T3 PP PMT
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell organelles pre2017[1-6]post2017[7-23] reproductionpost2017[24-49]post2017SC&E[50-
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
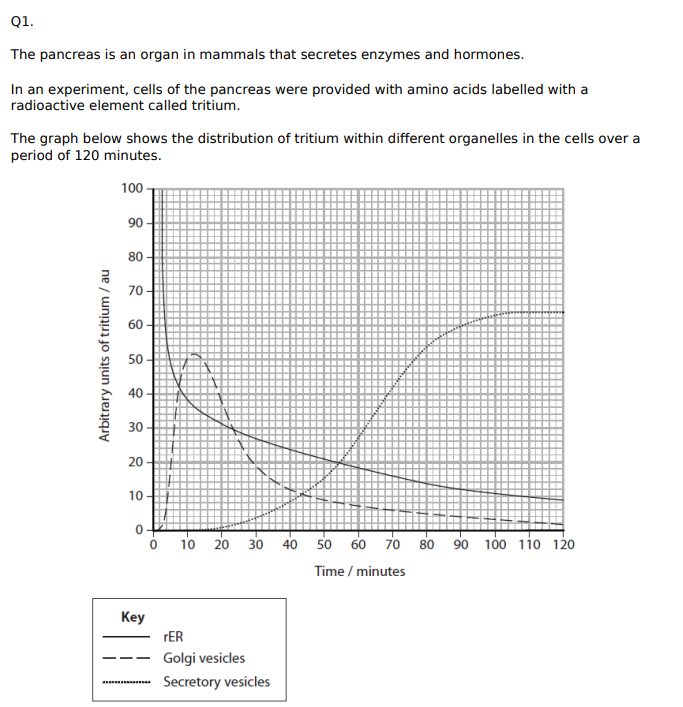
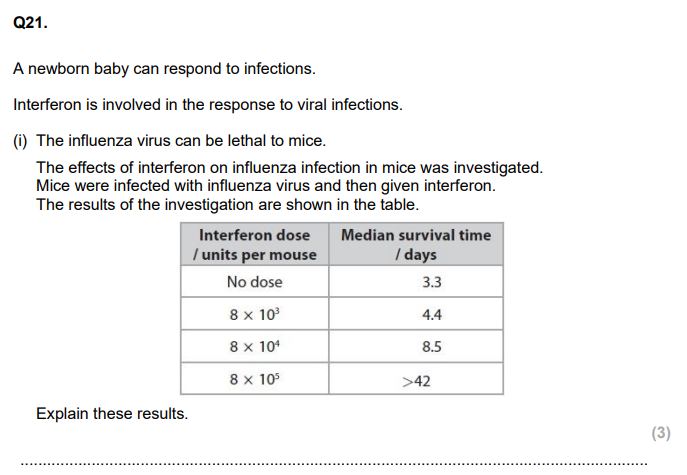
Analyse the graph to explain the route taken by these amino acids within the pancreatic cells. (4)
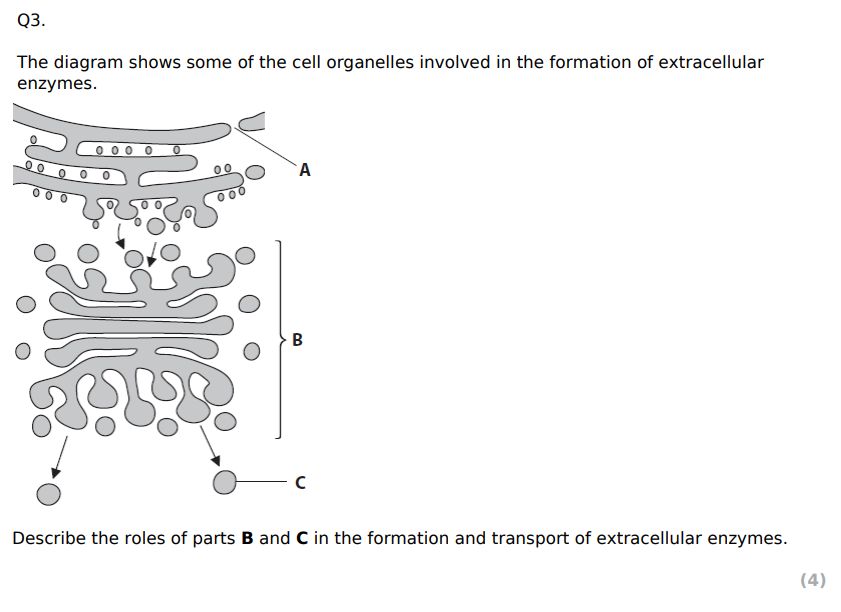

