spinal column & thorax
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
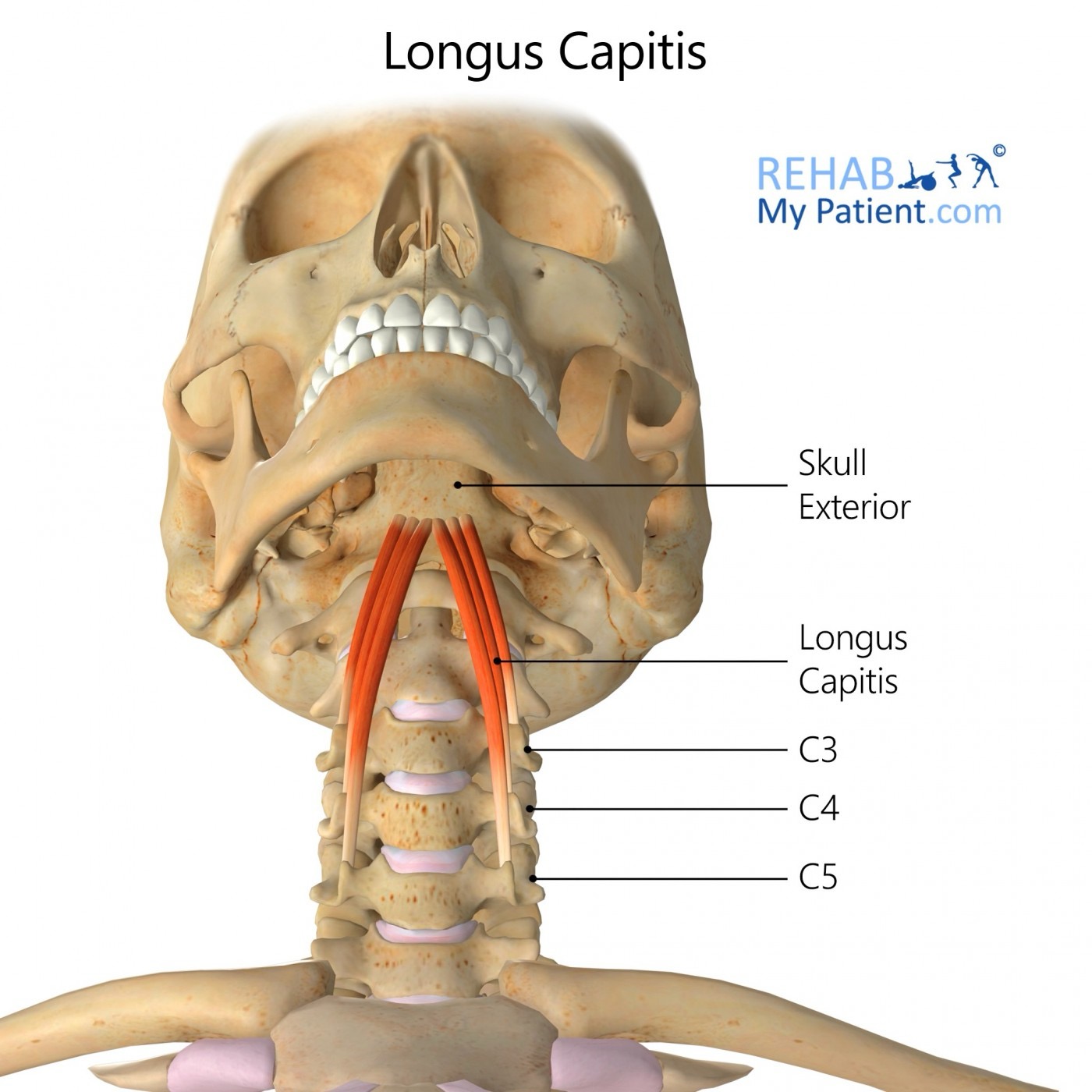
longus capitis action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex & rotate to the same side
bilaterally: flexion of the head & neck
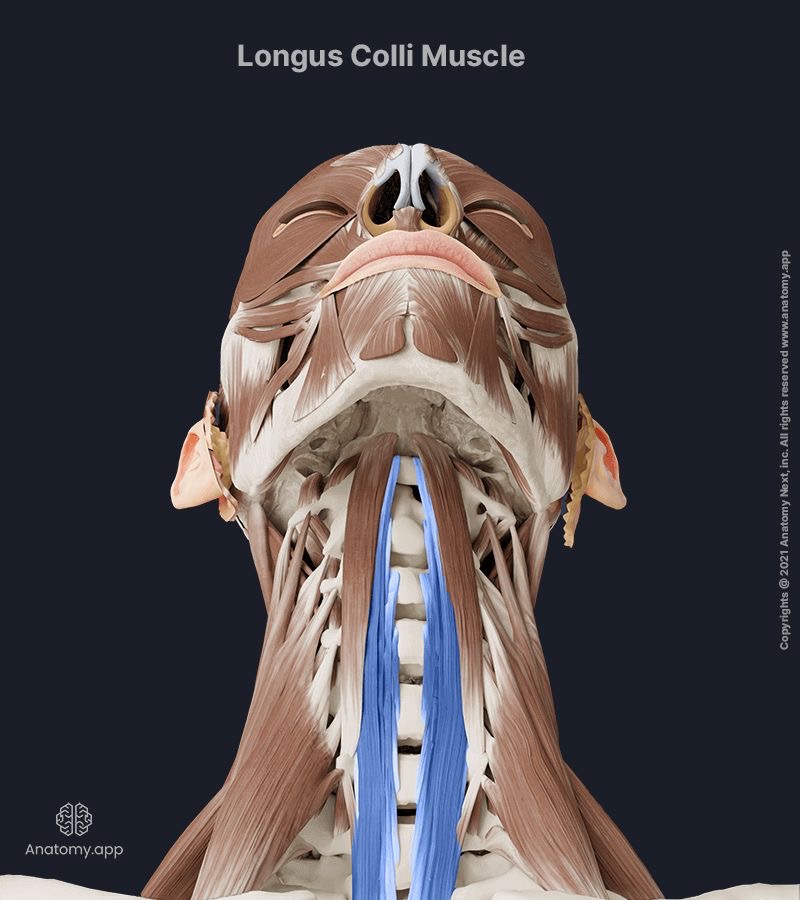
longus colli action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex & rotate to the same side
bilaterally: flexion of the head & neck
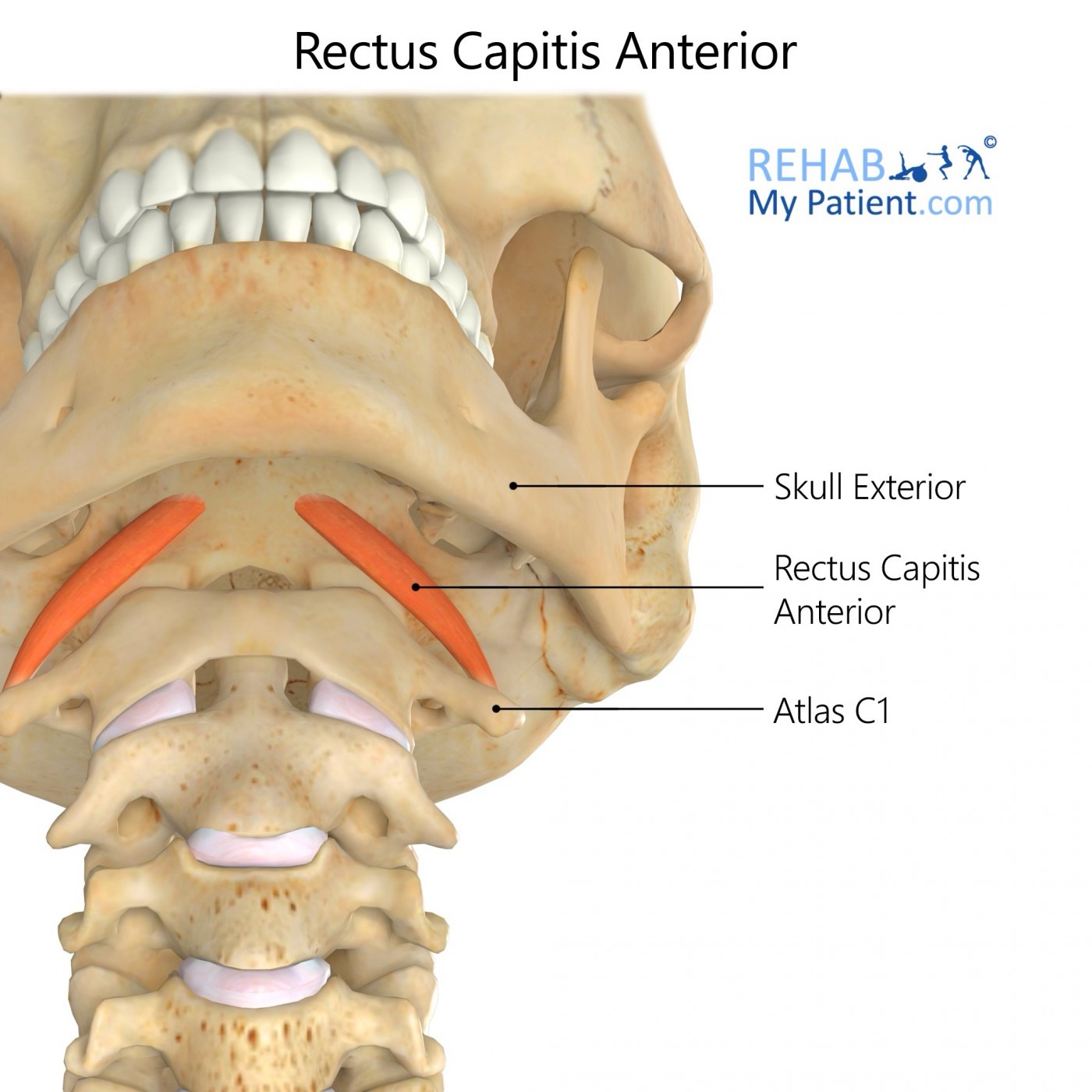
rectus capitis anterior action/function
bilaterally: flexion of the head & neck; stabilization of AO joint
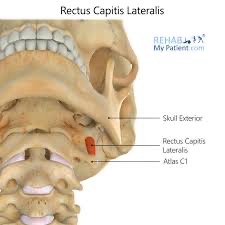
rectus capitis lateralis action/function
bilaterally: flexion of the head & neck; stabilization of AO joint
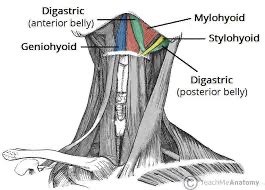
suprahyoids (geniohydoid, mylohoid, stylohyoid) action/ function
flexion of head and neck; aids in swallowing
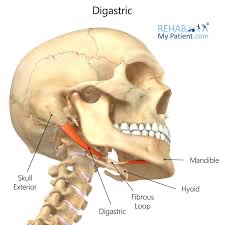
diagstric action/function
depression of the mandible (with hyoid bone fixed); elevation of hyoid bone (with mandible fixed); retraction of the mandible
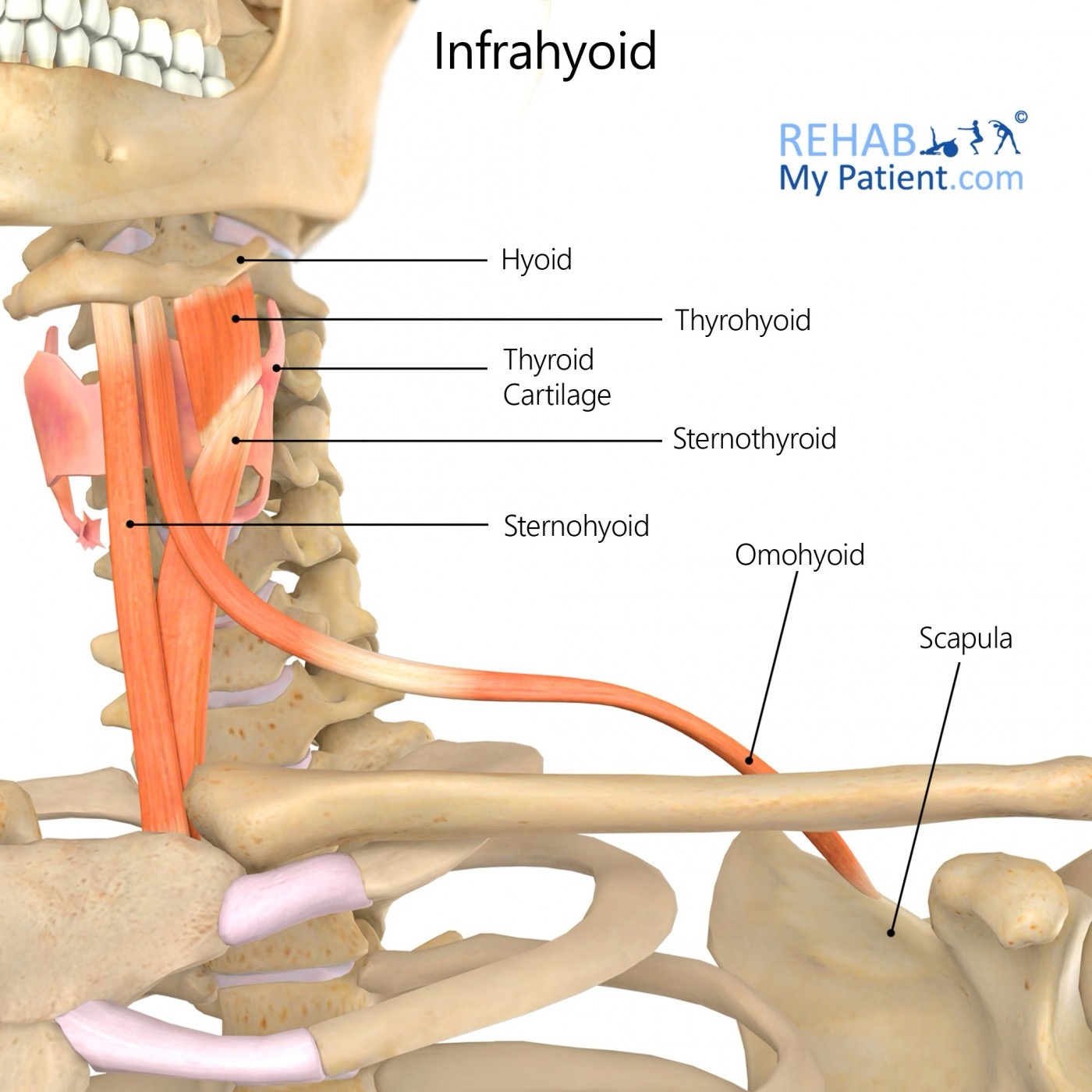
infrahyoids (sternohyoid, sternohyroid, thyrohyoid, omohyoid) action/function
depresses the hyoid bone and thyrohyoid cartilage
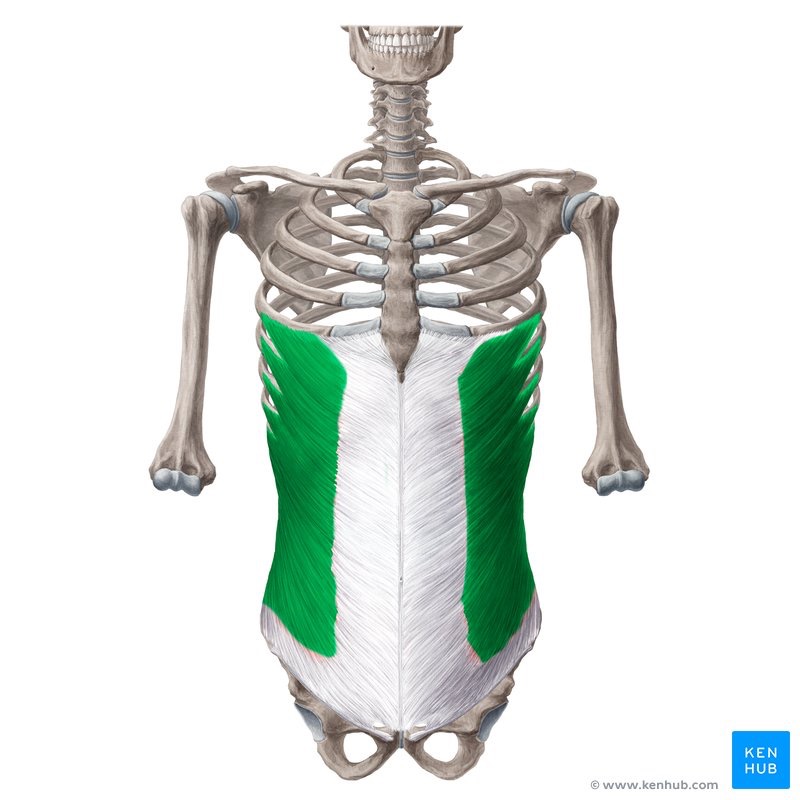
external oblique action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex to same side and rotate the spine to the opposite side
bilaterally: flexion of the thoracic & lumbar spine
