Lecture 8 - Neuroanatomy
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FINAL CUE CARDS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
dorsal
Top (superior)
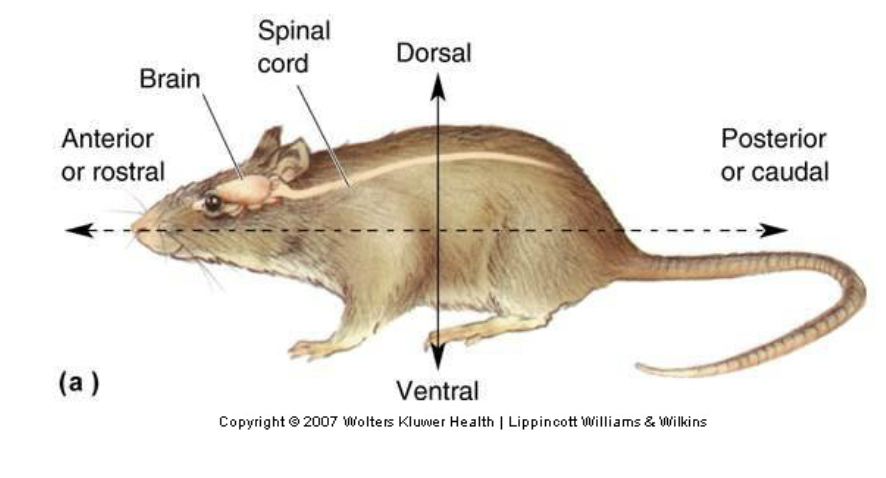
ventral
Bottom (inferior)
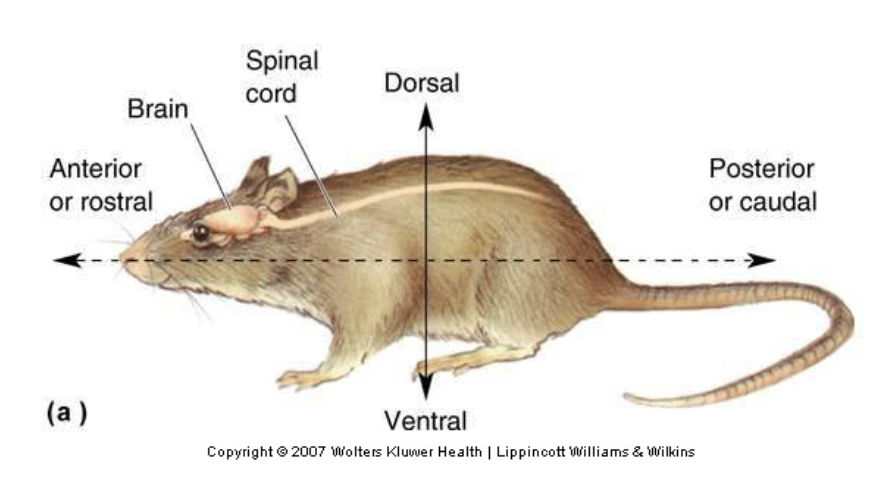
anterior (or rostral)
Toward the nose (front)
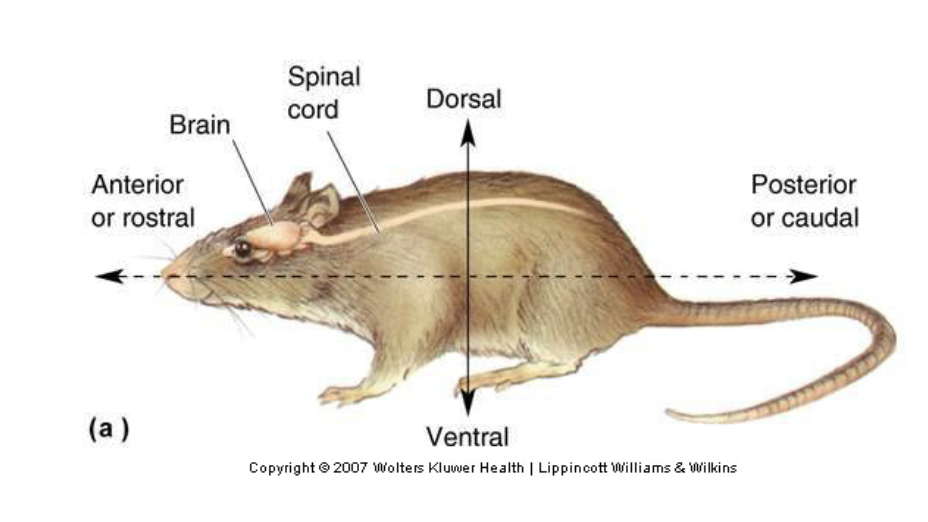
posterior (or caudal)
Toward the tail (back)
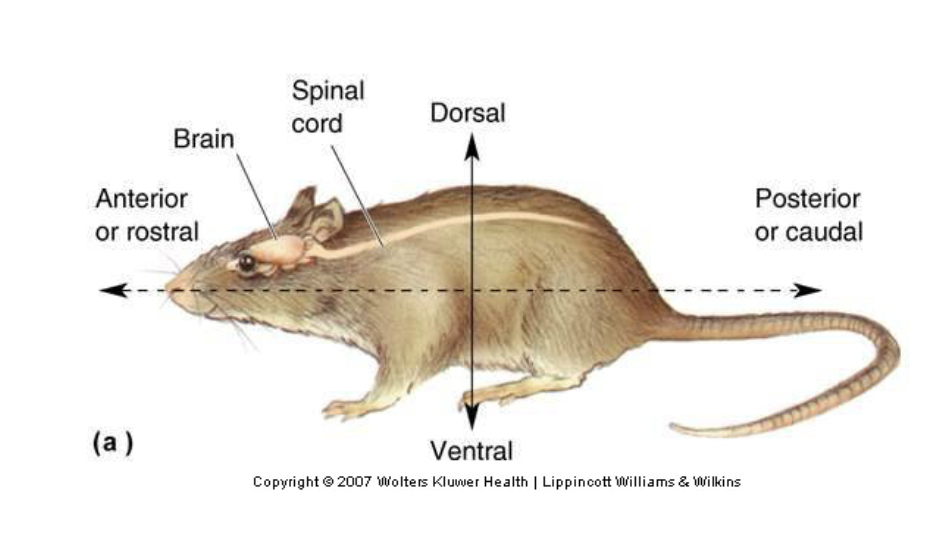
lateral
Toward the sides
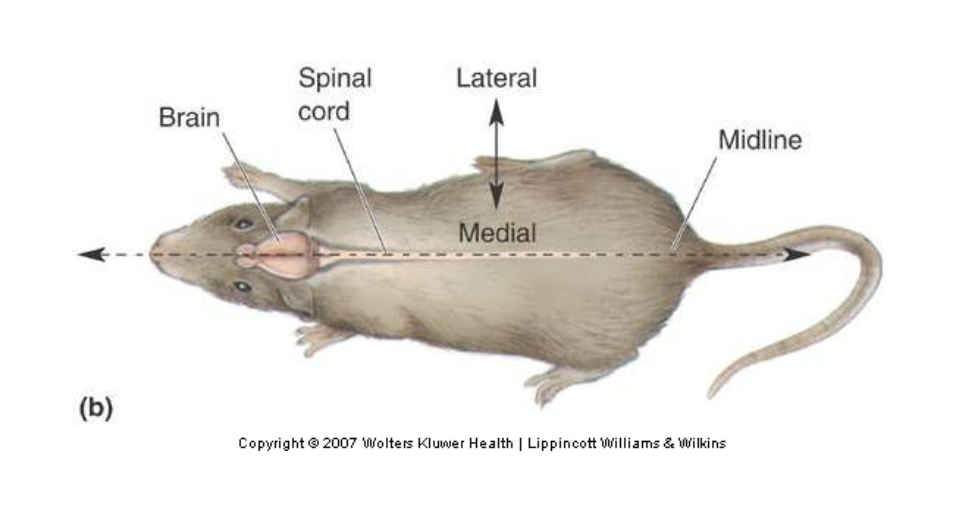
medial
Toward the middle
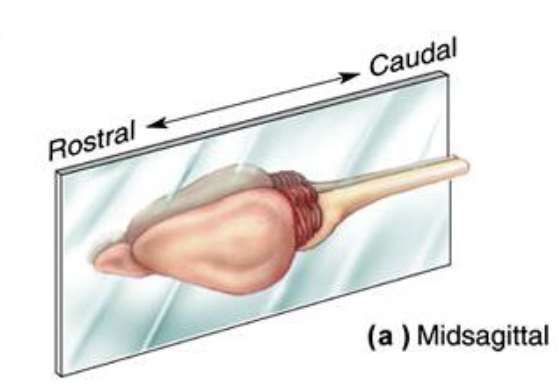
Midsagittal plane
Divides brain into left and right halves.
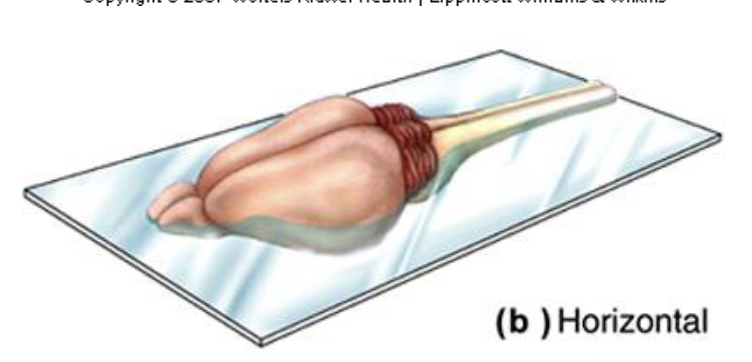
horizontal plane
Divides brain into top and bottom halves.
