CPIM Module 1.6
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
functional strategy
a strategy that is built from the business functions such as finance, marketing, and production
operations strategy
the total pattern of decisions that shape long-term capabilities of an operation and their contribution to overall strategy. Operations strategy should be consistent with overall strategy.
Distinguish between operational management and operations strategy.
Operations Strategy Traits
A longer time frame - consists of trends in demand and supply, the effects on new technology, and the opportunities for internal investment and development. Focus on long-term plans for the use of the resources and the development/improvement of process and capabilities.
A broader perspective - consists of effect of forces inside and outside organization on operations
A higher level of focus - provides direction to create policies and processes needed to develop the strategy.
Forces acting on operations strategy
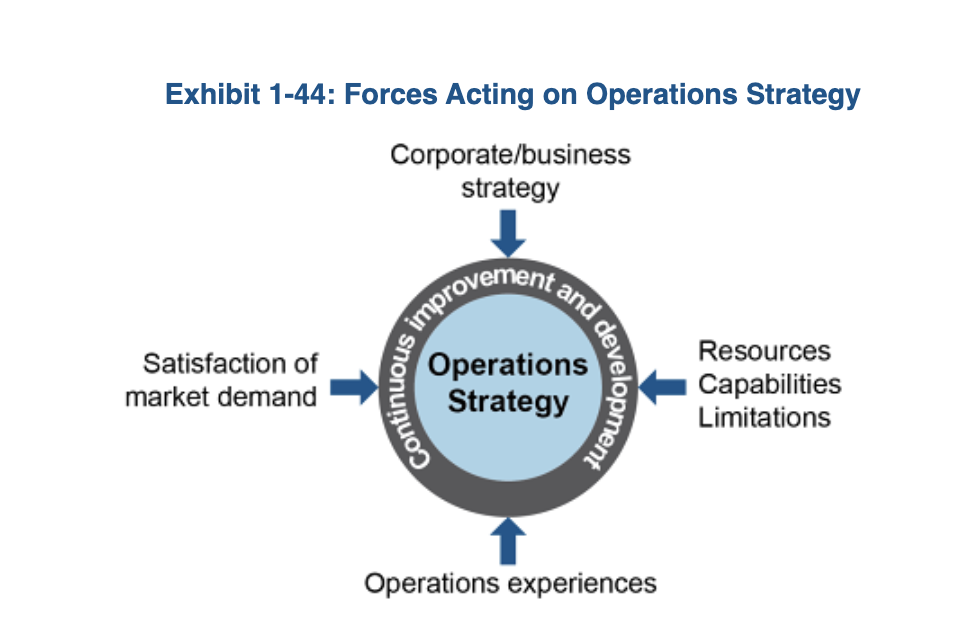
Requirements for a successful operations strategy
Consistent with the strategic choices made at the business strategy level
Mindful of the market requirements
Open to the lessons of experience from those involved in operations
Aware of the operation’s resources, capabilities, limitations.
Process Technology and Manufacturing
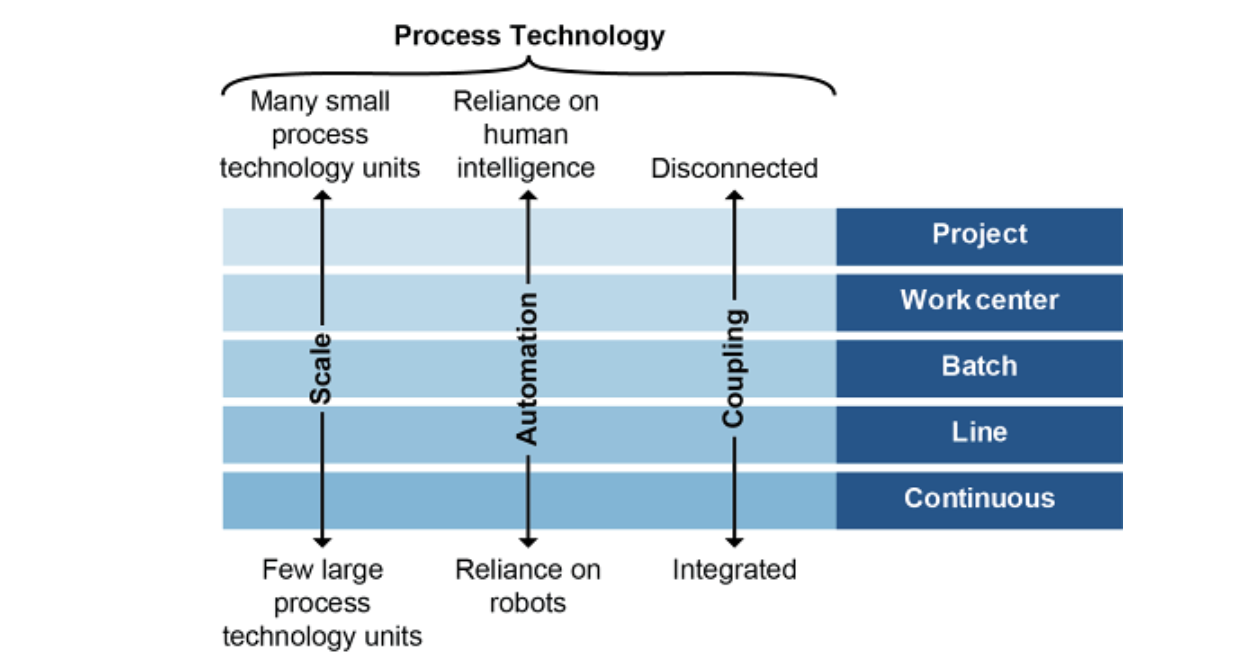
Project Manufacturing
a type of manufacturing process used for large, often unique, items or structures that require a custom design capability (ETO). This type of process is highly flexible and can cope with a broad range of product designs and design changes. This process usually uses a fixed-position type layout.