external oblique origin
external surface of 5th - 12th ribs
external oblique insertion
anterior iliac crest and abdominal aponeurosis (fascia)
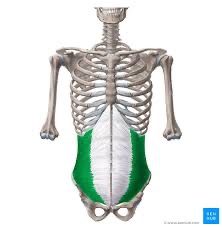
internal oblique action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex to same side and rotate the spine to the same side
bilaterally: flexion of the thoracic & lumbar spine
internal oblique origin
inguinal ligament, crest of ilium & thoracolumbar fascia
internal oblique insertion
internal surface of lower three ribs (10-12) and abdominal aponeurosis
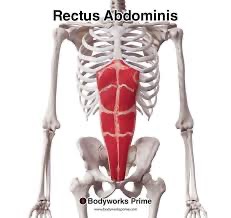
rectus abdominis action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex the spine
bilaterally: flexion of the thoracic & lumbar spine
rectus abdominis origin
pubic crest and pubic symphysis
rectus abdominis insertion
cartilage of ribs 5-7 and xiphoid process

transverse abdominis action/function
unilaterally: trunk rotation to same side
bilaterally: stabilize the trunk
transverse abdominis origin
inguinal ligament, iliac crest, thoracolumbar fascia
transverse abdominis insertion
abdominal aponeurosis
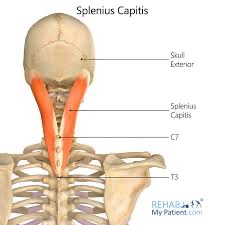
splenius capitis action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex head & neck; rotate to same side
bilaterally: extension and hyperextension of head & neck
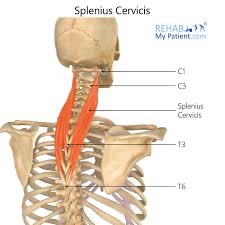
splenius cervicis action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex head & neck; rotate to same side