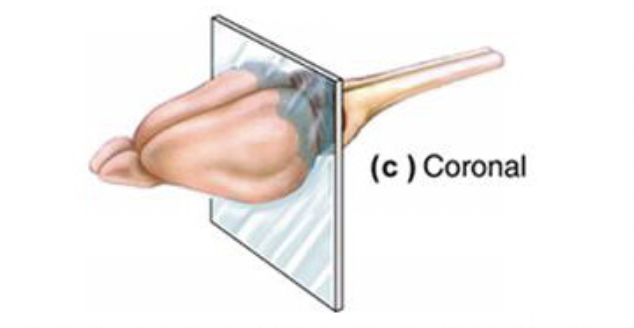
coronal plane
Divides brain into front and back halves
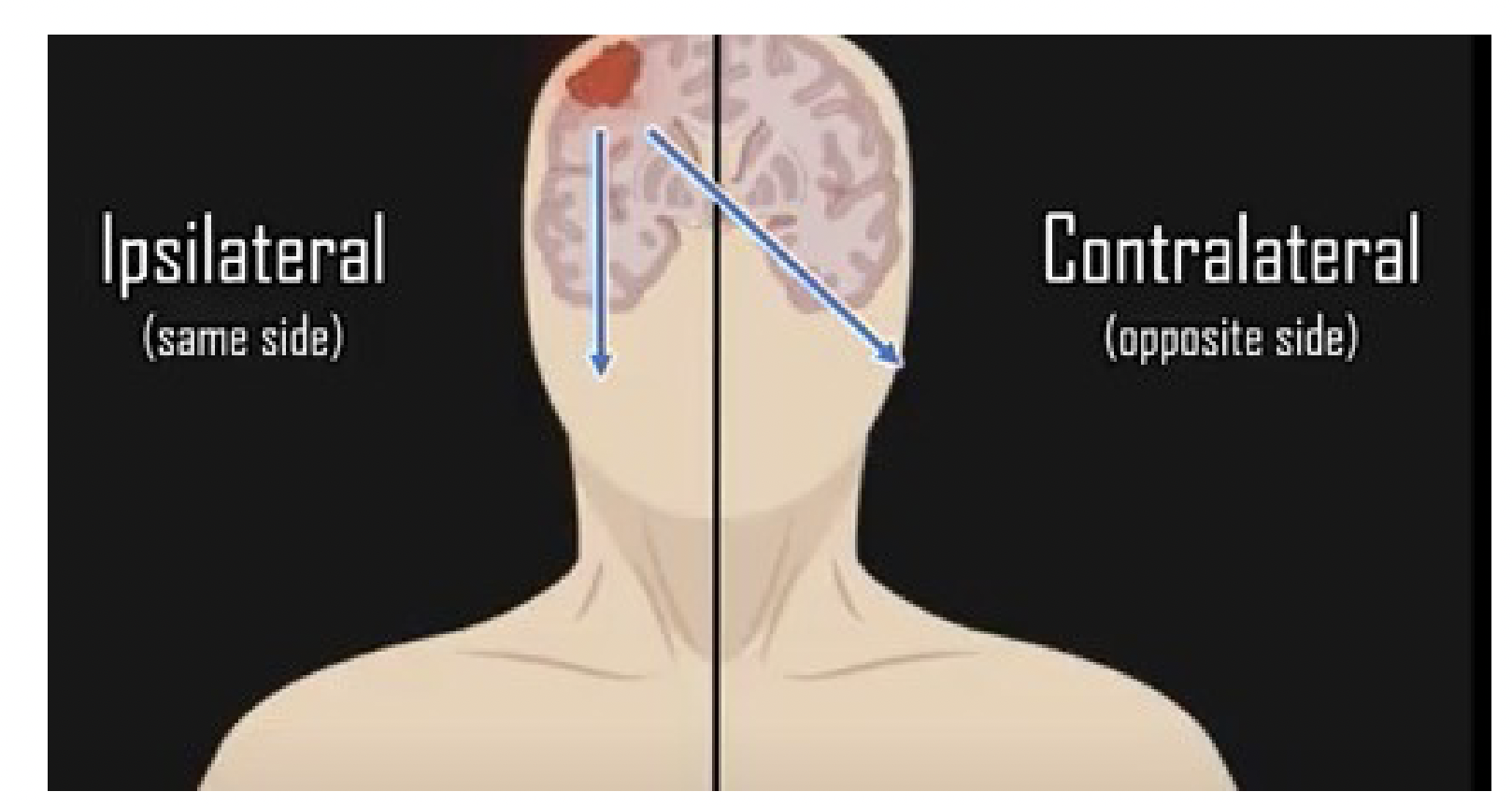
ipsilateral
same side
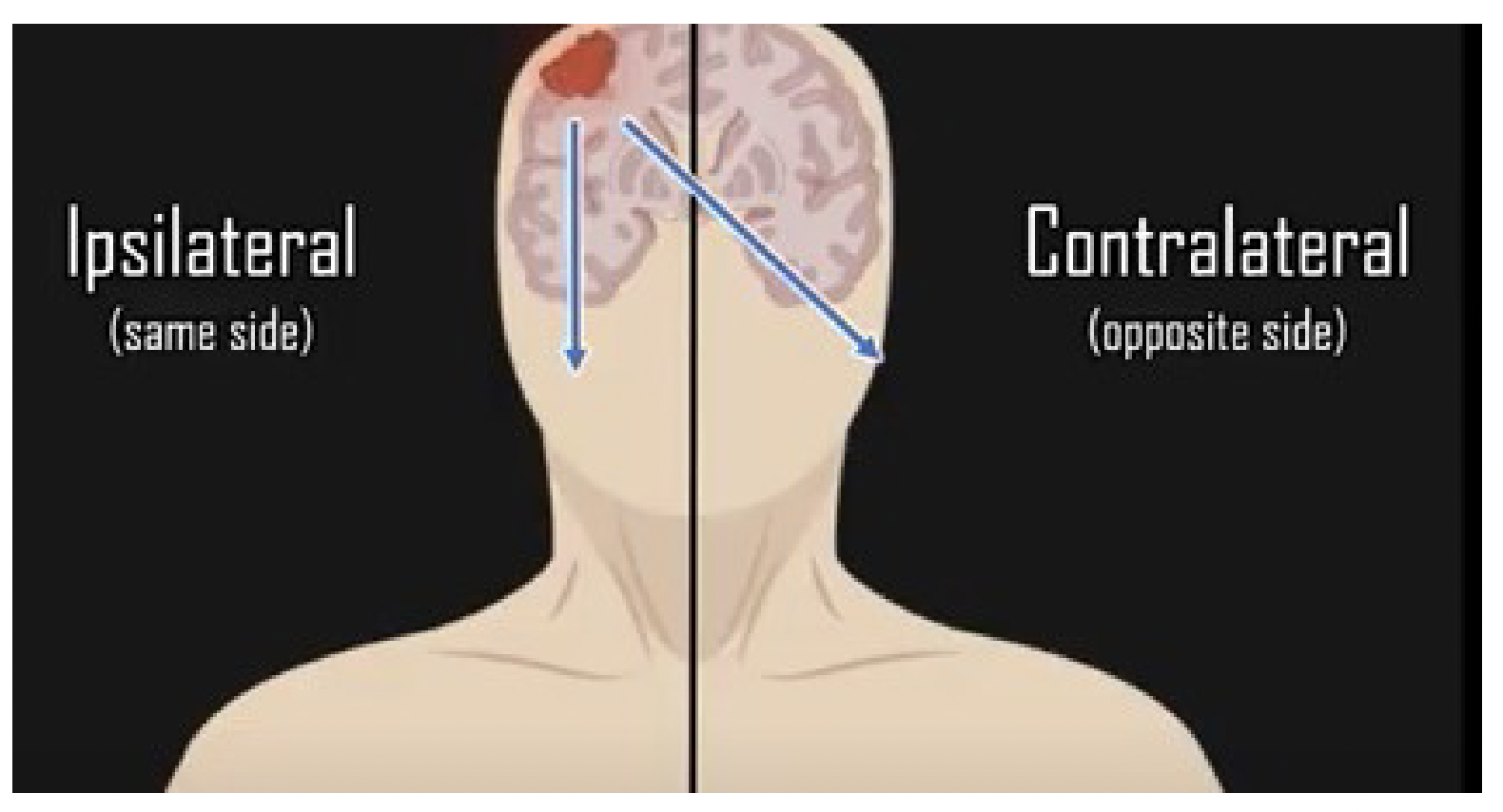
contralateral
opposite side
Parts of CNS common to all mammals
Cerebrum (Cortex), Cerebellum, Brainstem, spinal cord
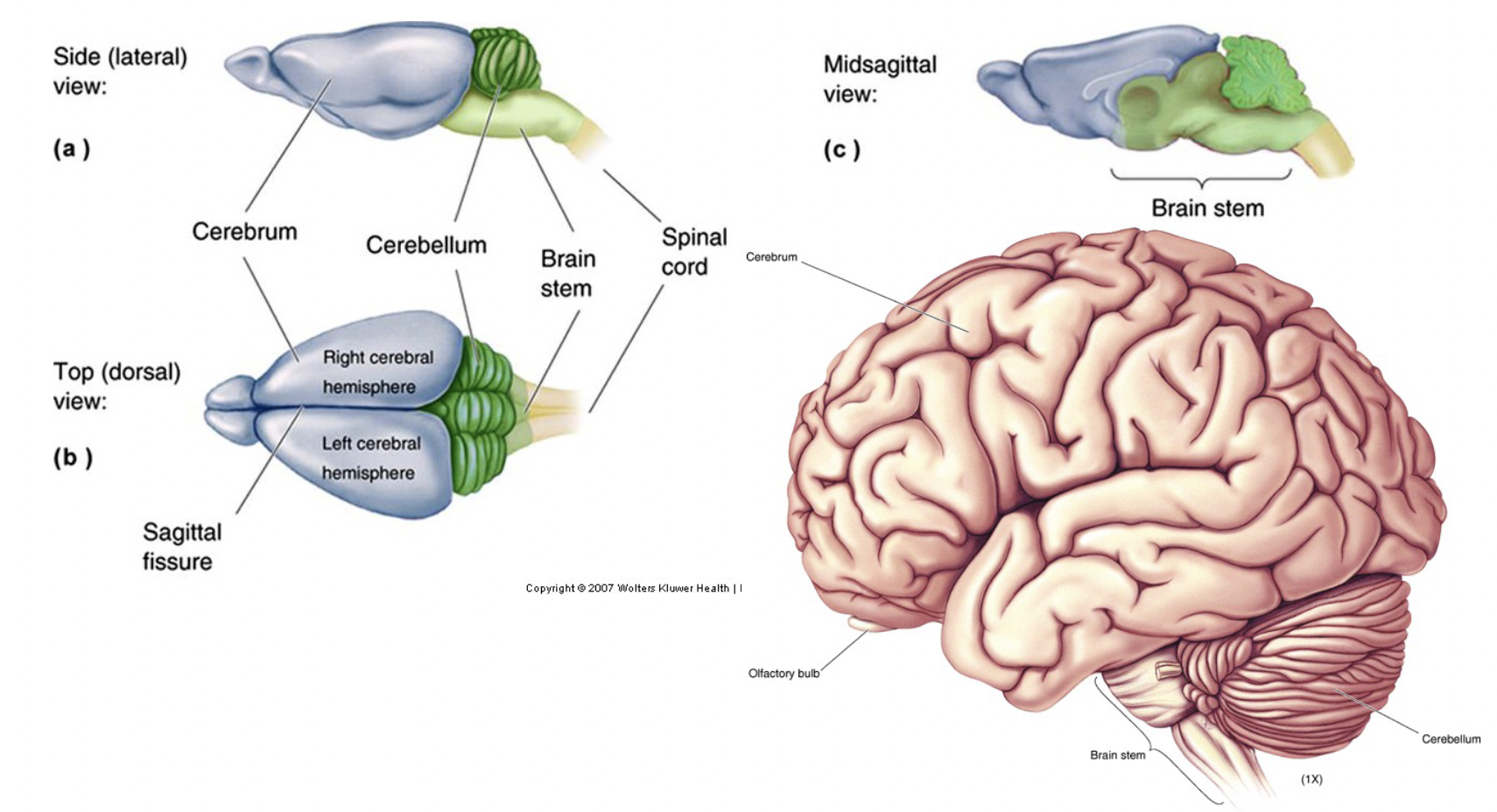
Spinal cord
part of CNS
sagittal fissure
deep groove that divides cerebrum into a left and right hemisphere
Five-Vesicle Stage (5 week in human)
Neural tube differentiates into five primary vesicles:
Telencephalon → Becomes the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia.
Diencephalon → Forms the thalamus and hypothalamus.
Midbrain (Mesencephalon) → Forms structures related to sensory and motor processing.
Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon) → Becomes the pons, medulla, and cerebellum.
