Glycosylation, Creatine, Nucleic Acids and Peptides - BioChem Genetics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDGs)
errors in enzymes that bind carbohydrates to organic molecules via glycosylation
Carbohydrates (-glycans)s help with protein folding + stability → effects cell trafficking, identification and cohesion
Exceedingly broad group of disorders: >80 identified so far and more each year b/c of WGS
2% of genes cod for glycosylation enzymes: Most endoplasmic reticulum proteins are glycosylated
Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation (CDGs): General clinical features
CNS (80%)
Seizures
Dystonia
Mental Retardation
Ophthalmology
Optic Atrophy
Coloboma
Growth Failure
Immunodeficiency
Coagulopathy
5 Major Types of Glycan Classes
***N-linked: Glycan on Nitrogen*** most common disorder → CDG1-a most often
O-linked: Glycan on Oxygen
Glypilation: Glycolipid on Amino Acid c-terminus
C-Linked: Glycans on carbon of TRYPTOPHAN
Phospho-Glycans: glycan on Phospho-SER (?)
Phosphomannomutase 2 (PMM2) Deficiency: Overview
***MOST COMMON N_GLYCOSATION DISORDER**8
N-Glycosylation Defect
Inheritance: Autosomal defect
Phosphomannomutase 2 (PMM2) Deficiency: Presentation
Infantile onset:
can be lethal form or nonlethal, neurological form
Fail to thrive, low muscle tone, and UNUSUAL PATTERN OF FAT (fat pads over chest + inversion of nipples)
Childhood Axatia:
Ataxia, Intellecualt diabiltiy, Hypotoinia, Nerupathy
Stablizes in Adulthood
Phosphomannomutase 2 (PMM2) Deficiency: General Diagnosis + Treatment
Diagnosis
Transferrin Isoform analysis screening: transferrin is N-linked glycosylation —> deficiency of glycosylated transferrin = CDG
CDG-1a: PMM2 enzyme analysis
CDG-1A: PMM2 mutation analysis
Treatment: Primarily supportive —> no effective treatments
Mannose-6-Phosphate Isomerase (MPI) Deficiency: Overview
An N-Glycosylation Defect
Autosomal Recessive
MPI gene mutation
Mannose-6-Phosphate Isomerase (MPI) Deficiency: Presentation
Infantile Failure to thrive
Cyclic Vomiting
Liver Dysfunction
Coagulopathy (bleeding) / Thrombosis (abnormal clotting)
*** NO NEUROLOGICAL EFFECTS***
Mannose-6-Phosphate Isomerase (MPI) Deficiency: Diagnosis + Treatment
Diagnosis
Transferrin Isoform analysis (low glycosylated transferrin = n-linked CDG)
CDG-1b: MPI Gene Mutation Analysis
Treatment
Oral Mannose Supplementation 1gm/kg/day
CDG: O-Linked Glycosylation
More Dysmorphic features than N-Linked CDGs
