Protein Digestion & Protein Turnover
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Essential amino acids are from the _____?
diet
Non-essential amino acids are from the _____?
body
Non-essential amino acids are synthesized initially from ______?
glucose
What are the 2 ways non-essential amino acids are synthesized?
1. Glycolysis
2. TCA Cycle
What enzyme hydrolyzes proteins to smaller polypeptides in the stomach?
Pepsin
What enzymes turn the polypeptides into amino acids in the small intestine?
- trypsin
- chymotrysin
- elastase
- carboxypeptidases
- aminopeptidases
Amino acids are absorbed through the _________ and enter the _____?
absorbed through intestinal epithelial cells and enter the blood
The inactive form of digestive protease enzymes are called?
zymogens (-ogen)
Trypsinogen is activated by ________ to form active protease trypsin?
enteropeptidase
Which digestive enzyme plays a key role in activating other pancreatic zymogens?
trypsin
Trypsin cleaves peptide bonds with _______ groups?
carboxyl group
Chymotrypsin favors residues that contain _______ amino acids?
hydrophobic
Elastase cleaves ______?
elastin
Carboxypeptidase A releases ______ amino acids?
hydrophobic
Carboxypeptidase B releases ______ amino acids?
basic
Aminopeptidases is a ______ inhibitor?
trypsin
Absence of the trypsin inhibitor leads to what disease?
pancreatitis
(activation of zymogens --> digestion of intracellular pancreatic proteins)
What 3 transporters are used to absorb amino acids?
1. Na+-dependent carriers
2. ATPase pump
3. Facilitated transporter
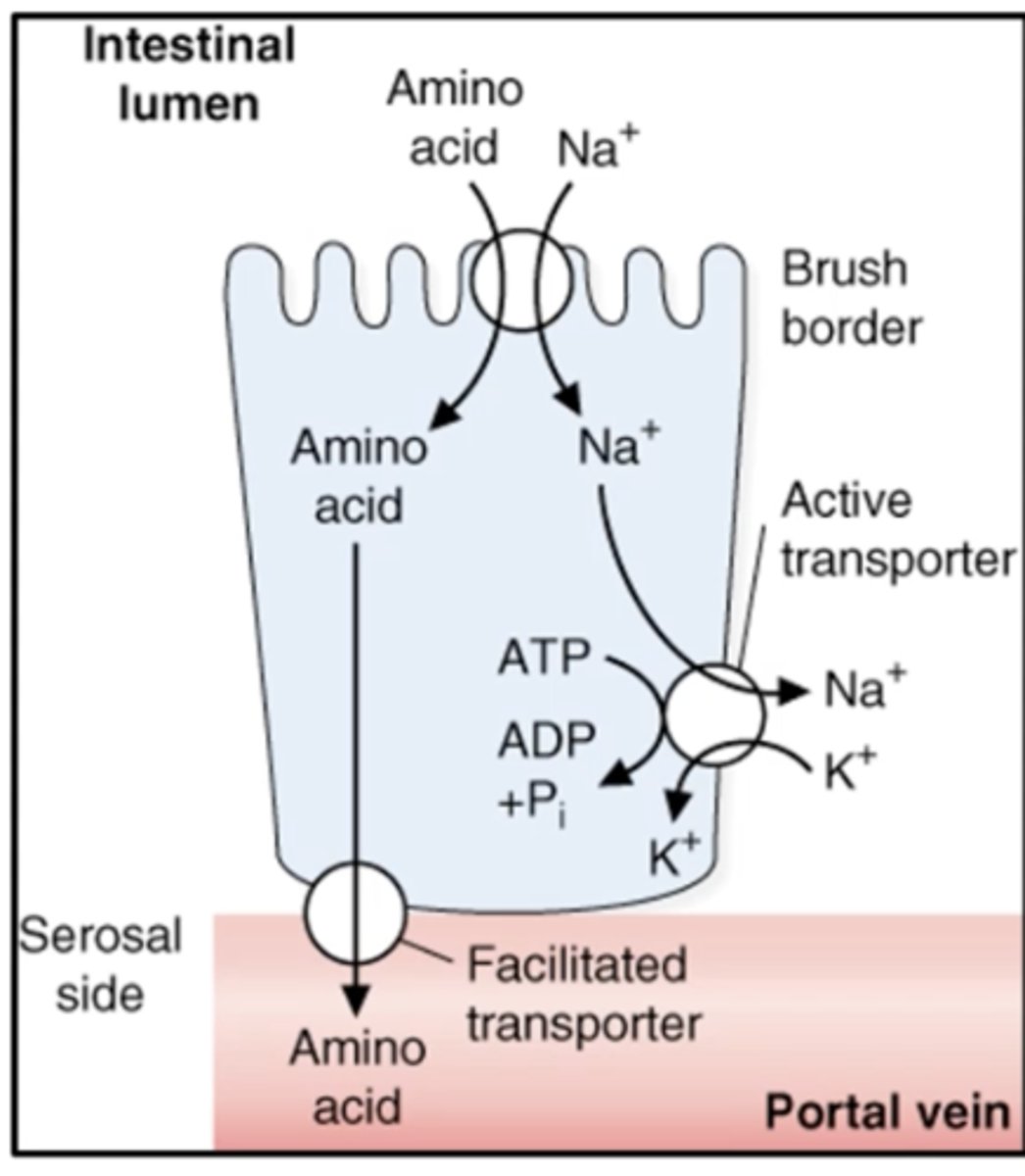