Spinal Cord → Develops into the central nervous system (CNS) communication pathway
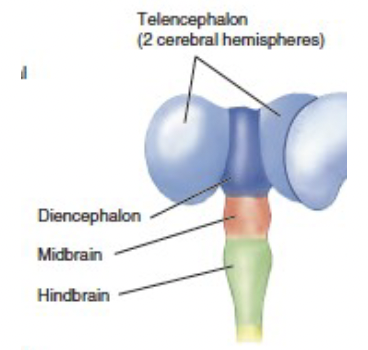
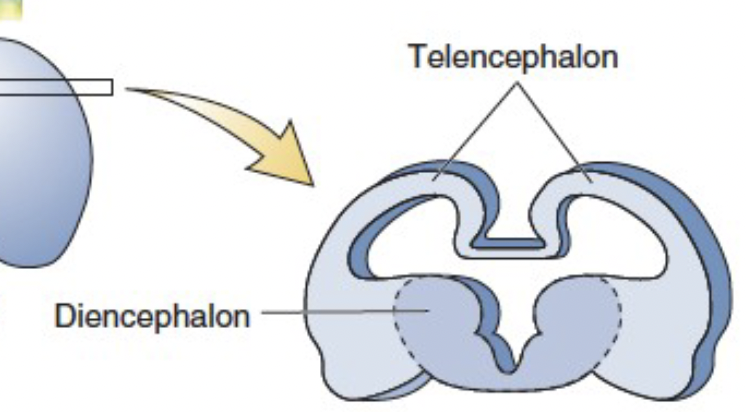
main divisions of forebrain
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
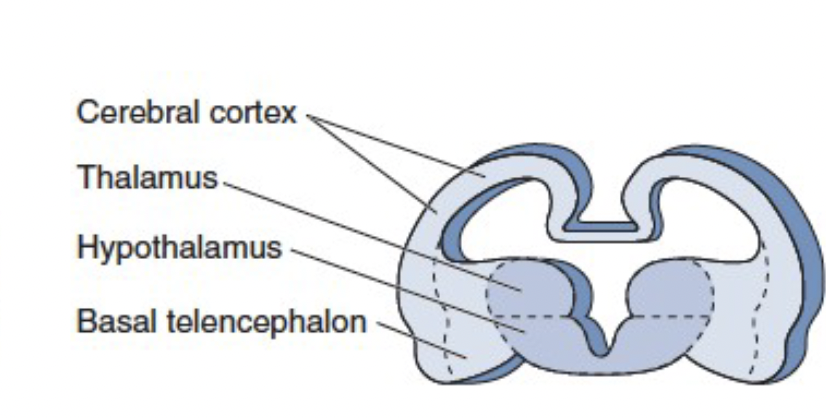
gray matter structure
neuronal cell bodies that process and relay information
cerebral cortex
thalamus (relay sensory information)
hypothalamus (control centre - homeostasis control)
basal telencephalon
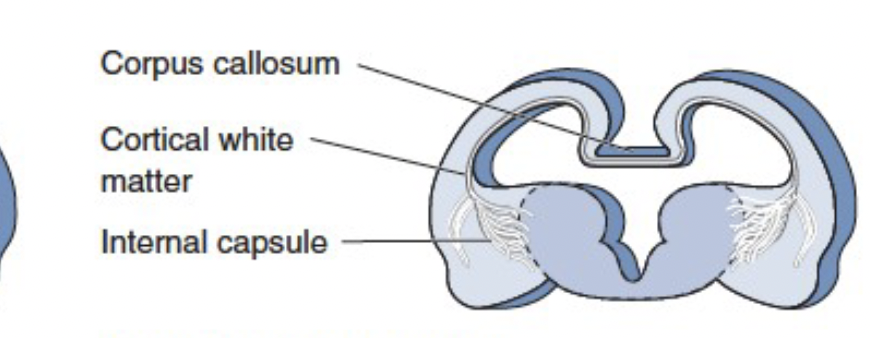
white matter structures
myelinated axons that connect different brain regions.
corpus callosum (main one, connects 2 sides of brain)
cortical white matter
internal capsule (lots of projections that go to and from cortex to different areas)
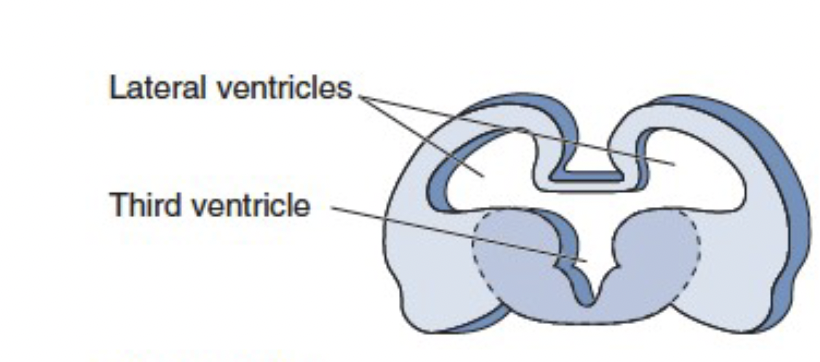
ventricles
fluid filled cavities that circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
lateral ventricles - adjacent from cortex
third ventricles - lines hypothalamus and thalamus
Gyri
bumps - raised ridges on the brain's surface.
sulci
grooves between gyri.
fissures
deep groves separating major brain regions.
central sulcus
groove separating precentral and postcentral gyrus
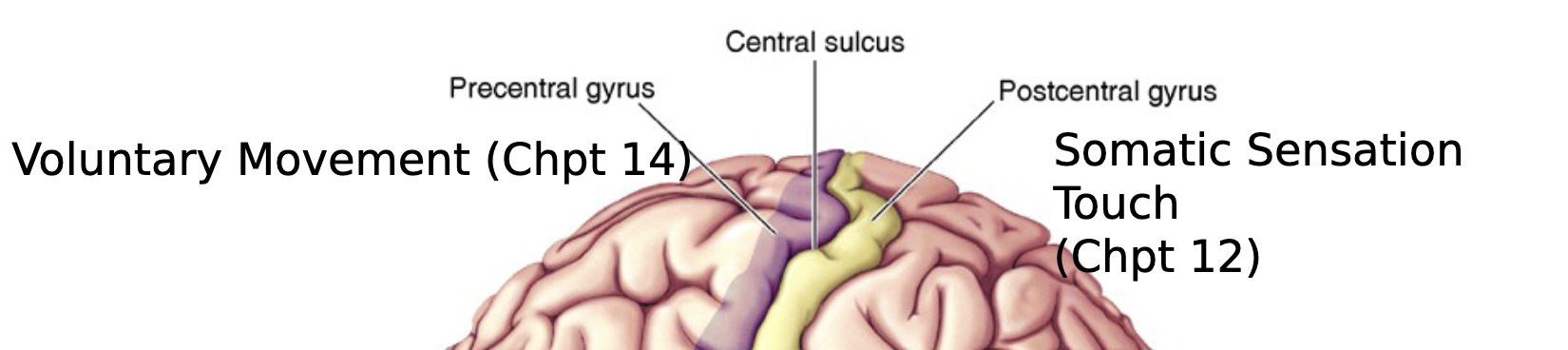
precentral gyrus
important for voluntary movement
postcentral gyrus
important for somatic sensation touch
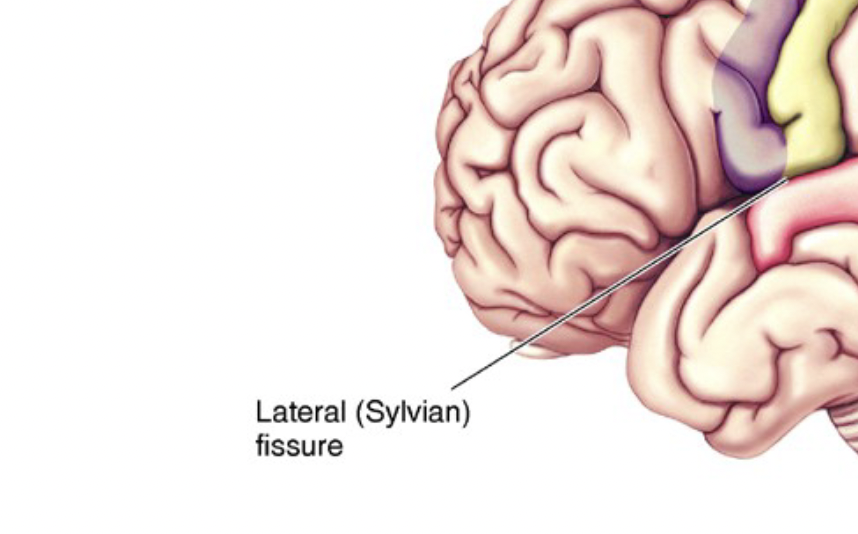
lateral (sylvian) fissure
separates different lobes
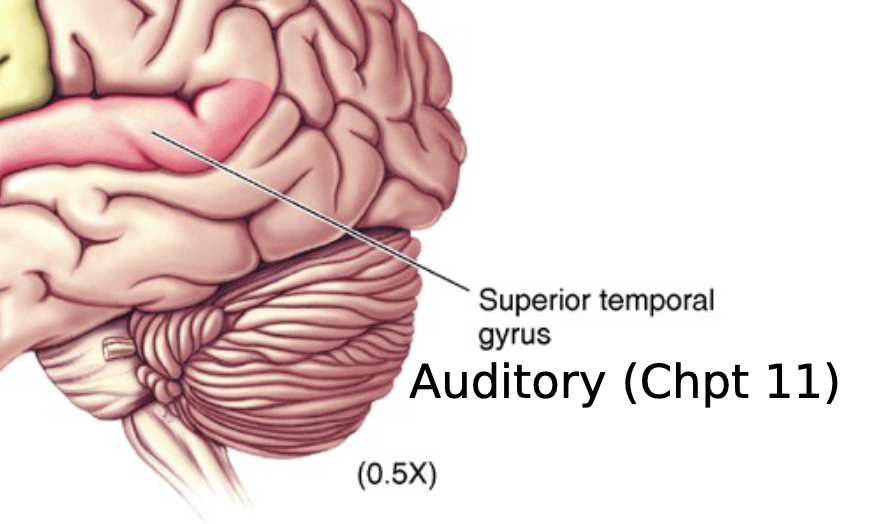
superior temporal gyrus
