General Biology: Chapter 30
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Plant Diversity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Order of adaptations critical for plant success on land
waxy cuticle, vascular tissue, seeds, flowers
First group of plants to adapt vascular tissue
pteridophytes
What did the evolution of vascular tissue allow plants to do?
become bigger and colonize terrestrial environments
5 things that set SED plants apart from all other plants
seeds, ovules, pollen, heterospory, reduced gametophytes
What makes a seed?
embryo, food supply, seed coat
What is the trend between sporophyte and gametophyte?
sporophyte dominant life-cycle
What are the advantages of needle-like structures?
they are evolved leaves that lived in different conditions, colder environments = needing more water (reduces surface area, less water loss)
Gymnosperms
“naked seed” plants, including conifers, typically on cones or spruces
Angiosperms
flowering plants, 90% of living plant species
Advantages of pollen
no need for water to bring sperm to egg, no flagella
What was the big event that allowed gymnosperms
permian mass extinction
What is the main distinctive feature from gymnosperm to angiosperm?
seed is now enclosed in either a flower or a fruit
If grasses are angiosperms, why do they not have colorful flowers?
they rely on wind dispersal
Advantages of Gymnosperms
reproductive independence from water, seed protection and nourishment, adaptation to harsh climates, ecological and economic importance
Advantages of Angiosperms
vast source of food (grain, fruit, vegetables) and medicine (pharmaceuticals, traditional remedies), ecosystems, biodiversity, provide habitats
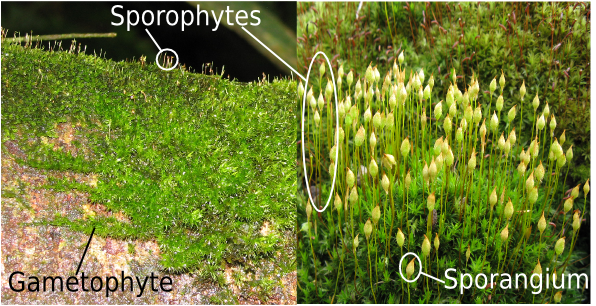
Sporophyte
Male vs Female Gametophyte
Monocots
have 1 cotyledon (seed leaf), parallel leaf veins, scattered vascular bundles, and flower parts in multiples of 3
Dicots
have 2 cotyledons, net-like leaf veins, vascular bundles in a ring, and flower parts in multiples of 4-5
Advantages of indigestible seeds (ecological)
seed dispersal, reduced competition, enhanced germination, nutrient-rich deposition, colonization of new habitats
Advantages of indigestible seeds (humans)
improved digestion and gut health, prebiotic effects, chronic disease management, cholesterol and blood sugar control, weight management
Wind Pollinated Plants
use of wind to transport pollen form one flower to another for reproduction
Insect Pollinated Plants
attract insects with bright colors, strong scents, and nectar
Wind Pollinated Plant examples
grasses (wheat, rice, corn, barely, oats, maize), trees (pines, spruces, oaks, birches, willows,) ragweed
Insect Pollinated Plant examples
fruits (apple, pear, cherries) vegetables (tomatoes, squash, cucumbers) flowers (sunflowers, roses, clover)
How and why will plants look different depending on their pollination method?
they have evolved specific physical adaptations (smell, color, size) to maximize efficiency of pollen transfer by their own pollinating agents, wind pollinated angiosperms don’t need flashy features
How will human population change the animal and plant diversity?
humans destroy habitats through deforestation and urban sprawl, increasing pollution and climate change