ALL of the Physics Required practicals
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Investigating Specific Heat Capacity
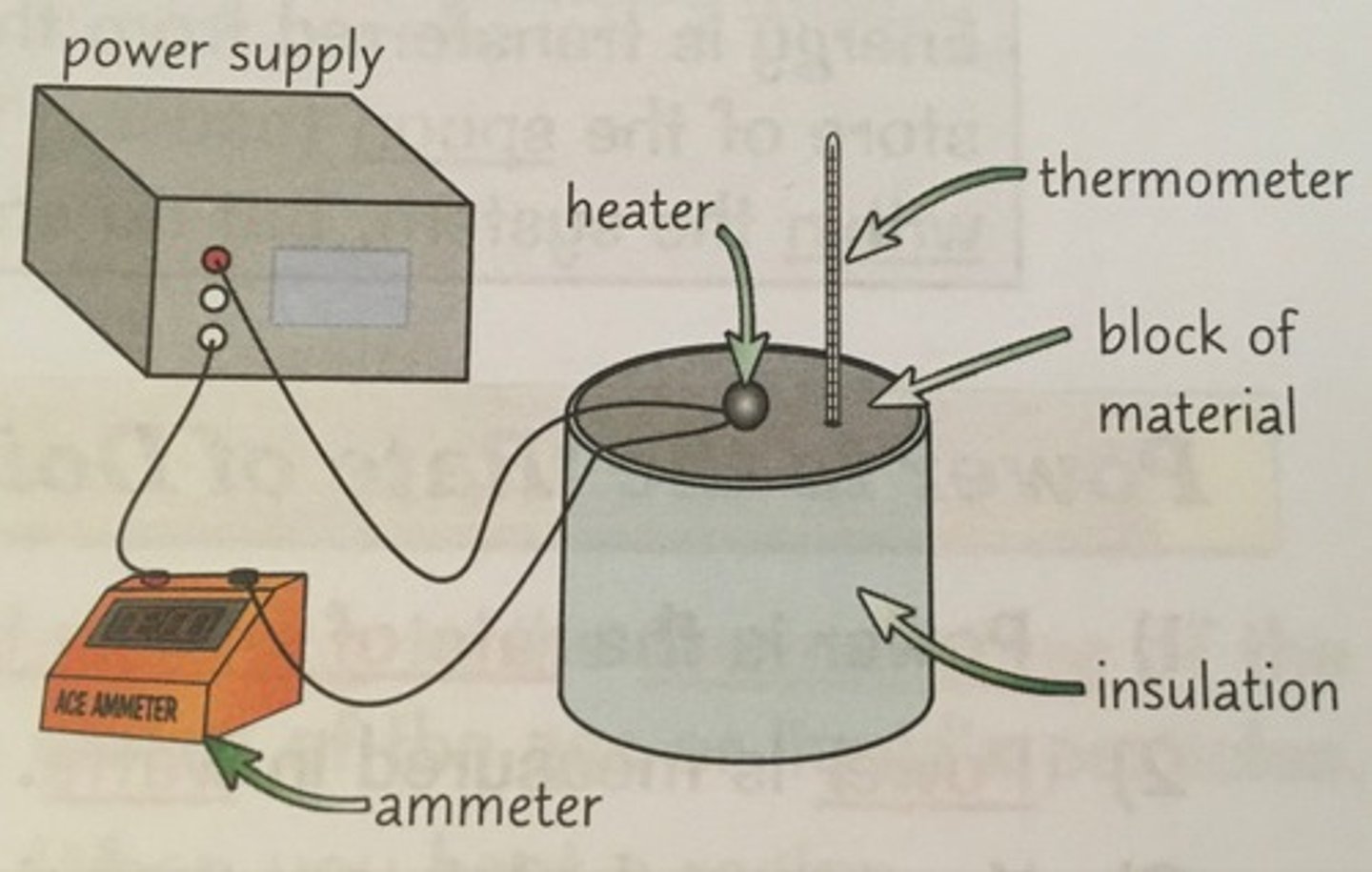
1) To investigate a solid material, you'll need a block of the material with two holes in it (thermometer and heater).
2)Measure the mass of the block .
3) Wrap it in an insulating layer.
4) Measure the initial temperature of the block .