important for auditory
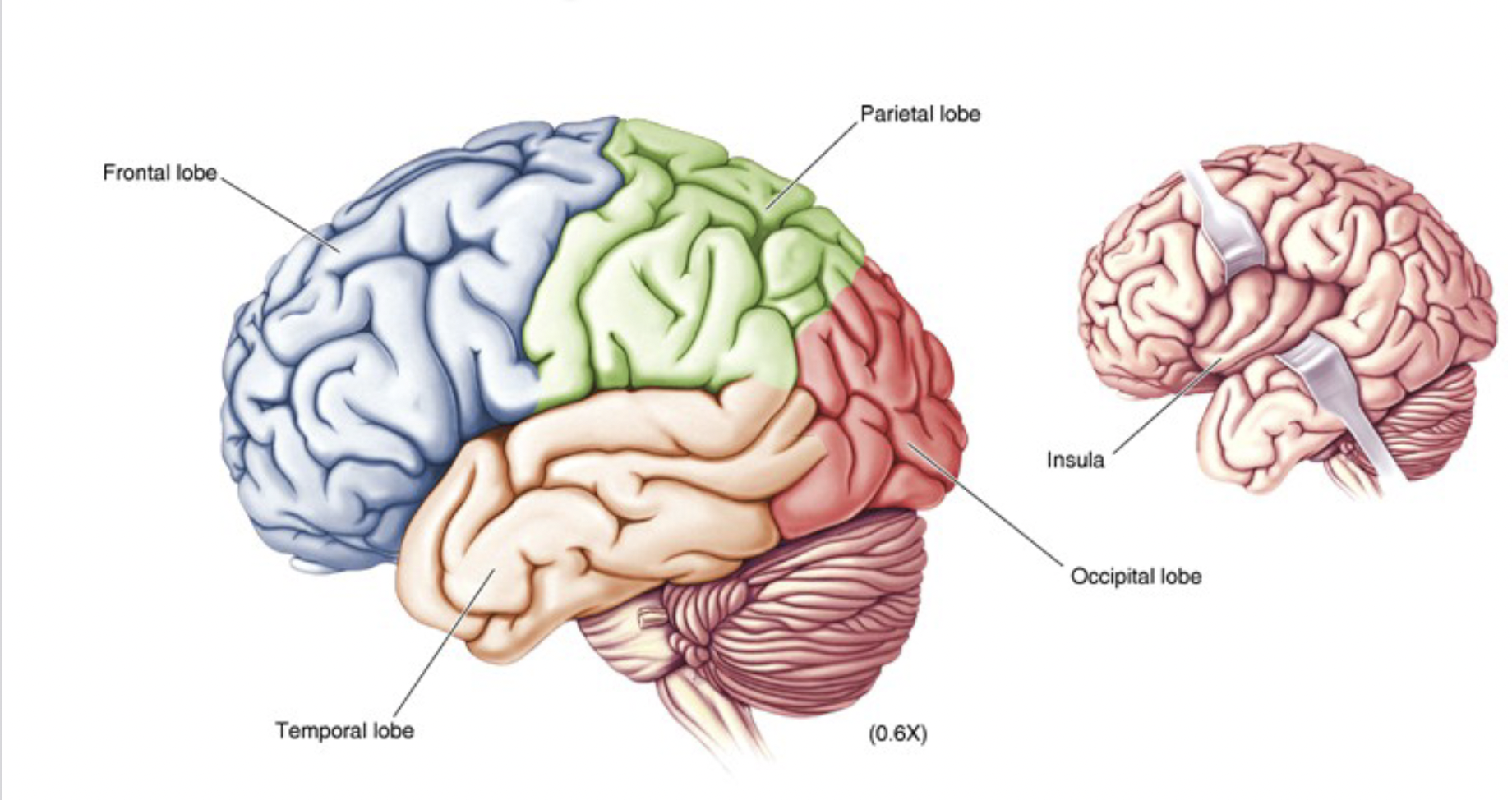
cerebral lobes (in telencephalon)
frontal lobe
temporal lobe
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
insula
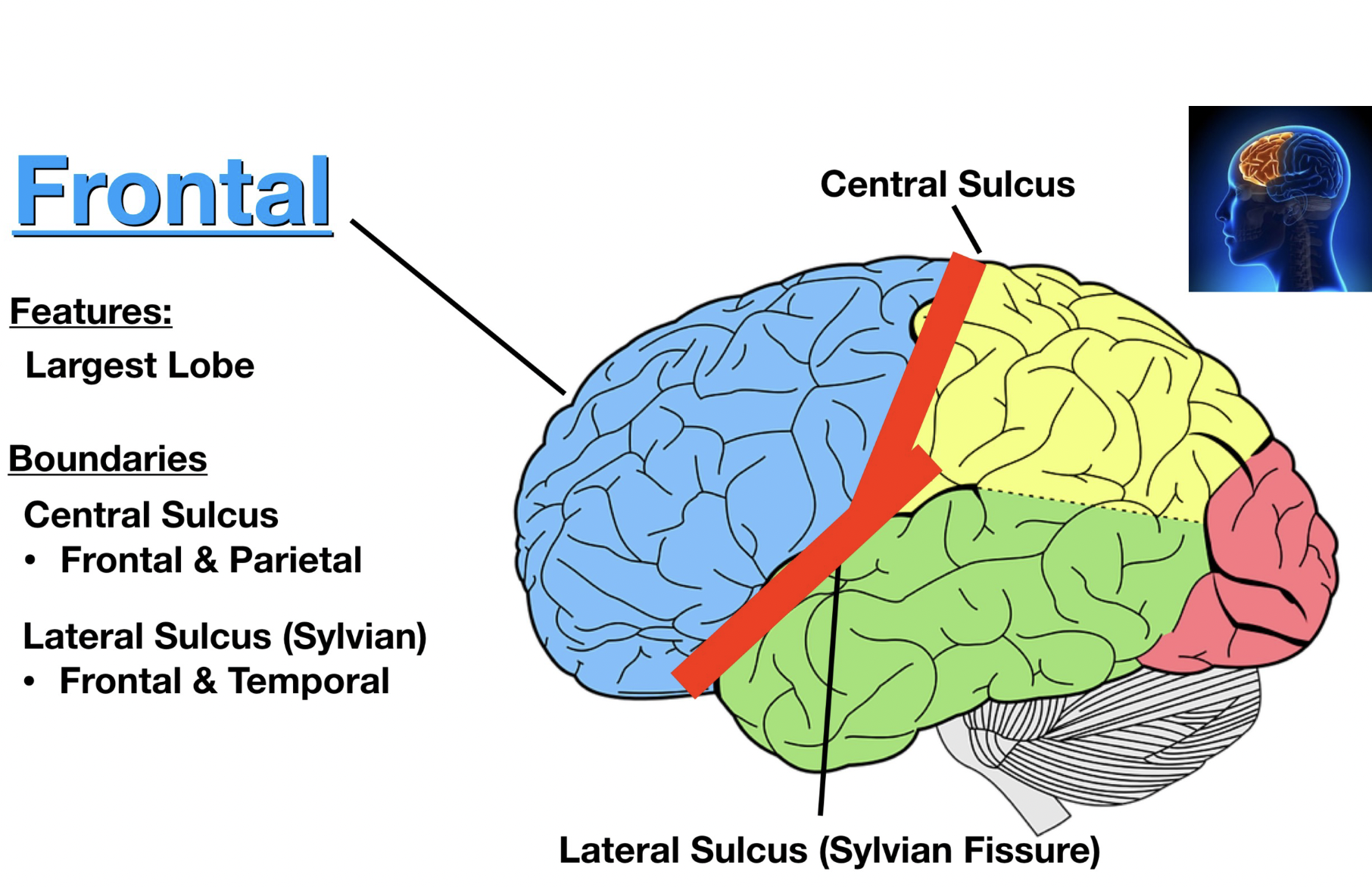
frontal lobe boarding
largest lobe
bordered by
Lateral sulcus (sylvian fissure)
frontal and temporal
central sulcus
frontal and parietal
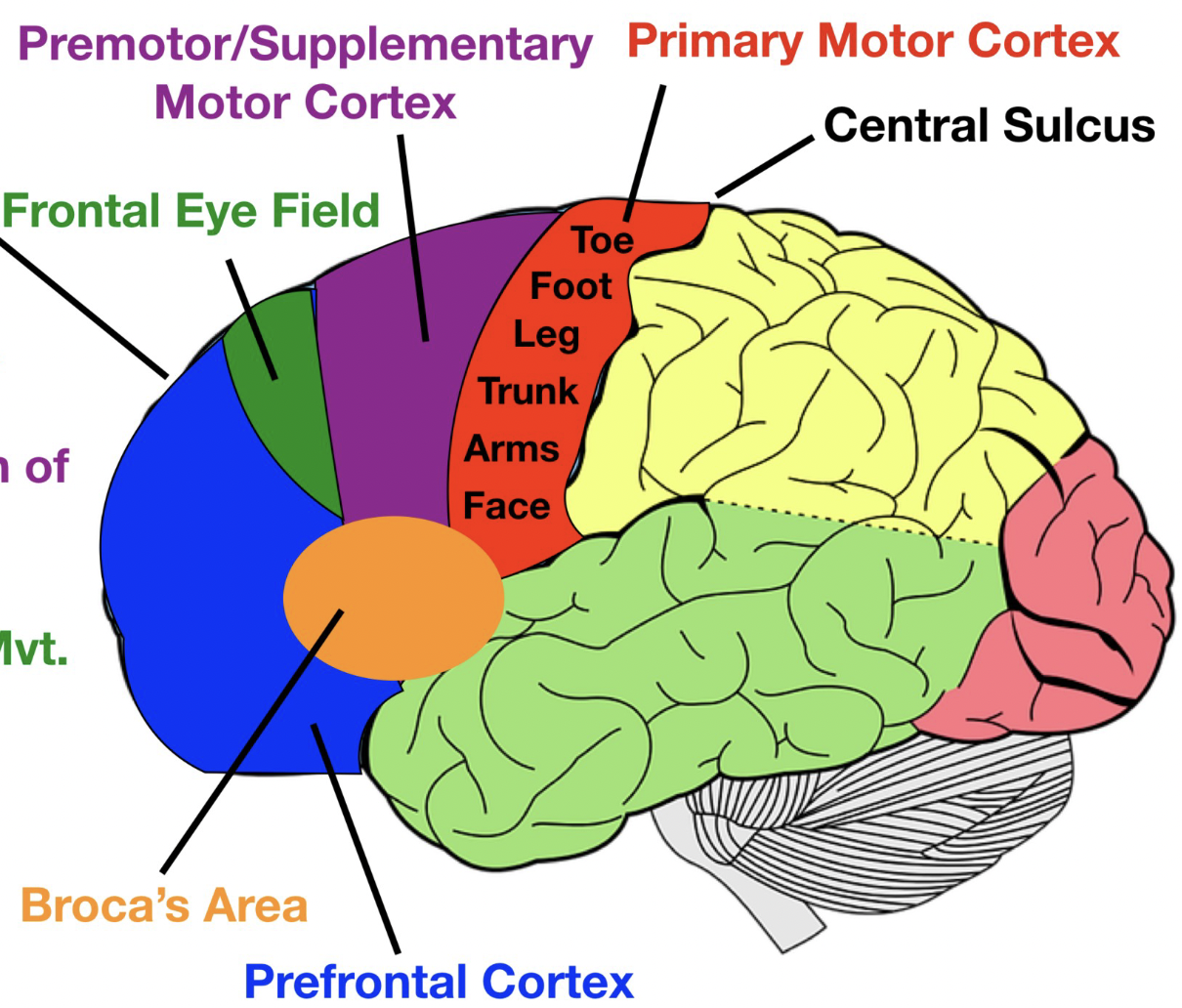
frontal lobe function
action (mental and physical)
executive functioning, ex. planning, problem solving, motivation, judgement, decision making, impulse control, social behaviour, personality, memory, learning, rewards, attention)
motor, ex. skeletal muscle movement, ocular movement, speech control, facial movement
functioning areas of frontal lobe
primary motor cortex - voluntary muscle movement
premotor/supplementary motor cotrex (MAC) - planning coordination of movement
frontal eye field - voluntary rapid eye movement
prefrontal cortex - executive functions, behaviour planning
brocas area - muscles of speech, production of speech (LEFT SIDE)
parietal lobe function
somatosensory
awareness of somatic sensation
touch, pain, temperature, pressure vibration
processing somatic sensation
analyzing, recognizing, memory of somatic sensation
proprioception
coordination of visual, auditory, and somatosensory stimuli
spacial and body awareness
somatosensory cortex
located in parietal lobe
processes sensory information from the body, including touch, pain, temperature, and pressure.
