AST101 - Lecture 22 (Radial Velocity)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
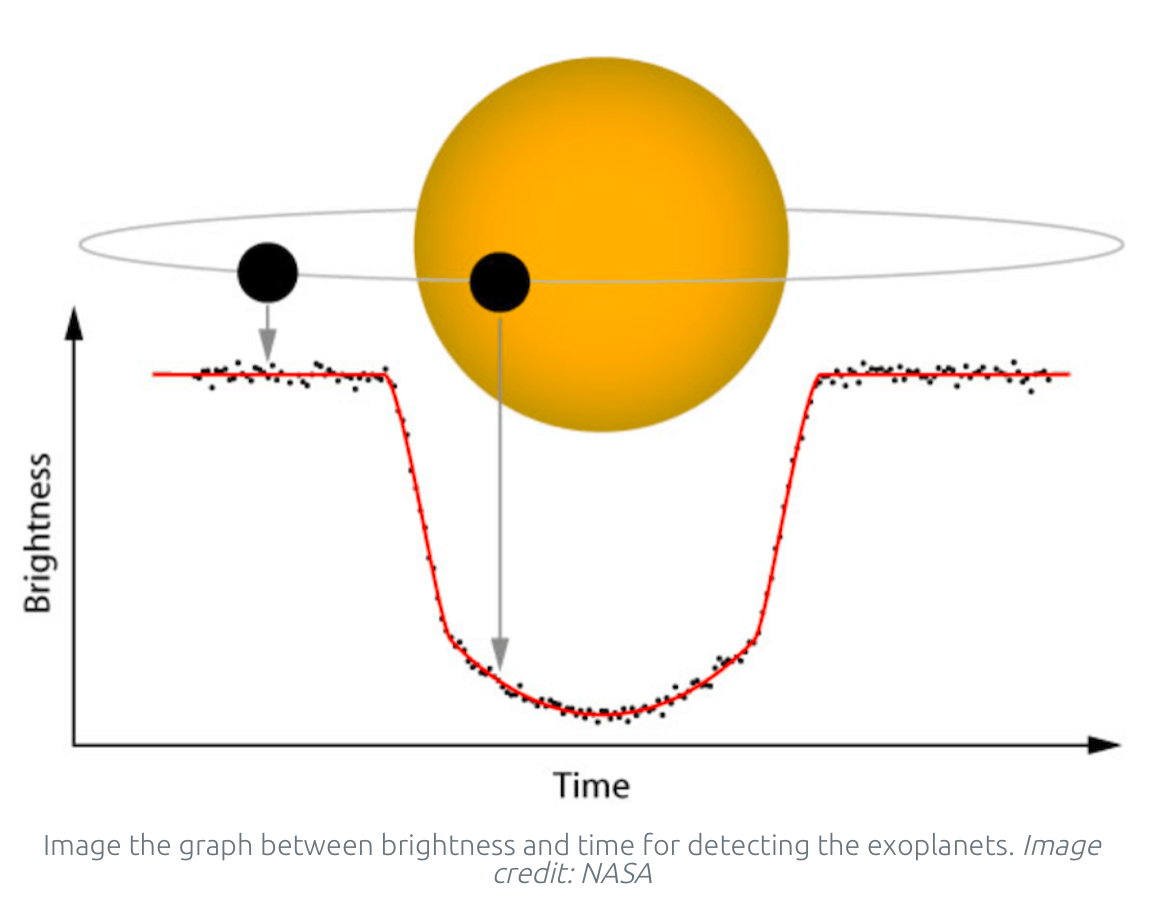
How can learn about a planet’s rings through the transit method
Can see extra small dips during transit
Use small variations in the light curve of the bottom of a transit to make surface maps of an exoplanet
If there was just a disk it’d just be flat
Can see variations in the light curve at the bottom to see what else is blocking out the light
Learn if there’s earthquake the way the light curves
What is the purpose of the Transit Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS)
Will look for transit toward 500,000 stars covering 85% of the sky
What is the problem with Kepler’s First Law
It orbits the sun in an eliptical patterns with the sun at one focus, but it’s a bit wrong as it orbits their common center of mass
What is the doppler effect?
