M3 | Scrum and Prototyping
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
A family of software development methodologies that produce software in short iterations and allow for greater changes in design
Agile Model
In software engineering, not all characteristics of this process are new and revolutionary; many come from years of experience
Agile Model
This process shares similarities with the iterative and incremental process model
Agile Model
The Agile Manifesto:
Individuals and interactions over processes and tools, Working software over comprehensive documentation, Customer collaboration over contract negotiation, Responding to change over following a plan
This development methods help guarantee that there is a finished product at all times, demanding only normal effort from developers
Agile Development
Using this approach, requirements do not need to be completely specified from the beginning
Agile Development
Many parts of these methodologies and processes hold high potential for both large and small projects
Agile Development
True or False:
Defined process are:
inspect and adapt
Not entirely planned
False
True or False:
Empirical process are:
Planned
Follow strict rules
Avoids deviations
False
A lightweight framework that helps people, teams, and organizations generate value through adaptive solutions for complex problems
Scrum
An Agile development methodology that employs an iterative, incremental approach to optimize predictability and control risk
Scrum
This methodology engages groups of people who collectively have all the skills and expertise to do the work and share as needed
Scrum
This Agile methodology is actually inspired by a rugby formation, where a team comes together to move the ball forward
Scrum
People often ask if this Agile framework is an acronym, but the answer is no
Scrum
In this Agile framework, the name represents the team coming together to move the product forward, similar to a rugby team moving the ball forward
Scrum
In Scrum, this role fosters an environment where work is organized, progress is tracked, and the team can perform effectively
Scrum Master
In Scrum, this role orders the work for a complex problem into a product backlog
Product Owner
In Scrum, this group turns a selection of the work into an increment of value during a Sprint
Scrum Team
In Scrum, this process involves the team and stakeholders inspecting the results, adjusting for the next Sprint, and repeating
Sprint Review / Iteration
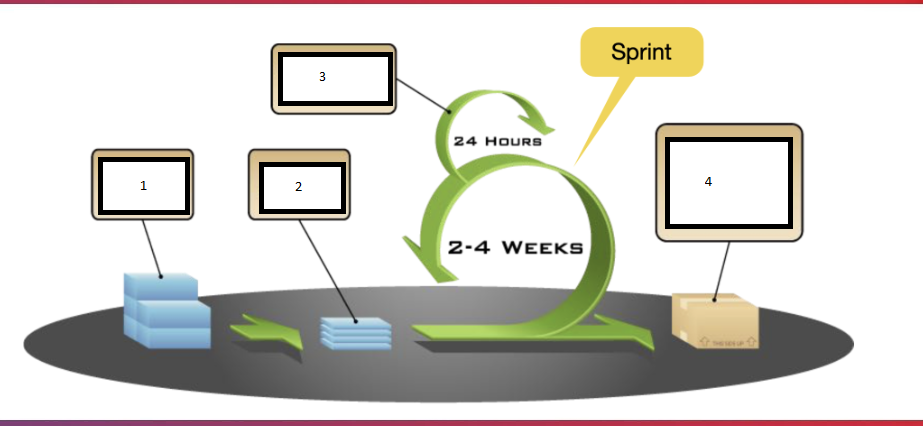
Fill in the blanks:
Product Backlog
Sprint Backlog
Daily Scrum Meeting
Potentially Shippable Product Increment
Scrum combines four formal events for inspection and adaptation within a containing event called the Sprint
Sprint
These events work because they implement the empirical Scrum pillars of transparency, inspection, and adaptation
Scrum Events
One critical Scrum Team characteristic that binds all elements together is trust
Trust
In Scrum, this pillar ensures that process and work are visible to both those performing the work and those receiving it
Transparency
In Scrum, this pillar ensures that progress is inspected frequently and diligently to detect undesirable variances or problems
Inspection
In Scrum, this pillar ensures that if any aspects of a process deviate outside acceptable limits or the product is unacceptable, the process or materials are adjusted, and the team adapts immediately upon learning new information through inspection
Adaptation
A Scrum Value where team members have the courage to do the right thing and work on tough problems, guiding how the team works and driving trust
Courage
A Scrum Value where everyone focuses on the work of the Sprint and the goals of the Scrum team
Focus
A Scrum Value where people personally commit to achieving the goals of the Scrum team
Commitment
A Scrum Value where team members respect each other as capable and independent
Respect
A Scrum Value where team members agree to be open about the work and all issues
Openness
In Scrum, this group is accountable for creating a plan for the Sprint, called the Sprint backlog
Development Team
In Scrum, this group is responsible for instilling quality by adhering to a definition of done
Development Team
In Scrum, this group adapts their plan each day toward the Sprint goal
Development Team
In Scrum, this group holds each other accountable for completing work and achieving the Sprint goal
Development Team
In Scrum, this role is responsible for developing and explicitly communicating product goals with the Scrum Team
Product Owner
In Scrum, this role is responsible for creating and clearly communicating the product backlog to the team
Product Owner
In Scrum, this role is responsible for ordering product backlog items
Product Owner
In Scrum, this role ensures that the product backlog is transparent, visible, and understood by the team
Product Owner
In Scrum, this role coaches the team in self-management
Scrum Master
In Scrum, this role helps the team focus on creating high-value increments that meet the definition of done
Scrum Master
In Scrum, this role causes the removal of impediments to progress
Scrum Master
In Scrum, this role ensures that all Scrum events take place, are positive, productive, and kept within the time box
Scrum Master
In Scrum, these are considered the heartbeat of the framework, where ideas are turned into value
Sprints
In Scrum, these are fixed-length events of one month or less to create consistency
Sprint
In Scrum, a new one starts immediately after the conclusion of the previous, and all necessary work happens within it
Sprint
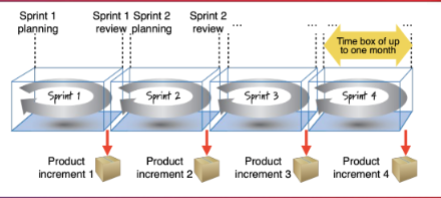
What Diagram is this?