D

A C D

B

Describe what happens to lysosomes once their contents have been digested. (2)
Describe how scientists could have determined that P. falciparum is a eukaryotic organism and not a prokaryotic organism. (4)
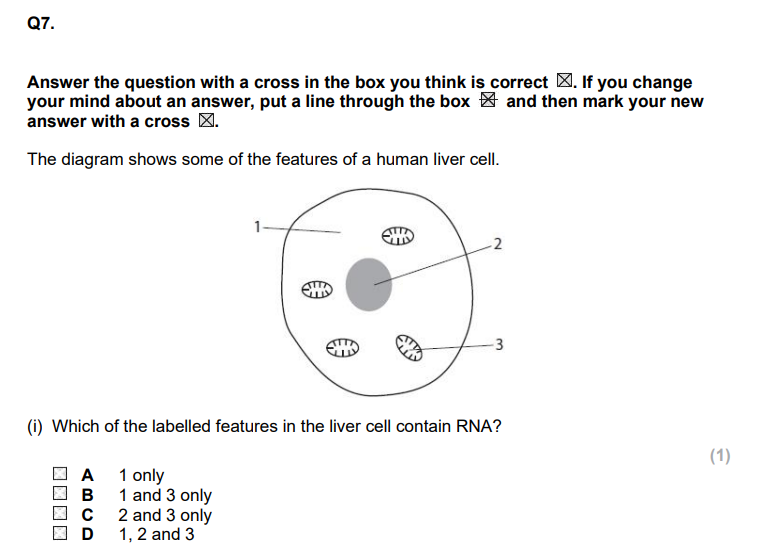
D
Liver cells can absorb lactate from the blood. Deduce what happens to the lactate in these cells. (2)
C - only animal/plant have ER
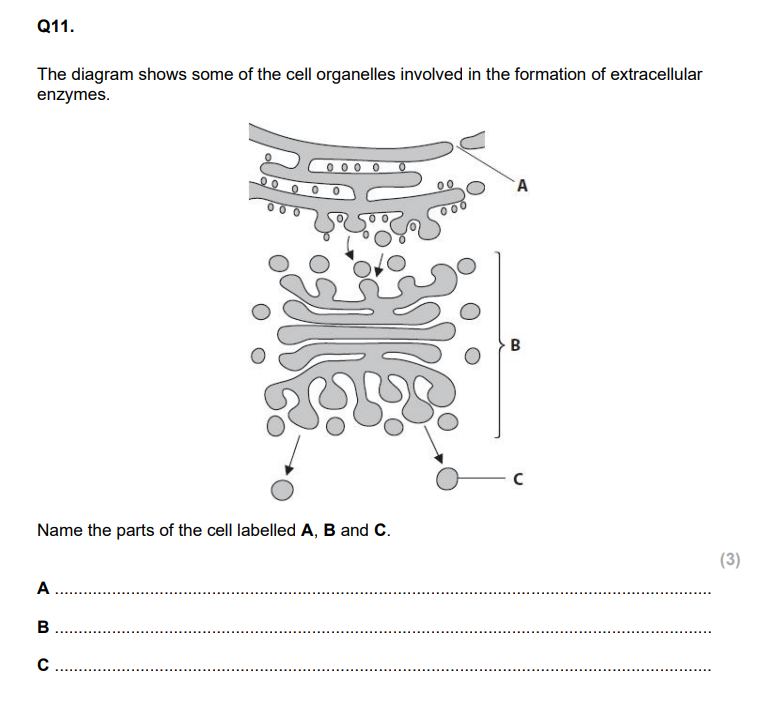
centriole, D
Explain why the nucleus cannot be observed at the end of prophase in a eukaryotic cell. (2)
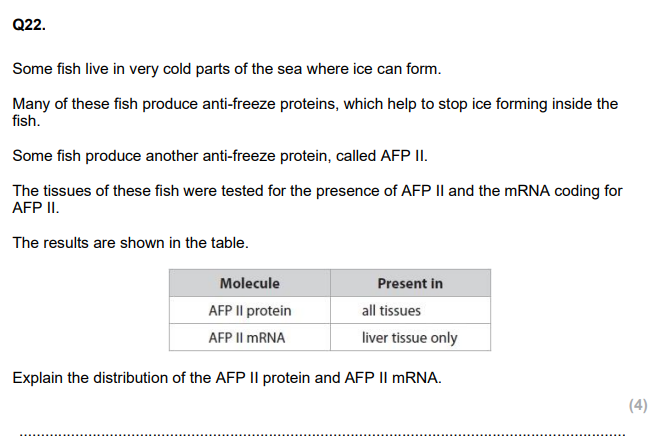
Describe how this polypeptide is then processed to make AFGP. (4)

