Biochemistry - Lipid Structure and Function
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Lipids class characterized by
- insolubility in water
- solubility in nonpolar organic solvents
lipids
major component of phospholipid bilayer (one of the most important structural parts of cell)
phospholipid bilayer
allows cells to function as they do; separate cell interior from surrounding environment
amphipathic molecule
- each of membrane components have hydrophobic (fatty acid tails) and hydrophilic (polar head) regions
formation of liposomes, micelles, & phospholipid bilayer
in aqueous solution, molecules spontaneously form structures (hydrophobic regions group internally & hydrophilic regions interact with water)
phospholipid
contains phosphate & alcohol (polar head group), hydrophobic fatty acid tail [connected via phosphodiester linkages]
- further classified according to backbone on which molecule is built (example: glycerol)
glycerol
3-carbon alcohol that forms phosphoglycerides & glycerophospholipids
Properties that determine molecule behavior
- length of hydrocarbon chain
- degree of saturation
saturated fatty acids
- only single bonds
- carbon atom is saturated when bonded to 4 other atoms (w/o pi bonds)
- have greater var der Waals forces
- more stable overall structure
- form solids at room temp
unsaturated fatty acids
- includes 1 or more double bonds
= kinks in fatty acid chain
= difficult to stack and solidify
- liquids at room temp
Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides)
- type of phospholipid
- glycerol backbone bonded by ester linkage to two fatty acids & phosphodiester linkage to highly polar head group
[head group: determines membrane surface properties, can be neg/pos/neutral charge]
[membrane surface properties = imporant to cell recognition, signaling, binding]
[w/in each subtype: fatty acid chains vary in length/saturation = variety of functions]
phosphatidylcholine
glycerophospholipid with choline head group
phosphatidylethanolamine
glycerophospholipid with ethanol-amine head group
Sphingolipids
- sphingosine/sphingoid backbone
- long chain, nonpolar fatty acids tails, polar head group
- many sphingolipids are phospholipids (contain phosphodiester linkage); others contain glycosidic linkages to sugars (glycolipid)
sphingolipid subclasses (based on head group)
ceramide
sphingomyelins
glycosphingolipids (glycolipids)
gangliosides
ceramide
- simplest sphingolipid
- single hydrogen head group
sphingomyelin
- major class of sphingolipids that are also sphingophospholipids
- either phosphocholine/phosphoethanolamine head group (no net charge) = phosphodiester bond
- major components in plasma membranes of cells (oligodendrocytes & schwann) producing myelin (insulating sheath for axons)
glycosphingolipids (glycolipids)
- sphingolipids with sugars bonded by glycosidic linkages head group
- not phospholipids; don’t contain phosphodiester linkage
- found on outer surface of plasma membrane; further classify into cerebrosides & globosides
- cerebrosides & globosides (neutral glycolipids ~no net charge at physiological pH)
cerebrosides
have single sugar
globosides
have two or more sugars
gangliosides
- composed of most complex sphingolipids
- glycolipids with polar head groups of oligosaccharide with 1 or more N-acetylneuraminic acid (NANA; sialic acid) molecules at terminus & negative charge
- glycolipid; glycosidic linkage, no phosphate group
- major role in cell interaction, recognition, signal transduction
Waxes
- esters of long-chain fatty acids with long-chain alcohols
- form pliable solids at room temp
- function as protection for plants (secreted as surface coating = prevents evaporation & protects against parasites) & animals (secreted to prevent dehydration, water-repellant to keep skin/feathers dry, lubricant)
wax examples
- carnauba wax: made from leaves of Copernica prunifera palm, used to coat candles and wax cars
- beeswax: secreted by bees to construct shelter
3 categories of signaling lipids
steroids
protaglandins
fat-soluble vitamins
(+ terpene precursors)
Terpenes & Terpenoids
- odiferous chemicals that have varied independent functions
- metabolic precursors to steroids & other lipid signaling molecules
Terpenes
- class of lipids built from isoprene (C5H8) moieties
- share common structural pattern with carbons grouped in multiples of 5
- produced by plants & insects (part of their protective mechanism)
- strong scent (primary component of pleasant smells)
- grouped based on number of isoprene units present
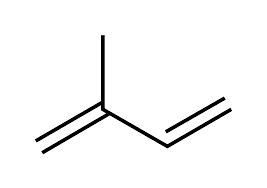
Monoterpene (single terpene unit)
2 isoprene units; abundant in both essential oils and turpentine
Sesquiterpene
3 isoprene units; sesqui = one-and-a-half
Diterpene
4 isoprene units; Vitamin A = retinal (visual pigment for sight) is derived
Triterpene
6 isoprene units; can convert to cholesterol & various steroids
Tetraterpenes (carotenoids)
(B-carotene & lutein)
8 isoprene units
Polyterpene
between 1000 and 5000 isoprene unit chain
Terpenoids (isoprenoids)
- derivatives of terpenes that have undergone oxygenation/rearrangement of carbon skeleton
> further modified by addition of extensive variety of functional groups
- share similar characteristics with terpenes (biological precursor function & aromatic properties = contribute to steroid biosynthesis & scents of cinnamon/eucalyptus/camphor/turmeric/etc)
- named in analogous fashion (example: diterpenoids = 4 units)
Steroids
- metabolic derivatives of terpenes