“Hereditary Multiple Exostosis” → Auto. Dominant
EXT1/EXT2 (AD)
“Progeroid Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome”
B4GALT7 (AR)
“Muscle-Eye-Brain Disease” (Walker-Warburg Syndrome)
POMT1, POMT2, POMGT1 (AR)
Cerebral Creatine Deficiency Syndromes (CCDS): Metabolic Pathway
Creatine primary created in the liver from → Glycine + Arginine to Orthenine + Guanidinoacetate
Creatine can be an energy storage molecule → conversion to Creatine Phosphate Kinase
Can be converted to CREATININE: released in the urine
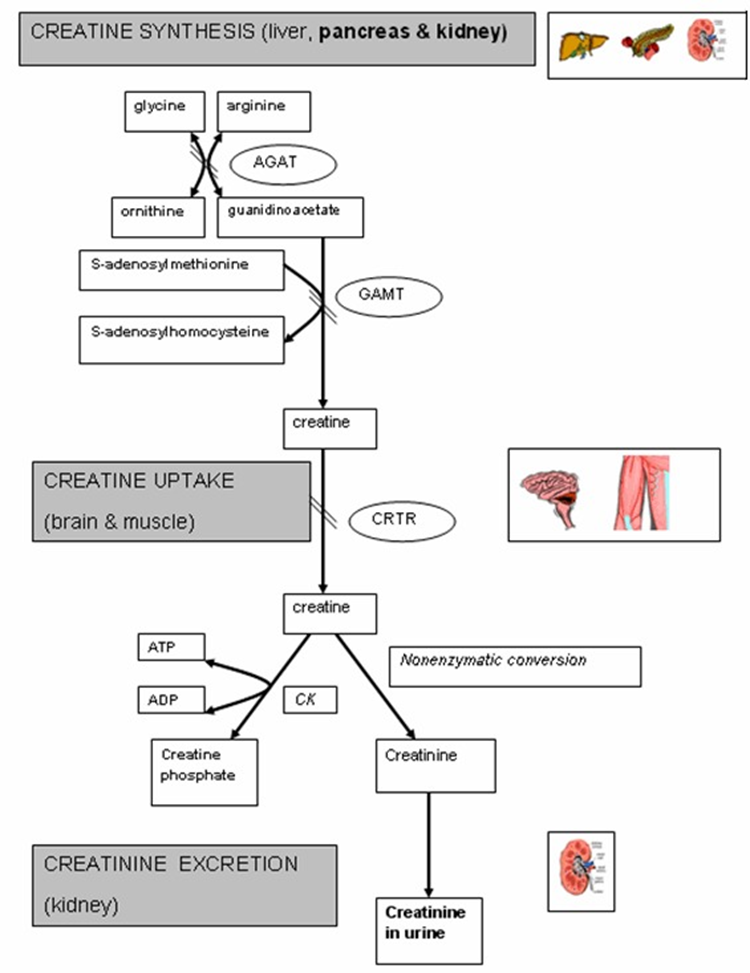
Cerebral Creatine Deficiency Syndromes (CCDS): Overview
3 Main Disorder: 3 main enzymes: 2 biosynthesis + 1 transporters
L-Argiine:Glycine Amidino Transferase (AGAT) Deficiency - AR
GuandiaoAcetate Methyl Transferase (GAMT) Deficiency - AR
Creatine Transporter Deficiency (SLC6A8) Deficiency - XLR
Cerebral Creatine Deficiency Syndromes (CCDS): Presentation
Similar features: Onset in childhood
Global developmental delay —> Mild/Sever mental retardation
Autism (self-injury in GAMT)
Muscle weakness
Movement Disorders: Ataxia, Dystonia (NOT in AGAT)
Dysmorphic Features (SLC6A8)
Milder Cases may have later Onset
Cerebral Creatine Deficiency Syndromes (CCDS): Diagnosis
Brain MR Spectroscopy: Creatine peaks in the brain can be detected
Screening Tests (Urine/Plasma/Spinal Fluid)
Guanidinoacetate (GAA) → High in GAMT :: Low in AGAT
Creatine → Low in GAMT + AGAT :: High in SLC6A8
Creatinine → Low in GAMT, AGAT and SLC6A8
Diagnostic
Enzyme Activity: AGAT + GAMT
Creatine uptake (fibroblasts) : SLC6A8
Gene Analysis: GATM (AGAT), GAMT (““) , SLC6A8 (transporter)
Cerebral Creatine Deficiency Syndromes (CCDS): Treatment
AGAT: Oral Creatine Monohydrate
GAMT: Oral Creatine Monohydrate and Decrease Guanidinoacetate production
Orthinine: Inhibits AGAT, lowers GAA
Arginine restriction: inhibits AGAT, lowers GAA
Benzoate: reduces glycine, lowers GAA
SLC6A8: Oral Creatine Monohydrate
Purine synthesis
Ribos-5-Phosphate → steps → Inosine Monophosphate (IMP) → either:
Adenosine monophosphate
Guanosine monophosphate
Inosine monophosphate can be converted to hypoxanthine via HPRT→ can be storge molecule for later conversation to IMP (?)
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: Metabolic pathway
Inosine monophosphate can be converted to hypoxanthine via HPRT→ can be storge molecule for later conversation to IMP (?)
