Psychology Unit 5: Mental and Physical Health
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
216 Terms
psychological disorder
deviant, distressful, and dysfunctional behavior patterns
medical model
view of mental illness as due to a physical disorder requiring medical treatment
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
disthesis-stress model
a diagnostic model that proposes that a disorder may develop when an underlying vulnerability is coupled with a precipitating event
DSM-5
the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition; a widely used system for classifying psychological disorders.
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
a psychological disorder marked by extreme inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity
anxiety disorders
disorders in which the main symptom is excessive or irrational worry and fearfulness
social anxiety disorder
an anxiety disorder involving the extreme and irrational fear of being embarrassed, judged, or scrutinized by others in social situations
generalized anxiety disorder
an anxiety disorder in which a person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in a state of autonomic nervous system arousal
panic disorder
An anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable minutes-long episodes of intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, or other frightening sensations.
agoraphobia
fear or avoidance of situations, such as crowds or wide open places
specific phobia
a disorder that involves an irrational fear of a particular object or situation that markedly interferes with an individual's ability to function
obsessive-compulsive disorder
An anxiety disorder characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsession) and/ or actions (compulsions).
obsession
an unwanted thought or image that takes control of the mind
compulsion
an unreasonable need to behave in a certain way to prevent a feared outcome
post-traumatic stress disorder
an anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience
major depressive disorder
severe form of lowered mood in which a person experiences feelings of worthlessness and diminished pleasure or interest in many activities
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger,sleep, arousal, and mood.
bipolar disorder
mood disorder in one experiences both manic and depressed episodes
mania
a mood disorder marked by a hyperactive, wildly optimistic state
Schizophrenia
a psychological disorder characterized by delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, and/or diminished, inappropriate emotional expression
positive symptoms
symptoms of schizophrenia that are excesses of behavior or occur in addition to normal behavior; hallucinations, delusions, and distorted thinking
negative symptoms
symptoms of schizophrenia that are marked by deficits in functioning, such as apathy, lack of emotion, and slowed speech and movement
Hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
Delusions
false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur, that may accompany psychotic disorders
flat affect
a lack of emotional responsiveness
dopamine hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia involves an excess of dopamine activity
somatic symptom disorder
psychological disorder in which the symptoms take a somatic (bodily) form without apparent physical cause
conversion disorder
A rare somatoform disorder in which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms for which no physiological basis can be found.
illness anxiety disorder
a disorder in which a person interprets normal physical sensations as symptoms of a disease
dissociative disorders
disorders in which conscious awareness becomes separated (dissociated) from previous memories, thoughts, and feelings
dissociative identity disorder (DID)
the occurrence of two or more distinct identities in the same individual
dissociative amnesia
Dissociative disorder characterized by the sudden and extensive inability to recall important personal information, usually of a traumatic or stressful nature.
dissociative fugue
disorder in which one travels away from home and is unable to remember details of his past, including often his identity
personality disorders
psychological disorders characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social functioning
anti-social personality disorder
A personality disorder characterized by a pattern of disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others.
paranoid personality disorder
type of personality disorder characterized by extreme suspiciousness or mistrust of others
schizoid personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by persistent avoidance of social relationships and little expression of emotion
schizotypal personality disorder
Person has several traits that causes interpersonal problems, including inappropriate affect, paranoid/magical thinking, off beliefs
borderline personality disorder
condition marked by extreme instability in mood, identity, and impulse control
histrionic personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by excessive emotionality and preoccupation with being the center of attention; emotional shallowness; overly dramatic behavior
narcissistic personality disorder
characterized by a grandiose sense of self-importance, a preoccupation with fantasies of success or power, and a need for constant attention or admiration
dependent personality disorder
A personality disorder characterized by a pattern of clinging and obedience, fear of separation, and an ongoing need to be taken care of.
avoidant personality disorder
A personality disorder characterized by consistent discomfort and restraint in social situations, overwhelming feelings of inadequacy, and extreme sensitivity to negative evaluation.
