ANA code of ethics
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Provision 1
The nurse practices with compassion and respect for the inherent dignity, worth, and unique attributes of every person
Provision 2
A nurse’s primary commitment is to the recipient(s) of nursing care, whether an individual, family, group, community, or population.
Provision 3
The nurse establishes a trusting relationship and advocates for the rights, health, and safety of recipient(s) of nursing care.
Provision 4
Nurses have authority over nursing practice and are responsible and accountable for their practice consistent with their obligations to promote health, prevent illness, and provide optimal care
Provision 5
The nurse has moral duties to self as a person of inherent dignity and worth including an expectation of a safe place to work that fosters flourishing, authenticity of self at work, and self-respect through integrity and professional competence.
Provision 6
Nurses, through individual and collective effort, establish, maintain, and improve the ethical environment of the work setting that affects nursing care and the well-being of nurses.
Provision 7
Nurses advance the profession through multiple approaches to knowledge development, professional standards, and the generation of policies for nursing, health, and social concerns.
Provision 8
Nurses build collaborative relationships and networks with nurses, other healthcare and non-healthcare disciplines, and the public to achieve greater ends.
Provision 9
Nurses and their professional organizations work to enact and resource practices, policies, and legislation to promote social justice, eliminate health inequities, and facilitate human flourishing.
Provision 10
Nursing, through organizations and associations, participates in the global nursing and health community to promote human and environmental health, well-being, and flourishing.
Ethics
The study of what is right and wrong
Morals
Judgment about behavior, based on specific beliefs
Value
Deeply held belief about the worth of an idea, attitude, custom, or object that affects choices and behaviors
ethic principles
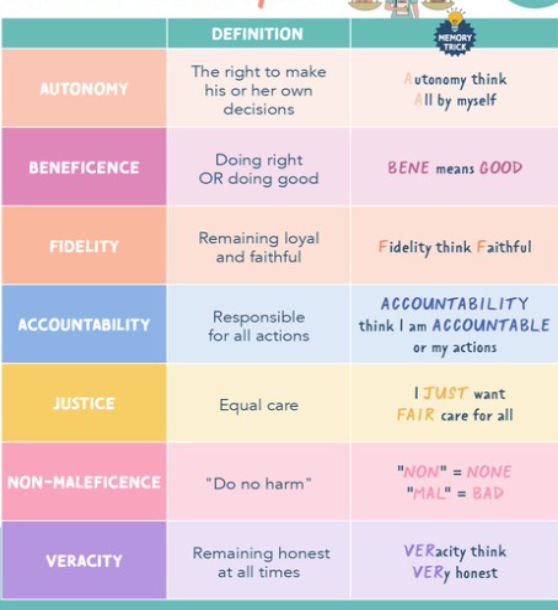
Veracity
The ethical principal of being honest and truthful based on trust and respect for our patients.
•Veracity requires nurses to be honest with patients about their diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis
Beneficence
Nurses acting in the best care of the patient.
Promoting a patient’s health and well being and
ensuring that their care benefits them.
Autonomy
Respect for autonomy: Patients have the right to make their own decisions about their care.
nonmaleficence
Do no harm
Justice
treat patients equality
Fidelity
The faithfulness or agreement to keep promises
Moral distress
when one knows the ethically correct action to take but feels powerless to take that action.
AACN’s Model to Rise Above Moral Distress & steps
• can be used to address a variety of moral distress situations in nursing
• a valuable tool for nurses who are facing moral distress. It can help nurses to make informed decisions about how to act in accordance with their values and beliefs.
1. Ask: Is this situation causing me moral distress?
2. Affirm: As a nurse, I have a professional responsibility to act in the
best interests of my patient.
3. Assess: What are the options available to me? I could talk to my
manager about my concerns, advocate for my patient's wishes, or
refuse to participate in the procedure.
4. Act: I will talk to my manager about my concerns and advocate for
my patient's wishes. If necessary, I will refuse to participate in the
procedure.
7 Step Ethical Dilemma Resolution Model
Step 1: Ask: Is this an ethical problem?
Step 2: Gather information relevant to the case. Patient, family, health care agency, and social perspectives are important sources of relevant information.
Step 3: Identify the ethical elements in the situation by clarifying values and recognizing the principals involved. Distinguish among fact, opinion, and values.
Step 4: Name the problem. A clear, simple statement of the problem is not always easy, but it helps to ensure effectiveness in the final plan and facilitates discussion.
Step 5: Identify possible courses of action. Access others for their input and be creative in identifying different options.
Step 6: Create and implement an action plan. Gather support from others and identify an alternative action if the chosen one does not achieve resolution.
Step 7: Evaluate the action plan to determine whether further action is needed or if lessons learned in this experience can be applied forward
Communication has many forms:
• Nonverbal behaviors (can be body language)
• Written communication
• Tone of voice
• Words
• Emotions
SBAR
S - situation
B - background
A - assessment
R - recommendation
SBAR
• Situation
• The situation describes the issue or reason for contacting the physician.
This is where you provide basic information about yourself and the patient.
• Your name (first name only)
• Your title (nurse)
• Facility/Unit (2 east, General Hospital)
• Patient's name (John Doe)
• Sex (male) and Age (68)
• Room number (242)
• Reason for contact (complaints of severe back pain)
SBAR
Background
• This is where you describe the patient's background information that relates to the situation you described previously.
• Reason for admission (increase in back pain)
• Date of admission (8/23)
• Medical history (chronic back pain for 5 years)
• Procedures done and date (spinal fusion 8/24)
• Current medications (5 mg oxycodone Q6 PRN)
• Allergies (morphine)
SBAR
Assessment
• This is where you describe what you assessed about your patient that relates to the situation. This can include all of the primary senses such as what you see, hear, smell, feel, etc.
• Vital Signs (BP 182/109, HR 116, RR 28)
• Lab values (none in this case)
• Head to toe assessment observations (sweating, shallow breaths)
• Alteration in physical status (shuffling gait while hunched over)
• Alteration in mental status (crying and moaning)
• Patient concerns (Asks "Did something go wrong with my surgery?")
• Patient complaints (States "I'm in much more pain now than I was before
surgery.")
SBAR
Recommendation
• This is where you either offer your own recommendation, or you ask the physician for their recommendation on how to move forward with your patient. In other words, the intervention for you to make.
• Medications needed (Change oxy to 10 mg Q4 PRN)
• Labs to be drawn (none in this case)
• Specimens to collect (none in this case)
• Procedures to be done (back x-ray)
• Further assessments to be done (vital signs Q1 until stable)
• Transfer orders (none in this case)
EXPLICIT BIAS
Explicit bias in nursing refers to conscious, intentional prejudiced beliefs or attitudes that a nurse is aware of and can report, such as making discriminatory remarks or implementing exclusionary policies that negatively affect patients or colleagues.
IMPLICIT BIAS
• Implicit bias refers to unconscious associations and stereotypes that
influence our judgments and behaviors without our awareness.