bilaterally: extension and hyperextension of head & neck
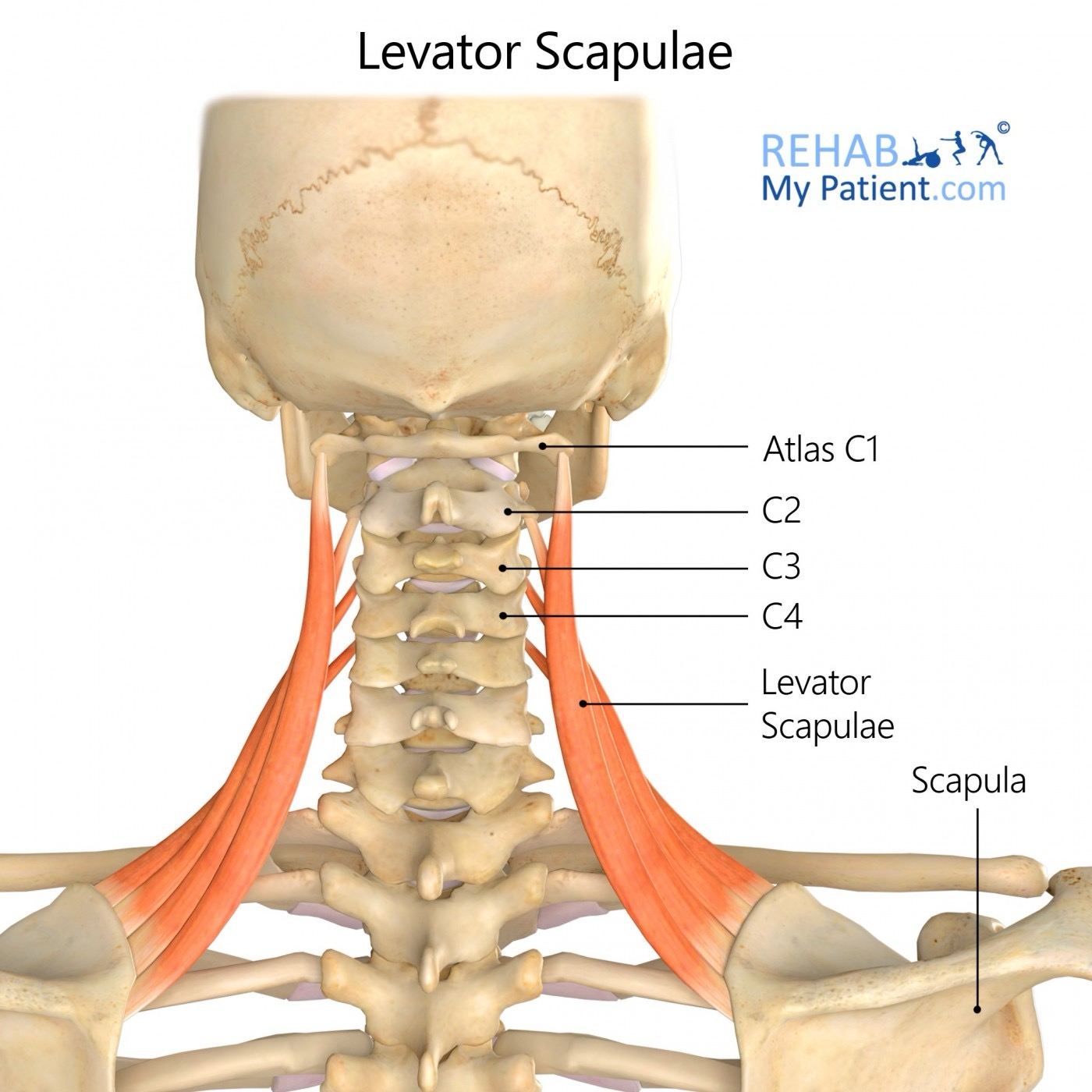
levator scapulae action/function
unilaterally: laterally flex the neck
bilaterally: stabilize the neck, extend the head and neck
levator scapulae origin
transverse processes of C1-C4
levator scapulae insertion
medial boarder of scapula
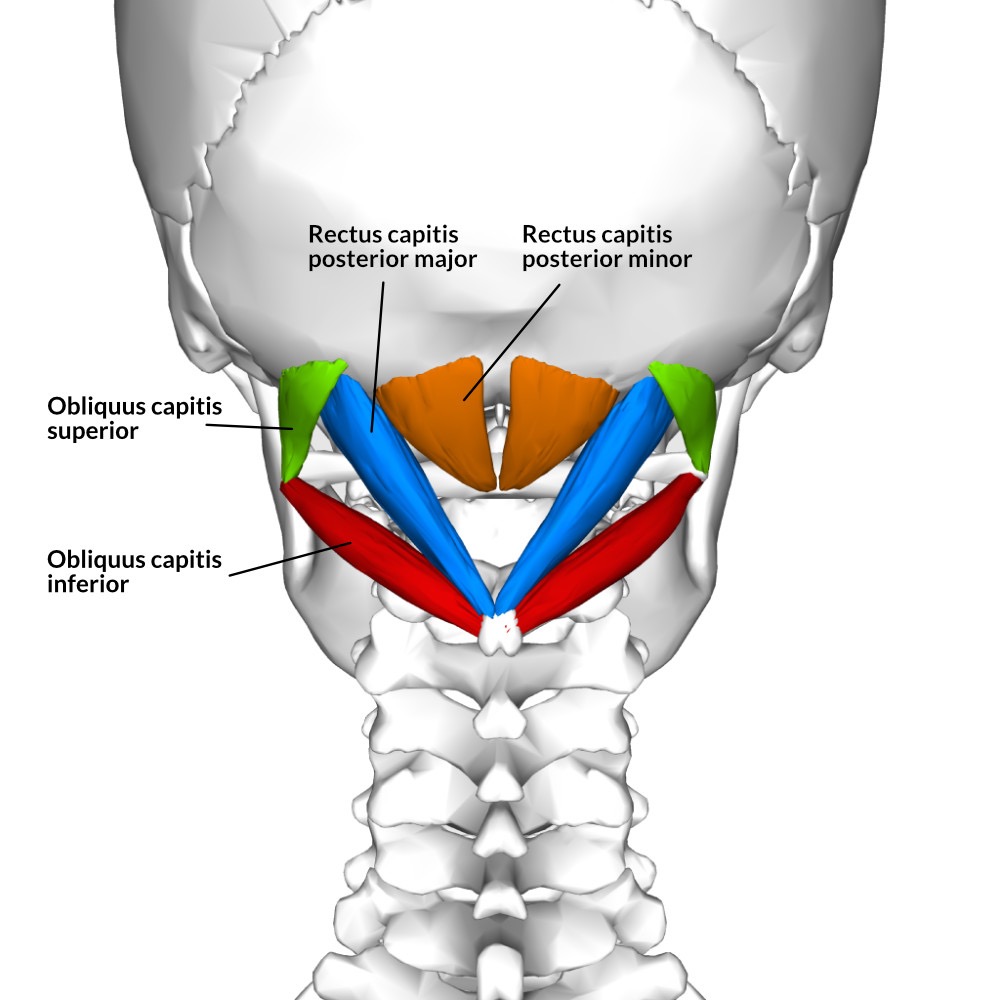
suboccipital group (rectus capitis posterior major, rectus capitis posterior minor, oblique capitis superior, oblique capitis inferior)- action/ function
unilaterally: laterally flex the head; rotate head to same side
bilaterally: extension & hyperextension of the head
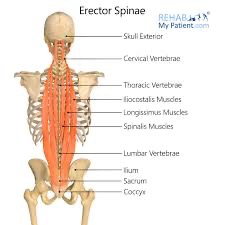
erector spinae action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion of the same side
bilaterally: extension of head and spine
erector spinae origin
thoracolumbar aponeurosis, posterior surface of the sacrum, iliac crest, spinous processes T11-L5
erector spinae insertion
posterior ribs, spinous and transverse processes of all thoracic and cervical vertebrae, and the mastoid process
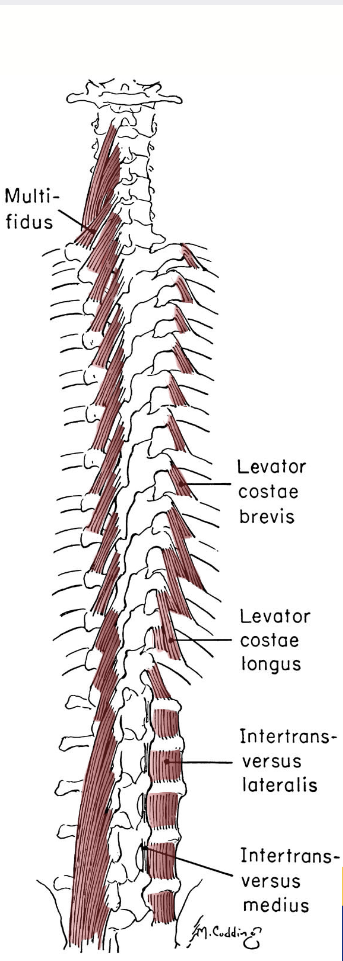
deep posterior spinal muscles (multifiuds & rotators) action / function
unilaterally: rotation of the spine to the opposite side; assists in lateral flexion
bilaterally: extension of the spine
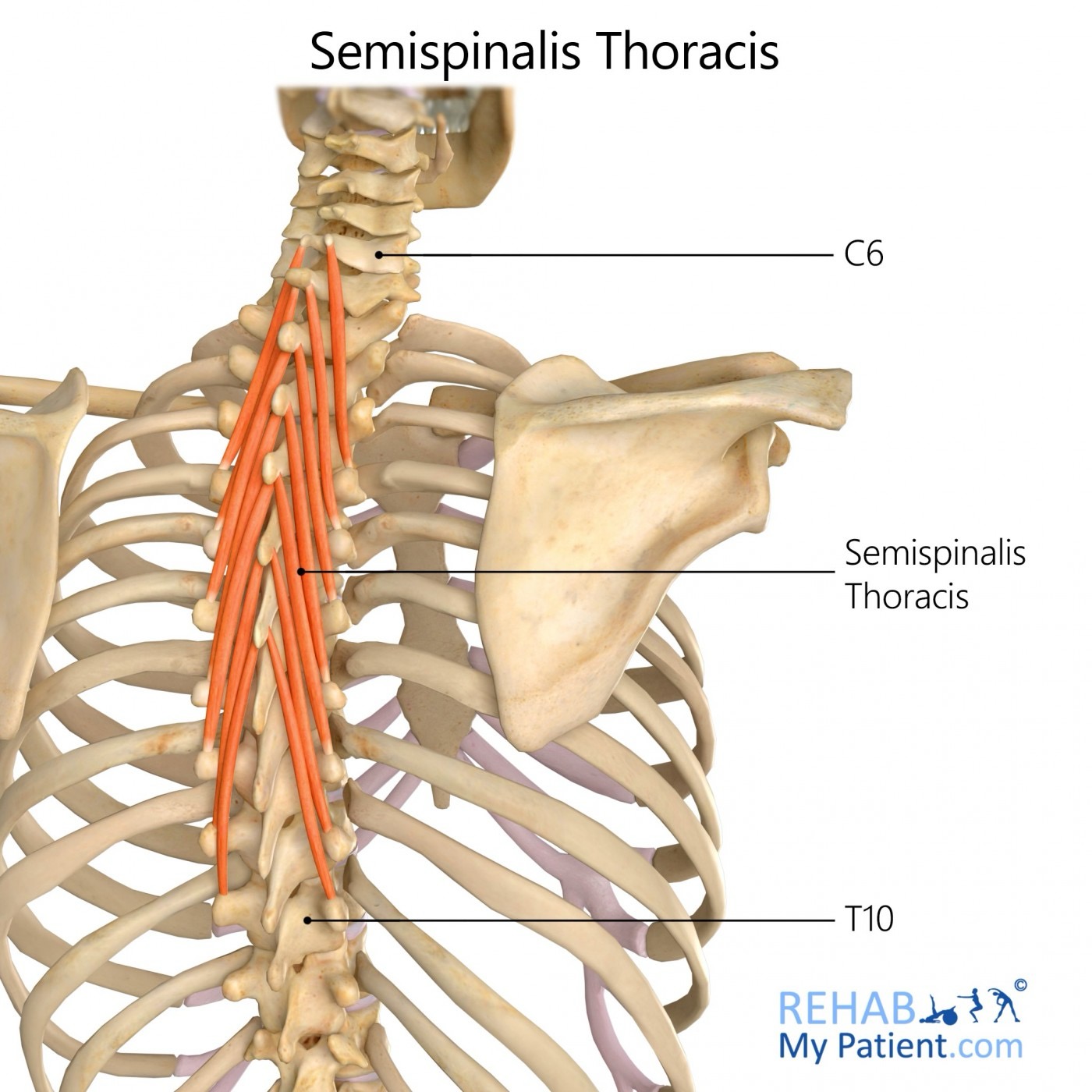
semispinalis thoracis action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion and rotates spine to opposite side