Scrum Sprint
True or False:
During the sprint, no changes are made that would endanger the Sprint goal
True
True or False:
During the sprint, quality may increase
False
True or False:
During the sprint, the product backlog should stay the same and not be refined.
False
True or False:
During the sprint, the scope may be clarified and renegotiated with the Product Owner as more is learned
True
A meeting held at the start of the project to create and prioritize the product backlog
Project Kickoff Meeting
A meeting held at the start of each Sprint to create the Sprint backlog
Sprint Planning Meeting
A 15-minute stand-up meeting held daily to share status, impediments, and promises
Daily Scrum
A meeting to demonstrate realized backlog items to the Product Owner
Sprint Review
A meeting to inspect the last Sprint and find improvements for the next Sprint
Sprint Retrospective
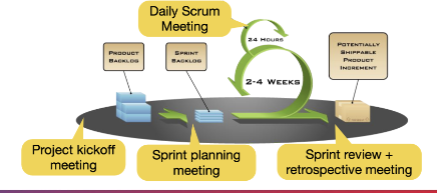
What Diagram is this?
Scrum Meetings
In Scrum, these represent work or value, and each contains a commitment that enhances transparency and focus against which progress can be measured
Scrum Artifacts
The Scrum artifact where the commitment is the Product Goal
Product Backlog
The Scrum artifact where the commitment is the Sprint Goal
Sprint Backlog
The Scrum artifact where the commitment is the Definition of Done
Increment
An activity in software development where incomplete versions of the product or program are created, not expected to be shipped as the final output
Prototyping
In software engineering, this typically simulates only a few aspects of the final product and may be completely different from it
Prototyping
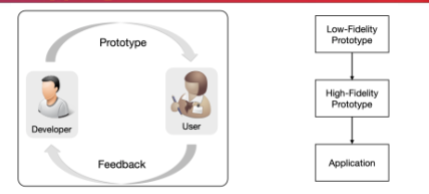
What model is this?
Prototyping
Advantages of Low Fidelity:
Easy to produce
More feedback
No design decisions
DIsadvantages of Low Fidelity:
Mostly not reused
Important details are ignored
Advantages of High Fidelity:
More realistic
More detailed problems can be identified
More impressive
Disadvantages of High Fidelity:
May cause much effort
Less feedback
High expectations (especially with interactive prototypes)
One reason for using this software development approach is that complex systems and user interfaces are hard to design and develop
Prototyping
This software development approach is valuable because communication between developers and users is necessary
Prototyping
This approach allows several iterations so the software can better meet user expectations
Prototyping
This approach provides value because the development team can get feedback from users early in the project
Prototyping
A type of prototype that models many features but with little detail, showing a wide but shallow range of requirements
Horizontal Prototyping
A type of prototyping often used in traditional, linear processes, with no full implementation of requirements until the end
Horizontal Prototyping
A prototype that models few features but with much detail, showing only a small range of requirements
Vertical Prototyping
A type of prototyping where there is full implementation of the requirements, commonly used in Agile processes
Vertical Prototyping
Prototyping that involves building initial ideas for interfaces, but the creation is eventually discarded and does not become part of the final software
Throwaway / Rapid Prototyping
A fast prototyping method that can include storyboards, drawings, or mockups, usually created quickly to test concepts
Throwaway / Rapid Prototyping
A prototyping method also known as breadboard prototyping, where a robust prototype is built and incrementally refined based on customer feedback until accepted
Evolutionary Prototyping
In this prototyping type, the initial prototype evolves into the final system through constant refinement, unlike rapid prototypes that are discarded
Evolutionary Prototyping
A prototyping method where the final product is built as separate prototypes, developed individually, and then merged into the overall design
Incremental Prototyping
In this prototyping type, functional small prototypes are created to reduce the time gap between user and software, then combined into the full product
Incremental Prototyping
A prototyping type used especially for developing web apps, where the first phase is a static prototype of HTML pages
Extreme Prototyping
In this type of prototyping, development goes through three phases: static HTML pages, functional screens with simulated back-end, and final implementation of services
Extreme Prototyping
Is an example of scrum tool
Figma
Is an example of prototyping tool
Miro
In this methodology, design is informal and iterative.
Agile
In this methodology, design is formal and done up front, after all requirements are known.
Traditional/Heavy
In this methodology, user involvement is crucial, frequent, and continues throughout the whole process.
Agile
In this methodology, user involvement happens only at the beginning and at the end.
Traditional/Heavy
In this methodology, documentation is minimal, only what is necessary, with source code serving as the ultimate documentation.
Agile
In this methodology, heavy, formal documentation is required for every phase of the project.
Traditional/Heavy
In this methodology, requirements are assumed to change, collected informally, and refined at each iteration through constant user interaction.
Agile
In this methodology, requirements are assumed to remain fixed, fully documented in detail, and costly to change once design or implementation has begun.
Traditional/Heavy
In this methodology, planning is minimal up front and done in small increments throughout development.
Agile
In this methodology, most activities are planned up front.
Traditional/Heavy
In this methodology, only the next few activities are scheduled, and schedules may change if scope is adjusted.
Agile
In this methodology, schedules are relatively inflexible and must be adhered to.
Traditional/Heavy
In this methodology, communication is informal and continuous throughout the project.
Agile
In this methodology, communication relies mainly on documents, memos, and formal meetings.
Traditional/Heavy