Work center or job shop
1) An organization in which similar equipment is organized by function. Each job follows a distinct routing through the shop. 2) A type of manufacturing process used to produce items to each customer’s specifications. Production operations are designed to handle a wide range of product designs and are performed at fixed plant locations using general purpose equipment.
Batch manufacturing
A type of manufacturing process in which sets of items are moved through the different manufacturing steps in group or batch.
Line Manufacturing/Repetitive Manufacturing
Performed by specialized equipment in a fixed sequence.
Continuous Manufacturing
A type of manufacturing process that is dedicated to production of a very narrow range of standard products. The rate of product change and new product information is very low. Significant investment in highly specialized equipment allows for a high volume of production at the lowest manufacturing cost. Thus, unit sales volumes are very large, and price is almost always a key order-winning criterion. Examples of items produced by continuous manufacturing include gasoline, steel, fertilizer, glass, and paper.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
The basic concept of cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis is that the selling price of a product or service impacts demand to a lesser or greater degree, depending on the item in question. (This is called price elasticity.) The level of demand then affects volume. If lowering a price increases volume sufficiently, it will make up for the lower profit per unit. Conversely, if raising a price does not decrease volume by too much, the higher profit per unit will cover the lost volume.
Contribution Margin (CM) Analysis
CM Ratio
Sales - Variable Costs
CM/Sales
Break-Even Analysis
a study of the number of units or amount of time required to recoup an investment.
Fixed Costs/Unit CM
Target Income Volume Analysis
(Fixed Costs + Target Income)/Unit CM
Sales-Mix Analysis
the proportion of individual product-type sales volumes that make up the total sales volume.
Factoring according to different proportions (product-based) of total sales of a company
capacity strategy
one of strategic choices a firm must make as part of its manufacturing strategy. There are 3 commonly recognized capacity strategy: lead, lag, tracking
capacity planning
the process of determining the amount of capacity required to produce in the future. This process may be performed at an aggregate product-line level (resource requirement planning), at the master-scheduling level (rough-cut capacity planning), and at the material requirement planning level (capacity requirement planning).
In general, 1-3 years time horizon.
surge capacity
the ability to meet sudden, unexpected increases in demand by expanding production with existing personnel and equipment.