obsessive-compulsive personality disorder
a personality disorder characterized by preoccupation with orderliness, perfection, and control
anorexia nervosa
an eating disorder in which an irrational fear of weight gain leads people to restrict their food consumption
bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise
binge eating disorder
significant binge-eating episodes, followed by distress, disgust, or guilt, but without the compensatory purging, fasting, or excessive exercise that marks bulimia nervosa
resilience
the personal strength that helps most people cope with stress and recover from adversity and even trauma
catatonia
a state of unresponsiveness to one's outside environment, usually including muscle rigidity, staring, and inability to communicate
Psychotherapy
treatment involving psychological techniques; consists of interactions between a trained therapist and someone seeking to overcome psychological difficulties or achieve personal growth
biomedical therapy
prescribed medications or medical procedures that act directly on the patient's nervous system
eclectic therapy
an approach to treatment in which the therapist uses whichever techniques seem most useful and relevant for a given patient
Psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud's therapeutic technique. Freud believed the patient's free associations, resistances, dreams, and transferences - and the therapist's interpretations of them - released previously repressed feelings, allowing the patient to gain self-insight.
resistance
in psychoanalysis, the blocking from consciousness of anxiety-laden material
Transference
in psychoanalysis, the patient's transfer to the analyst of emotions linked with other relationships (such as love or hatred for a parent)
humanistic therapy
Focuses on removing obstacles that block personal growth and potential.
insight therapies
a variety of therapies that aim to improve psychological functioning by increasing a person's awareness of underlying motives and defenses