bilaterally: extension and hyperextension of thoracic and cervical spine
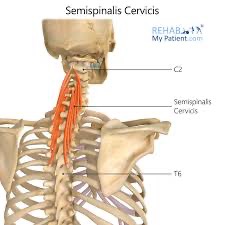
semispinalis cervicis action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion & rotates spine to opposite side
bilaterally: extension & hyperextension of thoracic and cervical spine
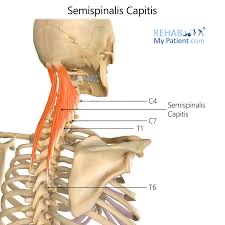
semispinalis capitis action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion & rotates spine to opposite side
bilaterally: extension and hyperextension of thoracic and cervical spine
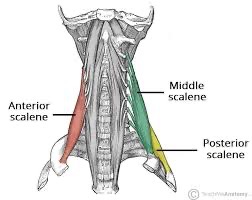
scalenus (anterior, medius, posterior) action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion of neck; rotate head and neck to the opposite side
bilaterally: flexion of cervical spine; elevation of ribs during respiration
scalenus anterior origin
transverse processes of C3-6
scalenus medius origin
transverse processes of C2-7
scalenus posterior origin
transverse processes of C6-7
scalenus anterior and middle insertion
1st rib
scalenus posterior insertion
2nd rib
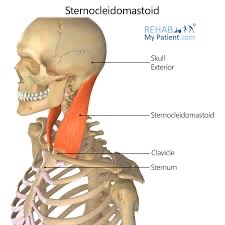
sternocleidomastoid action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion of head and neck & rotation to opposite side
bilaterally: flexion of head and neck
sternocleidomastoid origin @ sternal head
top of manubrium
sternocleidomastoid origin @ clavicular head
medial 1/3 of clavicle
sternocleidomastoid insertion