Sources moving towards you shift to higher frequency (shorter wavelength)
Sources moving away from you shift to lower frequency (longer wavelength)
Only measures line of sight
Object moving away directly measure all of its speed
Moving across our line of sight
Measure none of its speed
Moving diagonally measure only part of its speed
In all cases, the only part of the motion we can measure is the radial velocity
What is the center of mass
Point where one could put a fulcrum to keep system balance
For the Sun and the Earth, the center of mass is almost at the center of the Sun, as it’s much more massive
What is the orbits of stars like?
Most stars are much more massive than their planets
Therefore, center of mass is close to but not at the center of the star
From our perspective star wobbles toward and away from us
What is the doppler method?
Exoplanet moves in a large orbit but exoplanet is too faint to see
Parent star moves in a tiny orbit and is bright enough to see
Use doppler effect applied to the spectrum of the star to measure the radial velocity (wobble) of the star as it orbits the center of the mass
Measure the mass and where it is in its orbit
The fact that the sun wobbles is that there’s a planet making it wobble by changing it’s center of mas
The amount of wobble changes how much shift is seen
What is 51Pegasi B?
Exoplanet revealed off the doppler shifts of the star of 51 pegasi
Radial velocity peaked around 60ms
This was the first extrasolar planet to be discovered around a Sun-like star
What does the doppler method tell us
Tell us we found an exoplanet
Orbit cannot be face on
Calculate the orbit period
Big dip and little dip
Except sun exoplanet to do a wobble in one period
Using kepler third law we can use the period to calculate the distance of the exoplanet from its parent star
From the semi-major axis that we got from the orbital period
The velocity change gives us the star’s speed, which if we know the star’s mass, tells us the exoplanets mass
What are some characteristics of 51 Pegasi B?
4 day orbital period
0.053 AU semi major axis
Mass 0.47M
Half the mass of Jupier 7 times closer to the Sun orbited 4 days
Named hot jupiter