homunculus
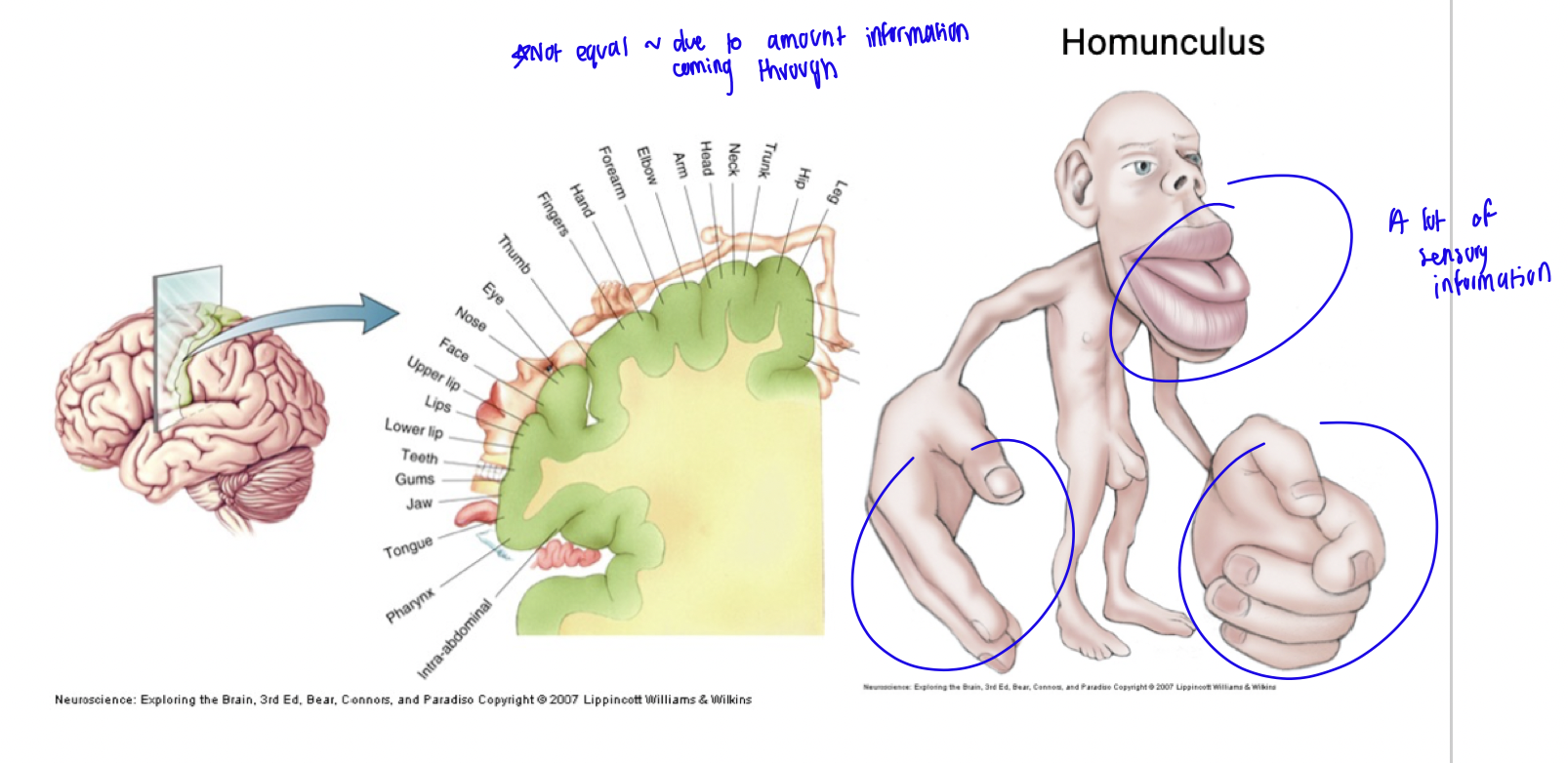
functioning areas of parietal lobe
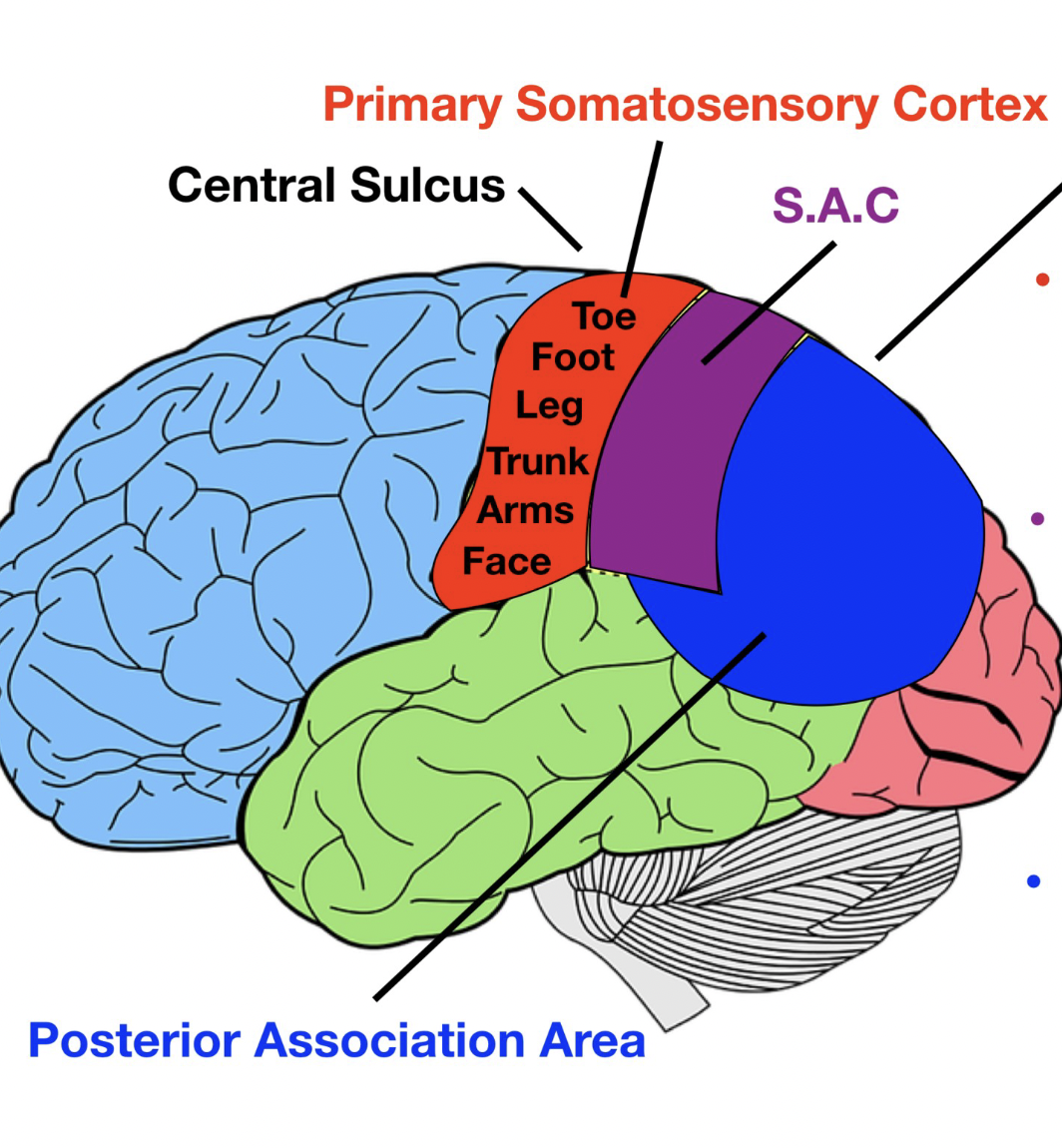
primary somatosensory cortex - awareness signal
somatosensory assoc. cortex (SAC) - processing and analyzing signal
posterior association area - visual, auditory, somatosensory areas meet, spacial awareness
occipital lobe function
visual
awareness of visual stimuli (seeing)
processing visual stimuli (analyzing, recognizing, memory, shapes, colours, sizes)
functional areas of occipital lobe
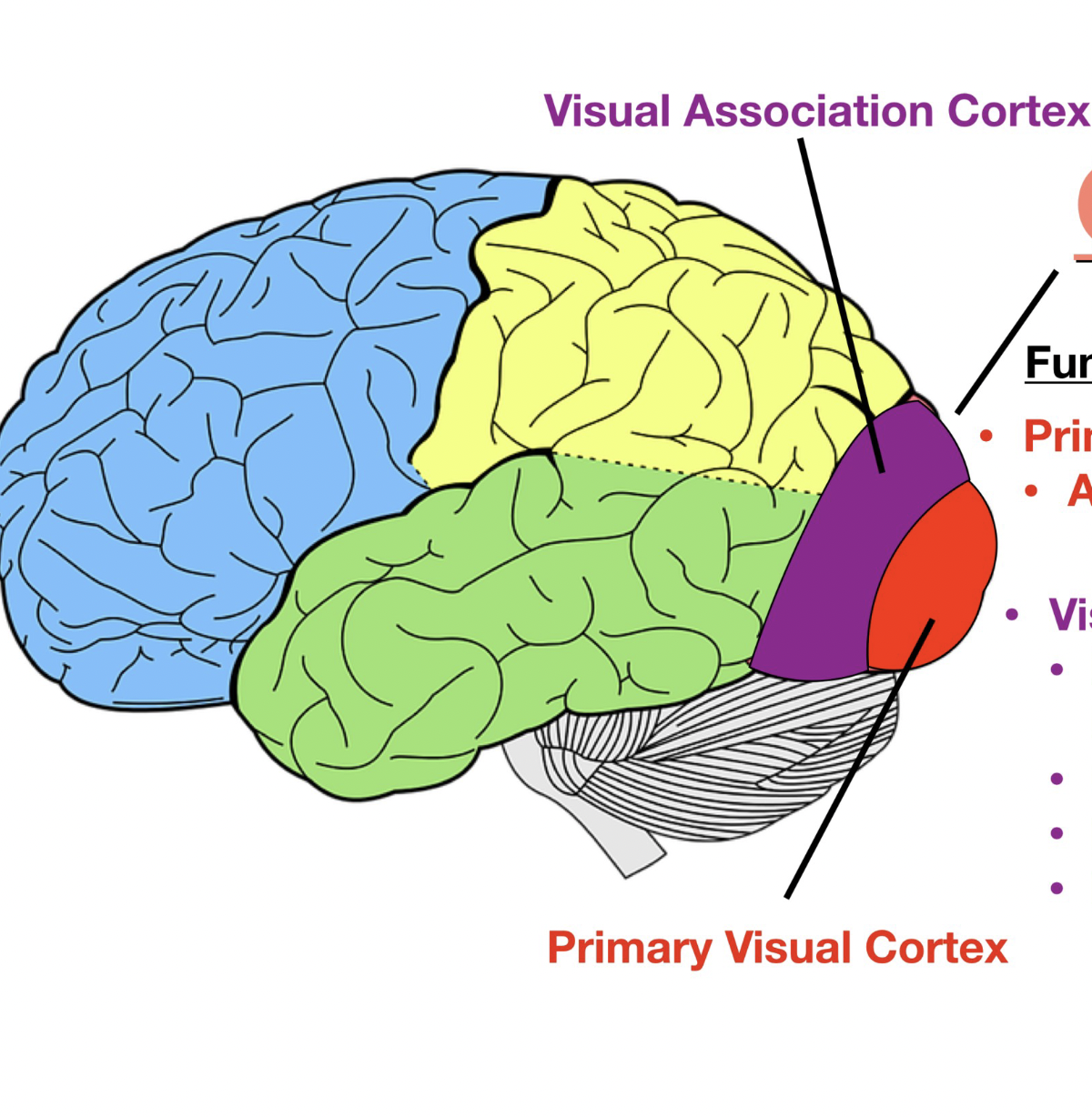
primary visual cortex - awareness visual stimuli
visual assoc. cortex - processing visual stimuli
temporal lobe function
auditory
awareness of auditory stimuli (hearing sounds, pitch, frequency)
processing auditory stimuli (analyzing, recognizing, memory)
functional areas of temporal lobe
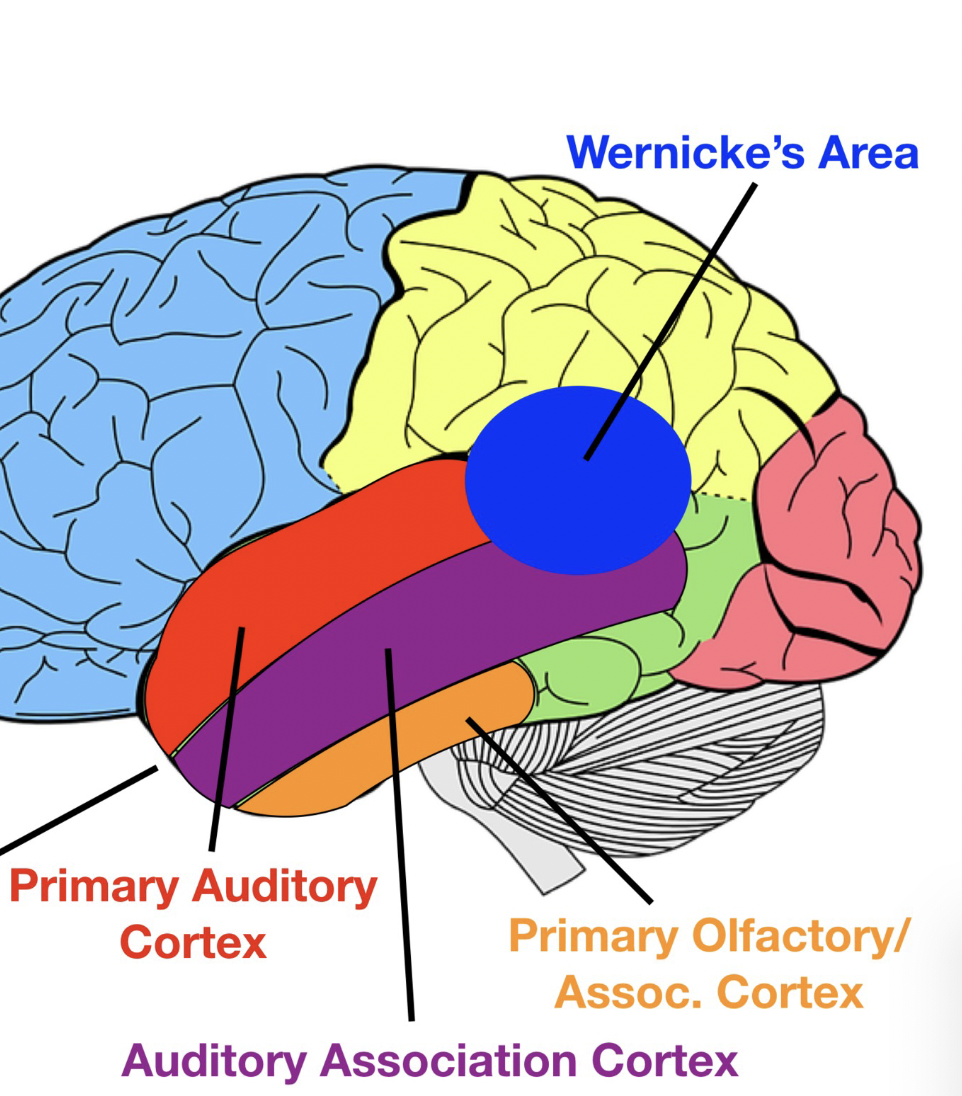
primary auditory cortex - awareness auditory stimuli
auditory assoc. cortex - processing sounds
wernicke’s area -comprehend/understand written/spoken language
primary olfactory cortex/association cortex - awareness and processing of smell