mastoid process and nuchal line of occiput
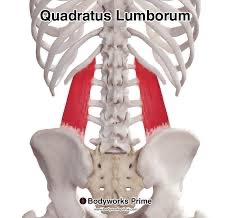
quadratus lumborum action/ function
unilaterally: lateral flexion of lumbar spine
bilaterally: stabilize pelvis and lumbar spine
quadratus lumborum origin
posterior iliac crest
quadratus lumborum insertion
rib 12 and transverse processes of L1-L4
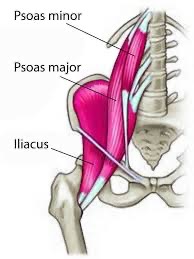
psoas (major and minor) action/function
unilaterally: lateral flexion of lumbar spine
bilaterally: stabilize the spine
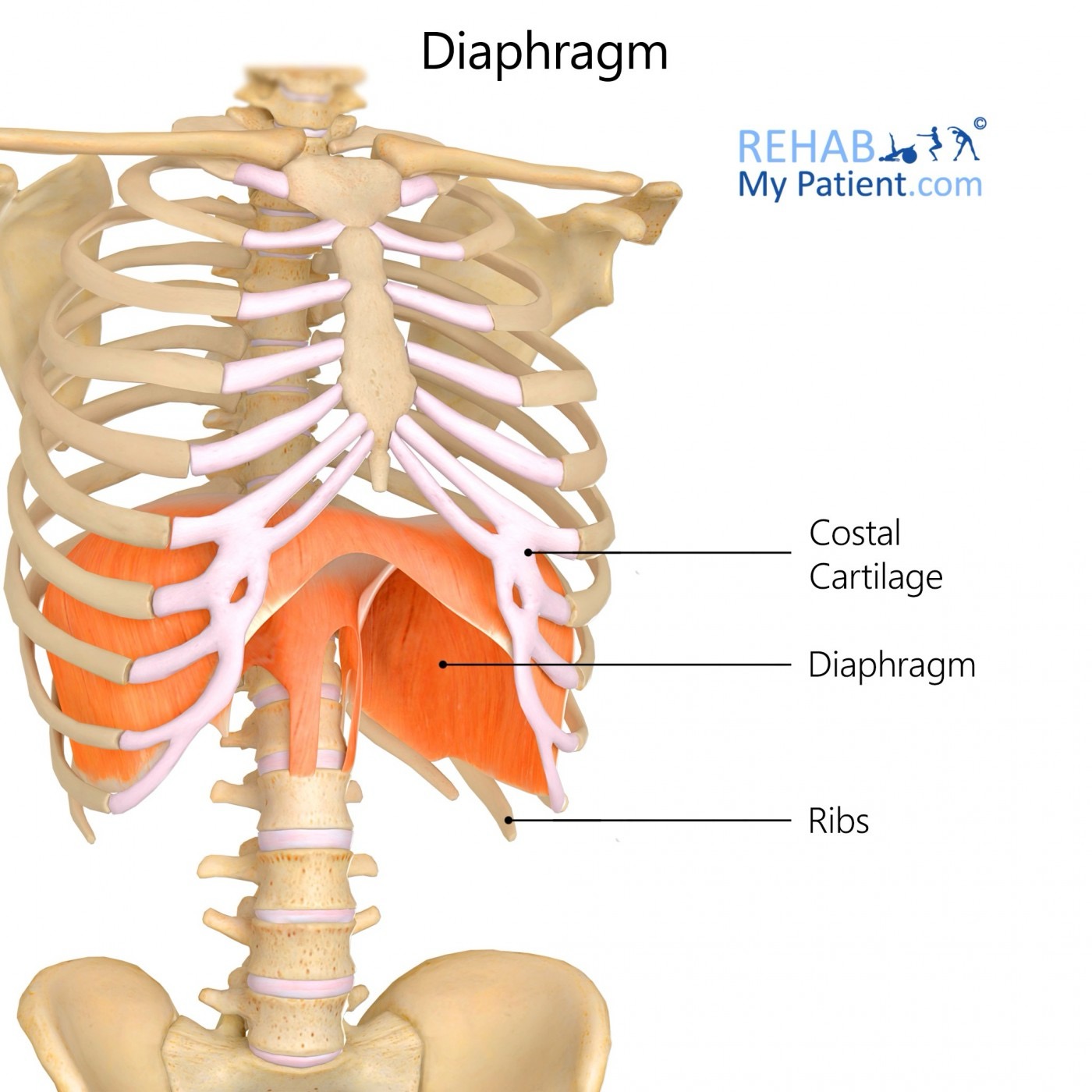
diaphragm (PF) action/function
inspiration
diaphragm (PF) origin
inner surface of ribs 7-12, L1-3, inner part of xiphoid process
diaphragm (PF) insertion
central tendon of abdominal cavity
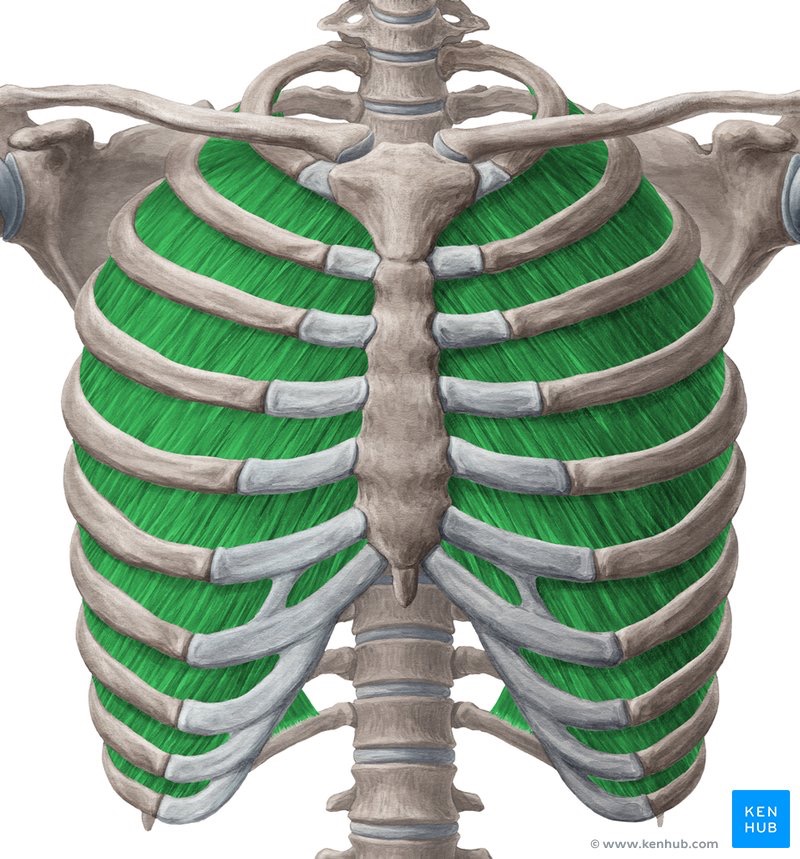
internal intercostales (PF) action/function
expiration, pull ribs in
internal intercostals (PF) origin
inferior border of the rib above
internal intercostals (PF) insertion
superior border of rib below
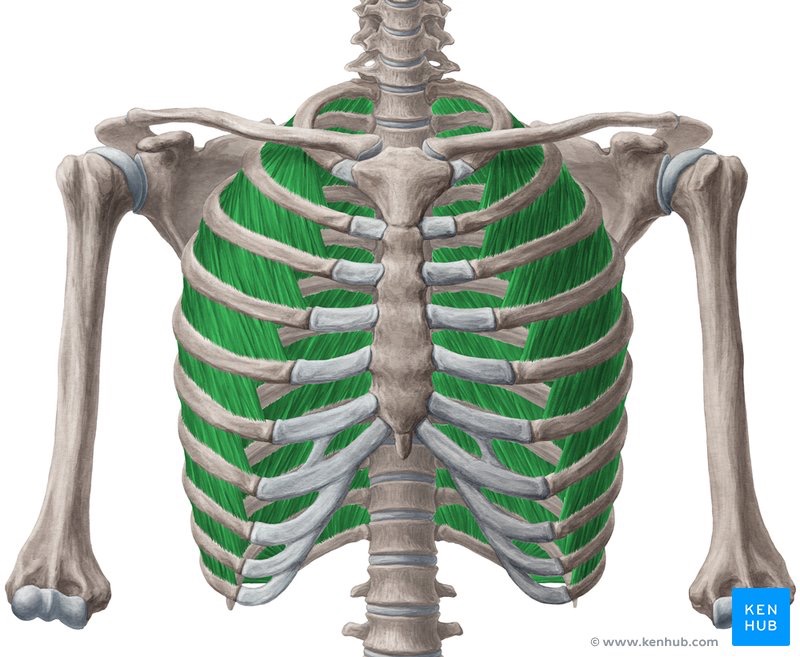
external intercostals (PF) action/function
inspiration, expand ribs out
external intercostals (PF) origin
inferior border of the rib above
external intercostals (PF) insertion
superior border of rib below
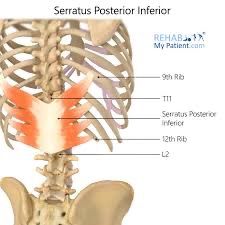
serratus posterior inferior (PF) action/function
depresses and stabilizes rib cage
serratus posterior inferior (PF) origin
spinous processes of T12-L3
serratus posterior inferior (PF) insertion
posterior surface of ribs 9-12