client-centered therapy
a humanistic therapy, developed by Carl Rogers, in which the therapist uses techniques such as active listening within a genuine, accepting, empathic environment to facilitate clients' growth.
active listening
Empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates, and clarifies. A feature of Rogers' client-centered therapy.
unconditional positive regard
according to Rogers, an attitude of total acceptance toward another person
behavior therapies
action therapies based on the principles of classical and operant conditioning and aimed at changing disordered behavior without concern for the original causes of such behavior
counterconditioning
behavior therapy procedures that use classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors; include exposure therapies and aversive conditioning
flooding therapy
A behavioral treatment for phobias that involves prolonged exposure to a feared stimulus, thereby providing maximal opportunity for the conditioned fear response to be extinguished.
systematic desensitization
A type of exposure therapy that associates a pleasant relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli. Commonly used to treat phobias.
aversive conditioning
a type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior (such as drinking alcohol)
behavior modification
the use of operant conditioning techniques to bring about desired changes in behavior
cognitive therapy
therapy that teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking and acting; based on the assumption that thoughts intervene between events and our emotional reactions
rational emotive behavior therapy
a confrontational cognitive therapy, developed by Albert Ellis, that vigorously challenges people's illogical, self-defeating attitudes and assumptions
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
a popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
meta-analysis
