Unit 1 Honors Economics Flashcards
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Scarcity
Limited quantities of resources to meet unlimited wants of people
Need
Something that is necessary for survival
Want
Item desired, but not essential to survival
Economics
The study of choices & how individuals and societies deal with scarcity
Microeconomics
The study of small economic units such as individuals, firms, and industries
Macroeconomics
The study of large economies as a whole
5 Key Economic Assumptions
Scarcity
Trade-offs
Selfishness
Marginal costs & benefits
Models and graphs
Trade-offs
Because of scarcity, choices must be made. These choices will always have a cost
ALL the alternatives that we give up when we make a choice
Selfishness
Everyone’s goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction
Marginal costs and benefits
Everyone makes decisions by comparing the costs and benefits of every choice
Models and Graphs
Real life situations can be explained and analyzed through simplified models and graphs
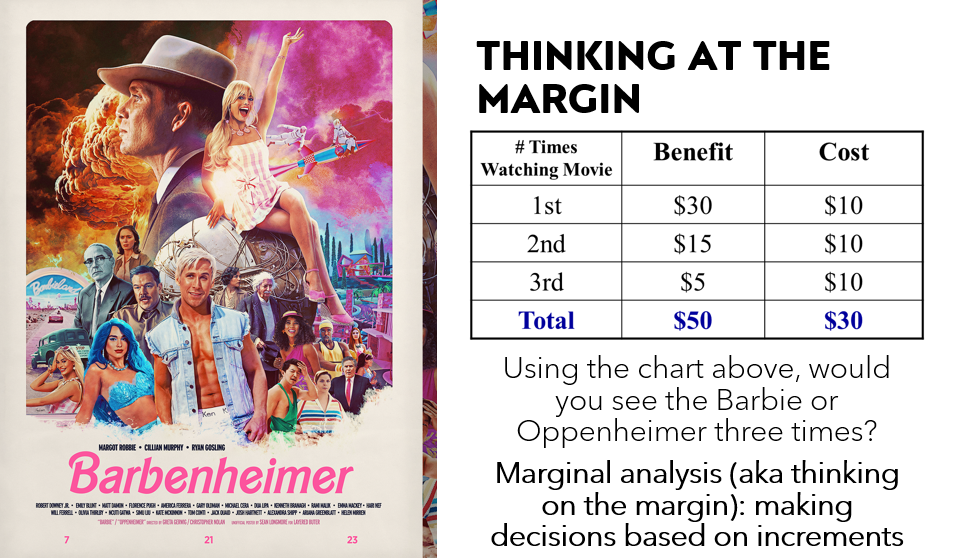
Marginal analysis (aka thinking on the margin)
Making decisions based on increments
Trade-offs vs Opportunity Costs
Trade-offs: ALL the alternatives that we give up when we make a choice
Opportunity Costs: MOST desirable alternative given up when making a choice
Opportunity costs
MOST desirable alternative given up when making a choice
Utility
Satisfaction
Marginal
Additonal
Allocate
Distribute
Price vs Cost
•Price – amount buyer (or consumer) pays for a good/service
•Cost – amount the seller pays to produce a good
Investment
The money spent by businesses to improve this production
Consumer goods
Created for direct consumption (ex. pizza)
Capital goods
Created for indirect consumption (the goods used to make consumer goods)
4 Factors of Production
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurship
Land
All natural resources (Land, water, animals, etc)
Labor
Effort a person devotes to a task for which they are paid
Capital
Human-made resources used to produce other goods or services
Entrepreneurship
Ambitious leaders that combine the other factors of production to create goods and services
Physical Capital
Also known as capital goods. These are human-made goods, such as tools or buildings
Human Capital
These are skills and knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience