Micro Lab 1 Questions
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Entero-
intestines
-osis
abnormal conditon
-phage
virus
retro-
backwards
pneumo-
lung
myc(o)-/mycet(o)
fungi/fungus
picorna-
small rna
baterio-/-bacter
relating to bacteria
vir(o)/vir
relating to viruses
adeno-
relating to a gland
gono-
relating to reproductive sytem
meningo-
relating to the meninges
strepto-
chain
spirillum/spirochete
spiral
staphylo-
cluster (of grapes)
vibrio
curved rod
diplo-
two/double/pair
oncorna-
cancer RNA
-coccus/-cocci
round
-bacillus/bacilli
rod shaped
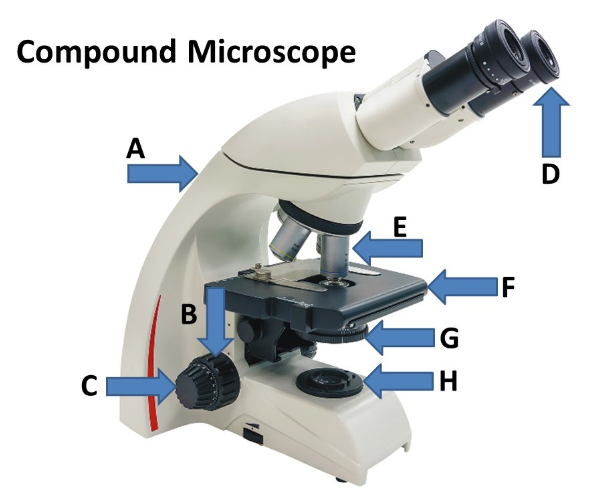
Match the listed parts of the compound to the corresponding letter designation located in the drop down menu.
A-Arm
B-Coarse Adjustment Knob
C-Fine Adjustment Knob
D-Ocular Lens
E-Objective Lens
F-Stage
G-Condenser
H-Light Source (Lamp)
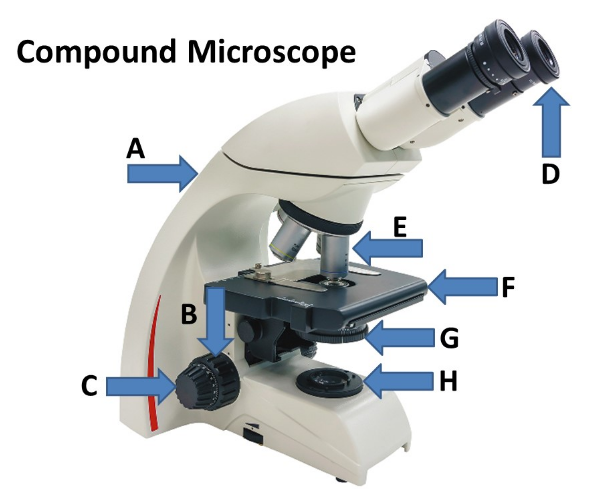
What is the total magnification of a specimen if you are using a compound light microscope with the 40x objective lens?
400x
Which type of oil is used to prevent the scattering of light when using the 100x objective lens making the specimen image clear when viewed?
immersion oil
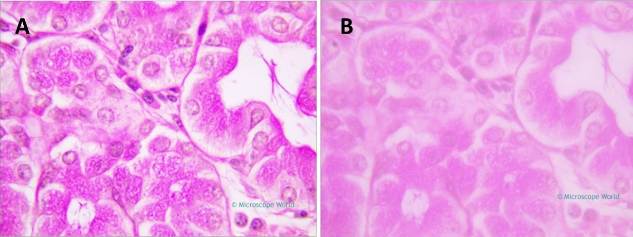
These images show stained specimens viewed using a compound microscope with the 100x objective lens. Which of the following images likely did NOT use immersion oil AND what is the total magnification of each specimen?
B; 1000x total magnification
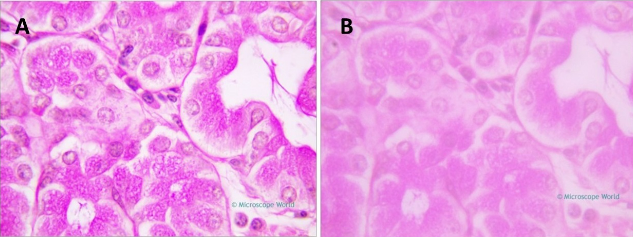
You are viewing a specimen using the 100x objective, but the image is fuzzy. Assuming that the microscope is clean and functioning properly, what is the likely reason why the image isn't clear?
you forgot to use immersion oil
When preparing a slide for bacterial staining, the _________________ step attaches the bacteria to the slide and kills the microorganisms.
heat fixing
True or False? Simple staining is used to visualize the shape, size, and arrangement of bacteria, but in general, it cannot determine any other bacterial properties.
True
The image shows the results of a staining method that differentiates between bacteria that have thick or thin layers of peptidoglycan in their cell walls. Match the statement to the correct answer located in the drop down menu.
name of the staining technique: gram stain
what color are positive bacteria stained?: purple
what color are negative bacteria stained?: pinkish red
name the primary stain: crystal violet
name the counterstain: safranin
name the mordant: iodine
name of the decolorizer: alcohol (or acid-alcohol)
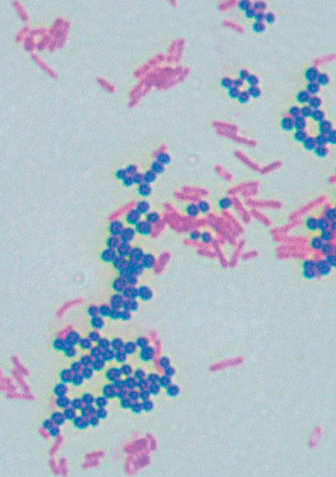
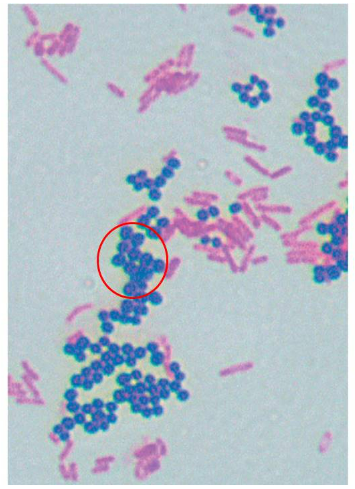
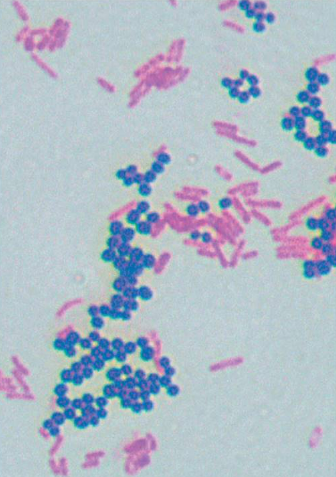
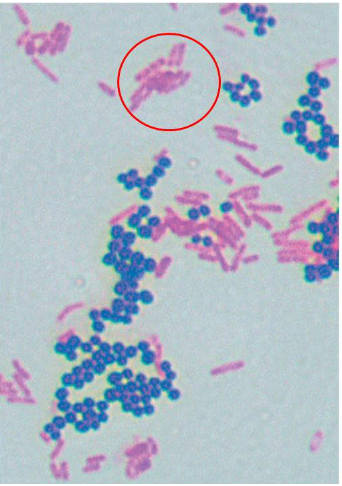
The image shows the result of a differential staining method called the Gram stain. What information can be concluded concerning the circled (purple) cells?
