Pediatrics - Exam 1
1/525
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
526 Terms
Term infants
delivery at or beyond 37 weeks
Preterm infants
delivery before 37 weeks
late: between 34-37
extreme: before 28
Newborn
first 28 days of life
Newborn medical history
maternal and paternal PMH/genetics
maternal obstetric history
Tool used to estimate gestational age
Ballard calculator
Birth weight classification
extremely low <1000 g
very low <1500 g
low < 2500 g
normal >= 2500
SGA
small for gestational age
symmetrical (ht, wt, and hc are all under 10%) - early pregnancy problem
asymmetrical (just wt under 10%) - late pregnancy problem
AGA
appropriate for gestational age
LGA
large for gestational age
IUGR
intrauterine growth restriction
Intrauterine growth curves
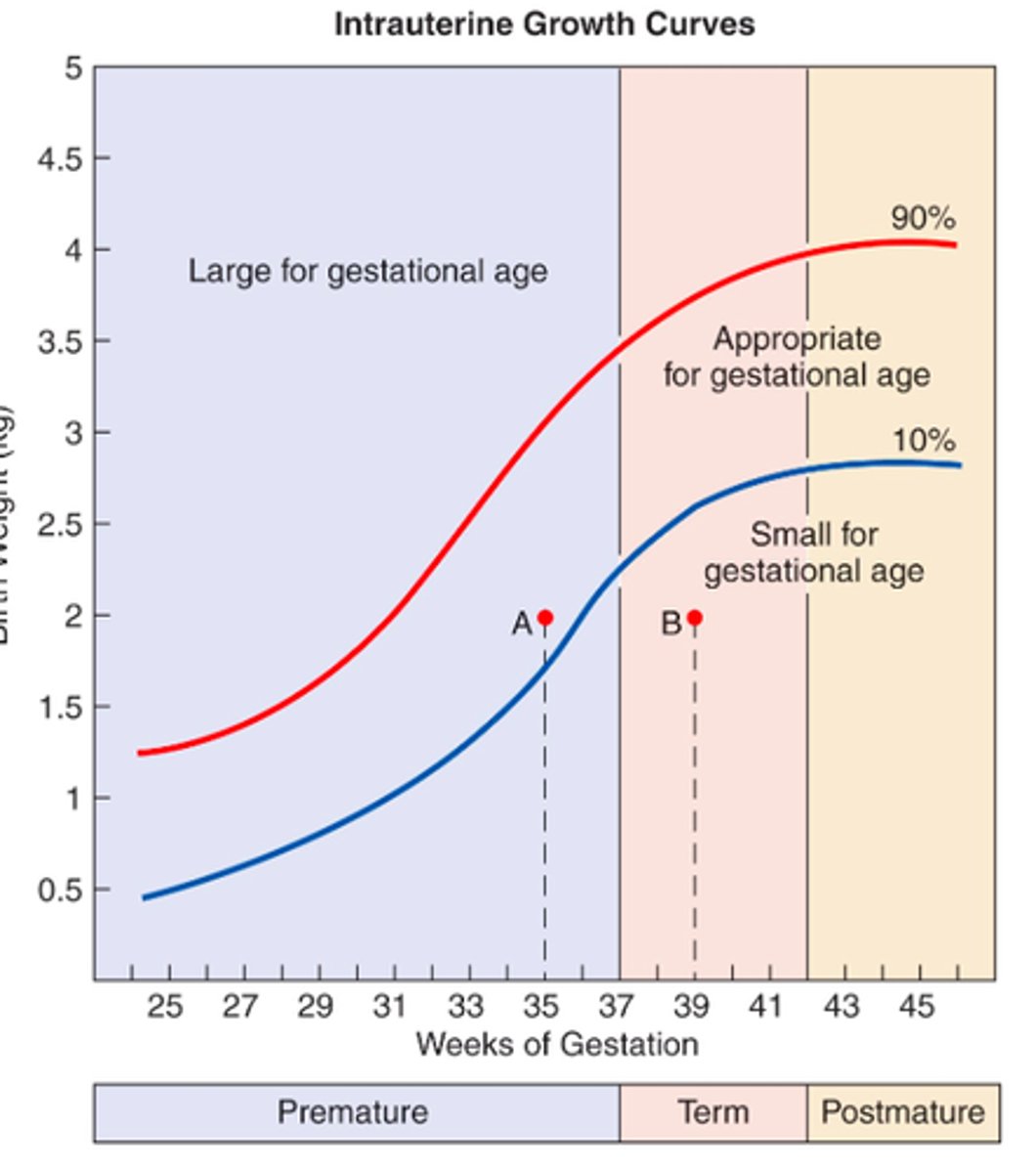
Asymmetrical SGA
event late in pregnancy
placental insufficiency
pregnancy induced HTN
maternal age over 35
poor weight gain during pregnancy
multiple gestations
Symmetrical SGA
event early in pregnancy
maternal drug/alcohol use
chromosomal abnormalities
congenital viral infections
Newborn exam
observation, chest auscultation, inspection
first look for airway/skin color
Cyanosis and pallor in newborn, concern about...