a procedure for statistically combining the results of many different research studies
evidence-based practice
clinical decision making that integrates the best available research with clinical expertise and patient characteristics and preferences
psychopharmacology
the study of the effects of drugs on mind and behavior
therapeutic alliance
a bond of trust and mutual understanding between a therapist and client, who work together constructively to overcome the client's problem
tardive dyskinesia
involuntary movements of the facial muscles, tongue, and limbs; a possible neurotoxic side effect of long-term use of antipsychotic drugs that target certain dopamine receptors
antipsychotic drugs
medications that are used to treat schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders-block dopamine receptors
mood stabilizing drugs
used to treat mood instability and bipolar disorders; an example is lithium
anti-depressant drugs
drugs used to treat depression; also increasingly prescribed for anxiety. Different types work by altering the availability of various neurotransmitters
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
a group of second-generation antidepressant drugs that increase serotonin activity specifically, without affecting other neurotransmitters
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
a biomedical therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient
transcraniel magnetic stimulation
Alters activity of neurons in the brain
Psychosurgery (lobotomy)
surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior
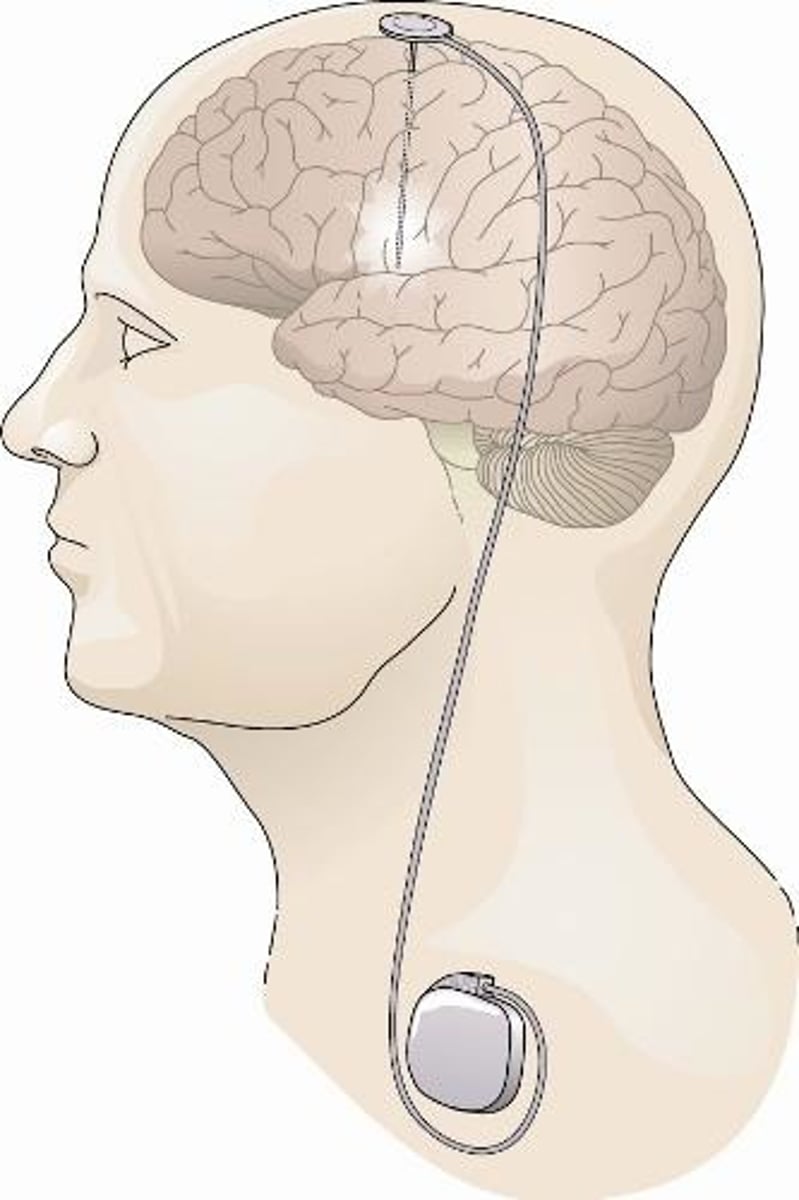
deep brain stimulation
electrical stimulation applied through surgically implanted electrodes; used to treat some anxiety and mood disorders
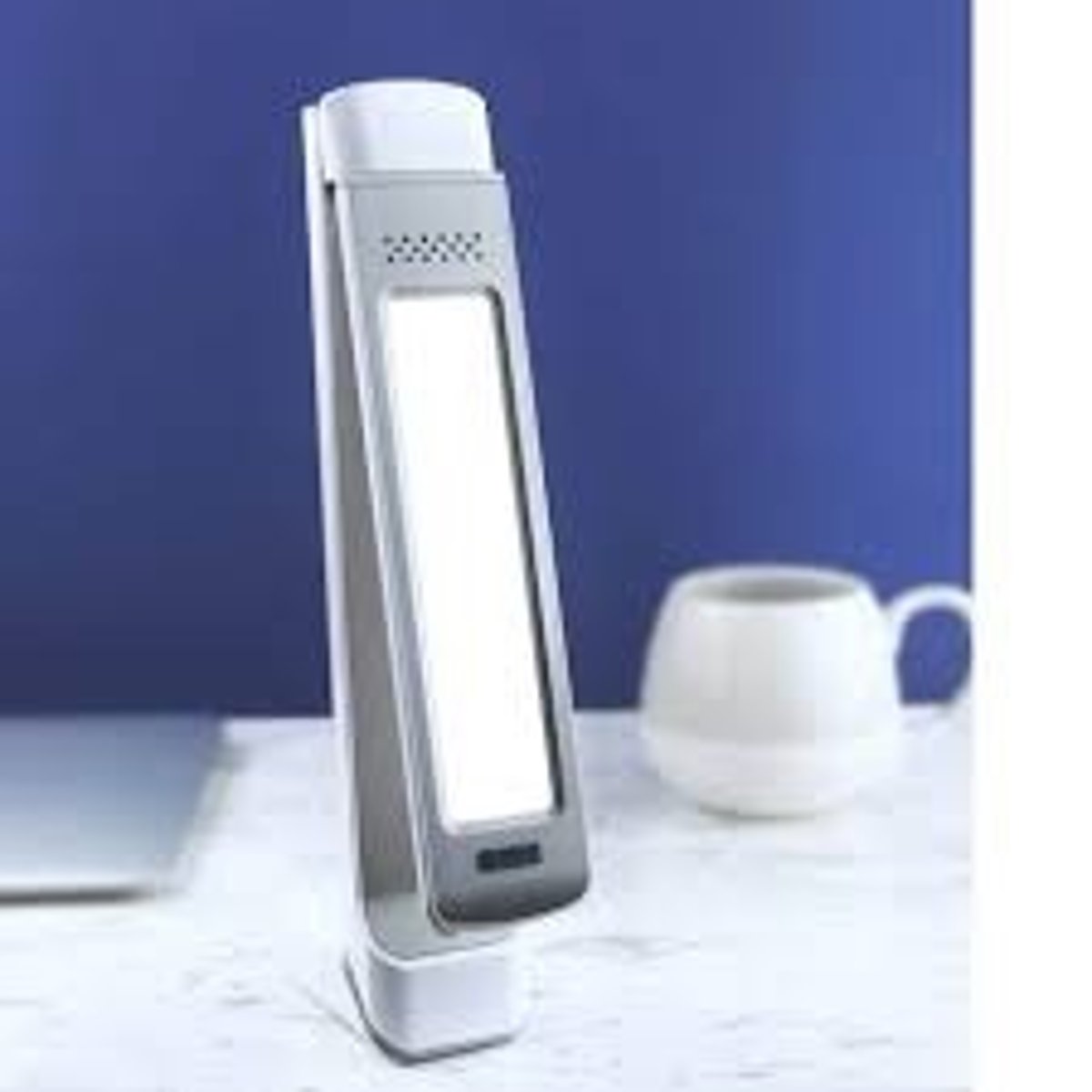
light exposure therapy
Treats seasonal affective disorder (SAD); scientifically proven to be effective, exposure to daily doses of intense light. Increases activity in the adrenal gland and the superchiasmatic nucleus.