Na+-dependent carriers transports _____ & _____ into intestinal epithelial cell?
Na+ & amino acid
ATPase pump lets _____ out of the cell?
NA+
Facilitated transporter lets _____ out of the cell into interstitial fluid?
amino acids
During starvation, the _______ takes up amino acids from the ______ to use as an energy source
facilitated transporter
blood
What is a deficiency of protein in a diet called?
Kwashiorkor
What are some effects of Kwashiorkor?
- muscle wasting
- decreased concentration of plasma proteins
- fluid retention
- permanent effects on growth & mental ability
Protein is a _____?
fuel
If their carbon skeletons can be converted to a precursor of glucose then it's a ______ amino acid?
glucogenic
If their carbon skeletons can be converted directly to acetyl CoA or acetoacetate then it's a ______ amino acid?
ketogenic
What are the products of glucogenic amino acids?
- glucose
- CO2
Glutamate --> _________ --> ________ --> glucose
glutamate --> alpha-ketoglutarate --> malate --> glucose
Glutamate is used for synthesis of what 4 things?
- glutamine
- proline
- ornithine
- arginine
What are the products of ketogenic amino acids?
- acetoacetate
- acetyl CoA
What enzyme synthesizes tyrosine?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
What coenzyme synthesizes tyrosine?
tetrahydro biopterin (BH4)
BH4 & tyrosin hydroxylase are required for synthesis of ________?
catecholamines
BH4 & trypotphan hydroxylase are required for synthesis of _______?
serotonin
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disorder resulting from loss of gene coding for _______?
Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH)
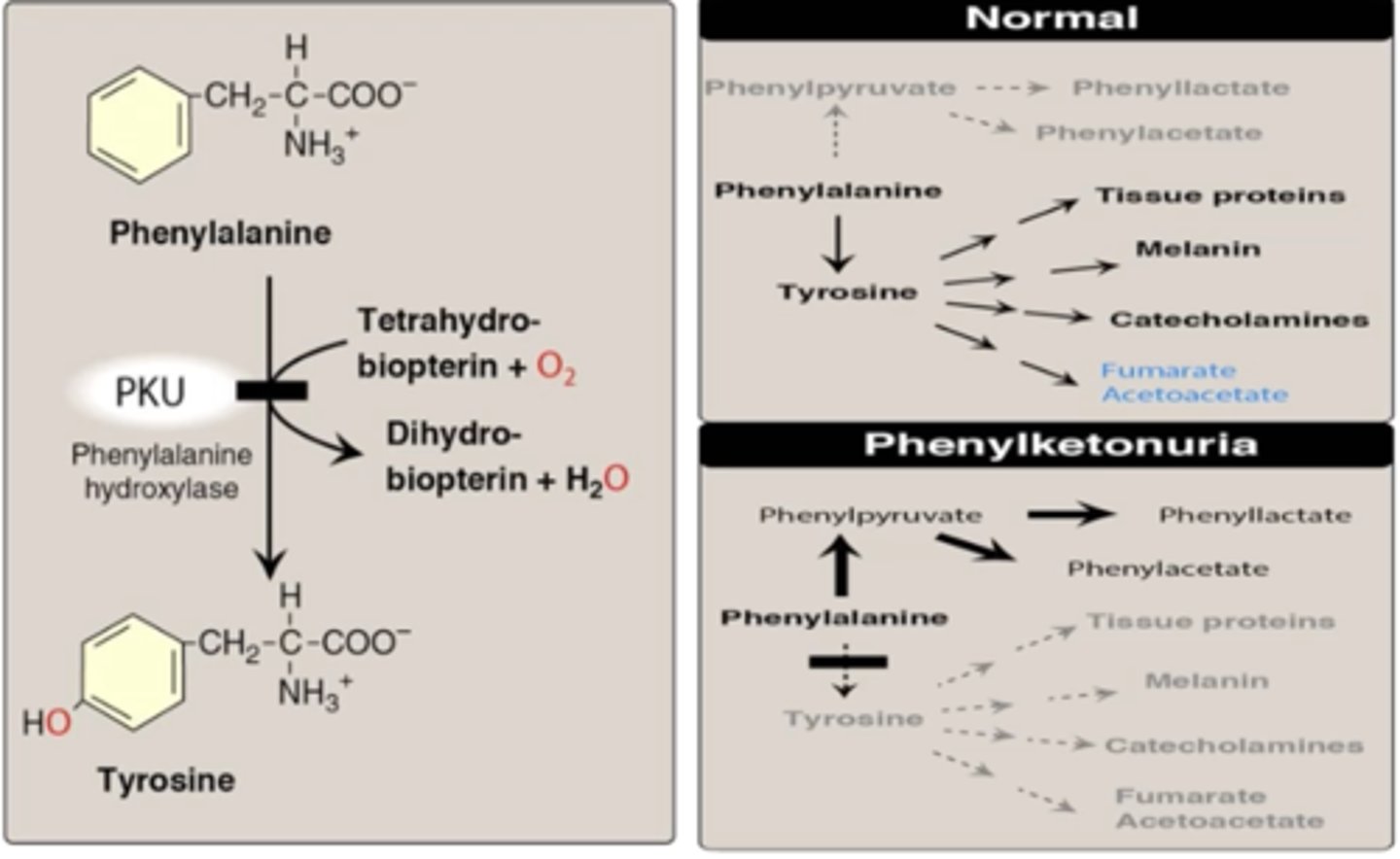
PKU will (drop/raise) phenylalanine concentration?
raise
What are the symptoms of PKU?
- jerky movements in the arms & legs
- mental retardation
- lighter skin & eyes
Albinism is a defect in ______ metabolism?