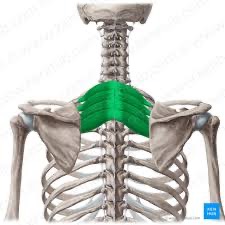
serratus posterior superior (PF) action/function
elevates ribs
serratus posterior superior (PF) origin
spinous processes of C7-T3
serratus posterior superior (PF) insertion
posterior surface of ribs 2-5
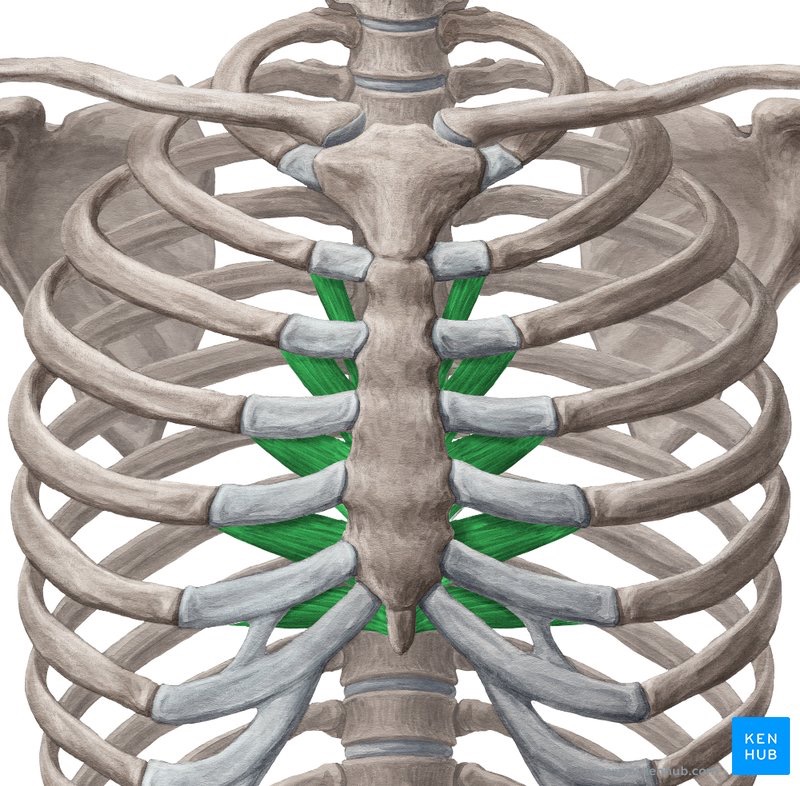
transversus thoracis (PF) action/function
expiration
transversus thoracis (PF) origin
lower half of the sternum and adjoining costal cartilages
transversus thoracis (PF) insertion
lower border and inner surfaces of the costal cartilages of 2-6 ribs
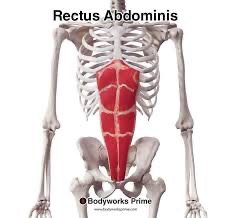
rectus abdominis (SF) action/function
passive in quiet breathing and active on forced expiration
rectus abdominis (SF) origin
pubic crest and pubic symphysis
rectus abdominis (SF) insertion
cartilage of ribs 5-7 and xiphoid process
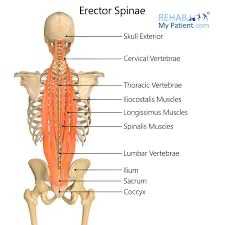
erector spinae (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
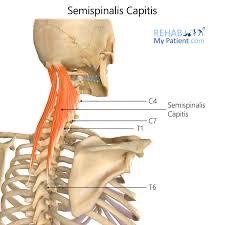
semispinalis capitis (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
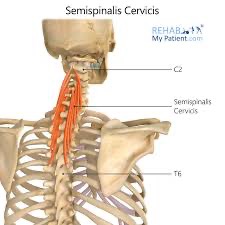
semispinalis cervicis (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
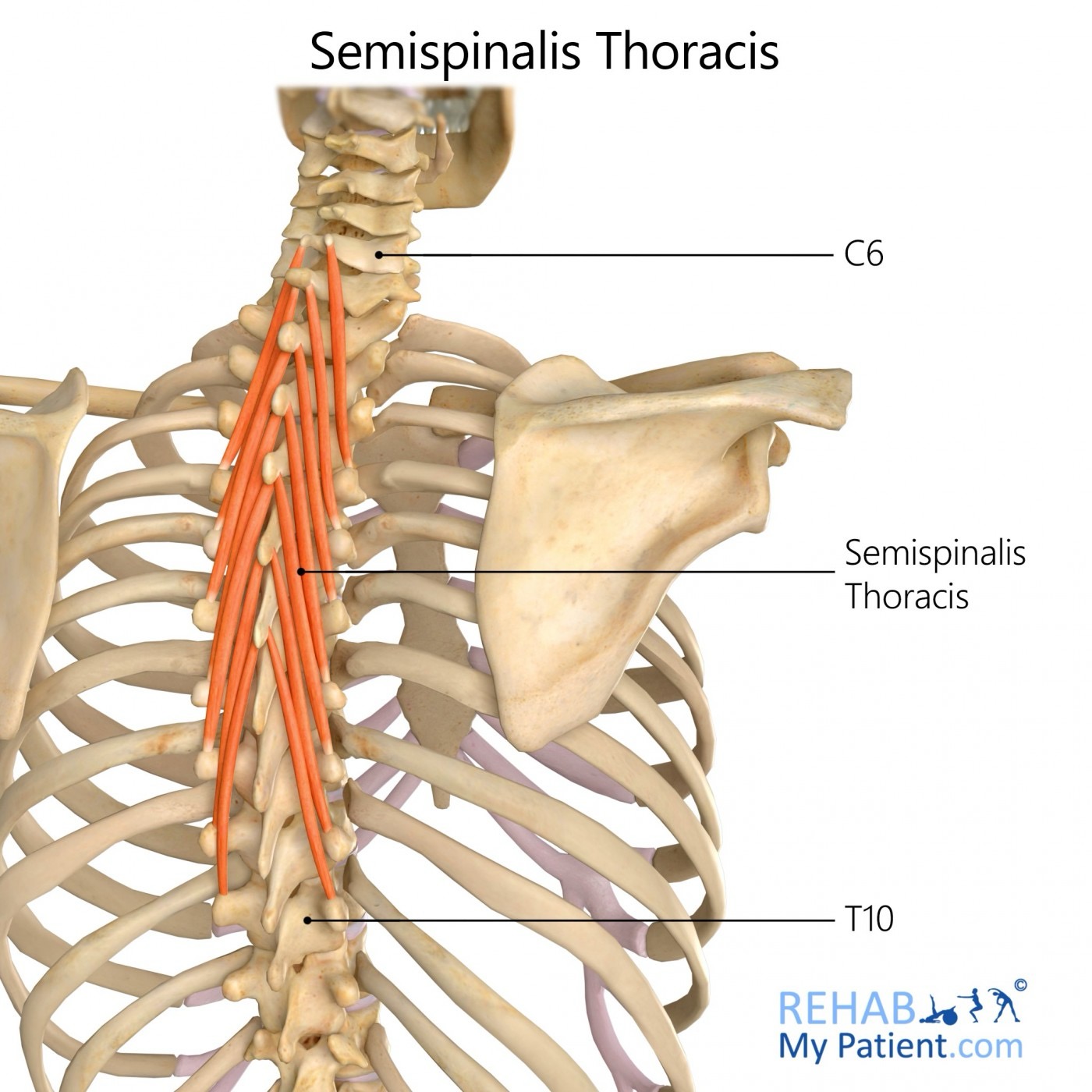
semispinalis thoracis (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
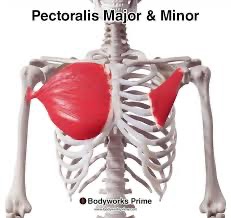
pectoralis major & minor (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
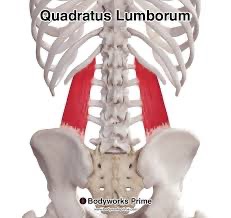