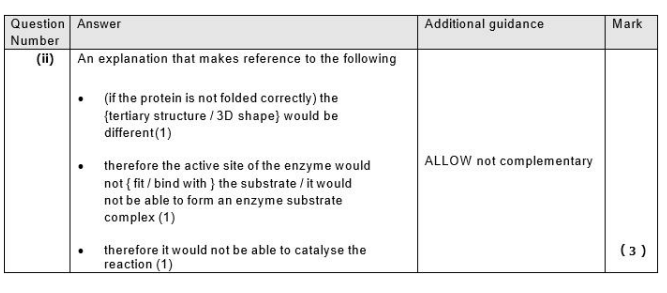
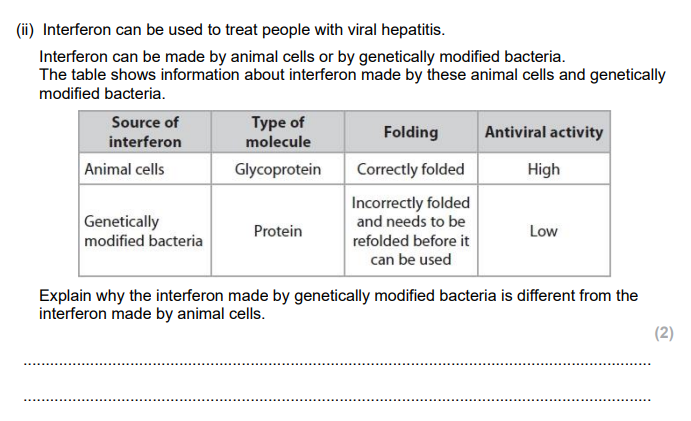
Explain why enzymes that are incorrectly folded cannot carry out their function. (3)
Some bacteria have a capsule that is located (1)
outside the cell wall
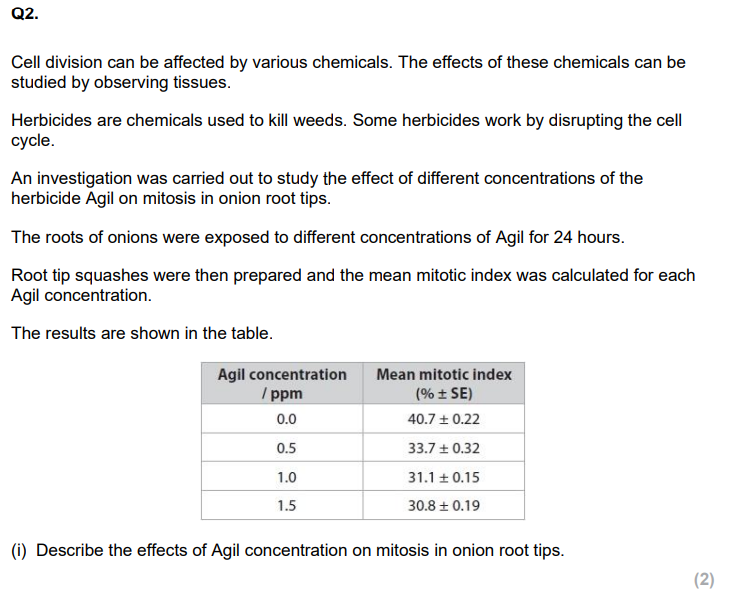

