Bio Unit 3
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
what does Carbon have the ability to do
bond with 4 other atoms
How is carbons unique prop. benefit it
it is the basis for building large and diverse organic compounds
what is the backbone of most organic mole.
carbon chains
what are isomers
have the same molecular formula but have different structures
what us an example of an isomer
sugar (C6H12O6) or methamphetamine (one is illegal drug other is sinus medicine)
what are hydrocarbons
composed of carbon and hydrogen
what is an example of a hydrocarbon
ethane
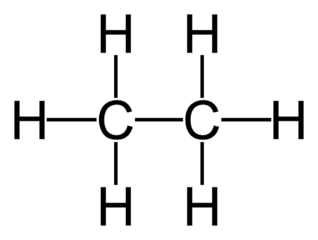
what is an example of both a isomer and hydrocarbon
1 Butane and 2 Butane
image of 1 butane
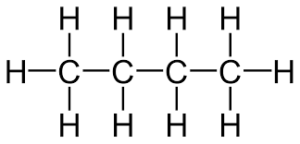
a organic compound’s prop. depend on
the size and shape of the C backbone
what atoms are attached to the skeleton
what are the atoms attached to the organic compounds called
functional groups
what do functional groups do
give organic mole. their specific prop.
what is a prop. of func. groups
hydrophilic
what are the 4 classes of bio. mole. that contain very large mole.
carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins
what is a macromolecule and why are the 4 classes called it
a giant mole. fromed by joining of other mole.
because of their large size
what is a polymer and why are the 4 classes called it
a large mole. with many similar monomers linked by covalent bonds (make up macro.)
because they are made from identical or similar building blocks strung together
what are dehydration reactions
water is taken out to LINK monomers to form polymers
what is hydrolysis
water is added in to BREAK polymers
what mediates these reactions
enzymes
what are enzymes
specialized proteins that speed up reactions
how does hydrolysis and dehydration work when we eat food
hydrolysis occurs to BREAK down our food and then dehydration occurs to LINK the broken down monomers into something more helpful
what is the mole. range for carbs
small sugar mole. (monomers) to big polysaccharides
sugar monomers are
monosaccharides
what are monosaccharides
small single sugars
a monosacc. has a formula that is …
and has what groups
a mult. of CH2O and has hydroxyl groups and carbonyl group
what is the chemical formula for a monosacc. that has 3 C or one for 24 C
C3H6O3
C24H48O24
what do carbs have in them
sugar
why do we eat carbs
to get the sugar for energy
in something ends in -ose
it is a sugar
2 monosacc. can bond to form __________ in a ___________
disaccharide
dehydration reaction
what does the FDA recommend be the % of daily cals come from added sugar
10%
what does research say about high sugar intake
it generally causes adverse health effects (diabetes and obesity being the most common)
____ and ______ are storage polysaccharides
starch
glycogen
what is starch
how plants store extra glucose/carbs (has dif. shape than glycogen)
what is glycogen
how animals store extra glucose (stored in muscles)
what is cellulose
structural, found in plant cell walls
what is chitin
component of insect and fungal cell walls (ex: crab exoskeleton)
7 food sources of carbs
pasta - cereal - bread - fruit - tacos - cookies - candy - honey - cheese - milk - potatoes
what are the characteristics of lipids
hydrophobic and made of C and H
what do lipids not have
monomers or polymers
Type of lipid - Fats (triglycerides) -
consist of glycerol linked to 3 fatty acid tails
it is non-polar so it has no charge
what are the 2 categories of fat
unsaturated and saturated
unsaturated fatty acids -
fatty acids with one or more double bonds
typical of plant oils
generally liquid at room temp
saturated fatty acids -
fats with max number of H
found in animal fats
generally solid at room temp
how is the double bond in an unsat. fat made
take an H out
what does having a double bond cause the triglyceride tail to do
it makes it bend - which then makes less room for other mole. to be closer together - so they are further apart - making them usually liquids
what are trans fats
unsat. fats that have been converted to sat. fats by adding H (associated with health risks)
what is an example of the exception of an unsat. fat being liquid
fat in fish
type of lipid - phospholipids -