the cells are gram positive and have a thick layer of peptidoglycan
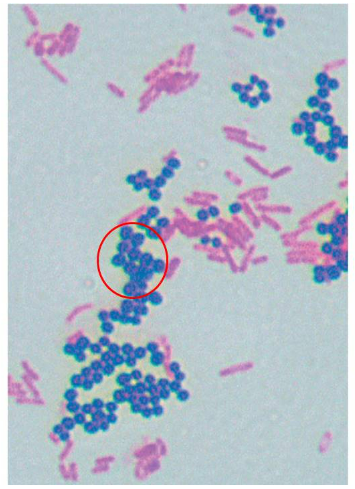
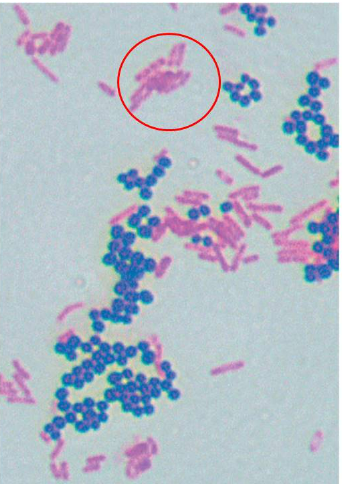
The image shows the result of a differential staining method called the Gram stain. What information can be concluded concerning the circled (pinkish) cells?
the cells are gram negative and have a thin layer of peptidoglycan
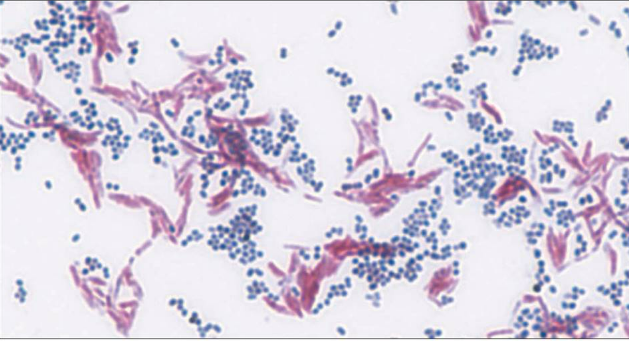
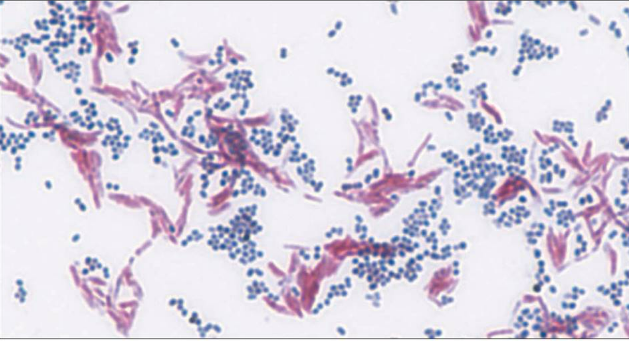
You have a mixture of gram positive and gram negative cells in culture. You prepare a slide from the culture and gram stain it, but when observing the sample using oil immersion, all cells appear purple. What is the likely technical reason why only purple-colored cells are observed?
you forgot the decolorization step
The image shows the result of a certain differential staining method that detects the presence of mycolic acid in a bacterial cell wall. Match the statement to the correct answer located in the drop down menu.
