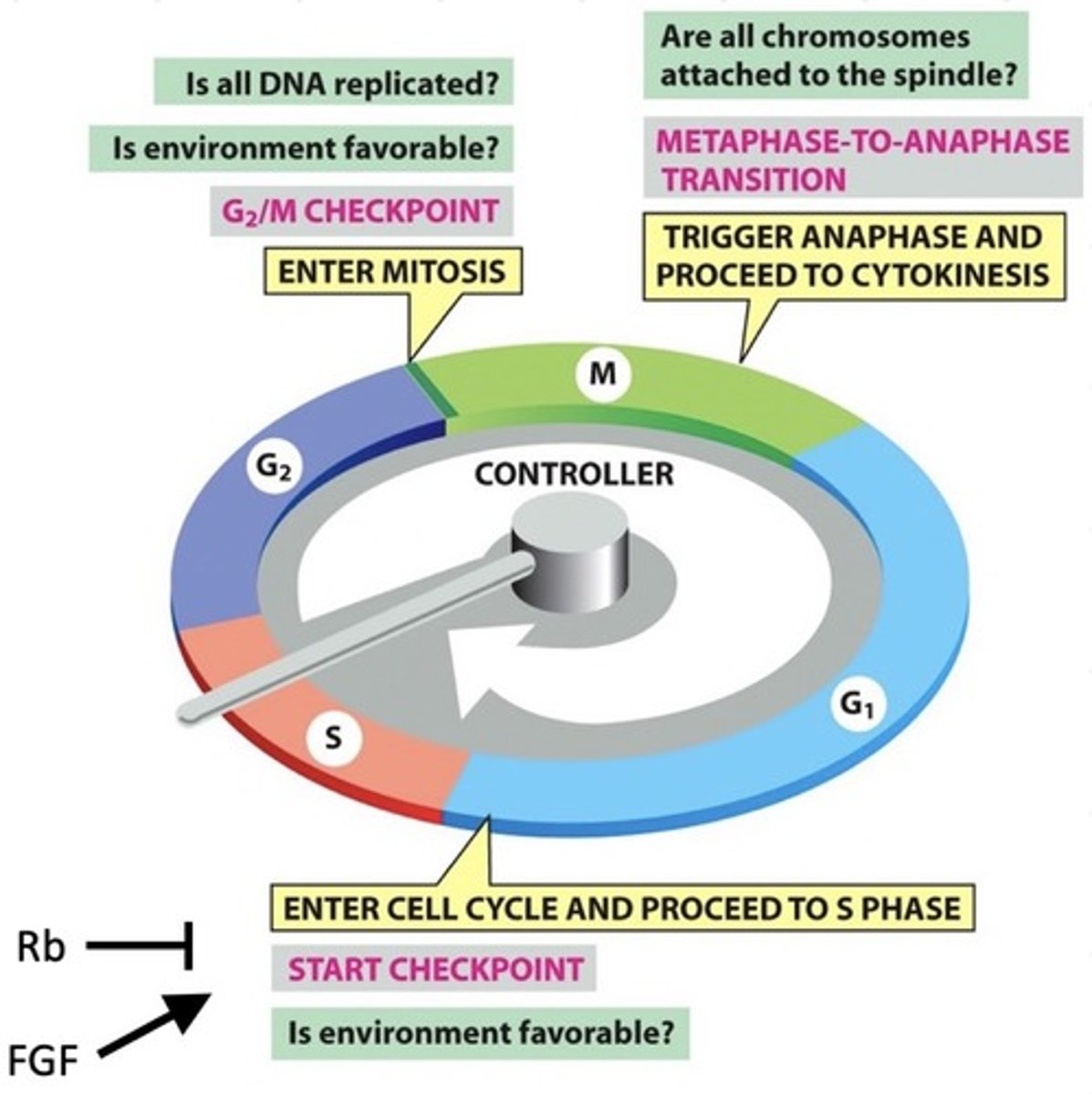
These checkpoints have to do with making sure everything is in order before _________ and _____________
Mitosis, cytokinesis
Which is the important checkpoint in development?