5)Turn on the power.
6) Take readings of the temperature and curry every minute for 10 minutes .
7) When you have collected enough readings, turn off power supply.
When completing calculations assume all energy was transferred to the block.
Investigating Factors Affecting Resistance
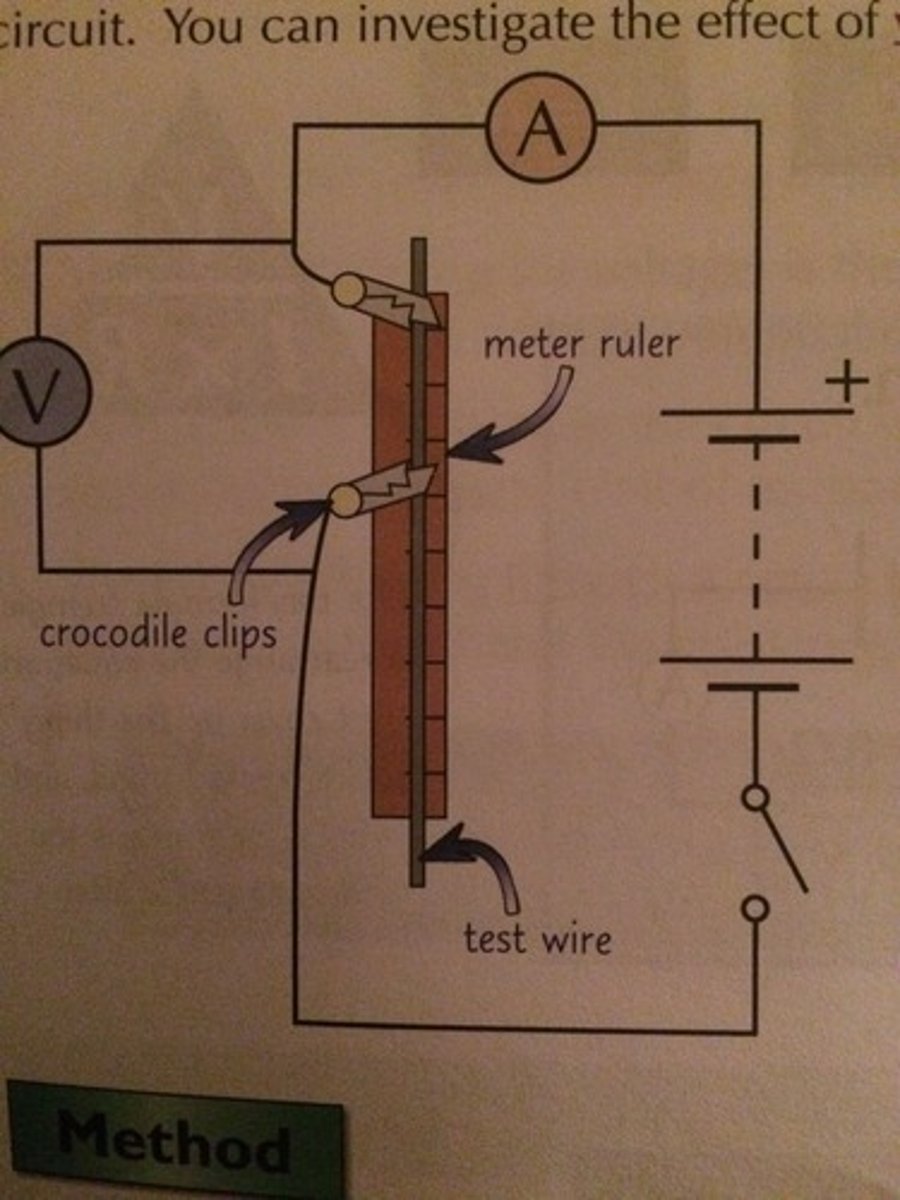
1) Attach a crocodile clip to the wire level with 0cm on the ruler
2) Attach a second crocodile clip to the wire 10 cm away from the first clip
3) Close the switch and record the current and pd flowing through it
4) Open the switch, removing the second crocodile clip and moving it further 10 cm from the first.
5) Repeat this for a number of lengths whilst recording current and pd
6) Using measurements and calculations, you can work out the resistance.
