Fish biology and fieldwork
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
sagittal line
top line of fish
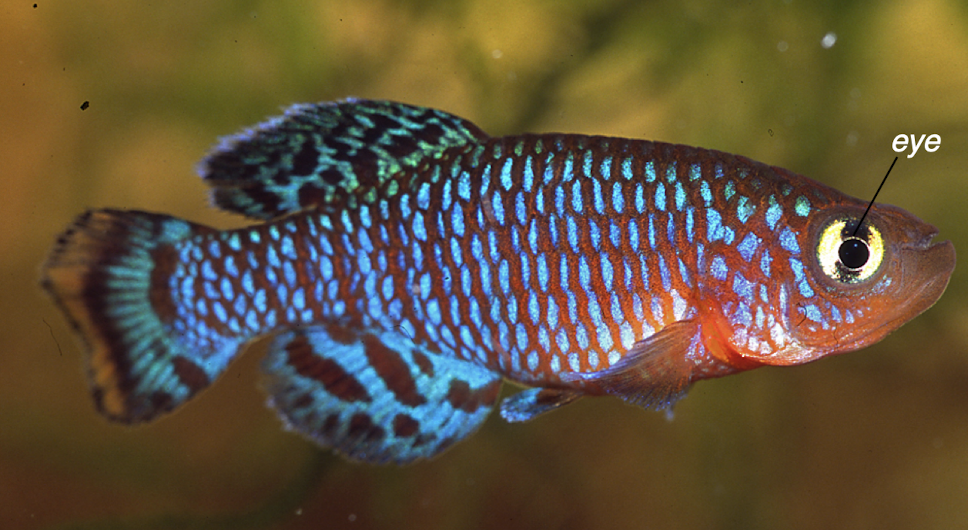

dorsal fin
fin/s along the sagittal plane
can be more than one, can be spiny or soft (rays)

anal fin
located on the ventral side of the fish along the medial plane
caudal fin
tail, single fin
pelvic fins
bilaterally paired fins located anterior to the anal fin
pectoral fins
paired fins located posterior to the head
tread water
adipose fin
featureless bump, important for ID
located posterior to the dorsal fin
operculum
forms the gill cover
shape can be important for ID
lateral line
along side of fish, ID for shape
generally has dashes or dots
organ of sense, can note changes in pressure, or electrical potential
caudal peduncle
base of caudal fin, shape can be ID
types of mouth shapes
terminal - at end of fish
upturned, downturned/subterminal, ventral
upturned fish
ideal for grabbing food from surface of water when swimming below surface
subterminal mouth
slightly downturned
ideal for feeding below the eye
barbel
organ for taste? or touch - feeling in turbid water or for organisms which live along the bottom of rivers
size, shape, presence imp for ID
ventral mouth
underslung or inferior for feeding on the bottom surface
fin spines
defensive
can accompany softer fins or no
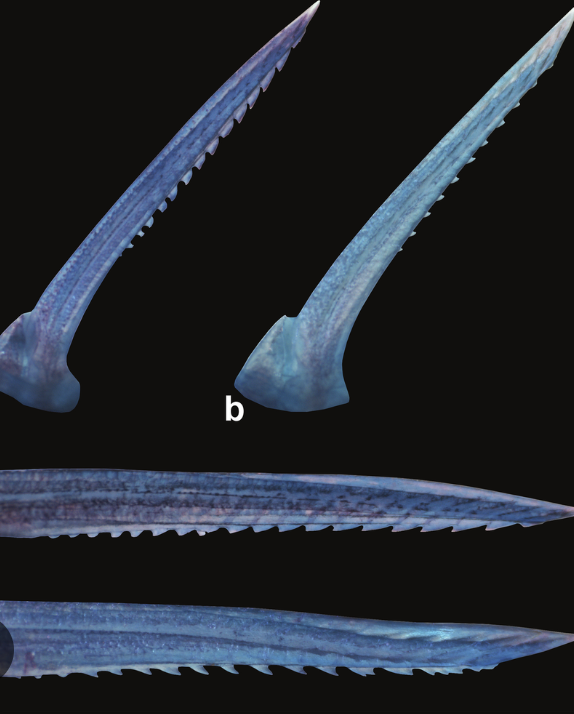

fin rays
support fins, slightly softer but still bone

bony armour
like scales but larger plates
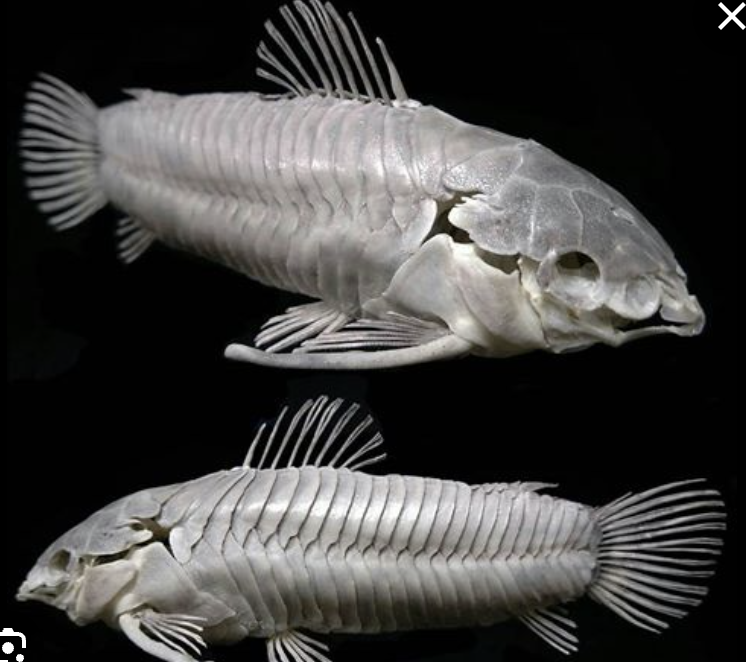