name of the staining technique: acid-fast stain
what color are positive bacteria stained?: pinkish purple
what color are negative bacteria stained?: blue
name the primary stain: carbolfuchsin
name the counterstain: methylene blue
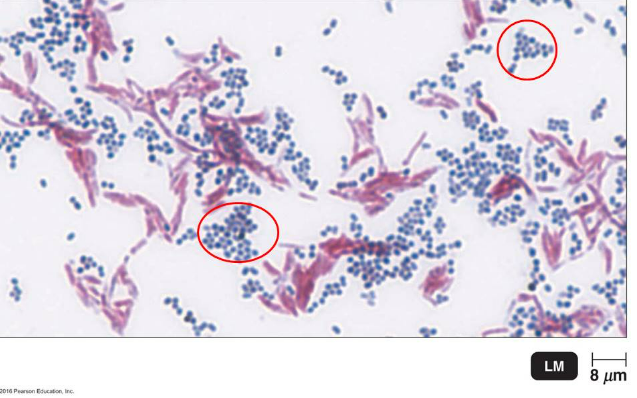
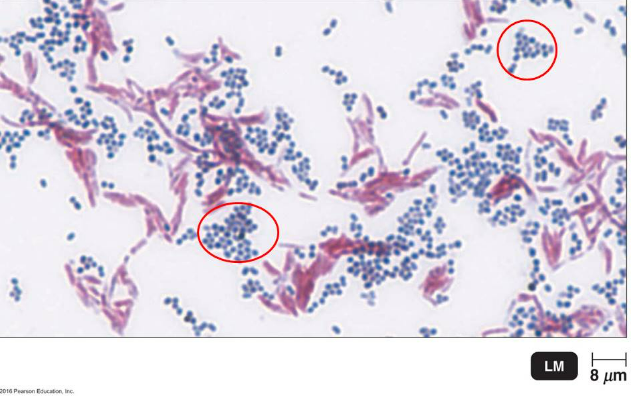
The image shows the result of a certain differential staining method that detects the presence of mycolic acid in a bacterial cell wall. What information can be concluded concerning the circled (blue) cells?
they are non acid-fast organisms that don't have mycolic acid in the cell wall
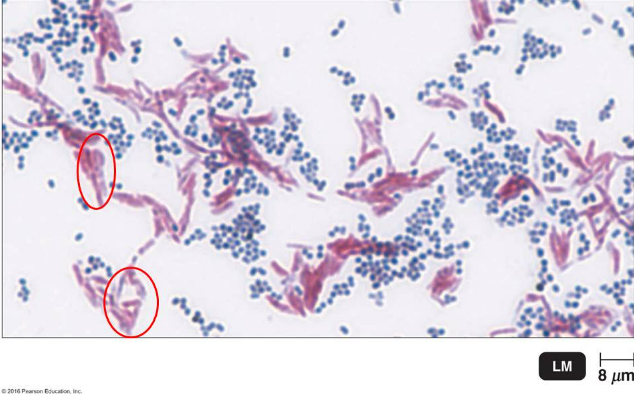
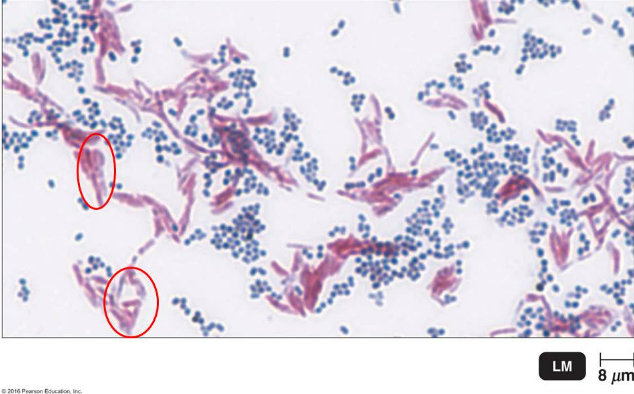
The image shows the result of a certain differential staining method that detects the presence of mycolic acid in a bacterial cell wall. What information can be concluded concerning the circled (pinkish purple) cells?
they are acid-fast organisms that have mycolic acid in the cell wall
A thick, detectable, discrete polysaccharide layer located outside of the cell wall that protects bacteria from the host's immune system and allow pathogens to invade the body is called a/an __________.