Deficiency in HPRT = inadequate IMP + Hypoxanthine → xanthine → uric acid (which builds up)
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: Overview
X-Linked Recessive
Etiology HPRT1 Deficiency → Decreased Inosine Monophosphate + Increase Uric acid / Xanthine
Evaluation:
Screening: Uric Acid levels
Diagnosis: Enzyme activity (blood, fibroblast, CVS) + HPRT1 gene analysis
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: Presentation
Neurologic
Mental retardation, seizures, cerebral palsy
motor dysfunction
Sel Mutilating (1-8yo)
Hyperuricemia:
uric acid kidney stones, renal failure, gout
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: Treatments
No Cure
Can lower uric acid, but cannot prevent the Neurologic conditions
Medications
Physical restraints are necessary
Monoamine Synthesis
Tyrosine → Dopa → Dopamine → Norepinephrine→ Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Tryptophan → 5-Hydroxytryphtoan → Serotonin
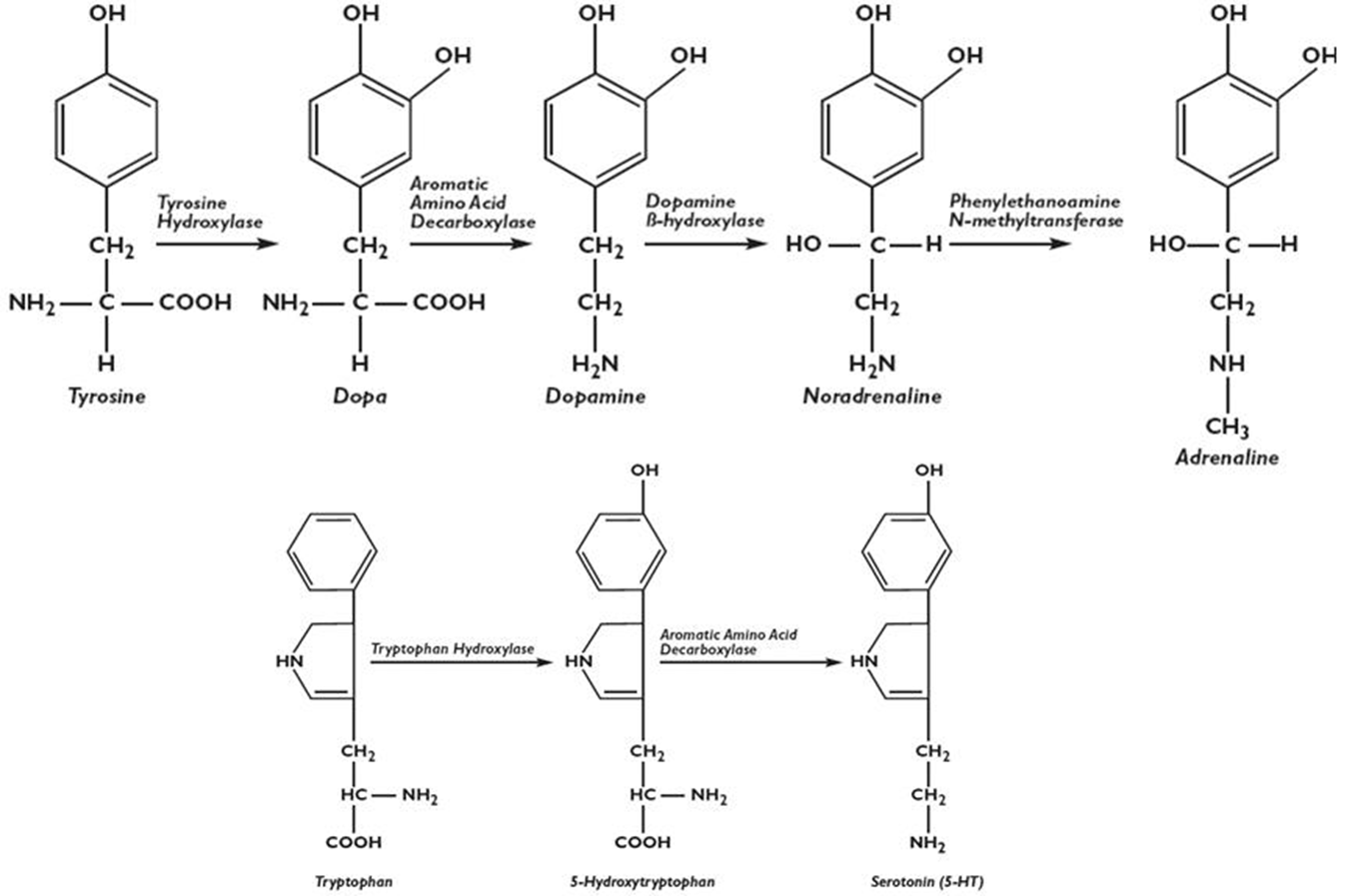
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) Deficiency: Metabolic pathways
BH4 a cofactor for Neurotransmitter synthesis enzymes (also important in the Aminoadipates → look at those cards)
ALSO: Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH), associated with PKU, need BH4
BH4 low → Monoamines Low
BH4 Synthesis: GTPCH1, PTPS, SR
BH4 Regeneration: PCD, DHPR
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) Deficiency: Differential Diagnosis
NBS with elevated Phenylalanine (b/c BH4 needs to be high for PHE → Tyrosine)
need to rule out:
PKU (PHE > 1200uM) (***MOST LIKELY***)
Fals positive or generalized liver dysfunction
Hyperphenylmaina (PHE 120uM-1200uM)
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) Deficiency: Diagnosis
PHE levels usually Heyperphanlamenima (120-1200uM) but not no the PKU range
GTPCH
PRPS
PCD
DHPR
PHE Normal form AD GRPCH1 and SR
Check for
Urine Ptertin
RBC DHPR levels
Do BH4 load test
Confirm diagnosis with enzyme activity / gene analysis
Elevated PHE BH4 (GTPCH, PRPS, PCD, DHPR): Presentation
At birth Asymptomatic