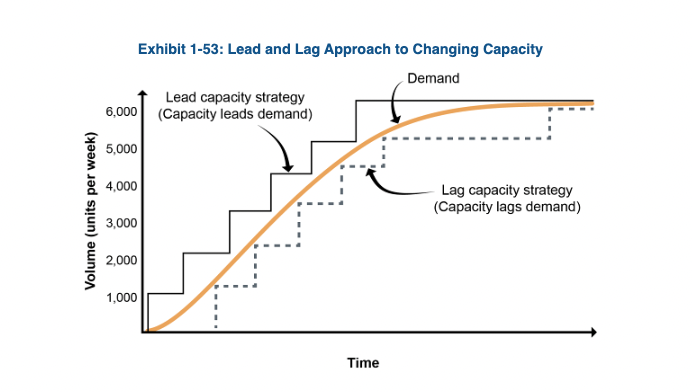
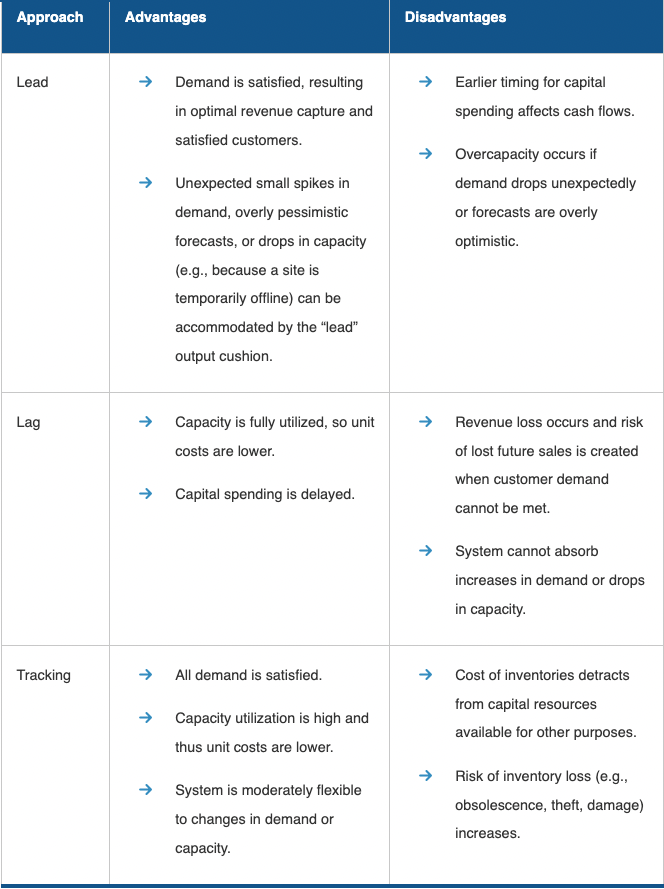
lead capacity strategy
adding capacity to a resource in anticipation of increased future demand. This is done to ensure the ability to satisfy market demand when increase occurs.
lag capacity strategy
not adding capacity until the firm is operating at or beyond full capacity. This keeps unit costs minimized by working at full capacity but does not satisfy total demand.
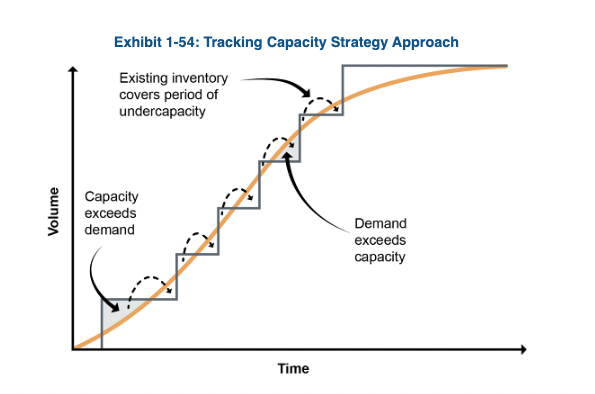
tracking capacity strategy
adding capacity in small amounts to attempt to respond to changing demand in real time in the marketplace. This approach may satisfy total demand and help minimize unit costs, but it can be difficult in some situations to add incremental amounts of capacity, especially if the facility has no more space available.
Lead and Lag Strategy
Tracking Capacity Strategy