Your graph should should a directional proportional relationship between resistance and length of wire
Diodes , Ohmic conductors and Filament lamps
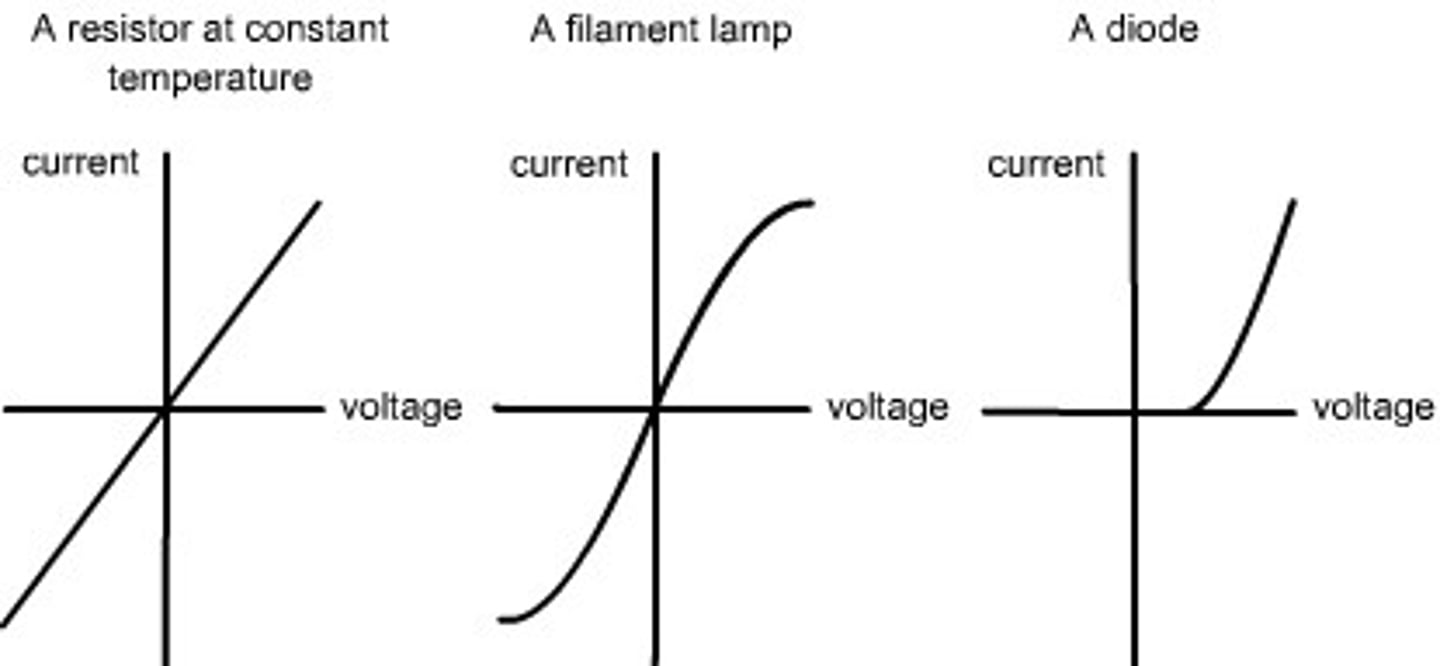
1) Set up a test circuit
2) Begin to vary the variable resistor. this alters the current flowing through the circuit and the pd across the component
3) Take several readings from the ammeter and voltmeter to see how pd across the components changes
4)Swap over the wires connected to the cell , so the direction of the current is reversed.
5) Plot graph for current against voltage for each component
Investigating Resistance in Series
1) Set up 4 identical resistors
2) Build a circuit
3) Measure the current through the circuit using the ammeter
4)Add another resistor in series with the first
5) Measure the current flowing through the circuit.
6) Repeat step 4 and 5 until all resistors have been added.