capsule
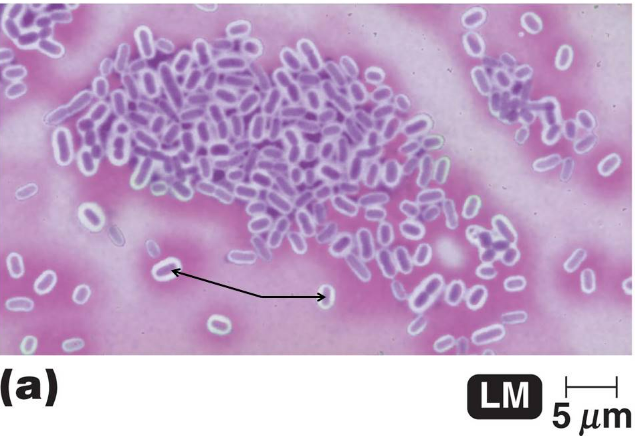
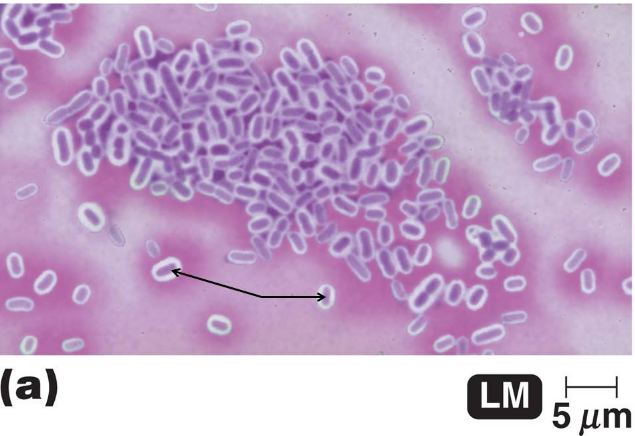
The image shows the results of a type of structural staining method called a negative stain that uses the dye, crystal violet. What are the purple colored structures depicted by the arrows?
bacterial cells
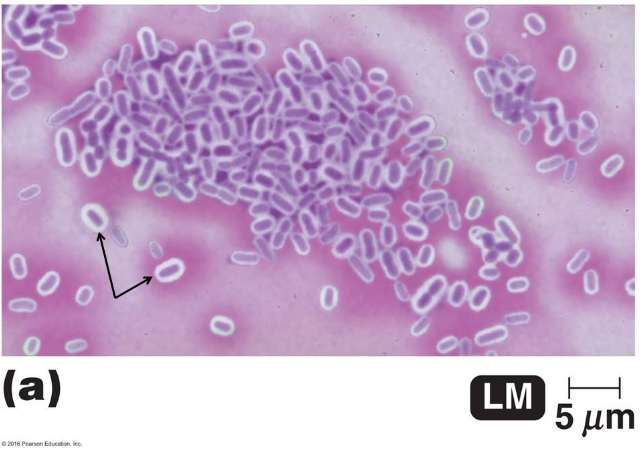
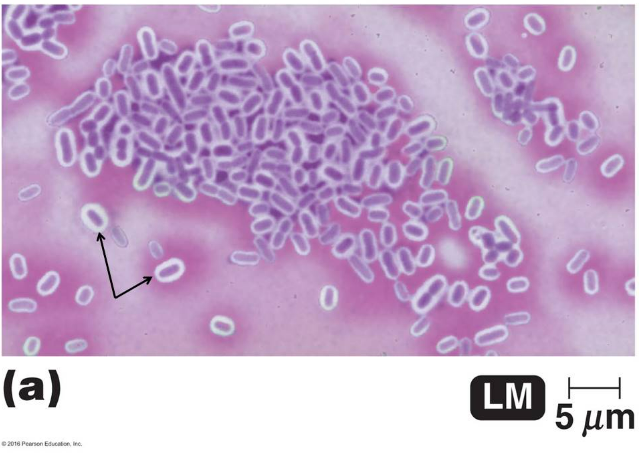
The image shows the results of a type of structural staining method called a negative stain that uses the dye, crystal violet. What are the clear areas surrounding the purple structures depicted by the arrows?