Advantages and Disadvantages
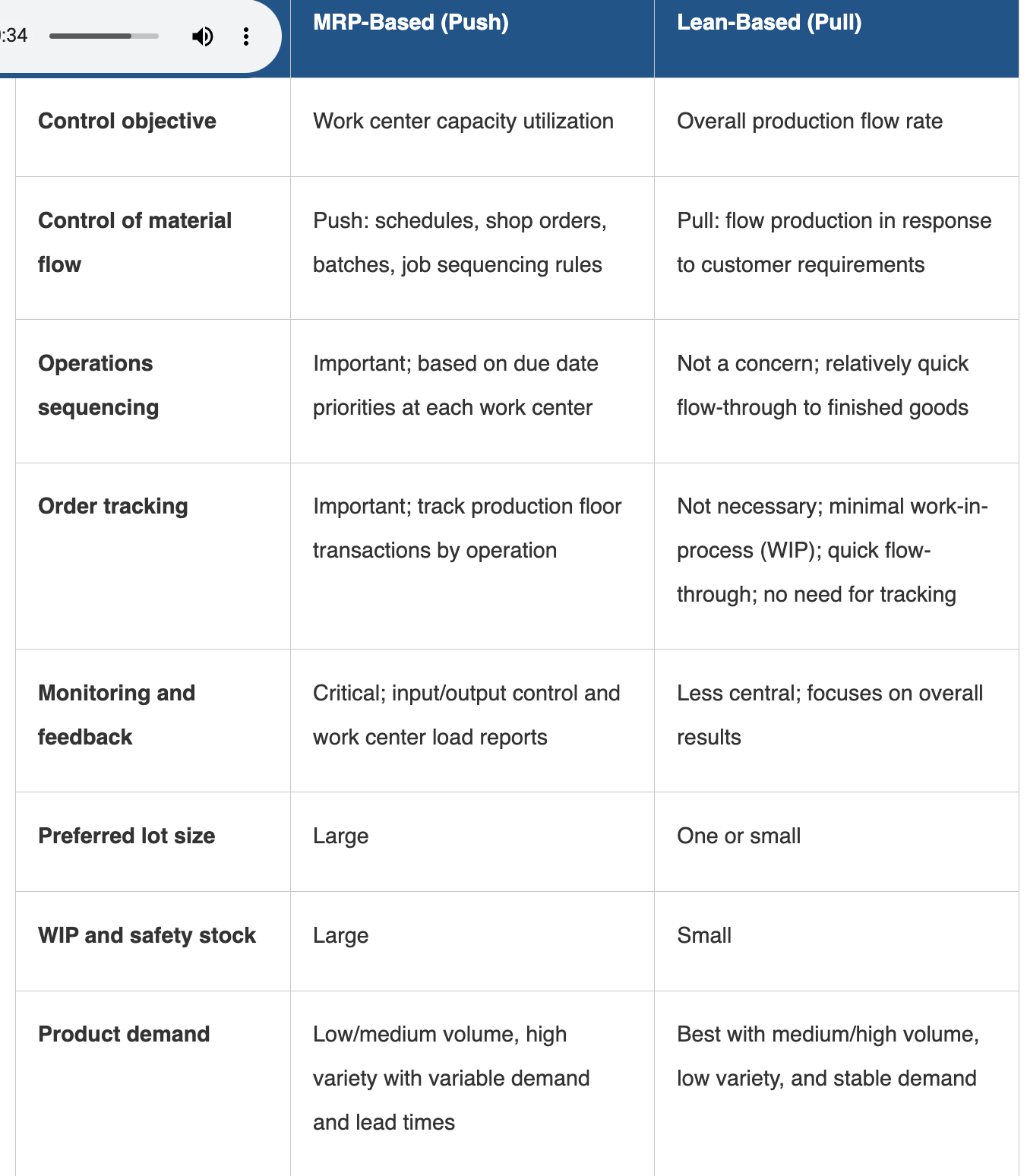
Control System (Push vs Pull)
Insourcing vs Outsouring
you insource activities according to you core competencies
Facility Location Selection Criteria
Market Factors
Operational Factors
Value Chain Activities Locations
Dispersed - advantageous in case of multiple foreign countries
Focused - production advantages, economies of scale, learning curve effects, better coordination with suppliers or customers
Options for entering global markets:
export
licensing
franchising
creation of subsidiaries
creation of local strategic alliances or joint ventures
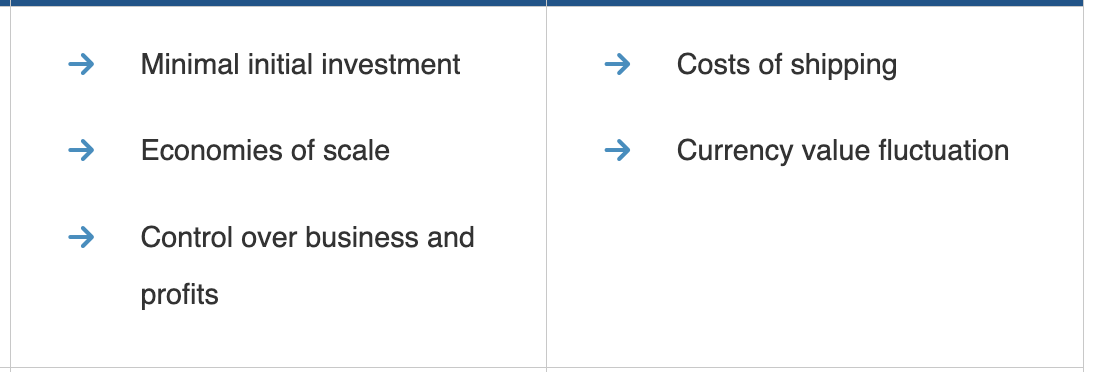
Advantages and Disadvantages of Export
Advantages and Disadvantages of Licensing

Advantages and Disadvantages of Franchising

Advantages and Disadvantages of Subsidiary

Advantages and Disadvantages of Strategic Alliance/Joint Veinture
