Computer Systems
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
System
A system is a combination of many connected parts all working together to achieve a common goal.
Computer System
A computer system can be described as a system that involves interaction between hardware, software, data and the user
Computer Architecture
A computer architecture is a specification of how a computer’s different parts are physically, and logically, laid-out or connected
Von Neumann Architecture
One of the most common computer architectures:
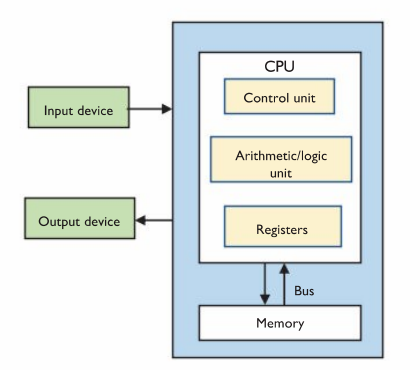
4 Components of Von Neumann Architecture
A central processing unit (CPU) which executes instructions.
Memory which stores both the data to be operated on, the insructions (programs) that operate on that data and the results.
A bus connecting the CPU and memory. This is represented by the pair of arrows (from memory to CPU and back).
Input and output devices that allow data to come into the computer and results to be sent out.
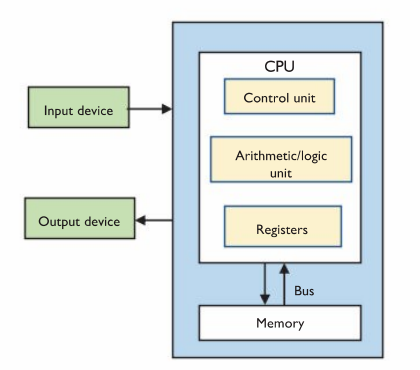
The CPU
The CPU carries out computations on data by following instructions, resulting in an output.
The CPU contains…
The Control Unit
The Arithmetic/Logic Unit (ALU)
Registers
The ALU
Arithmetic Logic Unit: where arithmetic and logical processing takes place. The ALU receives instructions and data, and operates on the data according to the instructions.
Registers
Registers are temporary storage locations that the CPU can access very quickly when carrying out operations on data (or data which may be accessed frequently)
Examples of Registers
The Program Counter (PC): stores where the CPU is in the program sequence, at any given time
Data Registers: Hold data temporarily
Address Registers: Address registers store memory addresses
Memory Address
A memory address is a value that indicates a specific location in memory. This could be the location in memory of data that is to be operated on, or the location of an instruction to be executed by the CPU
Memory
Memory refers to the physical devices used to store data and instructions for immediate access by the CPU. It includes both volatile and non-volatile storage types such as RAM and ROM
Volatile vs Non-Volatile Memory
Volatile memory is memory that, when the computer loses power, the data is lost
RAM
RAM (Random Accses Memory) is temporary memory. It holds the data and instructions of the program that is currently being executed by the CPU. RAM is known as volatile memory
ROM
ROM (Read-only memory) is non-volatile memory. A typical use of ROM is the computer’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
Primary Storage/Main Memory
Primary Storage/Main Memory is used to store information for immediate use by the CPU. RAM and ROM are both types of primary storage
The Fetch-Execute Cycle
The basic operation of a computer is called the ‘fetch-execute’ cycle. The CPU is designed to understand a set of instructions - the instruction set.
It fetches the instructions from the main memory and executes them.
This is done repeatedly from when the computer is booted up to when it is shut down.