lipid that has a phosphate group “head” (neg. charge) and 2 tails
what are phospholipids components of
cell membrane
type of lipid - steroids
include cholesterol and some hormones
20 C and 4 ring backbone
what is cholesterol
component in animal cell membranes and is a precursor for making other steroids, (including sex hormones)
what are the 2 main things cholesterol does
maintain fluidity of cell membrane and it is a chemical messenger
what makes our cholesterol
liver (about 70-80% of what we need of it daily)
but we can and do get 20-30% of it from the food we eat
what would the image of a phospholipid look like

what are anabolic steroids
synthetic variants of testosterone
proteins are
involved in almost every dynamic function in the body and are very diverse
proteins function as
enzymes
transport proteins embedded in cell membranes
defensive proteins (antibodies)
signal proteins such as most hormones (why doctors have to be very careful during and after a heart transplant so the body doesn’t reject the heart)
receptor proteins
contractile proteins found within muscle cells
structural proteins (ex collagen) (we are made of proteins
storage proteins
proteins are made of a different arrangement of…
a common set of 20 amino acids and monomers
the functions of proteins depend on what
individual shape
what is denaturation
protein unravels, loses its specific shape, and loses its function
how does denaturation happen
temp., PH, salt concentration
protein diversity is based on
the different sequences of amino acids
amino acids are monomers that contain…
an amino group, a carboxyl group, an H atom, and an R group
the R groups…
distinguish 20 amino acids each with specific properties
how are the amino acids monomers linked
dehydration
joining the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of the next amino acid creates
a peptide bond
additional amino acids can be added by the same process to create…
a chain of amino acids called a polypeptide
where are proteins made
in the ribsome
are R groups polar or non-polar
can be either
what are the 4 levels of structure for a protein
primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure
what is the primary structure
the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
what is the secondary structure
the coiling or folding of the chain, stabilized by H bonds
what is the tertiary structure
the overall 3D shape of the polypeptide, resulting from interactions among the R groups
what is the quaternary structure
proteins made of more than one polypeptide
what are the monomers and polymers of nucleic acids
m- nucleotides p-polynucleotide
nucleotides are composed of
a sugar and a phosphate group (side of the ladder) and the nitrogenous base (the information) (the letters)
DNA is
a double helix and it gets its name from its sugar (deoxyribose)
RNA is
a single polynucleotide and gets its name from its sugar (ribose)
DNA and RNA serve as the
blueprints for proteins and thus control the LIFE of a cell
DNA is a mole. of
inheritance
how are DNA and RNA the life of a cell
DNA (instructions)
RNA (Manuel)
Protein (Structure)
food sources of lipids
steak, milk, most (normal) dairy products, vegetable oil (or any oil), red meat, chicken, fried food, eggs
food sources of protein
chicken steak, fish, turkey, eggs, dairy, nuts, beans
what is the difference between the “organic” term we us in class vs. the way Whole Foods uses it
the way organic is used in class is having carbon/ being carbon based
in whole foods it means no pesticides or chemicals were used
What roles do lipids play in the body?
they store energy, make up the cell membrane, cushioning, help with vitamin absorption
what is the one enzyme we discussed in class
lactase
what is the term for making unsaturated fats saturated by adding H (aka making them trans fats)
hydrogenated vegetable oils
what are the main 3 types of lipids
fats (triglycerides), phospholipids, and steroids
why don’t we care about the food sources of nucleic acids
because any food that is/was made from anything living(animals and plants and fungi, etc) has nucleic acids
what are the monomers and polymers of proteins
m-amino acids p-polypeptides
what are the monomers and polymers of carbs
m-monosaccharides p-polysaccharides