The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Recall the components of the nervous system
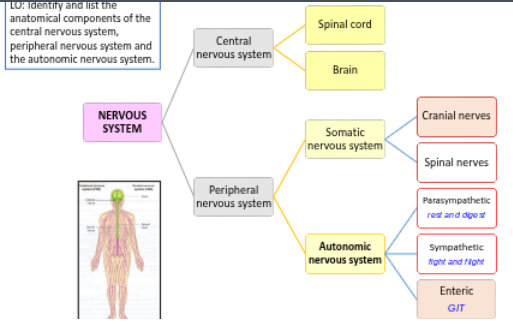
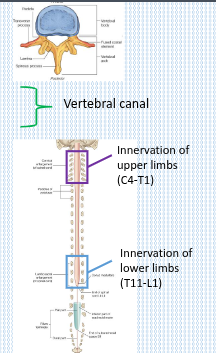
Describe the anatomical relationships of the spinal cord and spinal nerves with the vertebral column
• Tubular bundle
• Nervous & connective tissue
• Extends from brainstem to lumbar vertebral canal
• Continuation of medulla oblongata (foramen magnum)
• Terminates ~L2 with conus medullaris
How many paired spinal nerves are there in the human body?
31 paired spinal nerves.
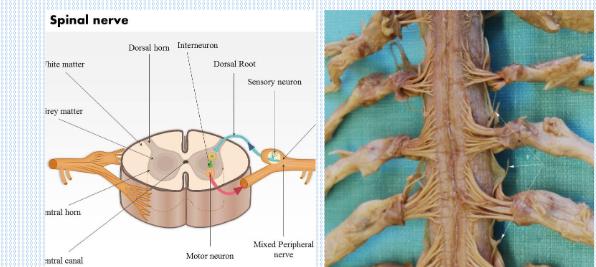
What are the two types of roots that connect spinal nerves to the spinal cord?
Dorsal roots (sensory, towards the spinal cord) and ventral roots (motor, away from the spinal cord).
Through which structure do spinal nerves exit the vertebral canal?
Intervertebral foramina.
After leaving the vertebral canal, into what two branches do spinal nerves divide?
Small posterior rami and large anterior rami.
What does the small posterior rami supply?
Deep muscles of the back and the overlying skin
What does the large anterior rami supply?
Most other skeletal muscles and the remaining skin, except for the head
Describe the anatomical relationships of the spinal cord and spinal nerves with the vertebral column.
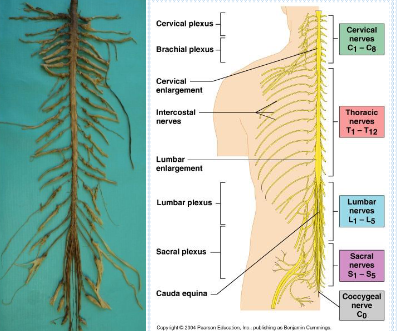
How are spinal nerves named?
According to the vertebrae they are associated with.
How many cervical spinal nerves are there, and what are they labelled as?
There are 8 cervical spinal nerves, labelled C1–C8
How many thoracic spinal nerves are there, and what are they labelled as?
There are 12 thoracic spinal nerves, labelled T1–T12.
How many lumbar spinal nerves are there, and what are they labelled as?
There are 5 lumbar spinal nerves, labelled L1–L5.
How many sacral spinal nerves are there, and what are they labelled as?
There are 5 sacral spinal nerves, labelled S1–S5.
What is the name of the single spinal nerve in the coccygeal region?
The coccygeal nerve, labelled Co
Why do spinal nerve roots become longer in the lower regions?
Because the spinal cord is shorter than the vertebral column, requiring lower spinal nerves to travel further before exiting.
Intervertebral disc herniation
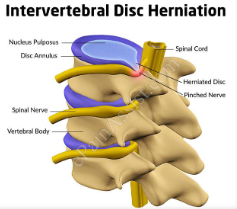
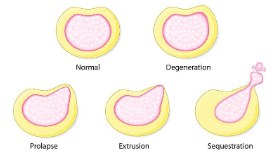
Recall the stages to a disc herniation
What is a nerve plexus?
A network formed by peripheral nerves that divide and join with other peripheral nerves
What is the function of a nerve plexus?
It allows individual nerve fibres to pass from one peripheral nerve to another, enabling redistribution of nerves.
What is a peripheral nerve?
A bundle of nerve fibres enclosed in a sheath, which can be either cranial or spinal
What is a ganglion?
A collection of nerve cell bodies located outside the central nervous system (CNS).
What is the main function of a nerve plexus?