- 4 cycloalkane rings fused: 3 cyclohexane + 1 cyclopentane
- functionality determined by oxidation status of rings & functional groups carried
- large number of carbons & hydrogens = nonpolar steroids
Steroid hormones
steroids that act as hormones:
- secreted by endocrine glands into bloodstream
- travel on protein carriers to distant sites
- bind to specific high-affinity receptors
- alter gene expression levelspotent biological signals that regulate gene expression and metabolism = affect biological systems even at low concentrations
Cholesterol
- steroid of primary importance; major component of phospholipid bilayer & responsible for mediating membrane fluidity
- amphipathic molecule containing hydrophilic & hydrophobic components
- hydrophobic tails & hydrophilic tails allow cholesterol to maintain constant fluidity in cell membranes (low temp: prevents membrane solidifying) (high temp: prevents increased permeability)
- precursor to many molecules (steroid hormones, bile acids, Vit D)
Prostaglandins
- produced by almost all cells in body, act as paracrine/autocrine signaling molecules
- 20-carbon molecules; unsaturated carboxylic acids derived from arachidonic acid, contain one 5-carbon ring
- regulate synthesis of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)
= cAMP mediates actions of other hormones
- affects smooth muscle function, influence over sleep-wake cycle, elevation of body temp (fever/pain)
cyclooxygenase (COX)
- aids in production of prostaglandins
- inhibited by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin
Fat-soluble Vitamins
- essential nutrient that can’t be adequately synthesized by body
= consumed in diet
- divided into water-soluble and lipid-soluble
- include vitamins A, D, E, K (important/varied functions)
water-soluble vitamins
excreted through urine
lipid-soluble vitamins
accumulate in stored fat
Vitamin A (carotene)
- unsaturated hydrocarbon
- important in vision, growth/development, immune function
- retinal (aldehyde form): most significant metabolite of vit A & component of light-sensing molecular system in human eye
- retinol: storage form of vit A, oxidized to retinoic acid, hormone regulating gene expression during epithelial development
Vitamin D (cholecalciferol)
- consumed/formed in UV light-driven reaction in skin
- converted to calcitrol (active form) in kidneys & liver
= increased calcium & phosphate uptake in intestines
= promotes bone production
Vitamin E
- group of closely related lipids (tocopherols & tocotrienols)
- t & t: hydrophobic substituted aromatic ring with long isoprenoid side chain
- tocopherols: biological antioxidants
- aromatic rings react with and destroys free radicals
= prevents oxidative damage (important contributor to cancer/aging development)
Vitamin K
- group of compounds: phylloquinone (K1) & menaquinones (K2)
- vital to posttranslational modifications to form prothrombin (important clotting factor in blood)
- aromatic ring undergoes oxidation & reduction cycle during prothrombin formation
- introduces calcium-binding sites on several calcium-dependent proteins
lack of Vit D
results in rickets; (condition in children) underdeveloped, curved long bones & impeded growth
Triaglycerols
- class of lipids for energy storage & insulation (retains body heat to reduce energy needed for maintaining constant internal temp)
Why lipids are good for storing energy
1- carbon atoms of fatty acids are more reduced (than those of sugars)
= oxidation of triacylglycerols yields x2 amount of energy per gram as carbs
2- triacylglycerols are hydrophobic (don’t draw in water nor require hydration for stability)
= helps decrease weight
Triaglycerol (triglyceride) compound
- 3 fatty acids bonded by ester linkages to glycerol
- physical characteristics determined by saturation/unsaturation of fatty acid chains
- nonpolar & hydrophobic
> contribute to insolubility in water: polar hydroxyl group of glycerol bond to polar carboxylate of fatty acid
= decreased polarity
Triaglycerol deposits
- observed in cells as oily droplets in cytosol
= depots of metabolic feul (recruited when cell needs additional energy to divide/survive when other fuel supplies are low)
- found in seeds as oils
- travel bidirectionally in bloodstream between liver & adipose tissue
Adipocytes
- special cells in animals that store large amounts of fat
- found under skin, around mammary glands, in abdominal cavity
Free fatty acids
- unesterified fatty acids with free carboxylate group
- circulate in blood bonded noncovalently to serum albumin
- make up soap (by saponification)
Saponification
ester hydrolysis of triacylglycerols using a strong base (lye ~sodium or potassium hydroxide)
= cleavage of fatty acid
= leaves sodium salt of fatty acid and glycerol
= fatty acid salt is soap
Surfactant
- lowers surface tension at surface of liquid = detergent or emulsifier
- soaps can act as surfactants: can combine separate phases (vinegar + olive oil)
Colloid
formed by combinding 2 phases (vinegar + olive oil)
Micelles
- tiny aggregates of soap with hydrophobic tails turned inward & hydrophilic heads turned outward
= shields hydrophobic lipid tails
= allows overall solvation
- absorbs fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) & complicated lipids (lecithins)
- fatty acids & bile salts form micelles
= increases surface area for lipolytic enzymes
Nonpolar compounds
- can dissolve in hydrophobic interior of water-soluble micelle
= cleaning agents can dissolve both water-soluble/insoluble (all washes away together)