glass & glazing
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
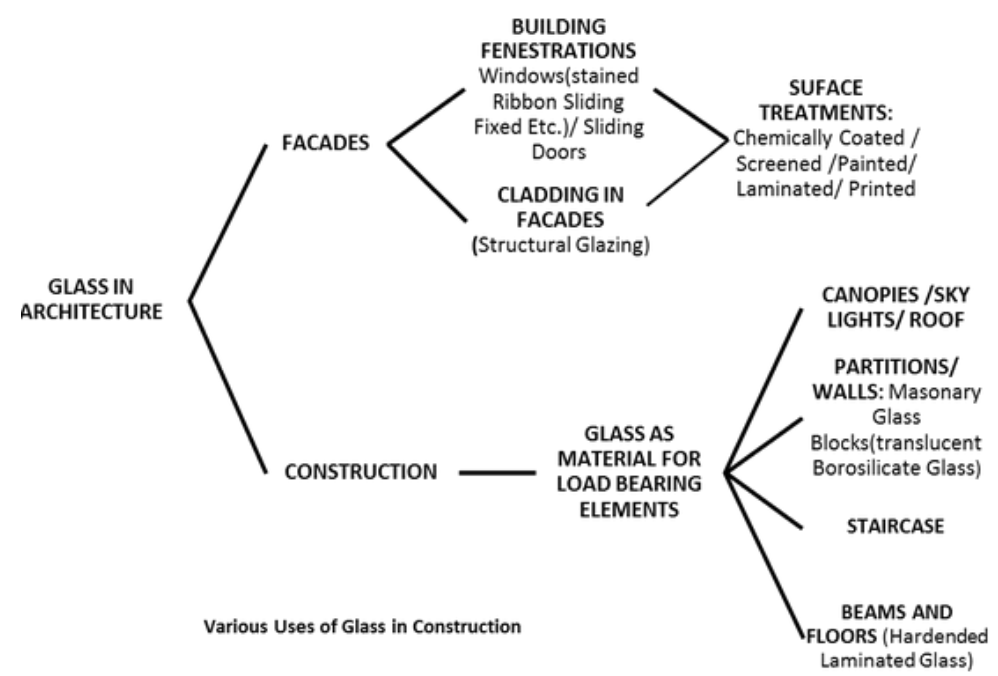
uses of glass in construction
Glass is the most-used cladding material for tall buildings due to its strength, light weight, durability, and wide range of available optical and thermal properties
glass ingredients & thicknesses
Glass is made from
Sand (silicone dioxide)
Soda ash (sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate)
Lime (calcium)
Alumina
Potassium oxide
Thicknesses range from approximately 3/32 inch (single strength) to 1/8 inch (double strength) to 1 inch.
Heat treatments such as tempering impact glass strength and uses
glass properties
Strong: Glass is a brittle material but with the advent of science and technology, certain laminates and admixtures can increase its modulus of rupture.
Recyclable: 100% recyclable.
Workable: can be molded into a variety of shapes and sizes.
Transparent: lets natural light into a building (can offset internal lighting needs)
glass terms (1/3)
U-value: Measure of how much heat is transferred through the window.
Greenhouse effect: short wavelengths of visible light from the sun pass through glass and are absorbed, but the longer infrared re-radiation from the heated objects are unable to pass through the glass. This trapping leads to more heating and a higher resultant temperature.
Solar heat gain coefficient: It is the fraction of incident solar radiation that actually enters a building through the entire window assembly as heat gain.
glass terms (2/3)
Visible transmittance: Fraction of visible light that comes through the glass.
Energy efficiency and acoustic control: Energy-efficient glazing is the term used to describe the double glazing or triple glazing use in modern windows in homes. The air barrier also enhances acoustic control.
Air Leakage: measures the rate of air leakage around the window under conditions of an assigned pressure differential. The rating is expressed in cubic feet per square foot of window
glass terms (3/3)
U-value
Solar heat gain coefficient
Visible transmittance
Air Leakage (construction)

glass types by heat treatment & strength
Float glass: Sheet of glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal
Annealed glass: Regular float glass which is cooled slowly to reduce built-in stress
Tempered glass: Produced by cutting annealed glass to required size, reheating and then cooling rapidly. Higher strength and breaks into small shards
Heat-strengthened glass: Between annealed and tempered with breakage behavior like annealed
Laminated glass: Sandwich of multiple layers of glass with polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer. Suitable for security applications as glass stays in place
Fire-rated glass: divided into two distinct categories: fire-protective and fireresistive glass. Can protect people and property in temperatures exceeding 1,600 degrees F
glass types by architectural treatments
Patterned glass: Hot glass can be rolled into sheets with many different surface textures and patterns to obscure vision for privacy
Fritted glass: Pigmented glass particles called frits are used to imprint glass. Glass is dried and fired in tempering furnace to make it permanent
Spandrel glass: Used to cover bands of floor/wall around the floor edges. Usually tempered or heat strengthened with insulation behind them
glass types based on solar radiation
Tinted Glass: Made by adding small amounts of selected chemical elements to the molten glass mixture
Reflective Glass or Solar Control Glass: Thin durable films of metal or metal oxide are deposited on the surface of either tinted glass or clear glass to make the glass reflective.
