analog 3 test 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
modulation
the process of putting information onto a high-frequency carrier for transmission
intelligence signal
low frequency information modulated onto a high frequency carrier in a transmitter
demodulation
process of removing intelligence from the high frequency carrier in a receiver
transducer
a device that converts energy from one to another
dB(decibel)
a unit of measurment used in frequently in electronic communication to describe power gain or loss
electrical noise
any desired voltages or currents that end up appearing in a circuit
man made noise
a noise produced by spark-producing mechanisms such as engine ignition systems and fluerescent lights
static electrical noise
a noise that may occur in the output of a receiver
external noise
noise in a recieved radio signal that has been introduced by the transmutting medium
internal noise
noise in a radio signal that has been introduced by the receivers internal components (resisters, transisters, excess noise
wave propagation
movement of radio signals through the atmosphere from transister to reciever
excess noise
a noise that occurs at extremely low and high frequencies in amplifiers contains resisters also known as transit-time noise
atmospheric noise
external noise caused by naturally occurring disturbances in the earths atmosphere
spare noise
external noise produced outside the earths atmosphere
solar noise
space noise originating from the sun
cosmic noise
spare noise originating from stars other than the sun
equivalant noise temperature
is a convenient means of handling noise calculations involved with microwave recievers
thermal noise
internal noise caused by thermal interactions between free electrons and vibrating ions in a conductor
shot noise
noise introduced by carriers in the Pn junction of semiconductors, directly related to DC currents
white noise
another name for thermal noise because its frequency content is uniform access its spectrum
johnson noise
another name for thermal noise
oscillator
most basic building block in a communication system. it is capable of converting energy from a dc form to ac; in other words, an oscillator generates a waveform
crystal oscillator
provides it highest frequency stability of any oscillator
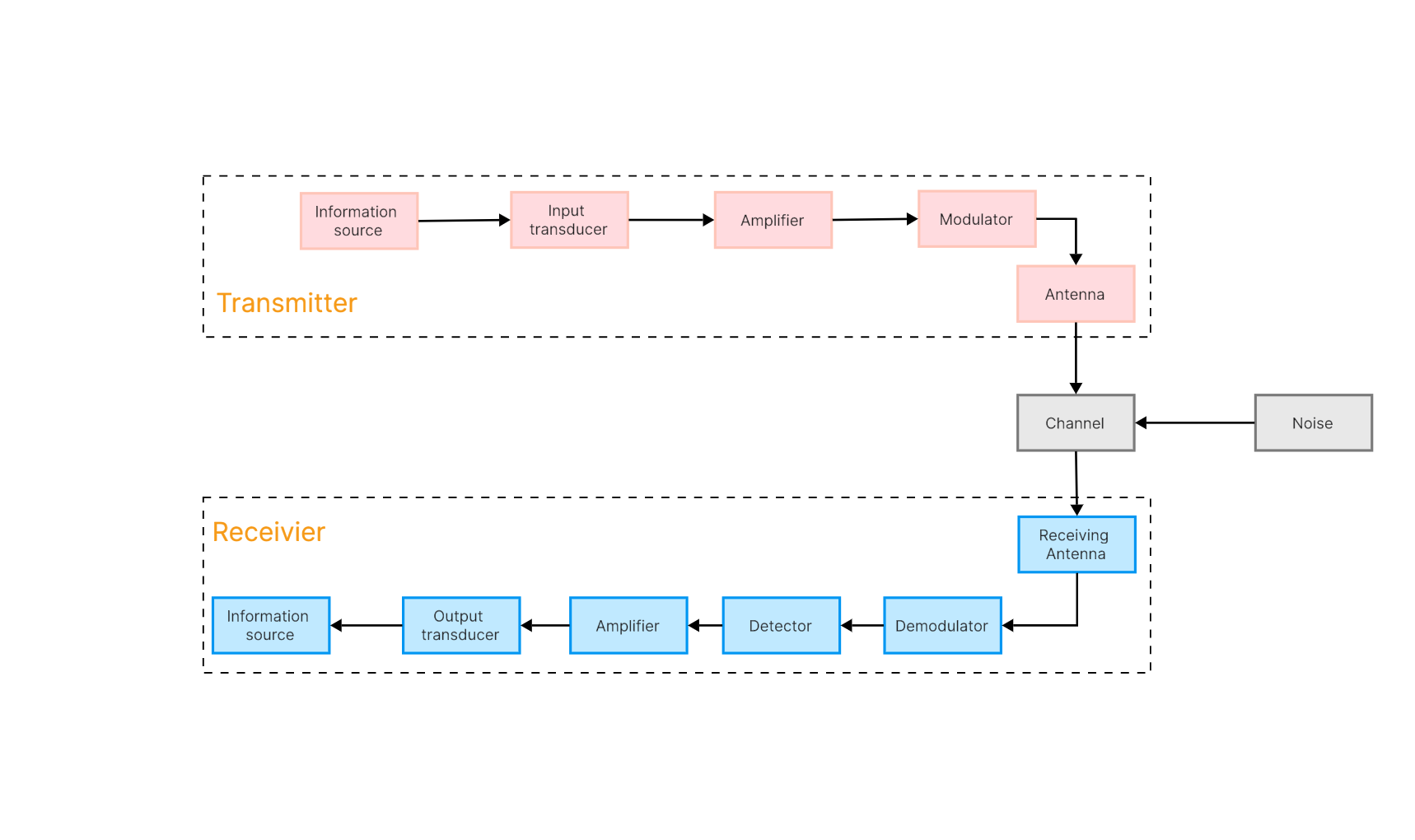
communication system block
dB References: Dbm
the db using a 1mw reference, is the typical measurment for audio input/output specification. this measurment is also used in low power optical transmitter specification
dB References: Dbm 50
standard defined by 1mw measured with respect to a 50 ohm load. this measurement is commonly used in radio frequency transmission/receiving system
dB References: Dbm 75
the standard defined by 1mw measured with respect to a 75 ohm load
dB References: Dbm dbw
common form per power amplification relative to a law reference(usually 50 ohm). typical applications are found in specification for radio-frequency power amplifier and high power audio amplifier
hartleys law
states that the information that can be transmitted is proportional to the product of the bandwidth utilized times the time of transmission. in other words , the greater the bandwidth, the more information that can be transmitted expressed as an equation
hartleys law example
the human ear is capable of hearing frequencies somewhere between 20hz and 20k hz. therefor, jf a radio station is to broadcast the full range they must have a minimum bandwidth allocates to from from the fcc,of 20khz this is why am stations have been allocated about 30khz and the fm stations about 20khz
fourier analysis
a method of analyzing complex repetitive waveforms. it permits any complex repetitive waveform to be resolved into a series of sine or cos waves. the mathematical tool provided in fourier analysis helps one to understand the meaning of hermonics
the fundamental frequency (sinwt) of a waveform is also referred to as _
the first harmonic w = 2pif. t= time
harmonics
sinusoidal waves whose frequencies are a multiple of the fundamental frequency
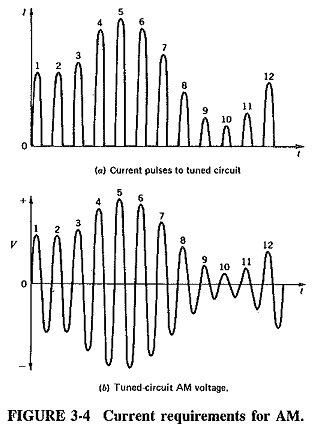
tank circuit
after capacitor has been charged to some potential the switch would then be closed, and the resulting waveform would then be created, this is the result of repetitive exchange in energy between the inductor and capacitor