It combines nerves from different sources or levels to form new nerves with specific targets
What are the two main types of nerve plexuses?
Somatic and autonomic plexuses.
What is the role of a somatic plexus?
It supplies skeletal muscles and skin with motor and sensory innervation.
What is the role of an autonomic plexus?
It regulates involuntary functions by supplying smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Where is the cervical plexus located?
In the posterior triangle of the neck.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the cervical plexus?
The anterior rami of C1–C4.
What is the function of the motor branches of the cervical plexus?
They support movement of the head and neck
How do the strap muscles contribute to bodily functions?
They assist with swallowing.
What areas do the sensory branches of the cervical plexus supply?
The inferior parts of the head, neck, and upper anterior thoracic wall.
The phrenic nerves arise from which spinal nerve roots?
The anterior rami of C3–C5
Along which muscle do the phrenic nerves travel?
They run down the surface of the anterior scalene muscle.
Through which region do the phrenic nerves descend?
They descend through the thorax on either side
What is the primary motor function of the phrenic nerves?
They provide motor innervation to the diaphragm
Besides motor function, what sensory information do the phrenic nerves carry?
They carry sensory information from the pleura and pericardium
Where is the brachial plexus located?
At the root of the neck, extending towards the axilla.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the brachial plexus?
The anterior rami of C5–C8 and T1
What does the brachial plexus innervate?
The skin and musculature of the upper limb
Where do the roots of the brachial plexus converge to form trunks?
At the base of the neck.
Which spinal nerves form the superior trunk of the brachial plexus?
C5 and C6
Which spinal nerve forms the middle trunk of the brachial plexus?
C7
Which spinal nerves form the inferior trunk of the brachial plexus?
C8 and T1
What happens to the trunks of the brachial plexus?
They divide into anterior and posterior divisions, which give rise to cords and the main branches of the brachial plexus.
What are the five major terminal branches of the brachial plexus?
Axillary nerve, musculocutaneous nerve, median nerve, radial nerve, and ulnar nerve.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the axillary nerve?
C5 & C6
What muscles does the axillary nerve supply?
Deltoid and teres minor.
What area does the axillary nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The sergeant’s patch (lateral aspect of the upper arm).
Which spinal nerves contribute to the musculocutaneous nerve?
C5, C6 & C7
What muscles does the musculocutaneous nerve supply?
Biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis.
What area does the musculocutaneous nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The lateral forearm.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the median nerve?
C6, C7, C8 & T1
What muscles does the median nerve supply?
Most forearm flexors, thenar muscles, and the two lateral lumbricals.
What area does the median nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The lateral palm and the lateral 3½ fingers (thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger).
Which spinal nerves contribute to the radial nerve?
C5, C6, C7, C8 & T1.
What muscles does the radial nerve supply?
Triceps brachii and the extensors of the wrist and fingers
What areas does the radial nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The posterior arm & forearm and the postero-lateral hand
Which spinal nerves contribute to the ulnar nerve?
C8 & T1.
What muscles does the ulnar nerve supply?
Most hand muscles (except thenar muscles & lateral lumbricals) and some medial forearm flexors
What areas does the ulnar nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The medial palm and the medial 1½ digits (little finger and half of the ring finger).
Which spinal nerves form the intercostal nerves?
The anterior rami of T2–T11.
Where do the intercostal nerves lie?
In the intercostal spaces, between adjacent ribs.
What is the nerve called that lies inferior to rib XII (T12)?
The subcostal nerve.
How do intercostal nerves travel in the thoracic wall?
They pass laterally around the thoracic wall.
Where is the lumbar plexus located?
In the lumbar region
Which spinal nerves contribute to the lumbar plexus?
The anterior rami of T12–L5
What does the lumbar plexus supply?
The skin and musculature of the lower limb
What are the six major peripheral nerves that branch from the lumbar plexus?
Iliohypogastric nerve, ilio-inguinal nerve, genitofemoral nerve, lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh, femoral nerve, and obturator nerve
Which spinal nerves contribute to the femoral nerve?
L2, L3 & L4.
What muscles does the femoral nerve supply?
Iliacus, pectineus, sartorius, and quadriceps femoris
What areas does the femoral nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The skin of the anterior thigh and the medial surface of the leg.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the obturator nerve?
L2, L3 & L4
What muscles does the obturator nerve supply?
Obturator externus, pectineus, and muscles of the medial thigh
What area does the obturator nerve provide sensory innervation to?
The skin of the medial thigh
Where is the sacral plexus located?
In the posterior pelvic wall.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the sacral plexus?
The anterior rami of L4–S4
What does the sacral plexus supply?