capsules
Metabolically inactive (dormant) forms of bacteria that can survive harsh environmental conditions such as heat and UV radiation are called ____________.
endospores
Lethal _____________-forming bacteria, such as Bacillus anthracis, can be used for bioterrorism.
endospore
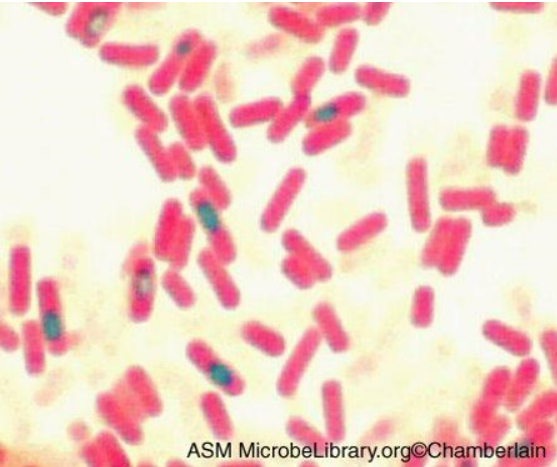
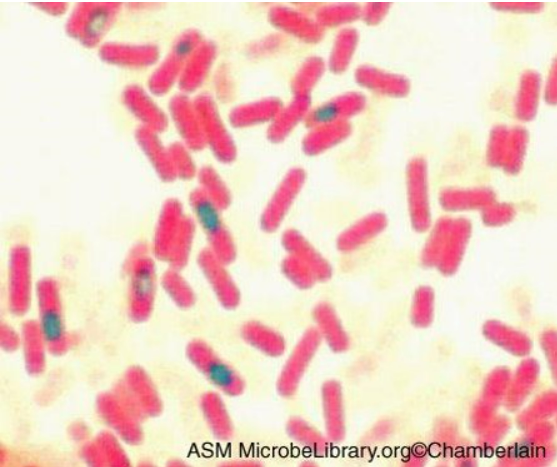
The image shows the results of a structural staining method that can used to detect certain structures that can be found in bacterial species such as Bacillus anthracis and Clostridium tetani. Match the statement to the correct answer located in the drop down menu.
name of the staining technique: endospore stain
what color are positive bacteria stained?: vegetative cells
what color are negative bacteria stained?: endospores
name the primary stain: malachite green
name the counterstain: safranin
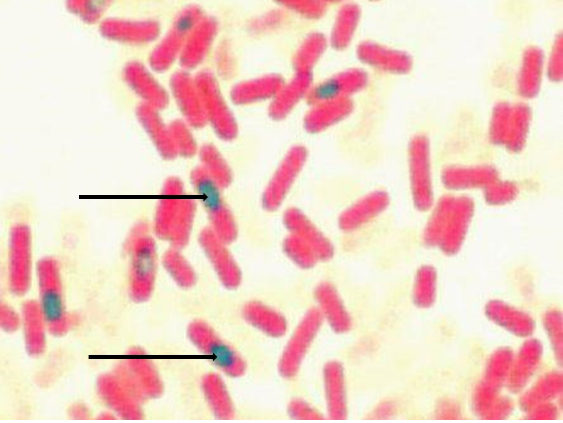
The image shows the results of a structural staining method that can used to detect certain structures that can be found in bacterial species such as Bacillus anthracis and Clostridium tetani. Identify the green structures depicts by the arrows.