homocercal tail
caudal peduncle is symmetrical and therefore usually so is the caudal tail
heterocercal tail
the caudal peduncle is not symmetrical and therefore neither is the caudal fin
dorsal spines
anti predator structures located along the dorsal sagittal plane

maxilla
prominent bone which bears upper teeth, used for ID
same as mammals

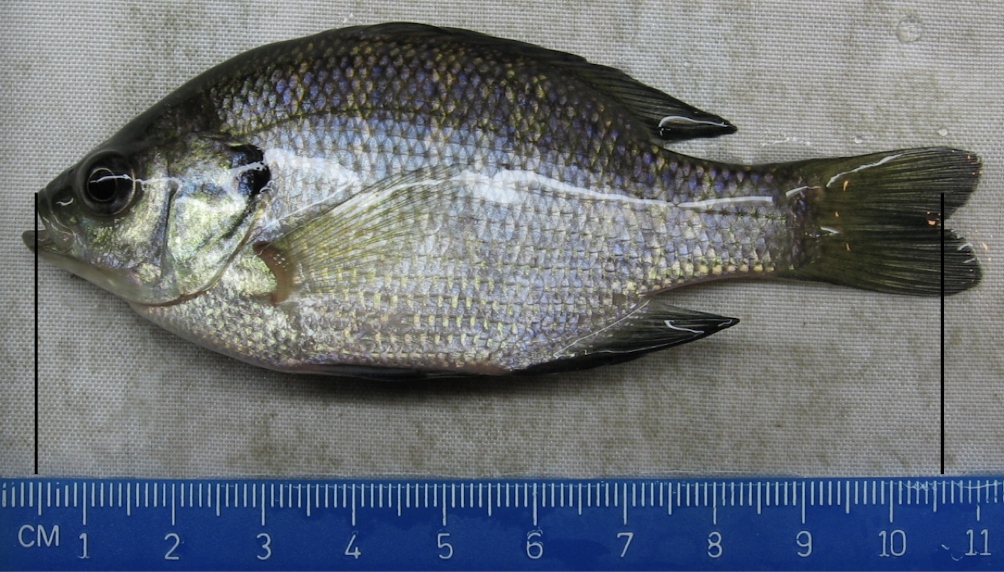
how to measure length of fish
start at tip of upper jaw/maxilla and to the fork of the caudal fin
fork length

aquatic fieldwork
to better understand limnology, food for different species, ecology, connectivity between other species, etc.
triangular net
can scrape along the bottom of a water body and pick up bottom dwellers better than other nets
heavy duty dip to keep small organisms from passing through
field supplies
triangular net, white pan for identification of bugs against a clean background
waterproof gear and bag, waders
aquatic habitats
can be streams or lakes
or can be small and short in duration such as plant pots left outside, tracks from cars,
water quality factors
temperature, dissolved oxygen (cold water increases), flow rate, clarity, TSS - hardness, conductivity/salinity, pH (diversity)
concentrations of toxins, nutrients, etc
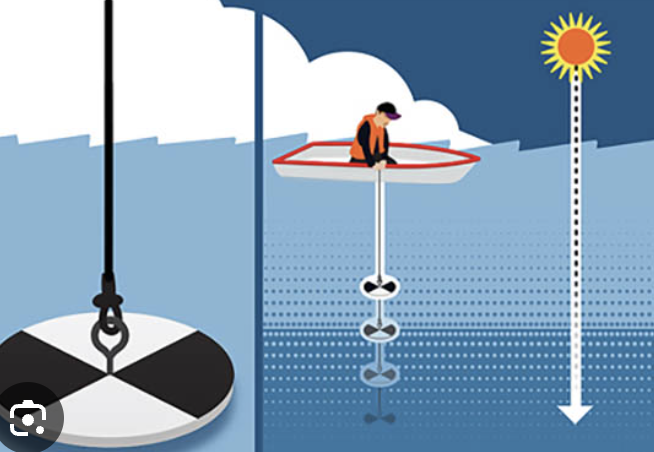
secchi disk/depth
black and white disk attached to a marked cord (in length)
you drop the disk slowly unless it disappears from view (algae, sediments, tannins, etc)
next raise it to the point it reappears
the depth is midway between the bottom and where it reappears
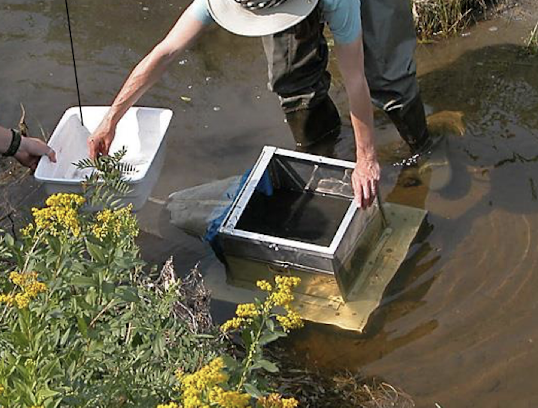
surber sampling
a standard sized box is place in a flowing river anchored in the mud
stir up the mud to pick up things to catch within the net behind the contraption
often white pan for ID

funnel traps/gee traps
rigged set up with rocks to hold down into the current
based on principle that animals which get in cannot understand how to get out

how did crayfish get across rivers in AB
either they swam up stream to all rivers
or people brought them
unconclusive evidence