Investigating Resistance in Parallel
1) Use same equipment as investigating in series
2) Measure total current through the circuit without a resistor
3) Add another resistor in parallel
4) Measure the total current and pd (to calculate resistance)
5)Repeat steps 3 and 4 until all resistors are added
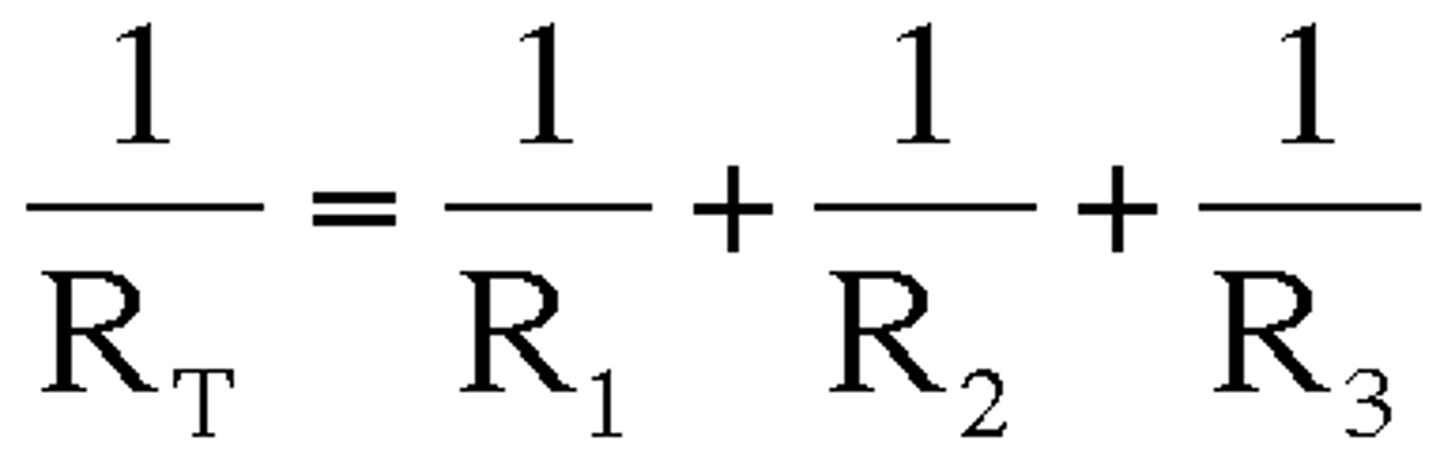
Measuring Density in a Solid
1) Use a scale to measure mass
2) Measure it volume ( of regular use volume equation)
3) For an irregular solid, you can work out its volume by how much space it takes up in water
4) Using a eureka can, you place the object in water; after next to the can have a measuring cylinder
5) Measure the amount in the measuring cylinder.
6) Use the formula for density

Measuring Density in a Liquid
1) Place a measuring cylinder on a balance and set it to zero
2) Pour 10ml of the liquid into the measuring cylinder, record the mass
3) Continue until you reach the maximum of the cylinder (10ml)
4) For each measurement, use the density.
5) Finally take an average of all your calculated density.

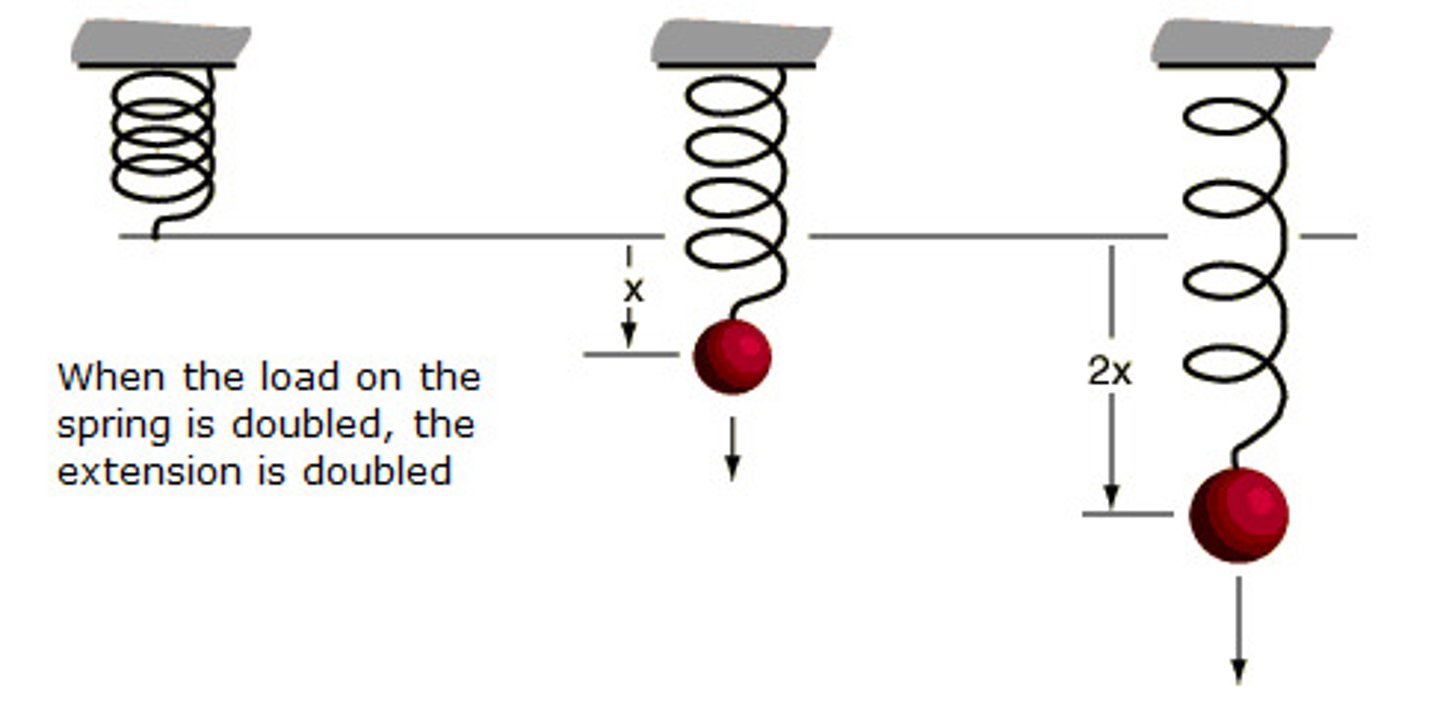
Hooke's Law
1) Measure natural length of the spring