endospores
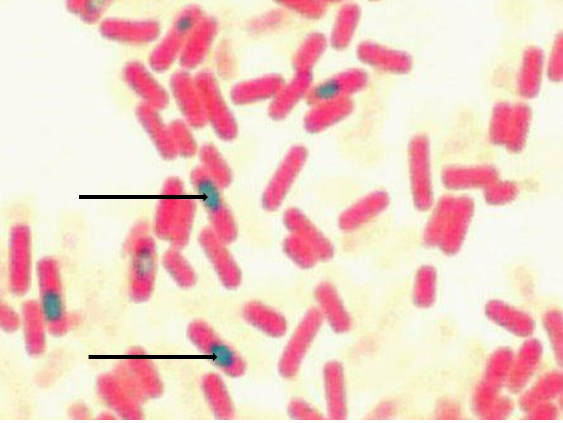
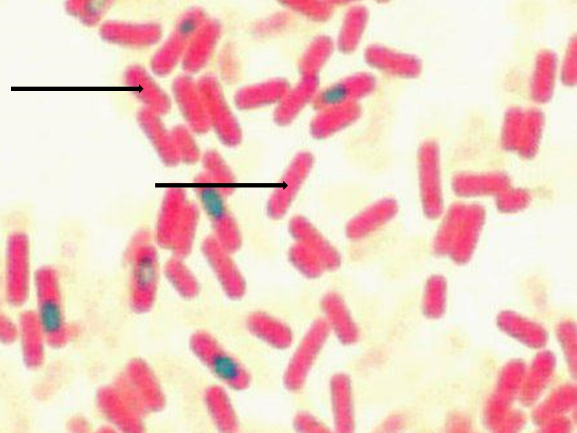
The image shows the results of a structural staining method that can used to detect certain structures that can be found in bacterial species such as Bacillus anthracis and Clostridium tetani. Identify the pinkish structures depicts by the arrows.
vegetative cells
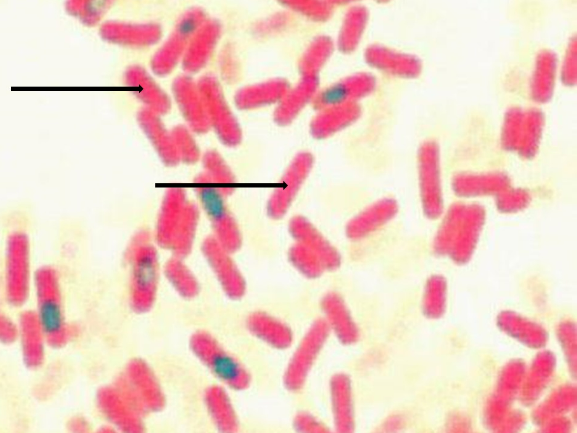
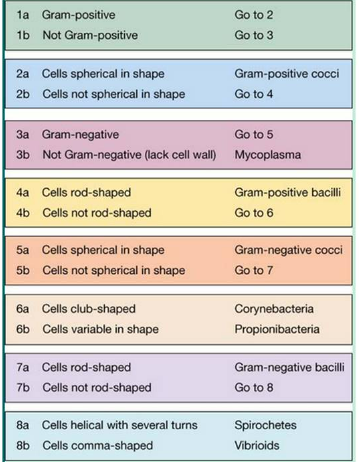
You observe gram-negative cells that aren't spherical in shape, but instead are rod-shaped. Use the information and the dichotomous key to identify the microoorganism.
gram-negative bacilli
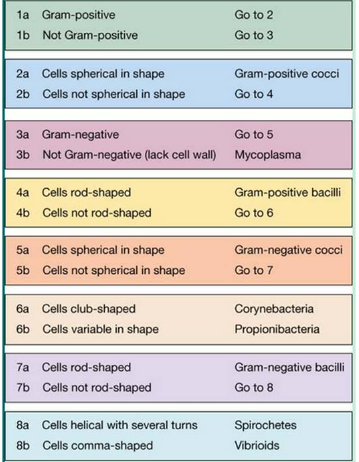
You observe gram-negative cells that aren't spherical in shape or rod-shaped, but instead are helical with several turns. Use the information and the dichotomous key to identify the microoorganism.
Spirochetes