Start
Checkpoint genes are often mutated in tumours to do what?
Enable cell proliferation (e.g. retinoblastoma, Rb)
What does retinoblastoma inhibit?
Division
Overall growth is important in setting ...?
The adult size
What regulate the secretion of GH?
Somatostatin, GHRH
Body size is centrally controlled by ...?
Hormones
Three ________ feedback loops acting on growth hormone proliferation, these interactions must be __________
Negative, balanced
What is IGF and what does it do?
Insulin-like growth factor, acts more locally to drive cell proliferation
What is GH and what does it do?
Growth hormone, made in the pituitary, secreted ind he blood and drives growth, acting on liver and bone, drives proliferation, activates IGF
How is IGF regulated once it is activated by GH?
Negative feedback loop turns down secretion of GH
What is GHRH?
Growth horomone-relasing hormone
Organs have ways of _________ their own _____
Measuring, size
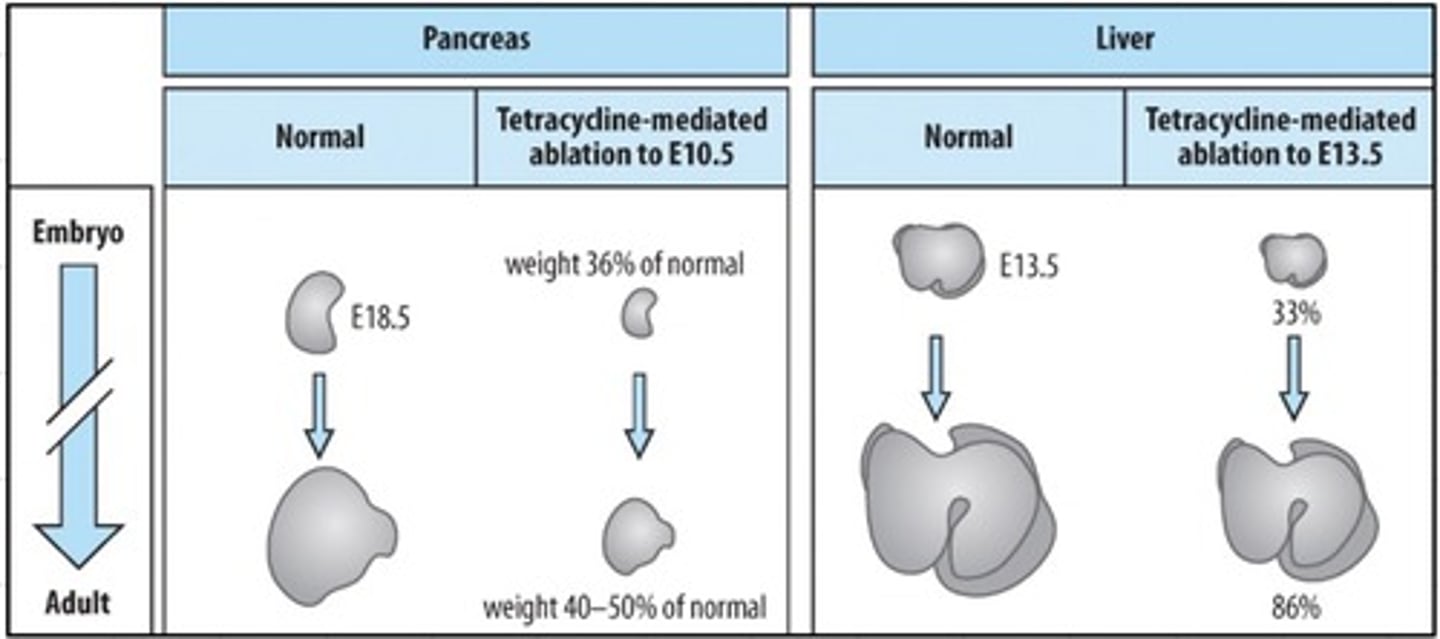
What is meant by ablation?