Infancy
Abnormal muscle tone
poor sucking
seizures
delayed motor development
Long term
Irreversible neurologic deterioration
mental retardation
seizures
death
Phenotypic severity varies response to treatment varies
Elevated PHE BH4 (GTPCH, PRPS, PCD, DHPR): Treatment
Oral BH4 Supplementation Sapropterin
Dietary Modification reduced PHE, add TYR
Neurotransmitter Replacement
L-Dopa
5-HT (serotonin) supplementation, SSRIs
MAO inhibitors
Cofactors: Folic Acid
AD GTPCH1 Dopa-Responsive Dystonia: Overview
*** PHE not ELEVATED *** → But Decreased Neurotransmitters (dopamine)
Clinical “Segawa Syndrome”: Childhood onset (avg 6yo) dystonia and progressive Parkinsonian: symptoms of dopamine deficiency (Parkinsons Disease) But at a much early age
Diagnosis
Decreased Neopterin + Biopterin
CTPCH1 enzyme activity
GCH1 gene mutation analysis
Treatment
L-Dopa/Carbidopa
Dramatic normalization with treatment
Sepiatrin Reductase: Overview
***PHE not ELEVATED***
Parkinson features at an early age → BUT more severe INTELLECTUAL DISABILITY
“Diurnal FLucation” : Better in the morning, but get worse throughout the day
Diagnosis
Decreased Homovalnic acid + HIAA (neurotransmitter metabolites) - CSF
Increased Neoprtrin - CSF and Urine
Treatment/Outcomes
L-Dope, 5-HT, SSRI, MAOIs
Normal outcomes with treatment
Glutathione Synthase Deficiency: Overview
Impacts pathway for mitigating Oxidative Stress: Glutathione is decreased
Clinical
Milder Deficney → Anmia and metabolic acidosis
Sever Deficiney → Neurodegenration and infection
Etiology: AR Glutathione synthease (GSS) mutation = Decreased free radical scavenging
Diagonsis
Low Glutahione, increased 5-Oxoproline
Enzyme activity + gene Anylsis
Treatment
Correct acidsoids
Supplment with anti-oxidant vitamins
Avoid oxidative stress
Trimethylaminuria: Overview
Prominent Fishy Order from body fluids
Etiology: AR FMO3 gene mutation: Increased Trimethylamine (TMA) → Urine TMA levles, gene testing
Treatment:
Restrict dietary trimethylamine, choline and lecithin
Decrease gut bacterial production
Riboflavin
Acididc skin/oral products