cardiac output
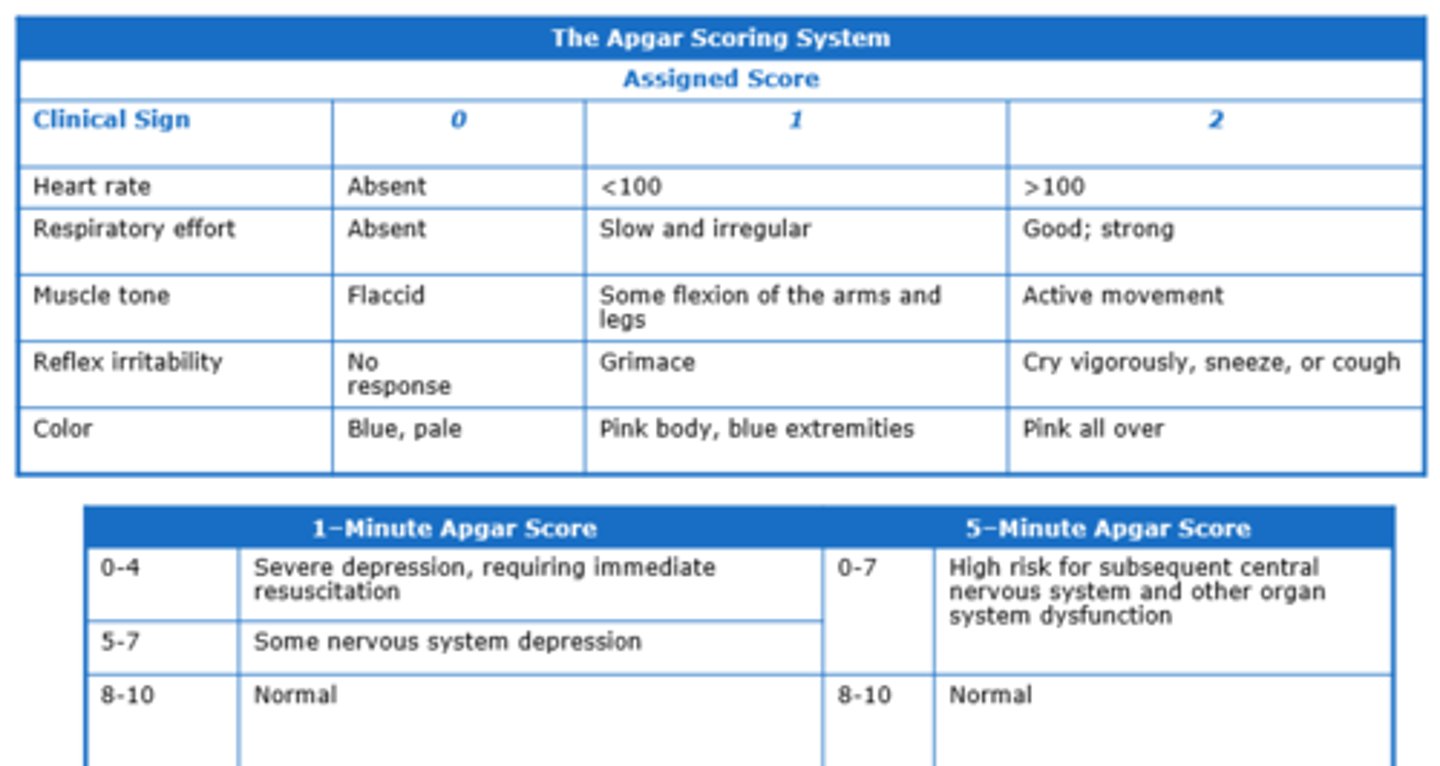
APGAR scoring system
done at 1 and 5 minutes
repeated at 20 if low
Nursery examination - vitals
HR: 120-160
RR: 30-60
SBP: 50-70 and increased during first week
Nursery examination - auscultation
cardiac murmurs are common in first few hours
MC heart disease presentation: cyanosis and CHF with abnormal pulses/perfusion
Hyperbilirubinemia
jaundice
caused by increased levels of bilirubin - byproduct of normal breakdown RBCs by liver
yellow color of skin and eyes
measured via total serum bilirubin
Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia
jaundice present to some degree in most newborns due to immature liver function
appears after 24 hrs between 2nd-5th day of life and clears by 2 weeks
Increased bilirubin production - hemolytic causes
antibody mediated hemolysis: Coombs+ with ABO incompatibility and/or Rh isoimmunization
non immune hemolysis: Coombs- with hereditary spherocytosis, G6PD deficiency or other enzymes, or infectious sepsis
Increased bilirubin production - nonhemolytic causes
enclosed hemorrhage (cephalohematoma)
polycythemia
bowel obstruction (increased enterohepatic circulation)
Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia - Decreased rate of conjugation
Crigler-Naijar: glucuronyl transferase deficiency
Gilbert syndrome: glucuronyl transferase deficiency
Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia - other/unknown causes
race
prematurity
breast-milk jaundice
breast-feeding jaundice
Breast milk jaundice
seen at 1 week and peaks during 2nd-3rd week
something in milk affecting infant liver function
resolves in 6-12 weeks
no evidence of hemolysis, hypothyroidism, etc
Breast feeding jaundice
occurs in first week of life
inadequate milk intake leading to dehydration/low caloric intake
supplementation/breast pump
2-3 day post discharge visit
Jaundice evaluation
predischarge TSB or transcutaneous bilirubin (TcB) measurement
follow up within 24-48 hrs for all infants before 72 hrs of age
feeding/elimination history
birth weight and changes
assessment of blood type, Coombs, CBC with smear, serum albumin, G6PD test, fractionated bilirubin level
Bilirubin toxicity
neurotoxic
acute bilirubin encephalopathy
kernicterus - staining of basal ganglia and nuclei
Bilirubin toxicity treatment
phototherapy
exchange transfusion
Conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia - anatomic causes
biliary atresia
choledochal cyst
Conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia - metabolic causes
alpha 1 anti-trypsin deficiency
neonatal hemochromatosis
cystic fibrosis
hypothyroidism
hypopituitarism
Conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia - infectious causes
TORCH
sepsis
UTI
Conjugated (direct) hyperbilirubinemia - toxic causes
parenteral nutrition
drugs
Respiratory distress in the newborn
meconium aspiration
hyaline membrane disease
persistent pulmonary HTN
pneumothorax
transient tachypnea
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
apnea of prematurity
Respiratory distress treatment
supplemental oxygen - PaO2 60-70mmHg
umbilical or arterial blood line with frequent blood gas