Destruction
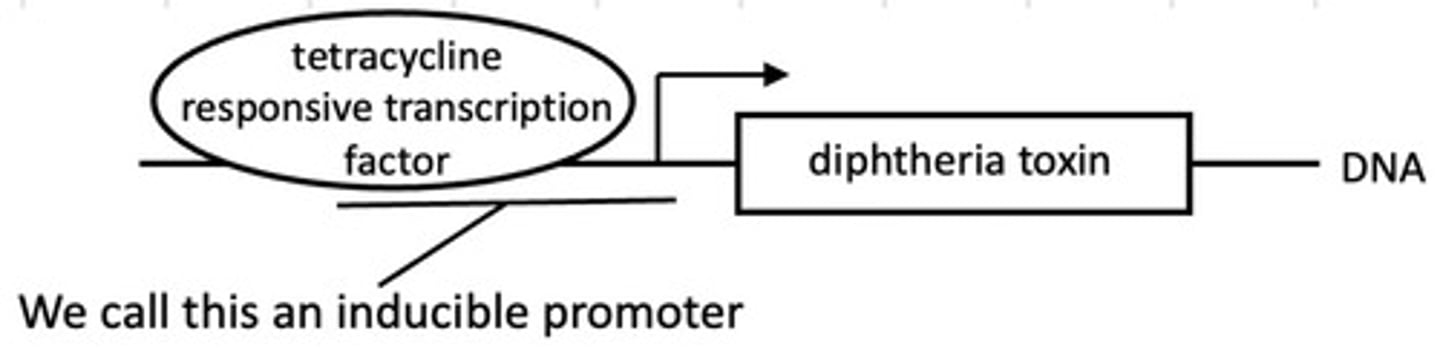
A strain of mice is generated that carries an introduced gene for diphtheria toxin under the control of what?
A tetracycline repressible promoter
Regulation of organ size by _____ and _______ pathways
TOR, Hippo
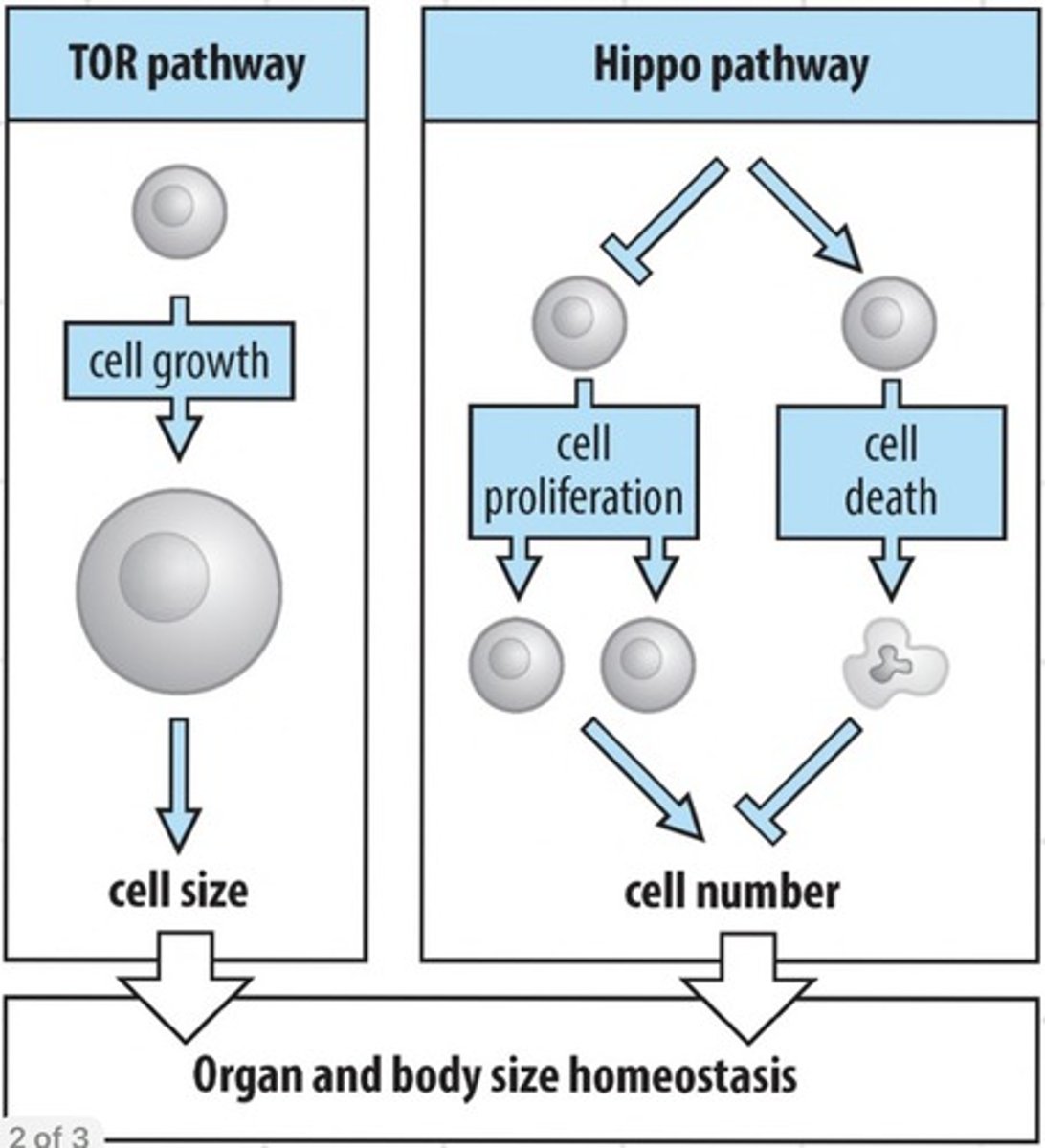
TOR pathway promotes ...?
Cell growth
Hippo pathway promotes ...?
Cell death (apoptosis)
Hippo inhibits _______ ____________ -> turn down the rate of cell division
Cell proliferation
Mutations in hippo cause ...?
Organ hypertrophy
Apoptosis is deliberate _______ of an _______ cell
Suicide, unwanted
What does apoptosis involve?
Careful coordination of the shut down of the cell -> followed by engulfment of the remnants by other cells
Apoptosis is caused ___________ by stress such as _________ or excessive _____ ________
Intrinsically, starvation, DNA damage
When is apoptosis used?
During development to cull unneeded cells
What is apoptosis used for in adult tissue?
Homeostasis (liver and mammary gland) and health (e.g. to get rid of infected, viral or genetically compromised tumour cells) and in the immune system ensure self reactive cells are removed
What can cause necrosis?
Injury, infection, cancer, infarction and inflammation
What is necrosis?
Disorderly, dying off of cell without any signal to or from the neighbouring cells
What happens to the cells during necrosis?
They split open and empty their contents into surrounding tissue
Myostatin is secreted/produced by ...?
Muscle
What does myostatin provide?
Negative feedback on muscle growth
Mutations that affect myostatin activity cause what?