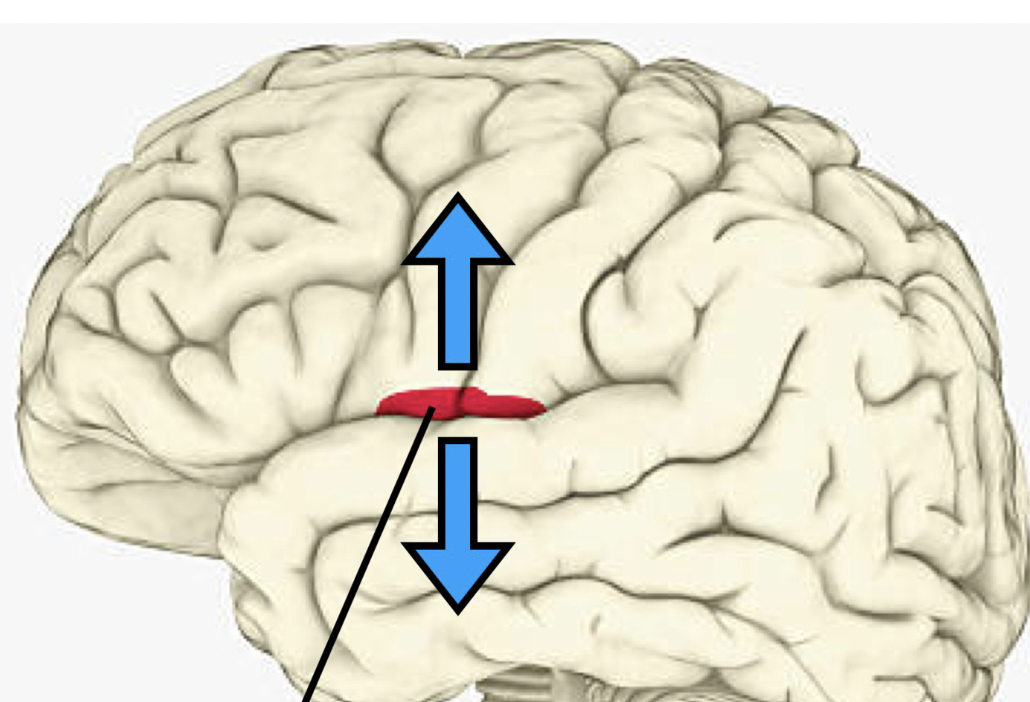
insular cortex
deep within lateral sulcus
responsible for taste, visceral sensation (ex. feeling full, bloated), autonomic control, vestibular information, equilibrium
neocortical evolution
cortex amount has changed (not structure)
conserved primary sensory areas, secondary sensory areas, motor areas
expansion of secondary sensory areas
ASSOCIATIVE AREAS - interpreting, organizing, remembering information
corpus callosum
part of telencephalon that joins 2 sides of brain
white matter structure
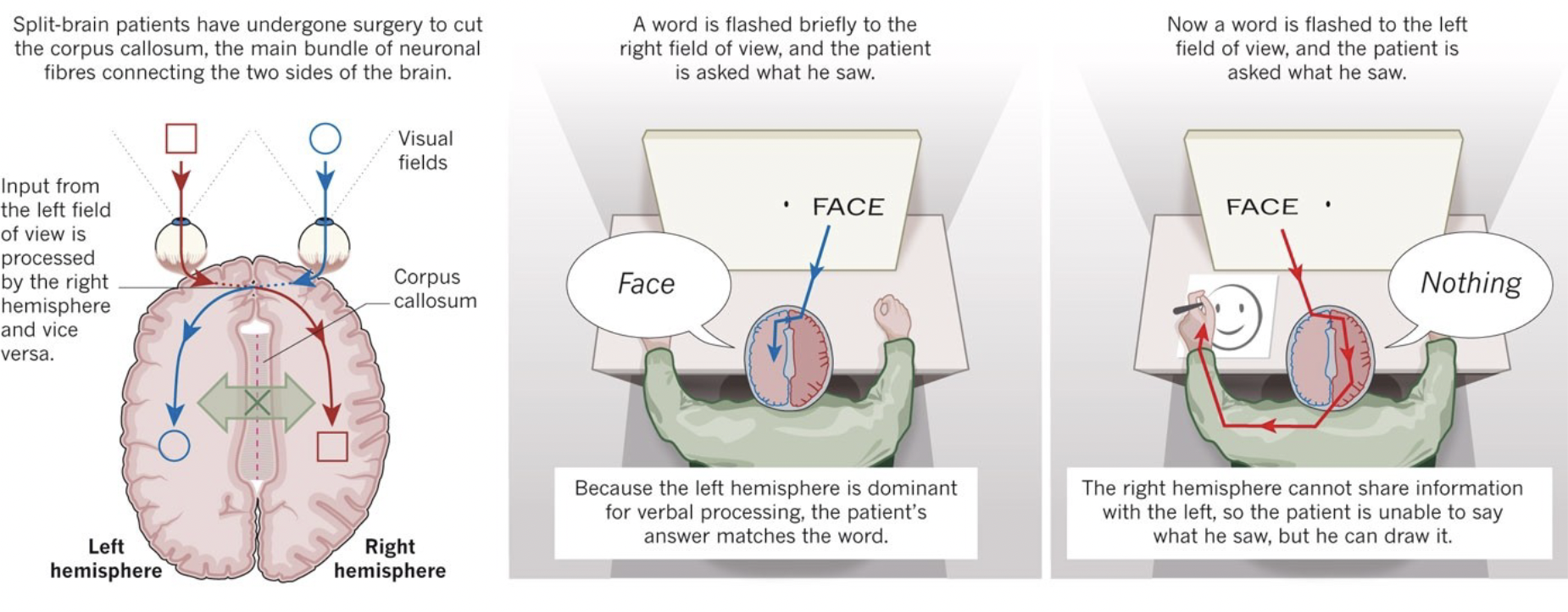
what side of brain is responsible for speech
LEFT side of brain
what side of brain is responsible for detecting faces
RIGHT side of brain
severed corpus callosum
separates 2 sides of brain, preventing left and side brain from communicating with each other
ex. if word flashed to right, it’s interpreted by left side of brain responsible for speech, so patient able to speak the word. but if flashed to left side, interpreted by right side of brain, and because 2 sides of brain can’t communicate, patient not able to speak.