Devise an investigation to determine the effect of exposure time to Agil on the rate of mitosis in onion root tips. (6)
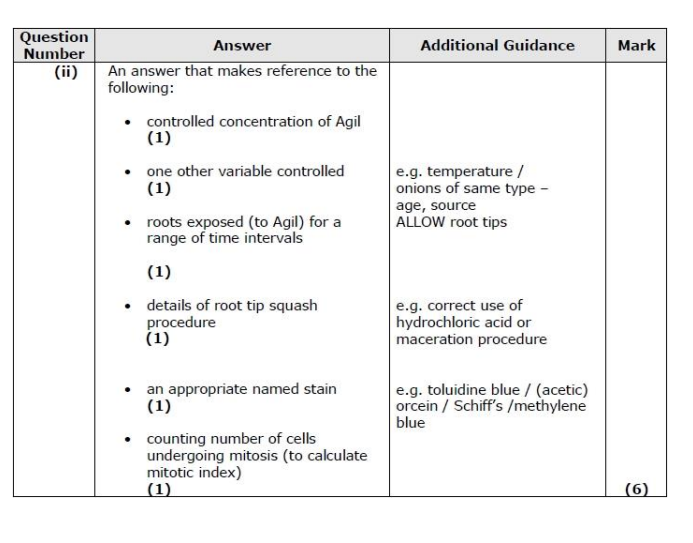
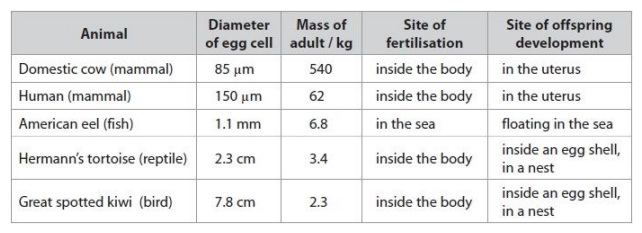
The eel egg cell is larger than the human egg cell, yet an adult eel is smaller than an adult human. Analyse the data in the table to explain why it is advantageous for the eel to have a larger egg cell. (2)
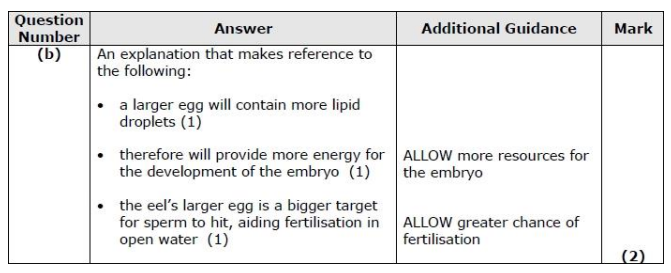
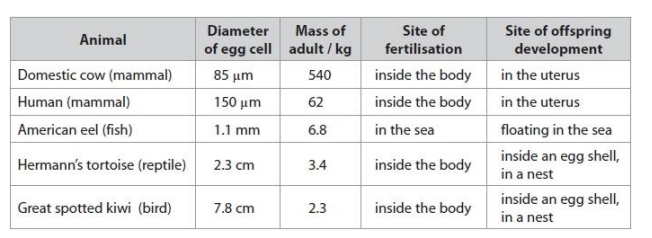
Criticise this data set as evidence for a relationship between egg cell diameter and the mass of the adult. (4)
B