What are hot jupiters?
Proven to be the most common type of exoplanet found in both transit and Doppler searcher for exoplanets
At odds with the nebular theory
Form in outer solar system but move inward via planetary migration
Interaciton with another object
Wind from the hot star pushes it
Migrated slowly towards the star
What are Hot Jupiters so Common?
Doppler: Heavy and close-in means they produce a large wobble in their parent star
Transit: Large and close-in means they produce a deep transit in the parent star light curve
Observational bias
Close-in means wobbles or transit repeat themselves quickly
With better instruments the fraction of these should go down
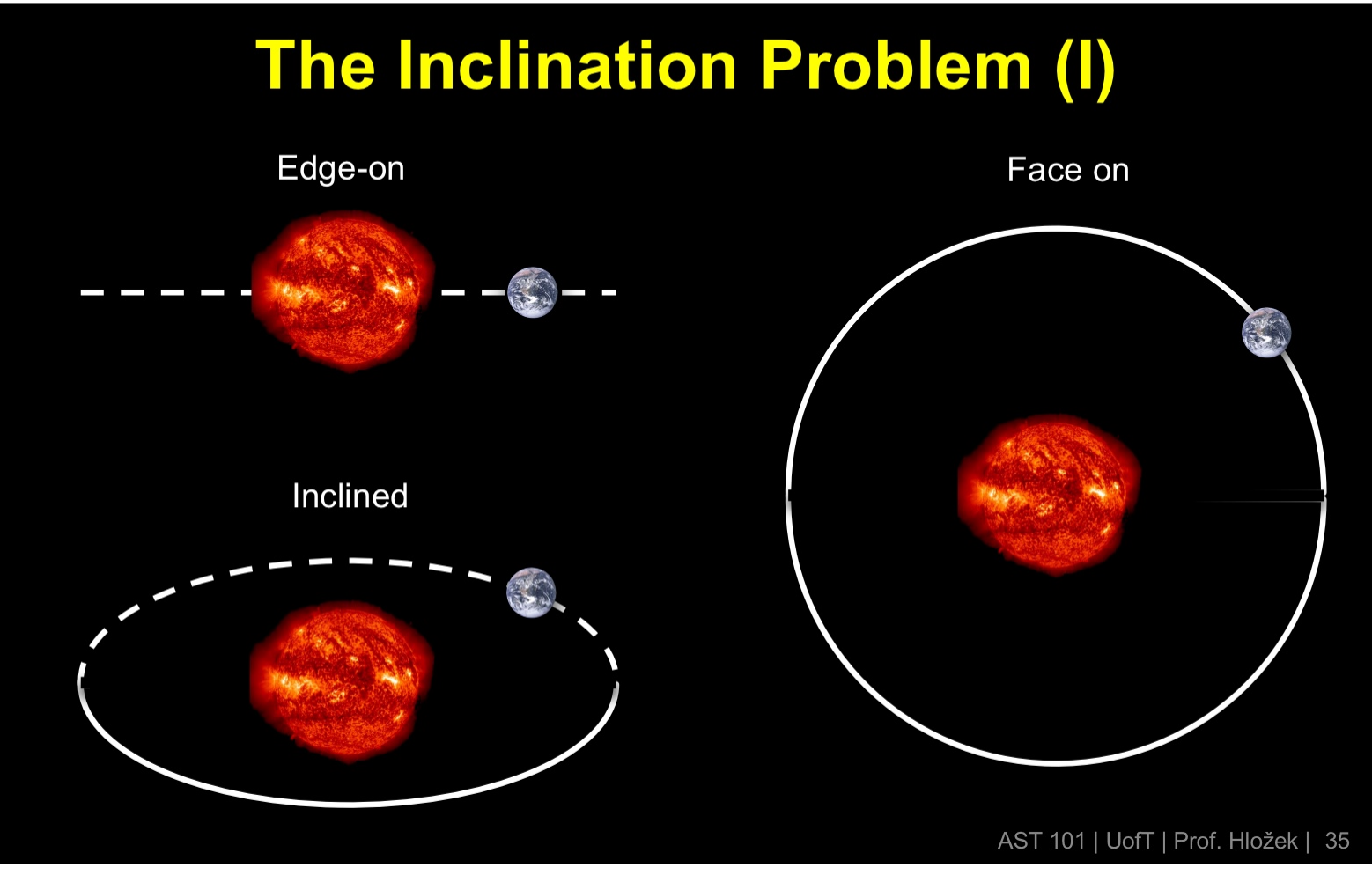
How does the inclination of a planet be a problem?
Easier to find things that are edge-on
One catch to the doppler method is that we can only measured the radial velocity
If the orbit is edge-on we see all the star’s motion
Hard to tell exactly what the angle is
If the orbit is inclined, we can see some of the star’s motion
If the orbit is face on, we don’t see any of the star’s motion (can’t detect the exoplanet
Can only find with the doppler method
Lower limit on true doppler velocity
Know the minimum possible mass of the exoplanet
If the exoplanet also transit we know it must be nearly edge-on and so we know its actual mass
What are the strengths of the doppler method?
Does not need continuous monitoring
Works for any orientation of the exoplanet’s orbit (beside face on)
Very good for massive planets in close-in orbits
What are the weaknesses of the Doppler Method?
Needs a big telescope to measure spectra and doppler shifts
Can only measure a minimum mass unless inclination is known
Can only study one star a time
Biased toward close-in exoplanets
What can we learn by comining the transit and doppleer method?
Transit measures size and inclination’
Doppler gives us an exoplanet’s mass
Measure the density by combining which we can begin to figure out its interior composition
Graph plot mass (horizontal) vs size (vertical axis)
Dotted lines show various possible densities
Solar system planets are shown in green
Selected transiting exoplanets are shown in red