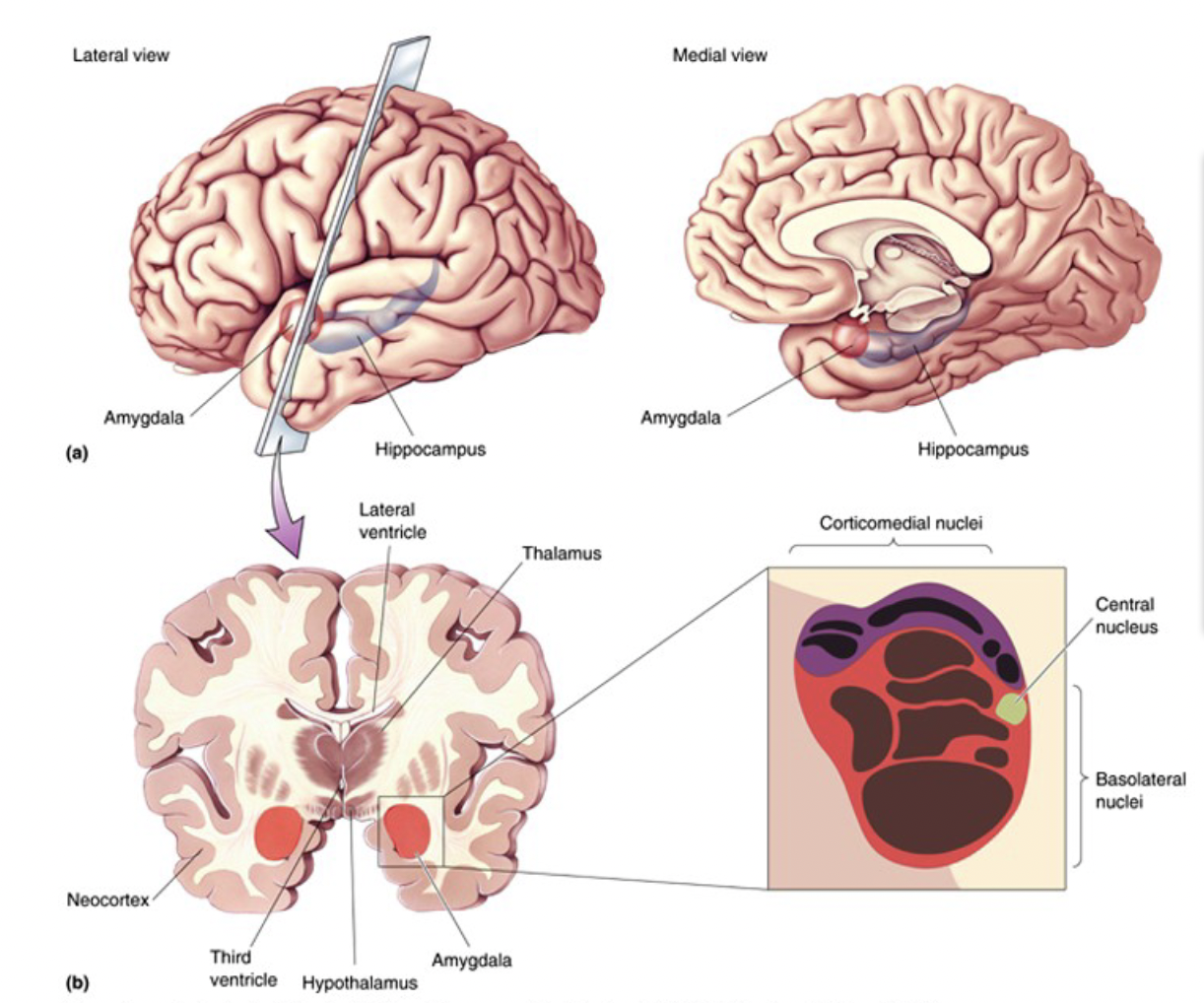
amygdala
part of telencephalon
function: fear response
composed of
corticomedial nuclei - receive olfactory (smell) nafferents
basolateral nuclei - receive visual, auditory, gustatory, and tactile afferents
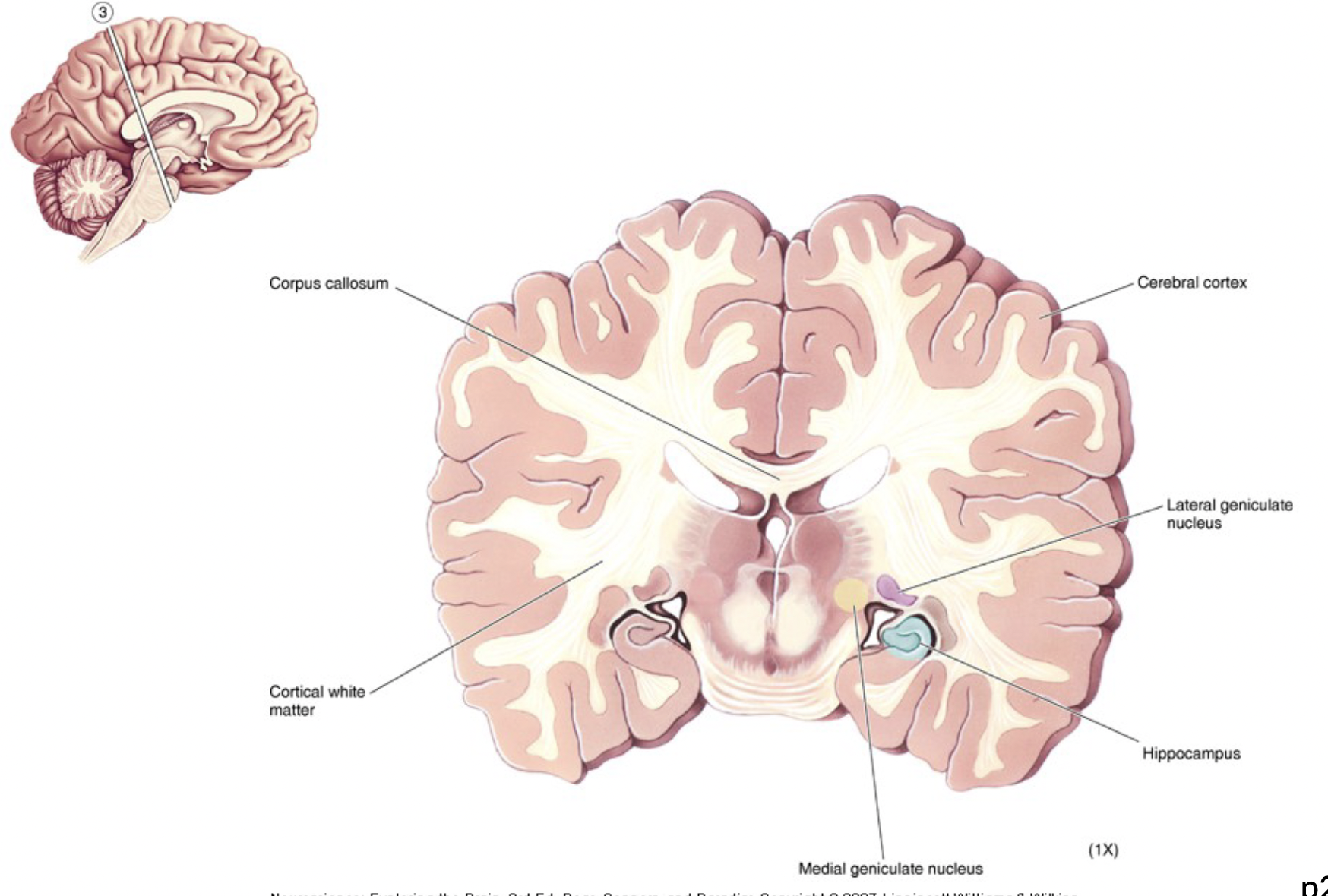
hippocampus
part of telencephalon
function: learning and memory
“sea horse” shape
proximity to lateral geniculate nucleus, and medial geniculate nucleus
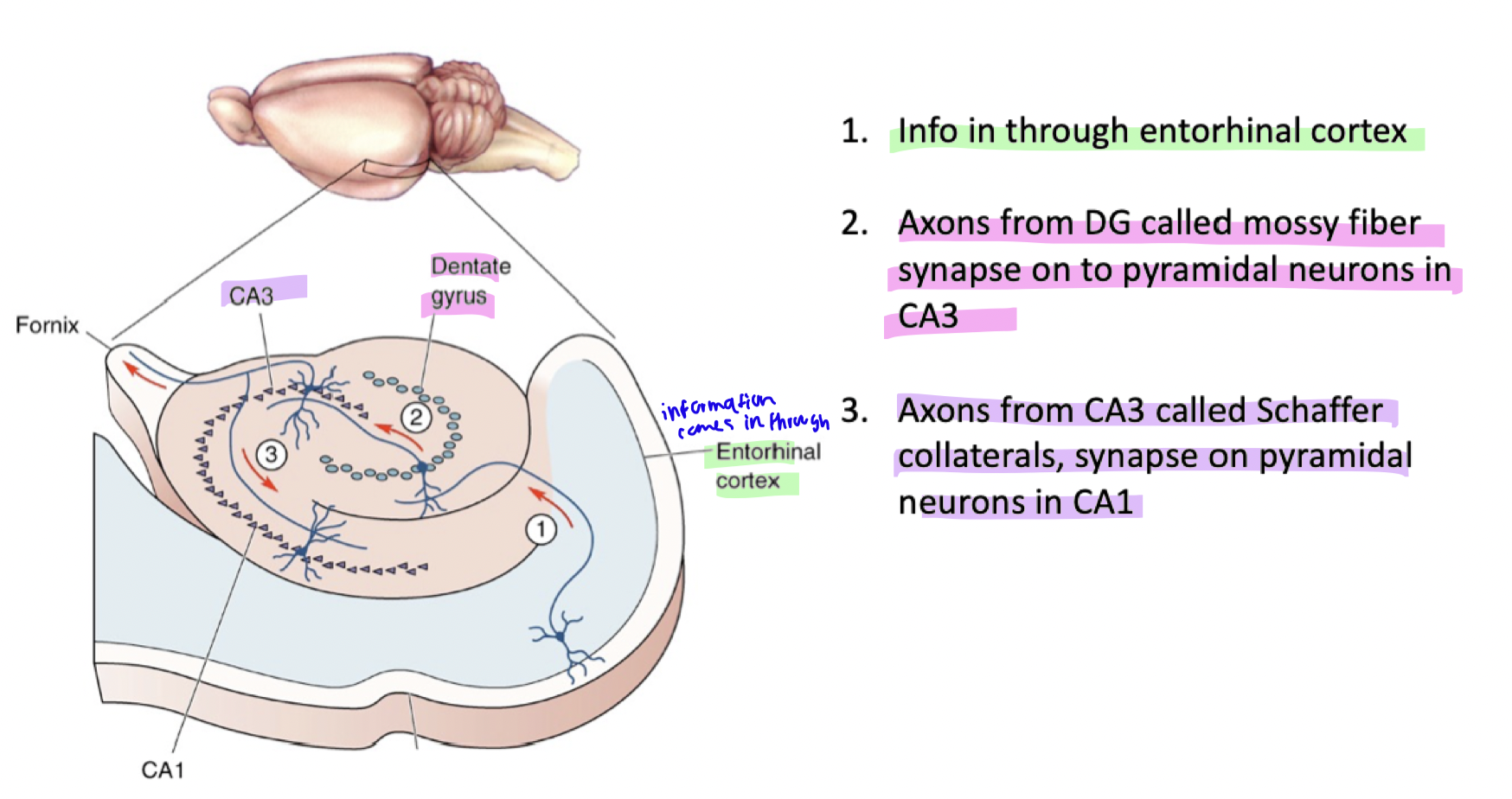
hippocampus trisynaptic pathway
Information enters via the entorhinal cortex → Sent to dentate gyrus (DG).
Mossy fibers from DG synapse onto CA3 pyramidal neurons.
Schaffer collaterals from CA3 synapse onto CA1 pyramidal neurons.
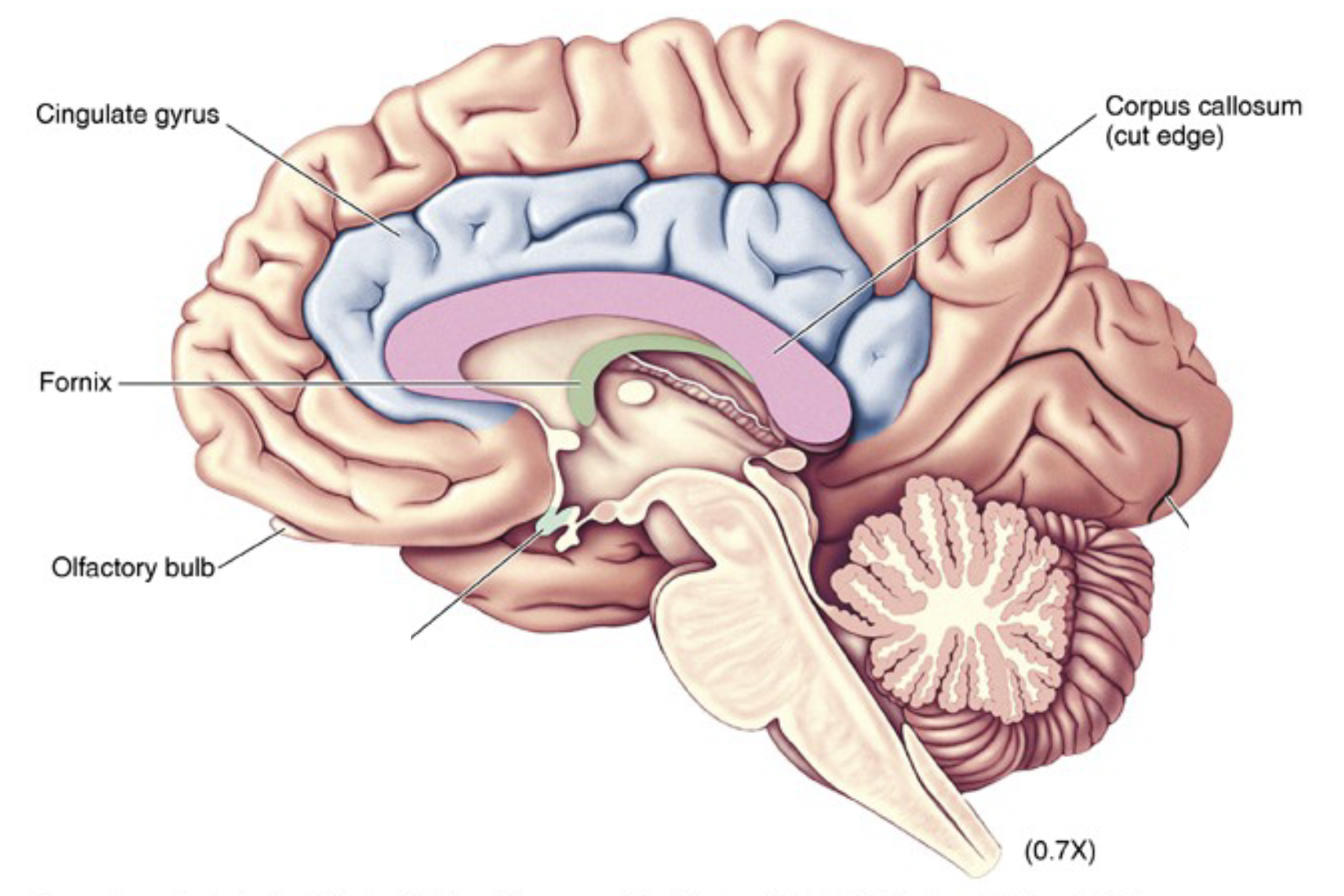
Brocas Limbic System (telencephalon)
cortex forming a ring around corpus callosum: Cingulate gyrus, medial surface temporal lobe, hippocampus
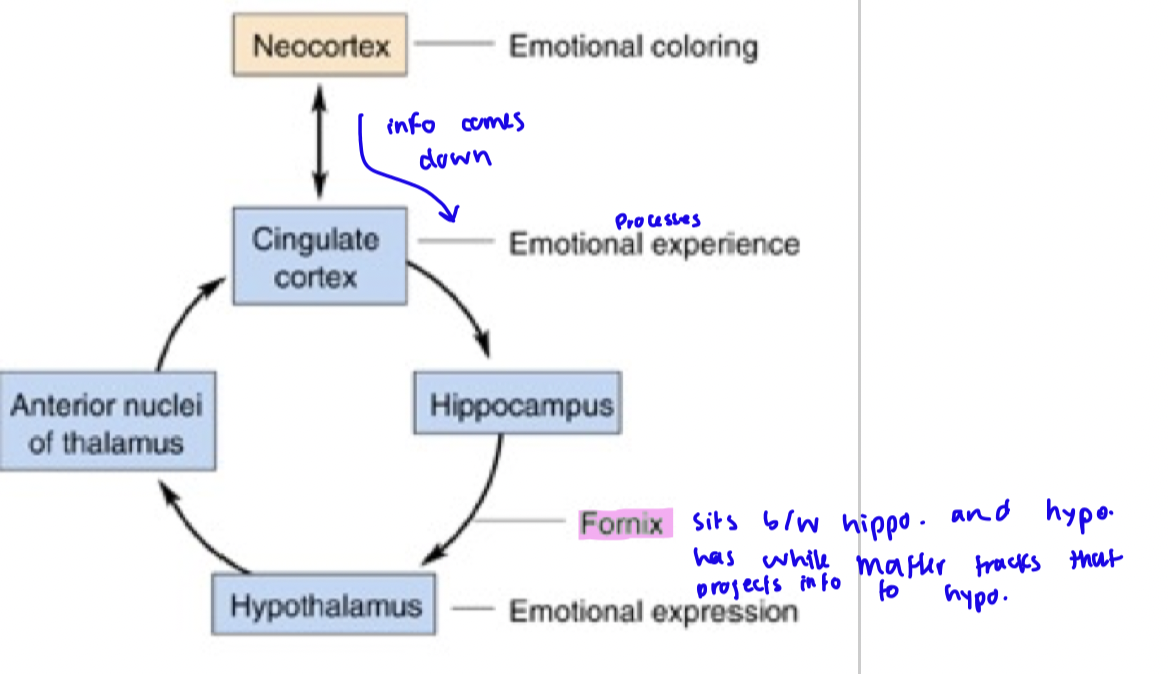
the papez circuit
important in memory and ability to process emotions
Cingulate Cortex → Receives emotional input from the neocortex (thinking part of the brain).