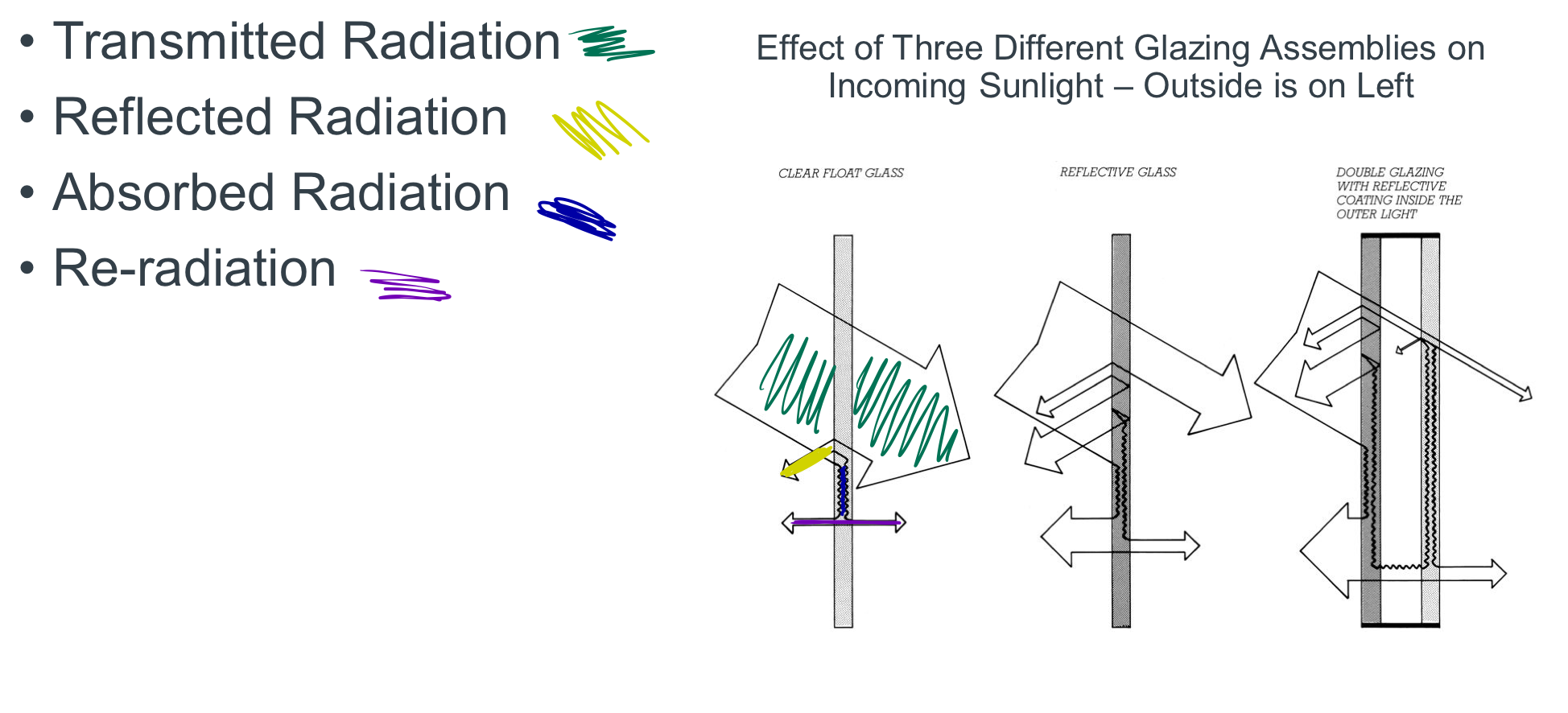
control of visible light & solar radiation
Transmitted Radiation
Reflected Radiation
Absorbed Radiation Re-radiation
glass & thermal considerations
IGU – Insulating Glass Unit
Made of multiple glass layers with sealed air space reducing conductance
Space filled by air or inert gas in a hermetically sealed cavity
Performance given in terms of U values
Low Emissivity coated glass (low-e) •
Formed with transparent metallic coating to improve thermal performance
Located on surface 2 and sometimes on surface 3.
Improves thermal performance
glazing small lights
Not subject to excessive wind force or stresses due to thermal expansion
glazing large lights (1/3)
Large lights, those over 6 ft2 require more care in glazing due to stresses
Design objectives are
Support weight of glass without abnormal stress patterns
Support glass against wind pressure and suction
Allow for expansion and contraction of glass and frame without damage
Avoid contact of glass with any hard material such as frame
glazing large lights (2/3)
Setting blocks are of synthetic rubber and support weight of glass
Bite or depth of grip on the edge of glass of certain amount is required to resist wind load
Glazing components used between frame and glass are either wet or dry such as
Preformed solid tape sealant made of polybutene
Wedge or roll in gasket
Lock strip gasket
In good design, waterproofing relies on wet and dry seals in conjunction with pressure equalization and drainage
glazing large lights (3/3)
Lockstrip gasket is a dry glazing method. It is faster, easier and less dependent on workmanship then wet glazing method.
Wet glazing: (silicone) with good workmanship is more effective.
advanced glazing systems (1/3)
Butt-joint glazing system
Head and sill of the glass sheets are supported conventionally in metal frames, but vertical mullions are eliminated
The vertical joints between sheets of glass are made by injection of colorless silicone sealant
Horizontal strip windows that need to appear mullion-less only from the outside can use a mullion on the inside
Sill and head are conventionally glazed
advanced glazing systems (2/3)
Suspended Glazing Systems and Glass Mullion System
Used primarily for high walls of glass around building lobbies
Tempered glass sheets are suspended from above and stabilized by tempered glass perpendicular stiffeners
Metal fittings are used to join multiple sheets of glass
Stainless steel cables and fittings are used in roof applications
advanced glazing systems (3/3)
Four-point spider fitting
Adjustable vertical stainless steel rod carries the load to the structure
The spider fittings and cable system must resist wind, seismic, and dead loads without inducing bending forces in the glass or creating stress concentrations around the points of attachment.
A suspended glazing system with "saddle" curvature keeps the entire wall system in tension.