Seed banks store seeds to conserve different varieties of plants. Seeds are stored for long periods of time in conditions that allow them to be germinated when required. It is claimed that the percentage of cells in a root tip undergoing mitosis during the day is different from the percentage during the night. Devise an investigation to test this hypothesis. (5)
Describe the events of fertilisation that occur after the acrosome reaction. (3)
Even though both offspring are from the same father and the same mother, they may be genetically different. Explain why the offspring may be genetically different. (2)
Explain why a second sperm cell cannot fertilise the egg cell. (3)
Explain what is meant by the term sex-linked disorder. (2)
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a sex-linked disorder.
Explain why the genotype frequency for males with DMD cannot be calculated using this Hardy-Weinberg equation. (2)


Devise an investigation to test this hypothesis. (5)
Explain how vesicles are involved in the successful fertilisation of an egg cell by only one sperm. (2)
Describe how meiosis leads to genetic variation in the gametes produced. (2)
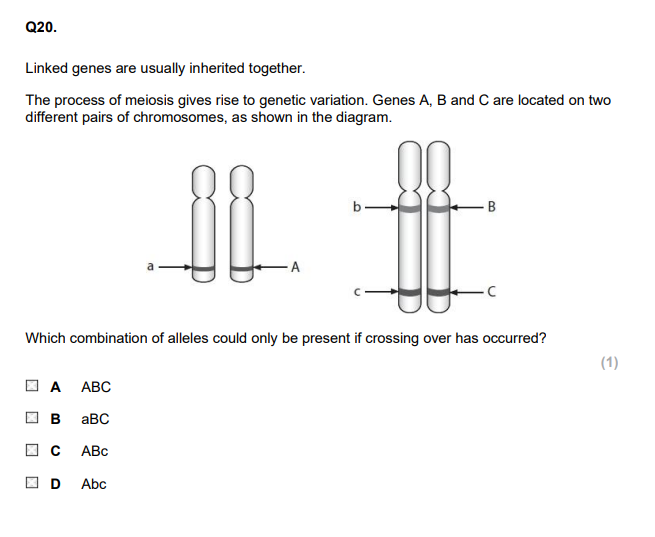