quadratus lumborum (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
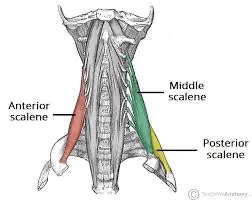
scalenes (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
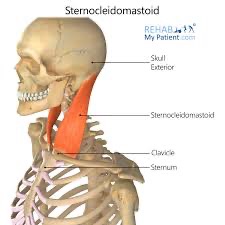
sternocleidomastoid (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
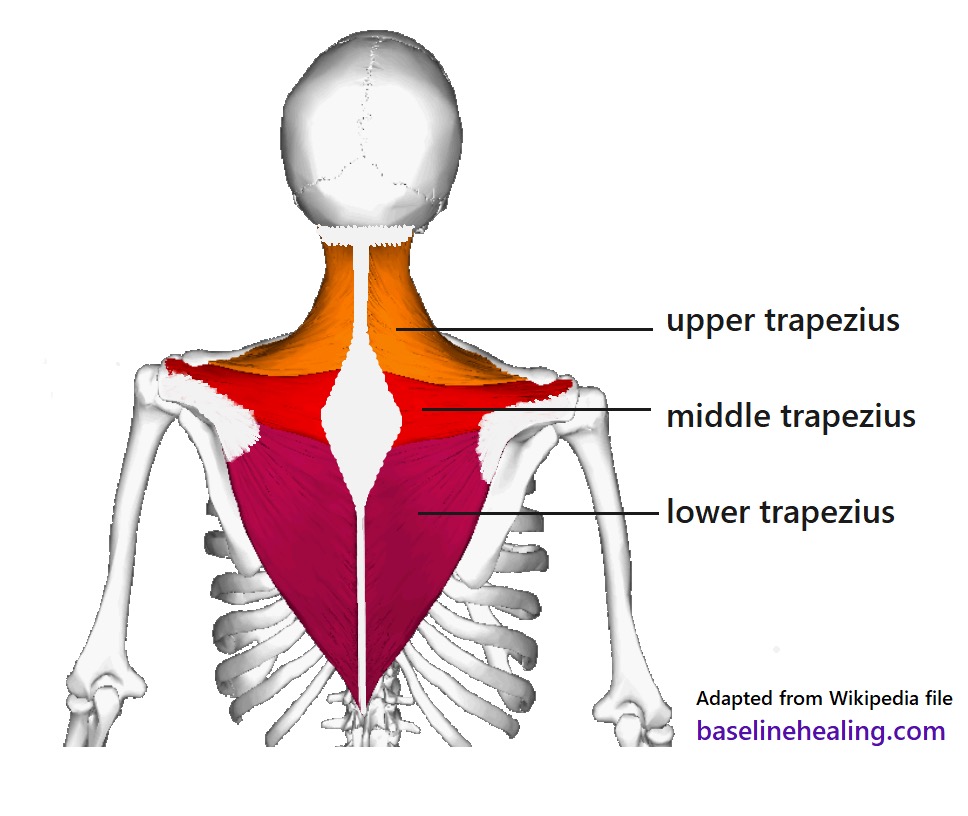
trapezius (SF) action/function
secondary respiration
unique role and function of the spinal column
give stability, permit movement & return to starting position, support structures, provide attachment for muscles, transmit gradually increasing weight, act as shock absorber, encase & protect cord
number of cervical bones
7 (C1-C7)
number of thoracic bones
12 (T1-T12)
number of lumbar bones
5 (L1-L5)
lordosis
posterior curve of lumbar and cervical
kyphosis
anterior curve of thoracic
lumbar kyphosis
reduction of normal lordotic curve, resulting in a flat back appearance
scoliosis
lateral curve or sideward deviation
postural sway influences
age, fatigue, injury, bracing, obesity, stability of external environment, adhd
factors affecting stability
size of base of support (wide is better), line of gravity to base of support, height of the center of gravity, external visual cues, fixed eyes, semicircular canals
hip strategy
penguin walk (waddle), trunk flexion/extension and hip/knee flexion; slippery surface
ankle strategy
ankle/ foot adopts a position that allows stability to be maintained; abrupt changes of surface
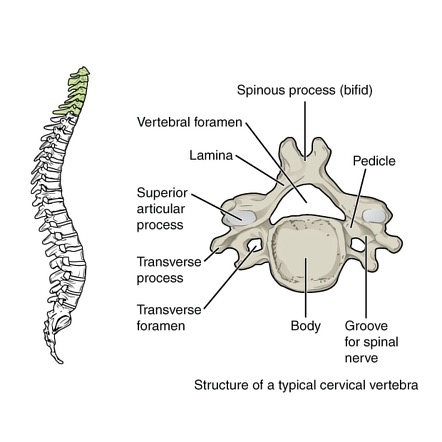