pulse ox monitoring
CXR, CBC, and blood glucose
Meconium aspiration
fetal aspiration of meconium and amniotic fluid with period of stress
respiratory distress, limpness, and cyanosis
Meconium aspiration risk factors
aging placenta past due date
hypoxia in utero
diabetic mother
difficult delivery
prolonged labor
preeclampsia/HTN
Meconium aspiration treatment
immediate suctioning
O2/ventilator support
ABX
Spontaneous pneumothorax
increased risk with positive pressure ventilation in delivery room
tachypnea at birth
confirmed with CXR
Spontaneous pneumothorax treatment
supplemental oxygen
needle thoracentesis or thoracostomy tube
Persistent pulmonary hypertension
respiratory distress day one of life
no decreased in pulmonary vascular resistance after birth
vasoconstriction post perinatal hypoxia
R--> L shunting through patent ductus arteriosus and/or foramen ovale
Persistent pulmonary hypertension treatment
oxygen and ventilatory support
correct underlying problems
Transient tachypnea
respiratory distress at birth
mild-mod O2 requirement
full or late term
non asphyxiated
short labor or C section
delayed clearance of fetal lung fluid
usual resolution in 12-24 hrs
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
newborn needs breathing support 28 days after birth
chronic lung disease
infants with RDS
structural immaturity of lung - surfactant deficiency, atelectasis, pulmonary edema, barotrauma from ventilation, oxygen toxicity
Apnea of prematurity
respiratory pause more than 20 sec or any pause with cyanosis and bradycardia
diagnosis of exclusion
Mixed apnea
immaturity of central regulation
airway obstruction-patency
Apnea of prematurity treatment
caffeine citrate and home monitoring
resolves within 2 weeks of life
Hyaline membrane disease
MCC of respiratory distress
especially in infants 26-28 weeks
deficiency of surfactant --> poor lung compliance and atelectasis --> increased work of breathing --> respiratory failure
Patent ductus arteriosus
persistent connection between aorta and pulmonary artery (L-->R shunting)
usually closes within minutes to days after birth
if persistent, can damage lungs and heart or lead to CHF
Patent ductus arteriosus S&S
continuous murmur, wide pulse pressure, increased peripheral pulses
respiratory distress
poor feeding/growth
sweating with feeding
Patent ductus arteriosus diagnosis
echo/doppler color flow
Patent ductus arteriosus (treatment)
indomethacin
surgery/catheterization
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
MC acquired GI emergency
abdominal distention, vomiting, heme+ stool
pneumatosis intestinalis on abd XR
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) treatment
bowel rest +/- NG tube
supportive care with IVF, +/-abx
surgery to remove necrotic bowel if perforation
Intraventricular hemorrhage
occurs in infants before 31 weeks by 4 days of life
subependymal germinal matrix by lateral ventricles
results from ischemia with reperfusion injury
Intraventricular hemorrhage S&S
CNS deterioration - ranging from rapid-gradual
Intraventricular hemorrhage diagnostics
routine cranial US on infants born before 32 weeks