tyrosine (tyrosinase deficient)
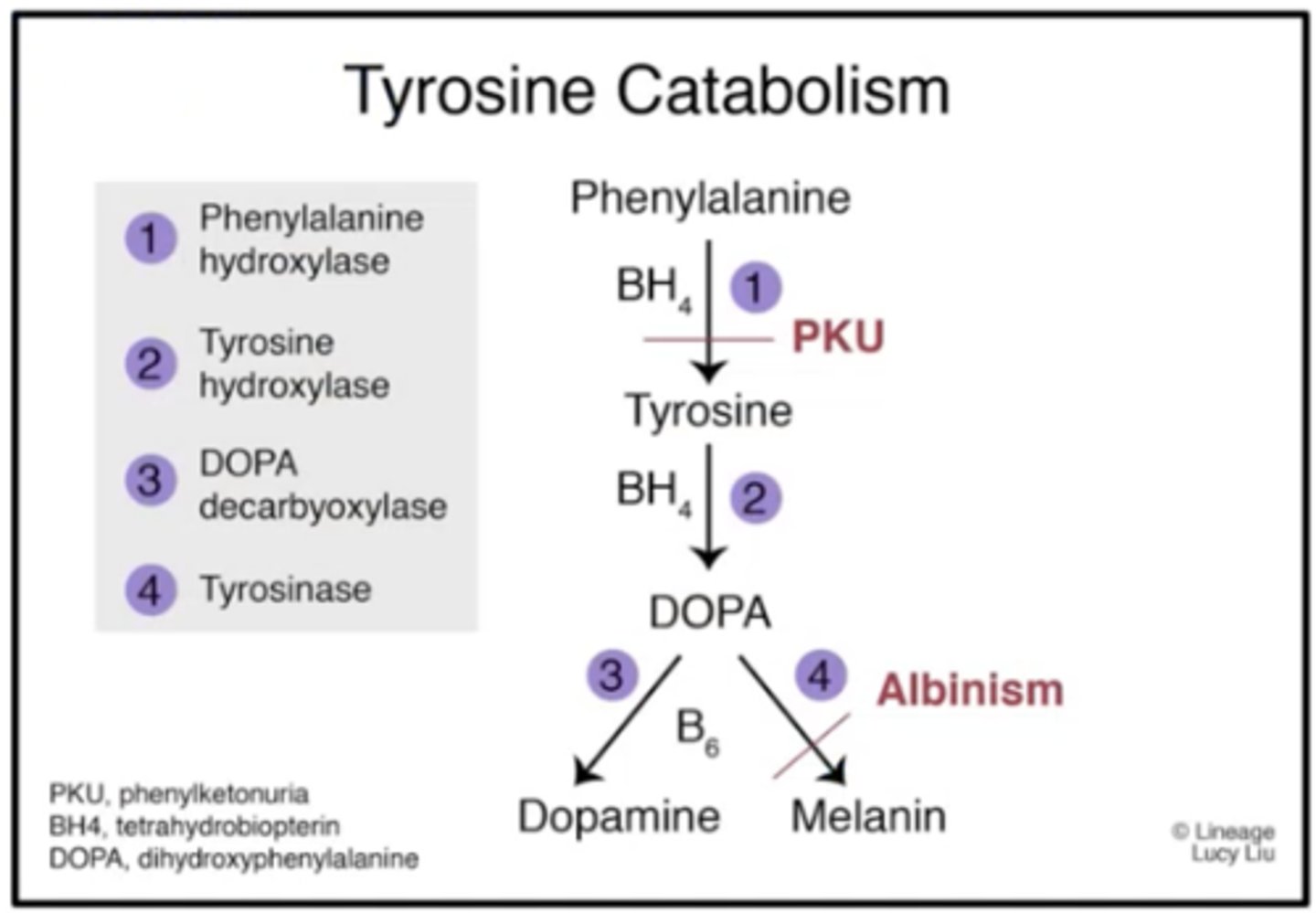
What are some symptoms of albinism?
- hypopigmentation
- vision defects
- photophobia
- increase risk for skin cancer
Alkaptonuria is a deficiency in ____?
homogentisic acid oxidase
Alkaptonuria will (increase/decrease) homogentisic acid?
increase
What are the symptoms of alkaptonuria?
- early onset of arthritis
- black urine
- black pigment in cartilage & collagenous tissue