cervical bones
7 vertebrae; flex/extend, lateral flex/extend
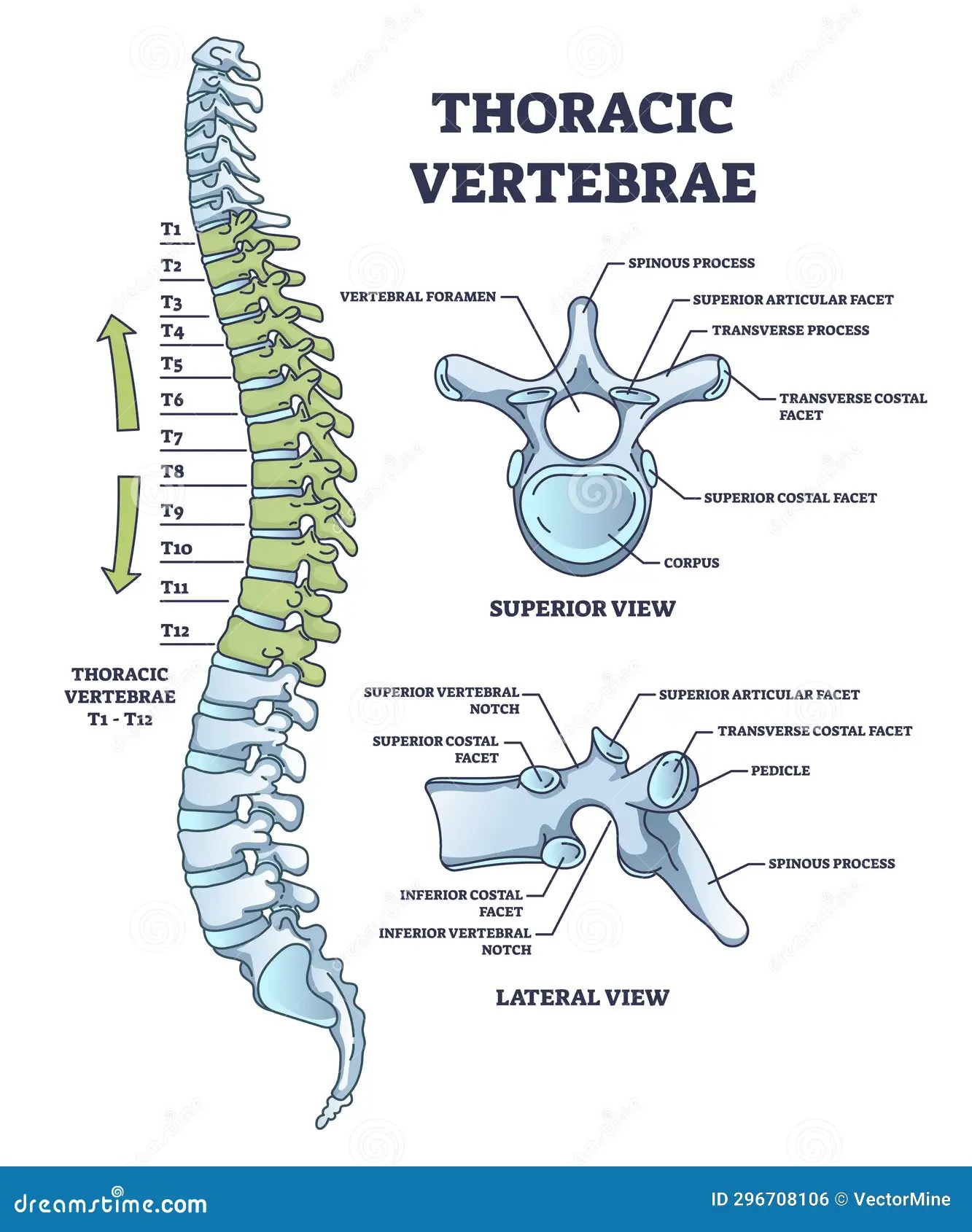
thoracic bones
12 vertebrae; lateral flexion & rotation
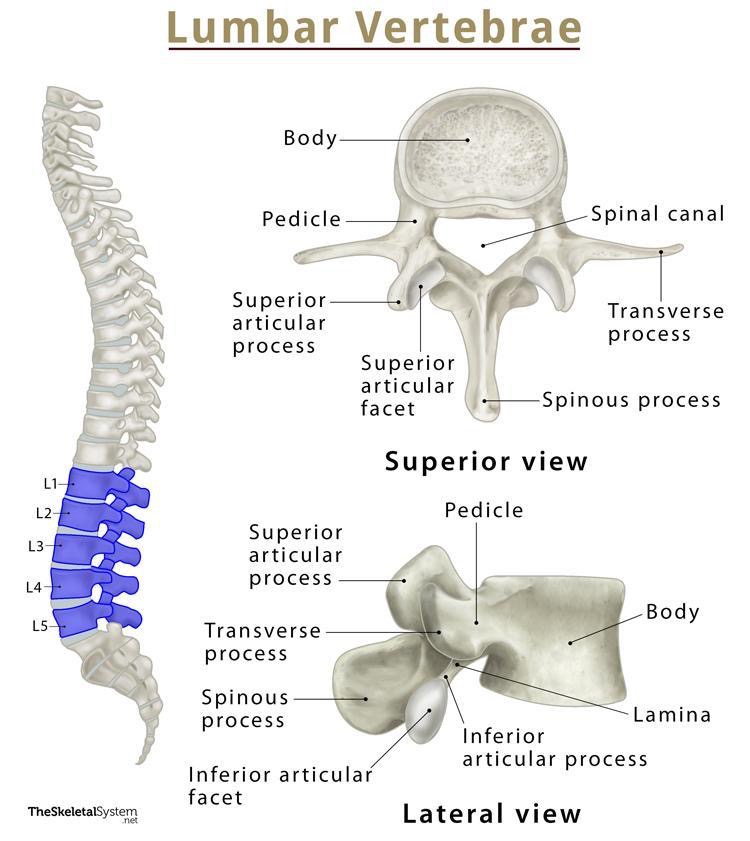
lumbar bones
5 vertebrae; flexion, hyperextension, NO rotation
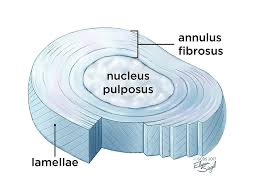
intervertebral discs
outer fibrous rim (annulus fibrosus) & jelly inside (nucleus pulposus)
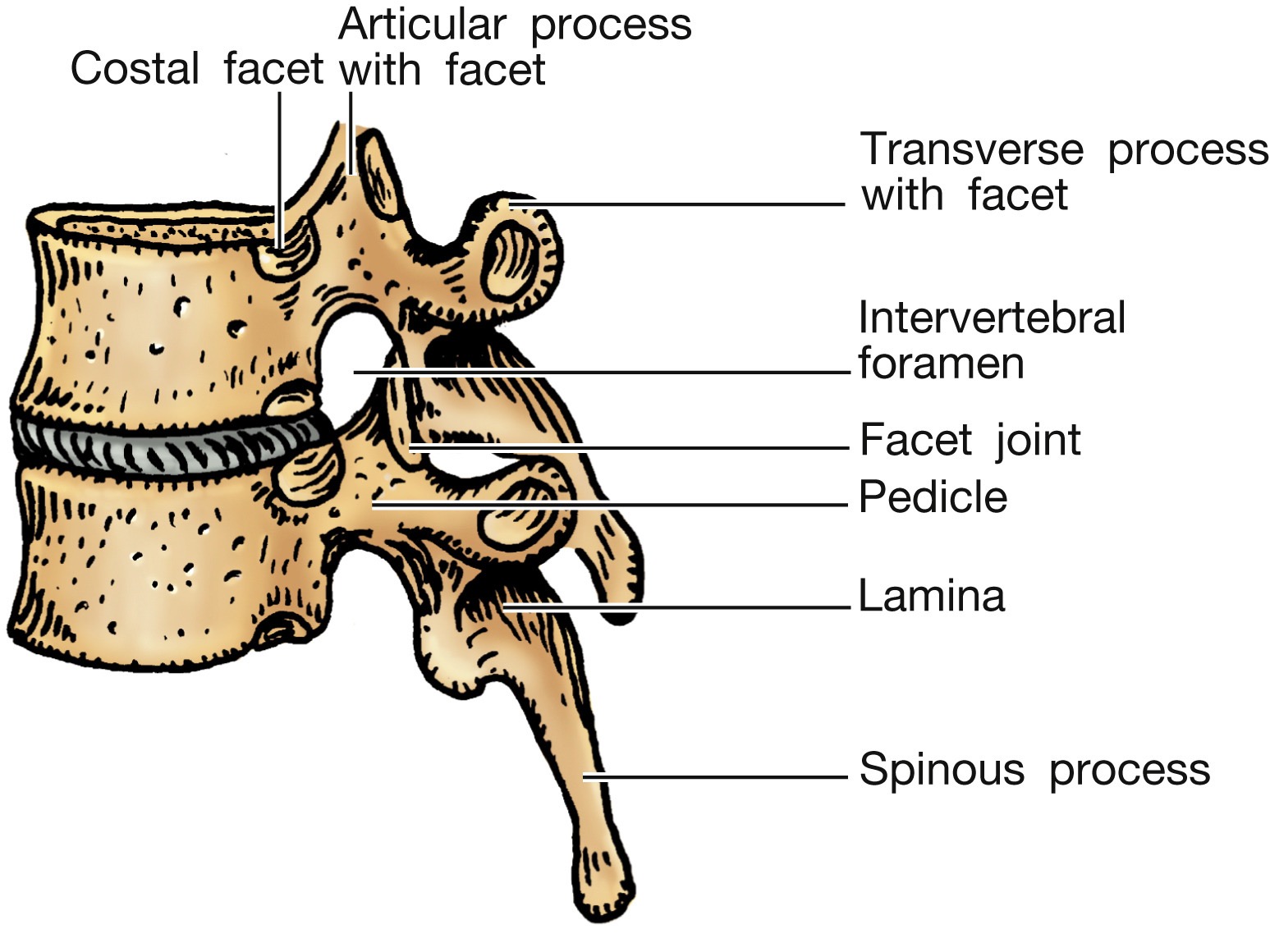
articulations of vertebral arches
facets are nonaxial and permit gliding; motion determined by the direction that the facets face
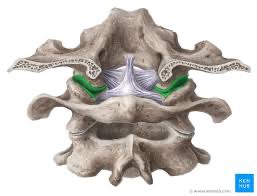
atlanto-occipital articulation
atlas (C1) to base of skull; hinge joint, permit flexion and extension
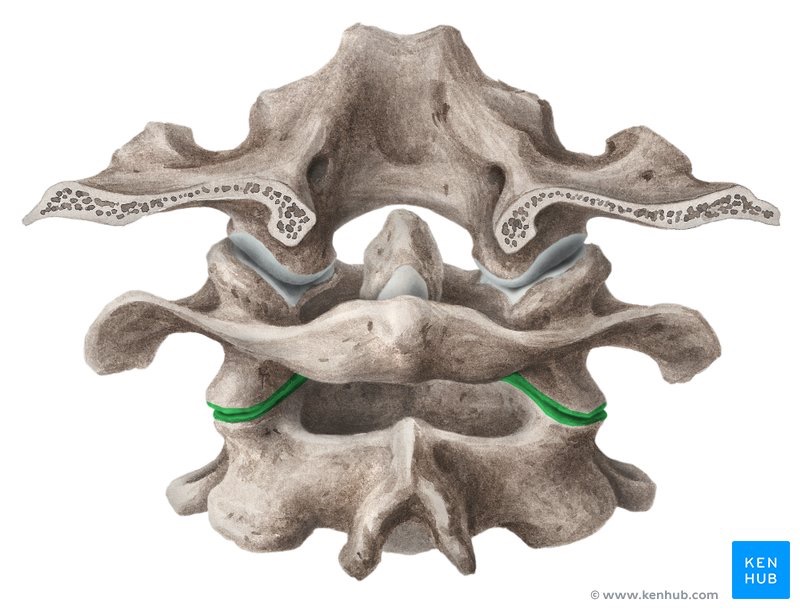
atlantoaxial articulation
atlas (C1) to axis (C2); pivot joint, permits rotation only
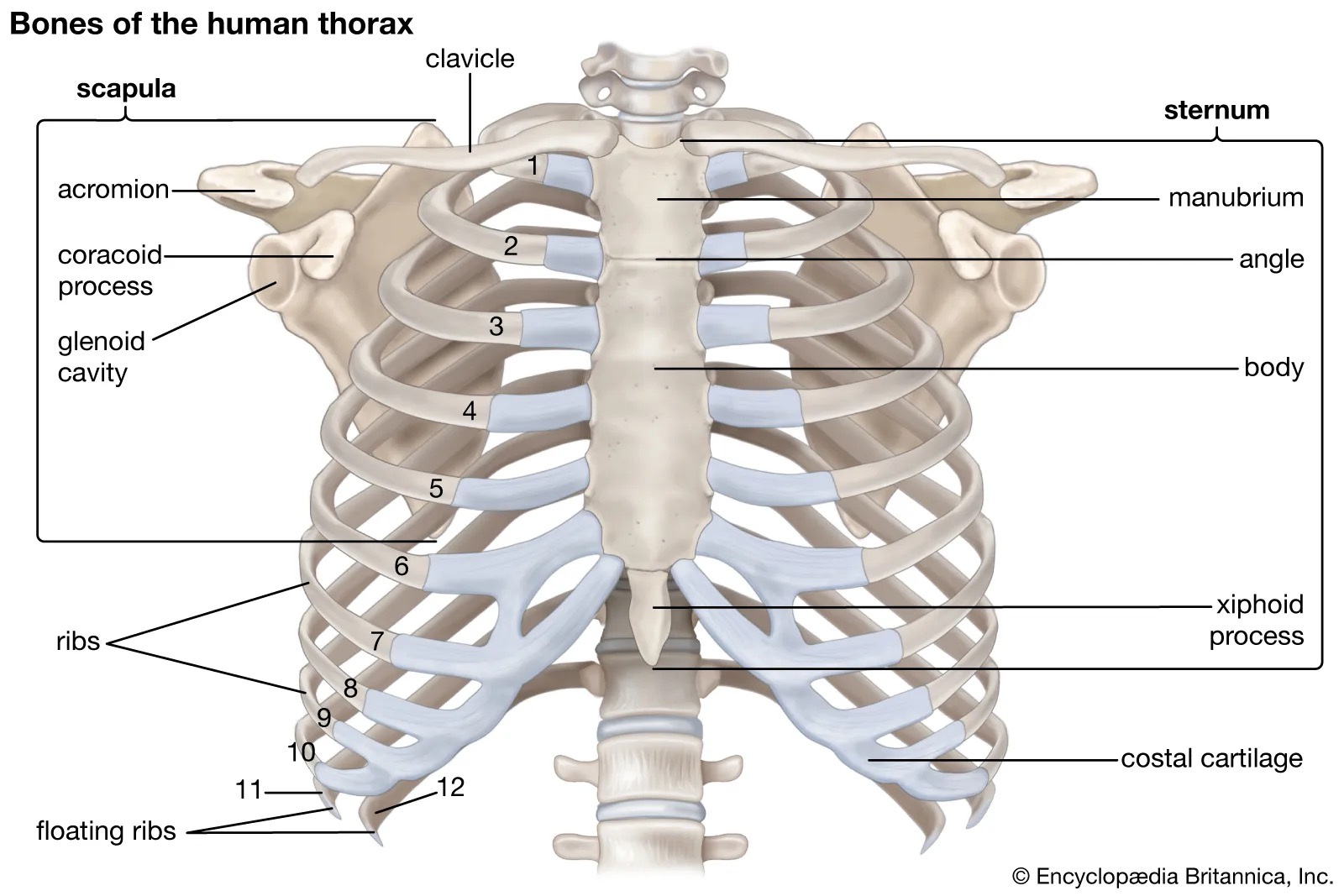
thorax structure
bony cartilaginous cage formed by ribs and cartilage and sternum; 7 true ribs, 5 false, 2 floating
phases of respiration
pre-inspiration: brief pause before inhale
inspiration: expand chest and inhale
pre-expiration: brief pause after inhale
expiration: decrease chest volume & exhale
primary muscles of respiration
diaphragm, internal & external intercostal, serratus posterior inferior & superior, transverse thoracis
secondary muscles of respiration
abdomials, erector spinae, scalenes, cervical & thoracic extensors, pec major & minor, quadratus lumborum