Hippocampus → Processes emotions and memory.
Fornix → A communication highway that sends signals from the hippocampus to the hypothalamus.
Hypothalamus → Controls physical emotional responses (e.g., heart rate, sweating).
Anterior Thalamus → Acts as a relay station, sending the processed emotion back to the cingulate cortex.
Cingulate Cortex → Completes the loop by helping process the emotion and connecting it to memories.
2 structures in diencephalon
thalamus
hypothalamus
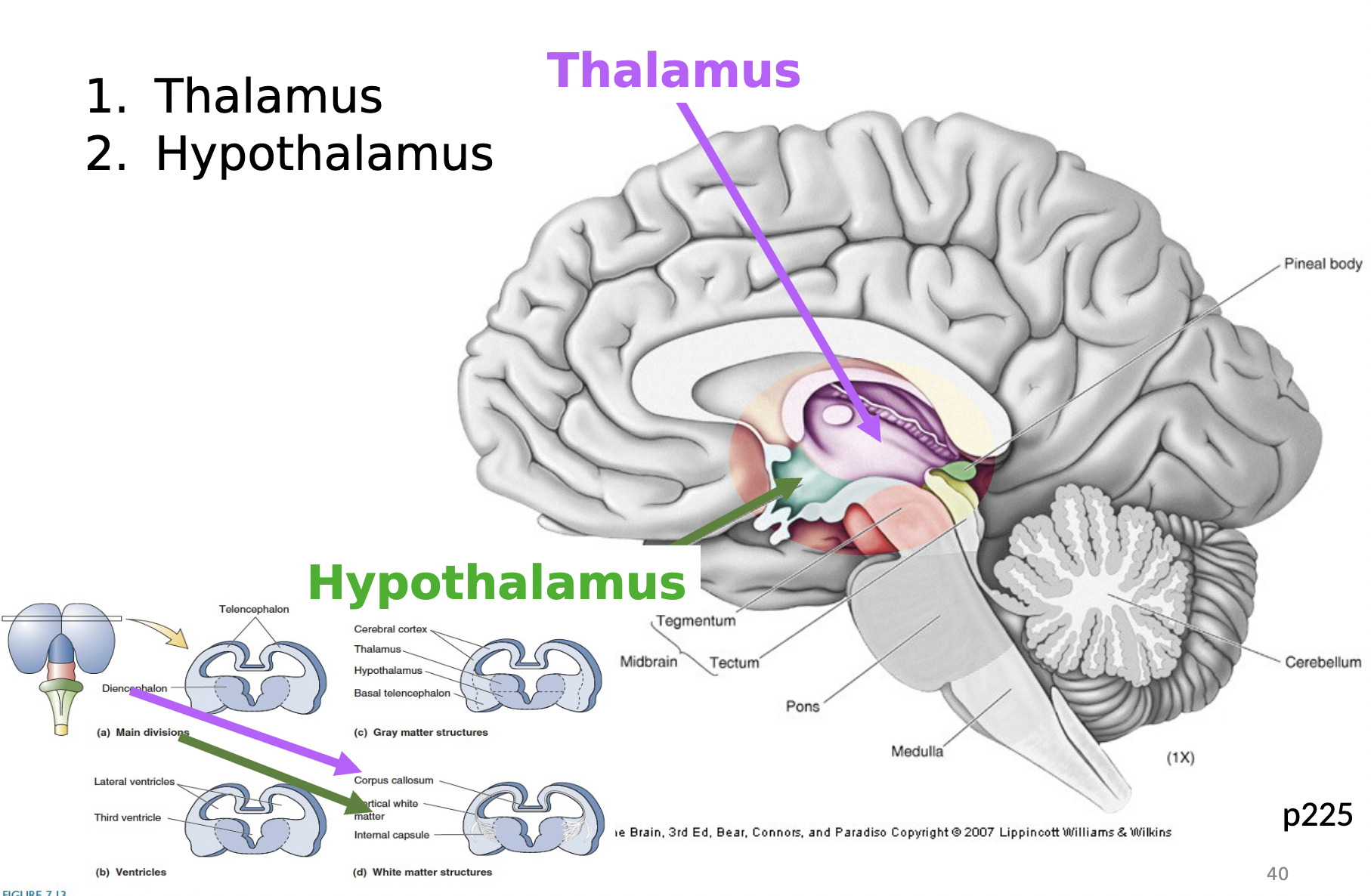
thalamus function
gateway to cortex
it takes in sensory information to cerebral cortex
hypothalamus function
homeostasis - regulatory process (ex. body temp. and blood composition)
commands in cold weather (shiver, goosebumps, turn blue)
commands in hot weather (turn read, sweat)
controls metabolism (eating energy)
structures of telencephalon
cerebral cortex - 5 lobes (brodman’s area)
subcortical structures
corpus callosum
amygdala
hippocampus
structures of brainstem
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
tegmentum and tectum
Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
pons and medulla
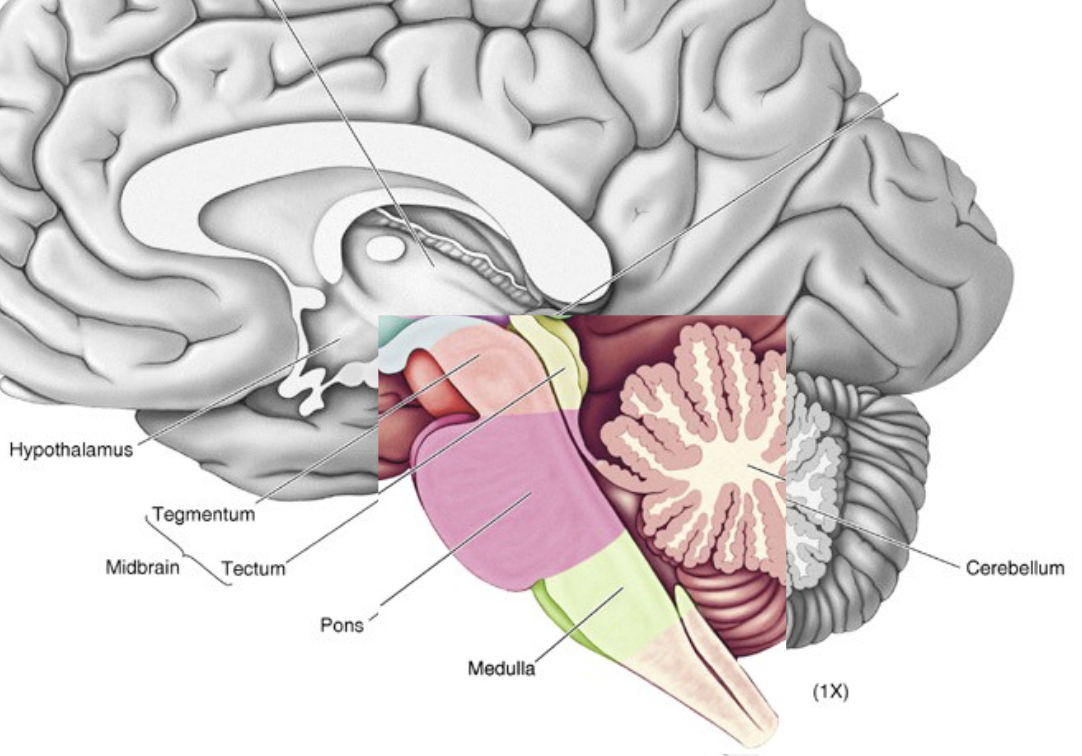
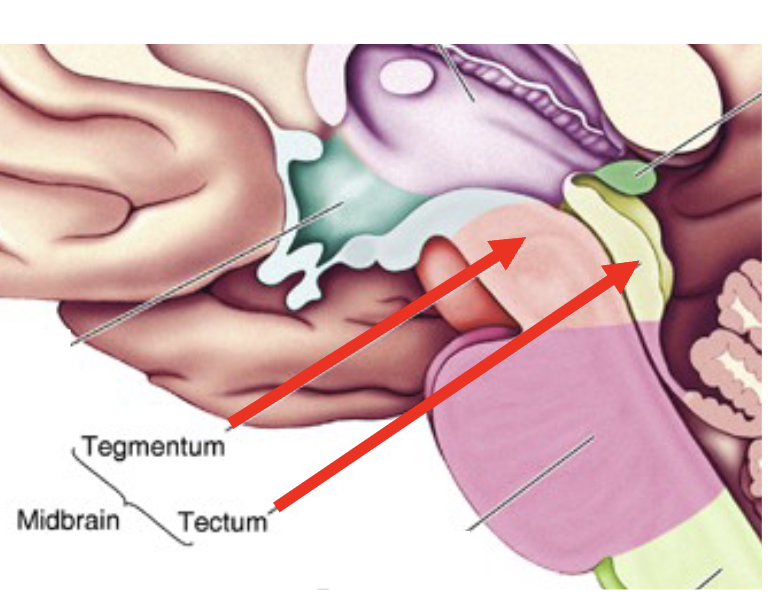
Tectum
the roof of the mesencephalon
superior colliculus - orientating, eye movements
inferior colliculus - auditory responses
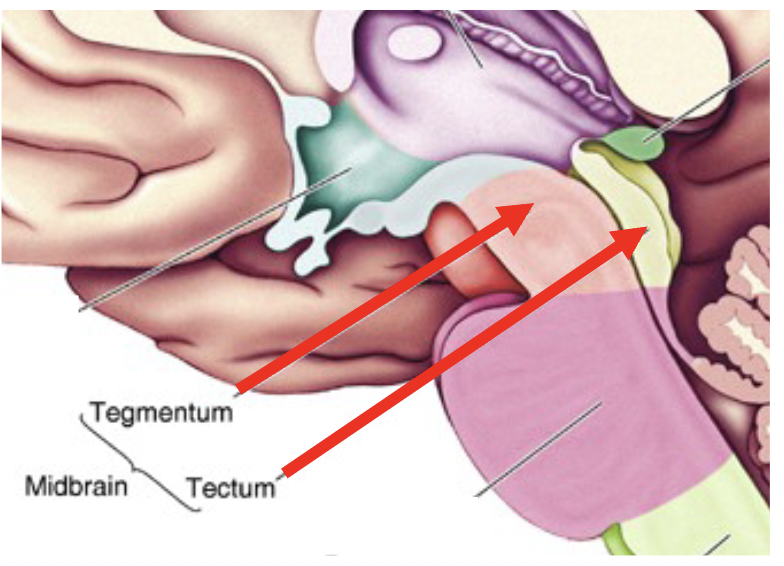
Tegmentum
the large covering of the mesencephalon
motor
attention, alertness
autonomic function
consists of cerebral aqueduct, periaqueductal gray, reticular formation, substantia nigra, and red nucleus
Pons
portion of hindbrain that connects the cortex with the medulla
communication and coordination centre between the two hemisphere of brain
(like white matter tracts)
Medulla
controls autonomic functions (ex. breathing, digestion, heart and blood vessel function, swallowing, and sneezing)
motor and sensory neurons from midbrain and forebrain travel through this
cerebellum
“little brain”
contains as many neurons as BOTH cerebral hemispheres
primary movement centre
**left controls left, right controls right
ventricles
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) filled caverns and canals inside brain
choroid plexus
specialized tissue in ventricles that secretes CSF. This circulates through ventricles, and is reabsorbed in subarachnoid space
hydrocephalus
abnormal accumulation of spinal fluid in the chambers of the brain. The most common symptoms include headaches, memory problems, walking difficulties and urinary incontinence.
cranial nerves
12 of them
olfactory and optic nerves serve olfaction and vision
other 10: contain axons of PNS