D
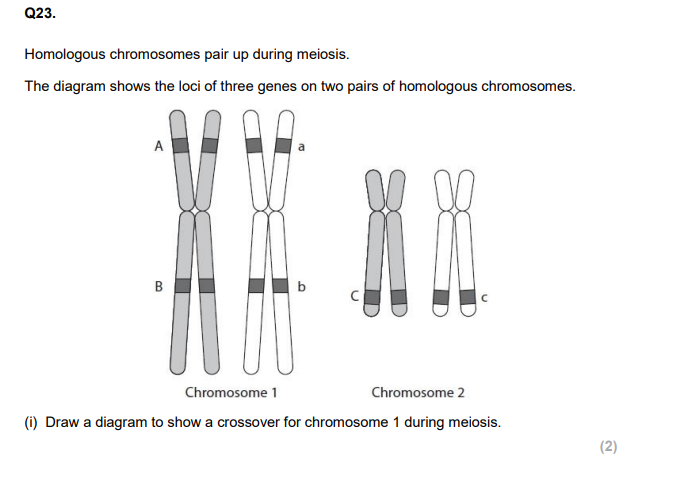

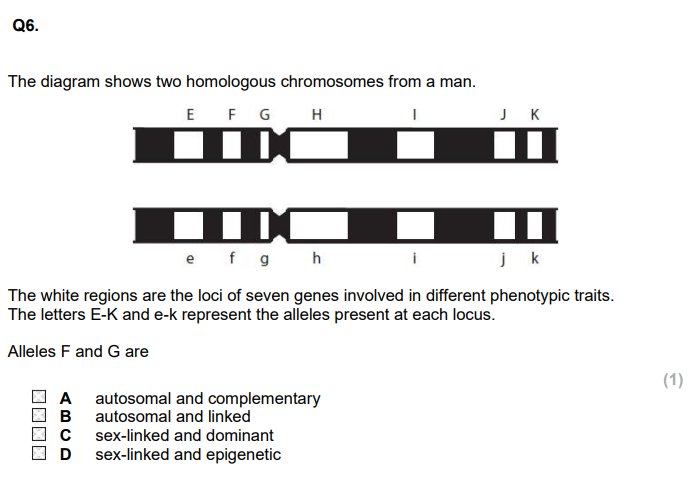
Explain how crossing over may differ in sex chromosomes. (2)
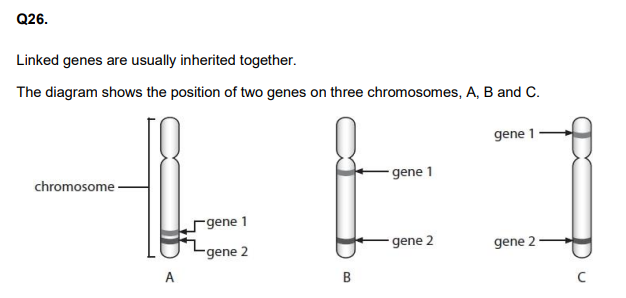
Explain which chromosome shows the weakest linkage between genes 1 and 2. (3)


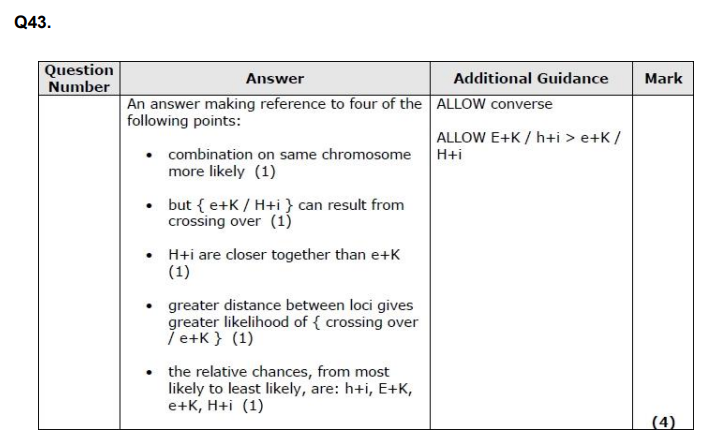
Give the meaning of the term polygenic. (2)



Describe the decisions that society has to make about the use of these embryonic stem cells. (3)
This ball of cells continues to divide to form the embryo. The cells of the embryo become specialised to form tissues and organs. Describe how cells become specialised. (3)
Explain why stem cells from the heart cannot be used to grow cells to repair the cornea. (3)
State what is meant by the term stem cell. (2)

Epigenetic changes can cause monozygotic twins to have different body masses. Explain how epigenetic changes can cause differences in a characteristic. (3)