family therapy
therapy that treats the family as a system. Views an individual's unwanted behaviors as influenced by, or directed at, other family members

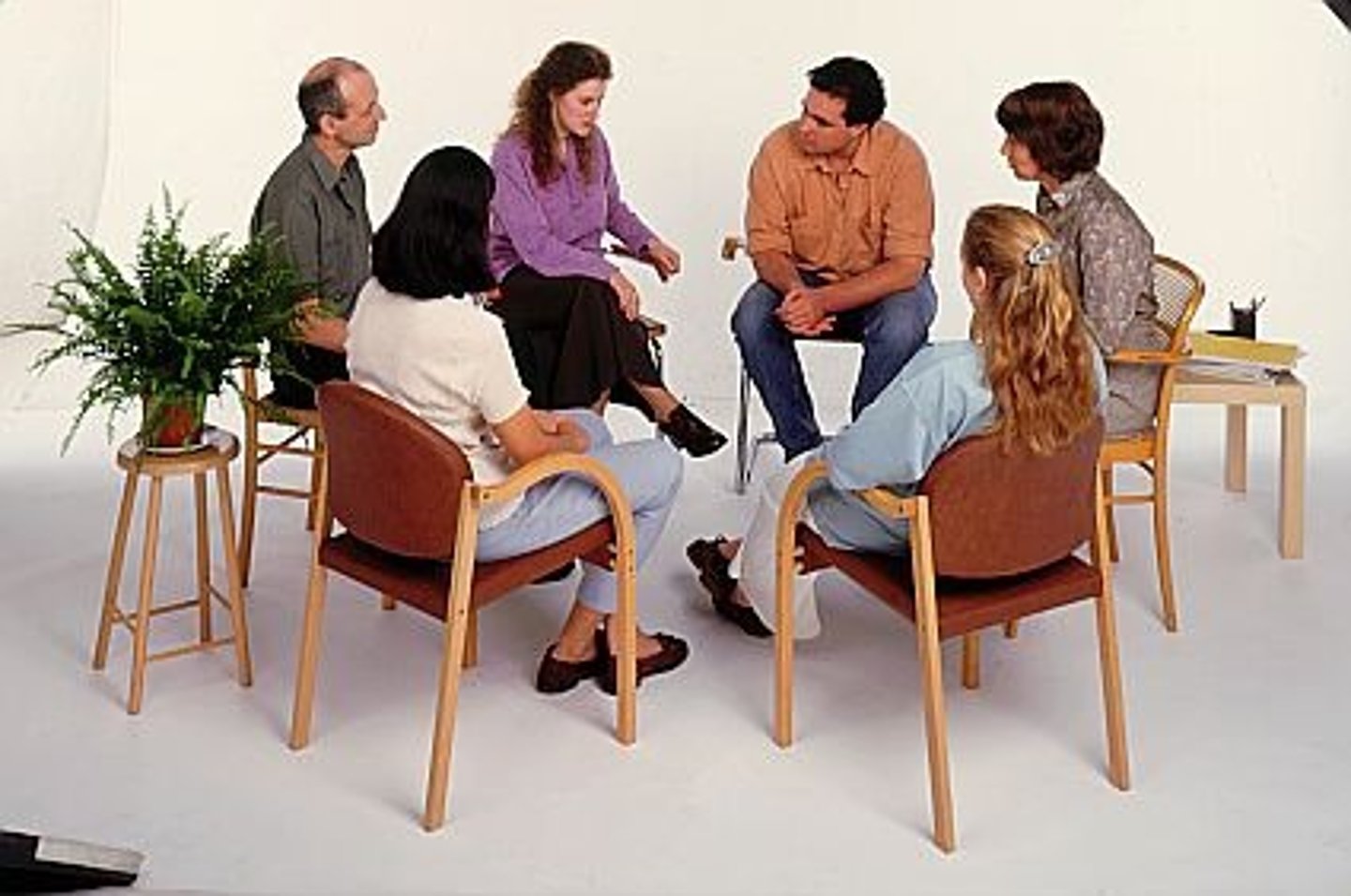
group therapy
therapy conducted with groups rather than individuals, permitting therapeutic benefits from group interaction

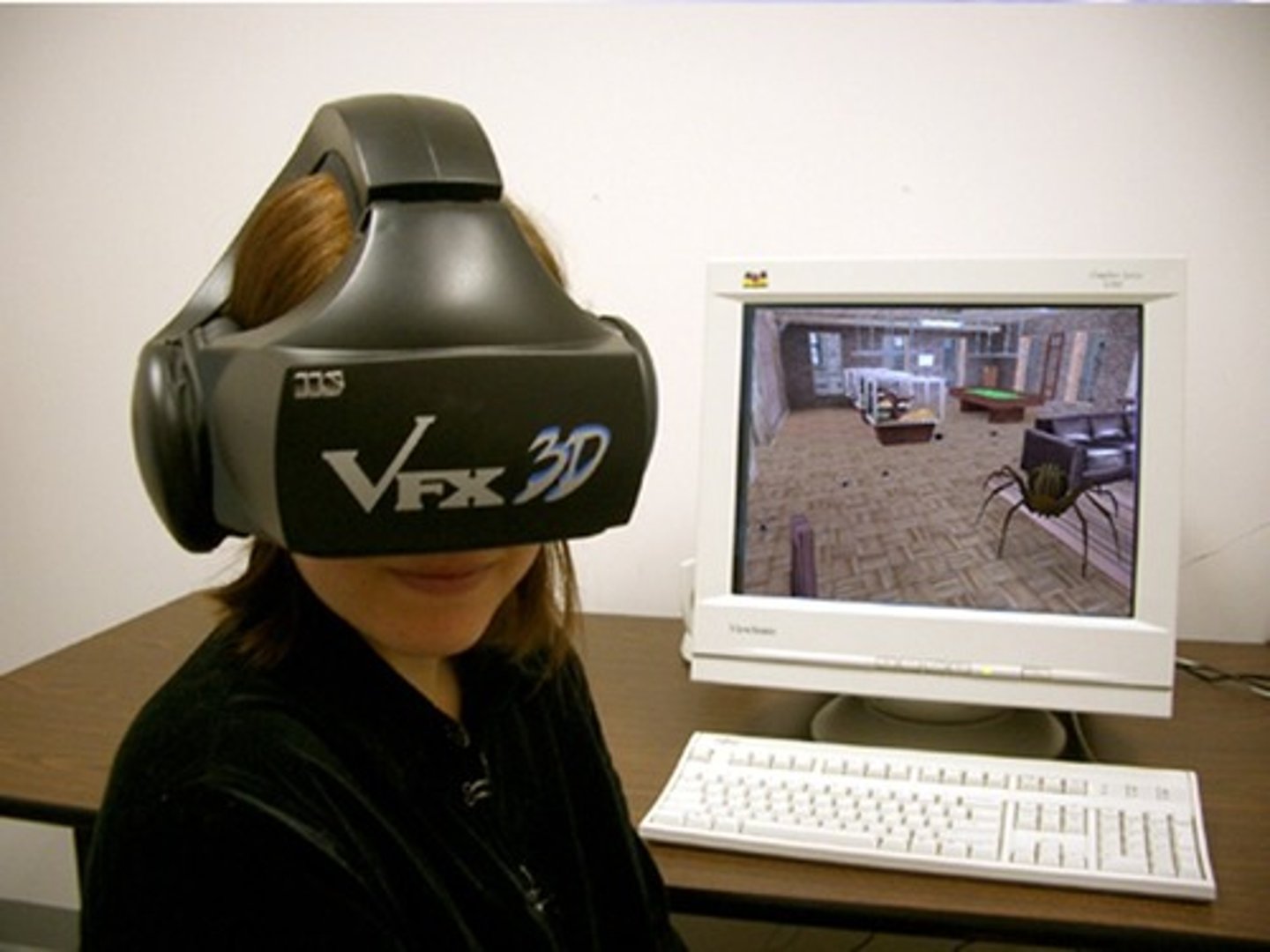
virtual reality exposure
Use of computer-generated images to present fear stimuli. The virtual environment responds to a viewer's head movements and other inputs.

token economy
an operant conditioning procedure in which people earn a token of some sort for exhibiting a desired behavior and can later exchange the tokens for various privileges or treats

health psychology
the subfield of psychology concerned with ways psychological factors influence the causes and treatment of physical illness and the maintenance of health
Psychoneuroimmunology
the study of how psychological, neural, and endocrine processes together affect the immune system and resulting health
Stress
the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors, that we appraise as threatening or challenging
Hypertension
higher than normal blood pressure
immune suppression
Any factor that prevents the immune system from working efficiently.
Eustress
A positive stress that energizes a person and helps a person reach a goal
distress
negative stress
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
Stressful or traumatic experiences, including abuse, neglect, and a range of household dysfunction, such as witnessing domestic violence or growing up with substance abuse, mental disorders, parental discord, or crime in the home.
General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)
Selye's concept of the body's adaptive response to stress in three phases—alarm, resistance, exhaustion.
alarm
the first phase of the stress response, in which the person faces a challenge and starts paying attention to it.
resistance
The second stage of the general adaptation syndrome, when there are intense physiological efforts to either resist or adapt to the stressor.