2) Add a mass to the spring and allow it to come to rest
3) repeat until you have enough measurements (min 6)
4) Plot a force-extension graph
The results will be directional proportional.
Investigating Acceleration in F=MxA
1) Set up a trolley so it holds a piece of card that will interrupt the signal on the light gate twice.
2) This will measure acceleration.
3) Using a light measure the first and second point it passes.
Work out an average acceleration.
To reduce the effect of friction use an air track.
Investigating Mass in F=MxA
1) Add masses to the trolley one at a time to increase the mass of the system
2)Record average acceleration for each mass
To reduce the effect of friction use an air track.
Investigating Force in F=MxA
1) Keep total mass of the system the same but the change the mass on hook
2) Start with all the masses onto trolley
3) Transfer the hooks one at a time to the hook, to increase the accelerating force
4) The mass of the system stays the same as you're transferring the masses from one part of the system to another (the hook)
5) Record the average acceleration for each force
To reduce the effect of friction use an air track.
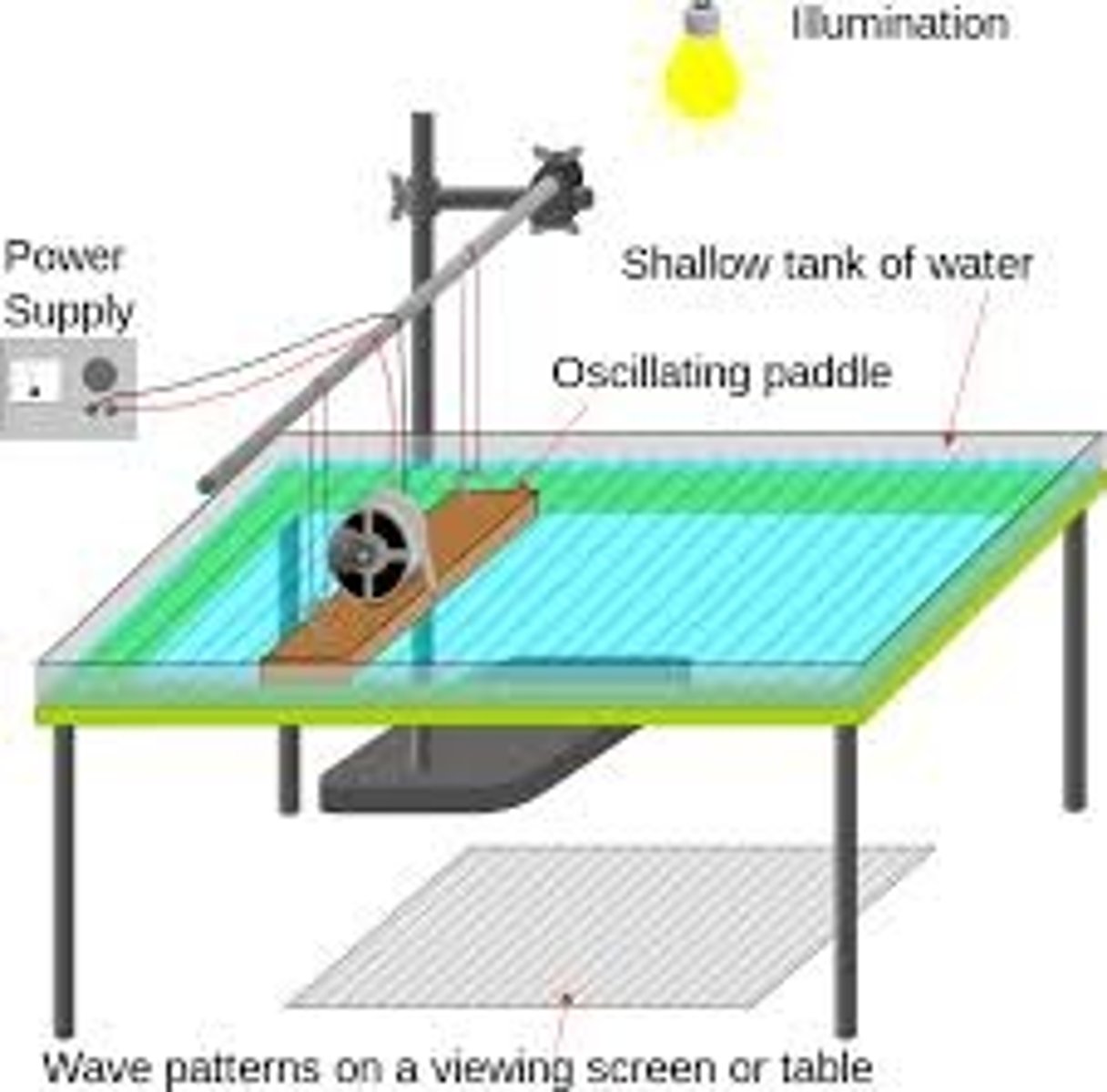
Ripple Tank Experiment
1) Using a signal generator attached to the dipper of a ripple tank, you can create waves at a certain frequency.
2)Use a strobe light to see wave crests on the screen
3)Increase the frequency until the wave pattern on the screen appears to have stops
-this happens when the frequency of the strobe light is equal to the frequency of the waves
4) Measure the distance between shadows lines that are 10 wavelengths apart then divide by 10 to find average wavelength.
Use formula to find wave speed
Investigating Waves on Springs
1) Turn on signal generator and vibration transducer.
2) Adjust the frequency of the signal generator until there is a clear wave on the string
3) The frequency of wave will depend on length of string and masses used
4) Measure the wavelengths of these Waves
- Calculate mean half -wavelengths , using a ruler to measure each one
5)The frequency of the wave is whatever the signal generator is set to.
Use formula to find speed of wave.
Measurements of waves are halves , as you measure the wave from pulley to signal generator not back.
This means you must always double the wavelength.