Increased muscle mass
Myostatin reduces ________ _________ and ________ ___________
Myoblast proliferation, muscle differentiation
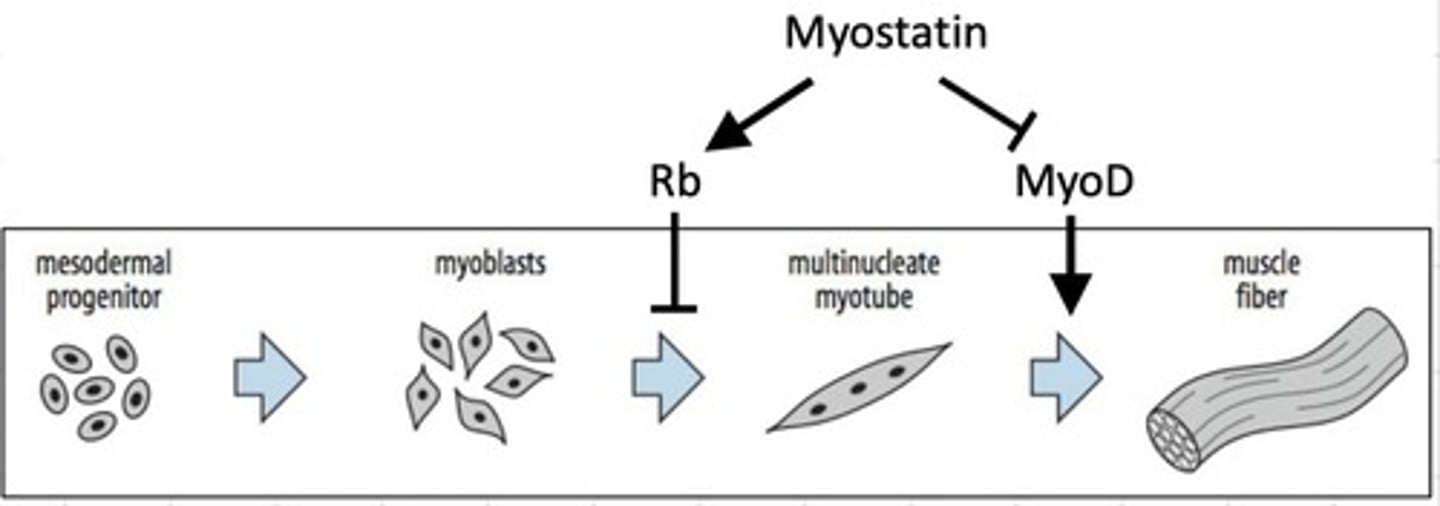
MyoD important in differentiation into _______ ______ -> myostatin blocks this
Muscle fibres
Myostatin activates ____ -> inhibits _____ ___________
Rb, cell proliferation
Removal of a kidney leads to what?
Increase in size of the remaining kidney
Why does this happen when you remove a kidney?
In response to a temporary rise in the concentration of creatinine in circulation (signals the need to increase kidney function)
The increase in kidney size is the result of ...?
Cell enlargement (hypertrophy)
The liver produces and regulates what?
Bile levels
Artificially increasing bile acid in circulation causes the liver to ______ in response, the _______ is the result of ___ _________. This leads to bile levels being ________ by liver absorption
Grow, increase, cell proliferation, reduced
Skeletal growth drives what?
Body growth
Most of the skeleton is formed as a _________ _________ in the embryo
Cartilage template
Most bones form initially as _________, over time bone cells secrete _____ to form _________ ________
Cartilage, bones, skeletal structure
Over time what is formed on the cartilage template?
Bone
What is a chondrocyte?
Cartilage cell
What is a osteoblast?
Bone cell
Where does cartilage remain?
In the joint areas
In long bones, chondrocyte proliferation drives what?
Post natal growth
Growth plates are formed by ...?
Chondrocytes
Chondrocytes are ___________ and then _______ in cell size (hypertrophy) give rise to ________ cells, invasion by __________ converting it to _____
Proliferating, increase, larger, osteoblast, bone
Once osteoblast converts larger cells into bone, _________ occurs and then ______ _______ is laid down in its place
Apoptosis, bone matrix
Growth driver at the _________ (between bone and cartilage caps) called the _______ ________
Interphase, growth plate
The growth plates close at the end of _________, all the chondrocytes ____ ____, all filled in with ____ ________
Puberty, die off, bone matrix
High levels of androgens in the ring finger ________ ______
Promote growth
High levels of oestrogen in the ring finger _________ ______
Repress growth