Intraventricular hemorrhage treatment
supportive care
shunt
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding
aka hemorrhagic disease of newborn
low levels of vit K in newborn is common --> normally rise within a month after birth
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding pathophysiology
immature liver does not efficiently utilize vitamin K
low vit K stores since low content in breast milk, sterile gut, poor placental transport
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding preventative treatment
IM 1mg of vit K
bleeding risk is over 80x greater in those that do not receive it
Vitamin K deficiency risk factors
did not receive vit K injection at birth
exclusively breastfed
maternal use of anticoagulants, certain abx (cephalosporins), and sum anti-convulsant meds
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding S&S
bleeding post circumcision, at umbilical cord, GI bleed, mucus membranes, site of injections, hematuria, bruising, hematomas of the skull, intracranial
Classic onset of vitamin K deficiency bleeding
in breastfed babies between 2-7 day of life
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding evaluation
PT
INR
CBC
neuroimaging
Vitamin K deficiency bleeding treatment
parenteral vitamin K - 1-2mg IV or subq
FFP or prothrombin complex concentration
Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula
blind esophageal pouch +/- fistula to trachea
hx of polyhydramnios
presents with copious secretions/drooling, choking with feeding, cyanosis and respiratory distress
Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula diagnosis
CXR after NG tube placement
tube seen in blind pouch
with a fistula --> gas in bowel
Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula treatment
supportive care with NG tube in proximal pouch low intermittent suction
surgery
r/o associated congenital abnormalities (VACTERL)
VACTERL association
V - vertebral defects
A - imperforate anus or anal atresia
C - cardiac anomalies (VSD)
TE - transesophageal fistula
R - renal anomalies
L - limb anomalies (radial agenesis)
babies with VACTERL have at least 3 or more of these
Intestinal obstruction
MC surgical emergency in neonates
MC caused by bowel atresias often caused by ischemic event during development
Duodenal atresia
congenital
higher the obstruction --> earlier presentation
emesis +/- bile
defects in vacuolization or ischemic event
often associated with Down Syndrome
Duodenal atresia diagnostics
Double Bubble on XR - dilated stomach and proximal duodenum and no air distally
Meconium ileus
at level of terminal ileum
failure to pass meconium in first 12-24 hrs
abdominal distention and bilious vomiting
high association with CF
Meconium ileus imaging
XR with multiple dilated loops of bowel, intra-abdominal calcification if in utero perforation occurred (meconium peritonitis)
barium enema shows microcolon
Meconium ileus treatment
radiographic contrast enema
surgery
Omphalocele
membrane covered herniation of abdominal contents in the base of the umbilical cord
most have abnormal karyotype or associated syndrome
Omphalocele treatment
keep it covered and moist at delivery