Explain why an individual may have a greater adult height than their biological parents. (4)
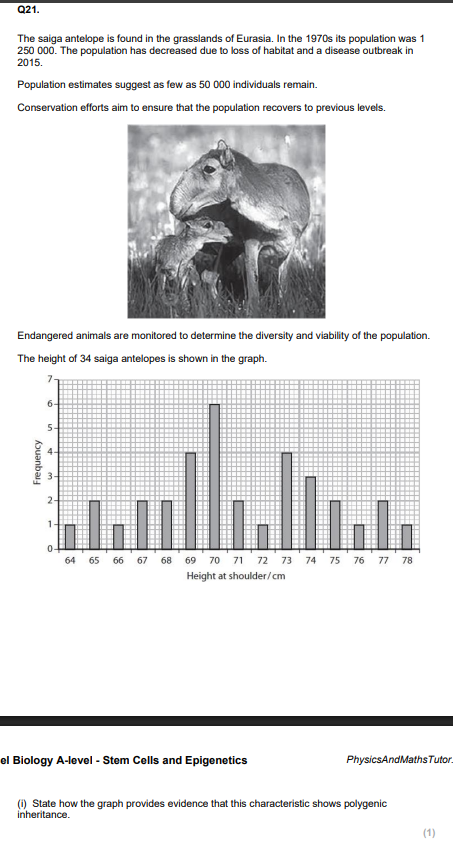
State and justify the mode for height of the saiga antelope. (2)
shows continuous variation
70cm - highest frequency of antelopes w this height
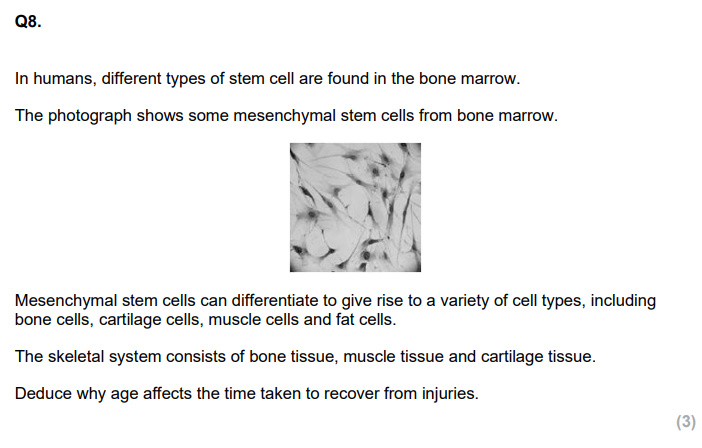
Mesenchymal stem cells are found in the bone marrow.
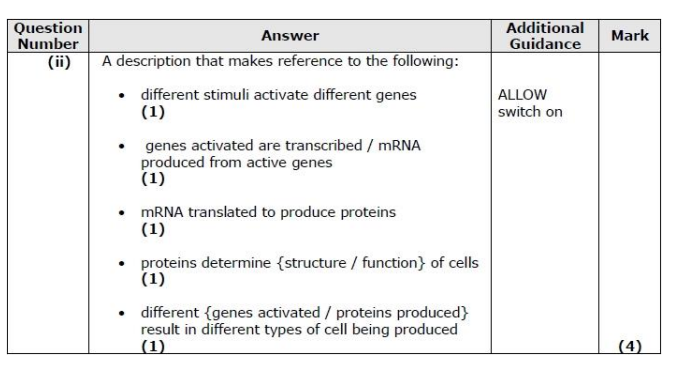
Describe how mesenchymal stem cells can give rise to different types of cell. (4)


how does change in base sequence affect tertiary structure?
How a Base Sequence Change Affects Folding:
DNA Mutation → Different Amino Acid
A change in the base sequence can alter the codon on mRNA, which may result in a different amino acid during translation.Different Amino Acid = Different R Group
Each amino acid has a specific R group (side chain). The properties of this R group — whether it's polar, non-polar, acidic, basic, or sulfur-containing — affect how it interacts with other R groups.R Group Interactions = Folding
The tertiary structure forms as the protein folds into its 3D shape. This folding depends on:Hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds
Disulfide bridges (between cysteine residues)
Hydrophobic interactions
Wrong Amino Acid = Misfolding
If the new amino acid has different chemical properties (e.g., polar instead of non-polar), it can:Disrupt existing interactions
Form new, incorrect interactions
Prevent proper folding of the protein
Why Folding Matters:
Correct folding = correct shape = correct function.
Incorrect folding = loss of function or a non-functional protein.