The skin and muscles of the pelvis and lower limb
What are the five major peripheral nerves that branch from the sacral plexus?
Superior gluteal nerve, inferior gluteal nerve, sciatic nerve, posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and pudendal nerve.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the superior gluteal nerve?
L4, L5 & S1
What muscles does the superior gluteal nerve supply?
Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae.
What sensory function does the superior gluteal nerve have?
It has no sensory supply
Which spinal nerves contribute to the inferior gluteal nerve?
L5, S1 & S2
What muscle does the inferior gluteal nerve supply?
Gluteus maximus
What sensory function does the inferior gluteal nerve have?
It has no sensory supply
What is the sciatic nerve?
The largest nerve in the body, approximately 2 cm wide.
Which spinal nerves contribute to the sciatic nerve?
L4, L5, S1, S2 & S3.
What is the motor function of the tibial nerve (branch of sciatic nerve)?
It provides motor innervation to the hamstrings, posterior leg, and sole of the foot.
What is the sensory function of the tibial nerve (branch of sciatic nerve)?
It provides sensory innervation to the lateral and sole of the foot.
What is the motor function of the common fibular nerve (branch of sciatic nerve)?
It provides motor innervation to the anterior and lateral leg muscles and the dorsal foot
What is the sensory function of the common fibular nerve (branch of sciatic nerve)?
It provides sensory innervation to the anterolateral leg and dorsal foot.
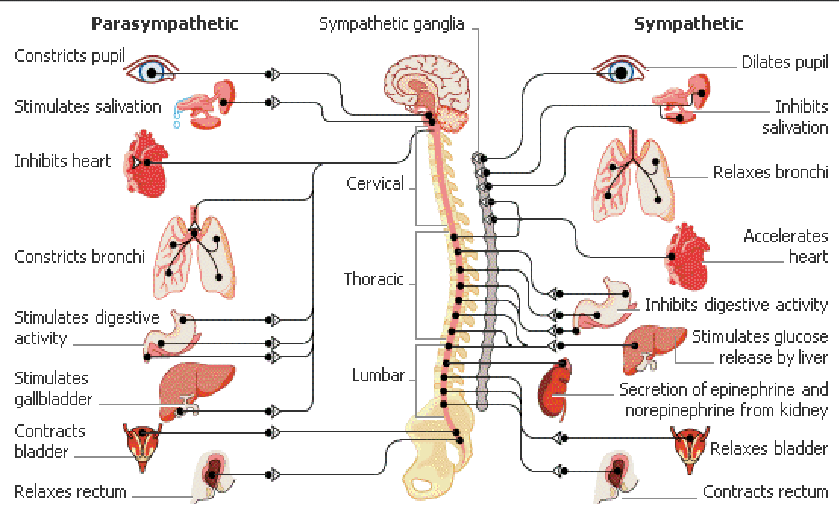
Somatic vs. autonomic
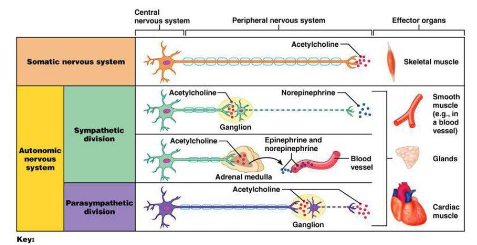
Parasympatheticus vs. sympatheticus
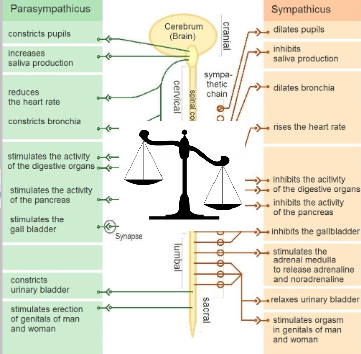
What two divisions of the autonomic nervous system control the heart?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
What factors are controlled by the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions?
Heart rate, force of contraction, and vascular tone
Which nerve provides parasympathetic input to the heart?
The vagus nerve (CN X).
What effects does parasympathetic input (via the vagus nerve) have on the heart?
It decreases heart rate (HR), decreases force of contraction, and causes coronary artery vasoconstriction
What effects does sympathetic input have on the heart?
It increases heart rate (HR) and increases force of contraction
What is the cardiac plexus?
A network of autonomic branches formed by the left/right vagus nerves and sympathetic trunk nerves.
What is the role of visceral afferents in autonomic control of the heart?
Visceral afferents return information to the CNS about blood pressure and chemistry via the vagal nerve, and cardiac pain sensation (e.g., ischaemia) via the sympathetic trunk