keep stalk free from vascular compromise
NG decompression and supportive care with IVF/glucose
rapid surgical correction
Gastroschisis
herniation of uncovered abdominal viscera through a defect in the abdominal wall
associated with IUGR and intestinal atresia
Gastroschisis treatment
place bowel or infant in silastic bowel bag
rapid surgical correction
Diaphragmatic hernia
herniation of abdominal organs into the hemi-thorax (left)
posterolateral defects in diaphragm
presents with respiratory distress from birth, poor breath sounds, scaphoid abdomen, and associated anomalies
Diaphragmatic hernia diagnosis
bowel loops seen in chest with mediastinal shift to opposite side on chest
Diaphragmatic hernia treatment
intubation, mechanical ventilation, GI decompression
surgery
pulmonary HTN may need ECMO
Neonatal sepsis - early
first day of life in first 12 hrs
low APGAR scores
poor perfusion
hypotension
respiratory distress - MC
Neonatal sepsis - late
greater than 3 days of life
decreased level of activity
poor feeding
hypotonia
increased oxygen requirement/apnea
associated with meningitis or other local infections
Neonatal sepsis - early etiologies
MC - group B strep or E coli
enterococcus
S aureus
streptococci
listeria monocytogenes
H influenza
Neonatal sepsis - late etiologies
coagulase neg staph aureus
gram negatives
candida
Neonatal sepsis diagnostics
CBC with low WBC, absolute neutropenia, elevated ratio of immature to mature neutrophils, thrombocytopenia
hyper or hypoglycemia
metabolic acidosis
CRP
cultures of blood, CSF, or other
Neonatal sepsis treatment
broad spectrum abx - ampicillin + 3rd gen cephalosporin or aminoglycoside
10-14 days of IV abx
supportive therapy
TORCH infections
pre and post natal
toxoplasmosis
other: varicella, syphillis, HIV, parvovirus B19, hepatitis B
rubella
cytomegalovirus
herpes simplex
Toxoplasmosis
transmitted via raw-undercooked meat with infective cysts or contamination from feline feces
asymptomatic, developmental delay, visual impairment, and learning disabilities
Congenital rubella
infection during first 8 weeks of pregnancy
microcephaly, encephalitis, cataracts, retinopathy, cardiac defects, deafness
CMV
MC virus transmitted in utero
hepatosplenomegaly
thrombocytopenia
microcephaly
intracranial calcifications-periventricualr
chorioretinitis
sensorineural hearing loss
treated with oral valganciclovir
Herpes simplex
perinatal infection transmitted from birth canal
localized, disseminated, or CNS disease
treated with acyclovir
Varicella
acquired in 1st 20 weeks of pregnancy
perinatal exposure
treated with varicella zoster immune globulin
Syphilis
transplacental passage
can lead to stillbirth or prematurity
asymptomatic newborns, hepatosplenomegaly, bony changes, hydrops, mucocutaneous lesions
Zika
can cause congenital anomalies
HIV
can be acquired in utero, perinatal, and via breast milk
treated with zidovudine
Parvovirus B19
erythema infectiosum - fifth disease
transmitted by respiratory secretions
anemia, hydrops, myocarditis, and fetal death
Hepatitis B
infants infected at birth
can develop chronic active hepatitis
born to HBsAg positive mothers