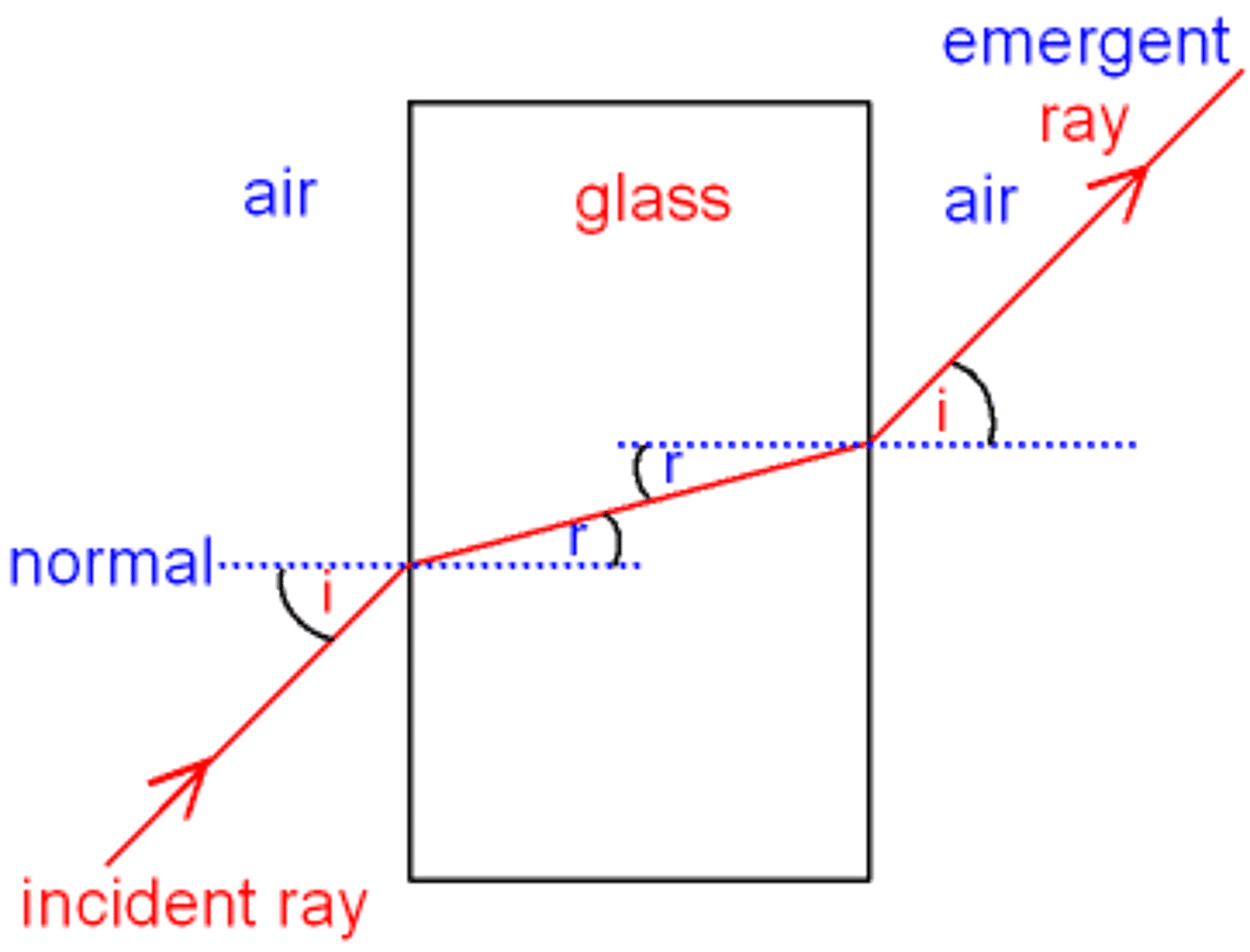
Using Transparent Materials to Investigate Refraction
1)Put it on paper and trace around it
2) Shine a ray of light using ray box at the middle of one side of the block
3) Trace the incident ray and mark where the light ray emerges on the other side of the block
4) Remove the block and draw a straight line in the middle of the tracing to show the path of the refracted ray through the block
5)Draw a normal at the point where the light ray entered the block
6) Using a protractor measure the angle between the incident ray and refracted ray
7) Repeat using different blocks of different materials
The angle of refraction changes due to different materials optical densities.
Investigating IR Radiation
A Leslie cube is a hollow, watertight cube. Four vertical faces which have different surfaces.
1) Place an empty Leslie cube on a heatproof mat
2)Fill it with boiling water
3)Wait for the cube to warm up and hold a thermometer against each of the sides
- each face will have the same temperature
4) Hold an infrared detector at a set distance and record the amount of IR radiation it detects
5) Repeat this for each of the cube's faces
More infrared radiation from the black surfaces than the white ones
this questions is often associated with risk assessments
-eg. wearing gloves when carrying boiling water etc.
