Histology of Nervous Tissue Study Guide
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters 11-15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Central nervous system
CNS
Peripheral nervous system
PNS
Sensory afferent division
Made up of somatic sensory fibers and visceral sensory fibers
Somatic sensory fibers
Convey impulses from skin, skeletal muscle, and joints to the CNS
Visceral sensory fibers
Convey impulses from visceral organs to o CNS
Motor efferent division
Transmits impulses from CNS to effector organs
Motor efferent division
Made up of the somatic nervous System and autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Somatic motor nerve fibers; conducts impulses from CNS to skeletal muscle; voluntary nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Visceral motor nerve fibers; Regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands; invuntary nervous system
Autonomic nervous system divisions
Sympathetic nervous system and Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Mobilizes body systems during activity
Parasympathetic nervous system
Conserves energy and promotes house keeping functions during rest
Neuron body
Biosynthetic center of the neuron, synthesizes proteins, membranes, and other chemicals
Axon
Generates nerve impulses, carries on conversations, lacks rough ER
Dendrite
In motor neurons, input region of the neuron, convey messages towards the cell body
Amitotic
Neurons can not divide or reproduce after they are formend
100 years or more
Life span of a neuron
High metabolic rate
Neurons require continuous supply of oxygen and glucose
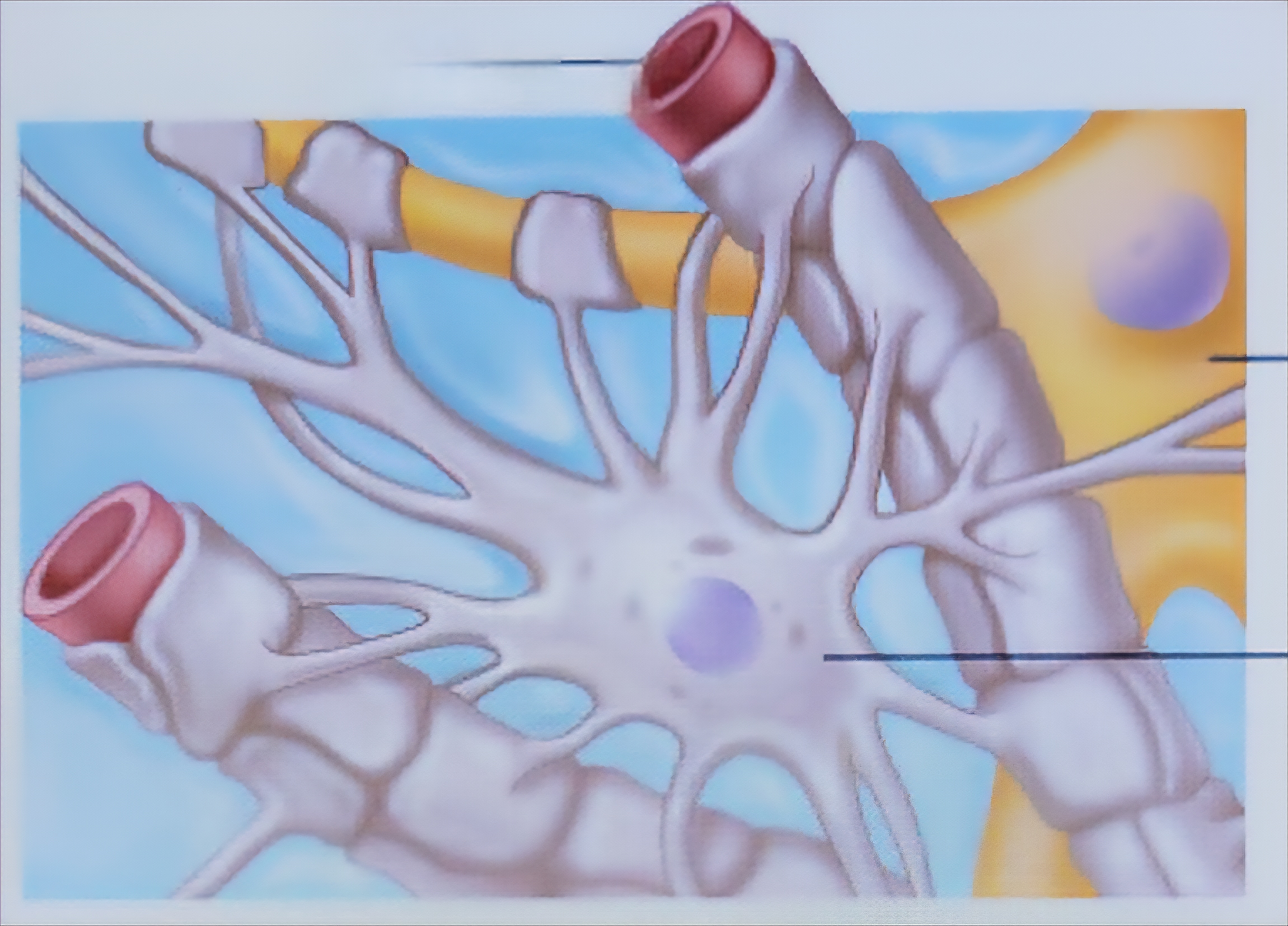
Astrocyte
Most abundant, supports, exchanges, guides, controls, and influences
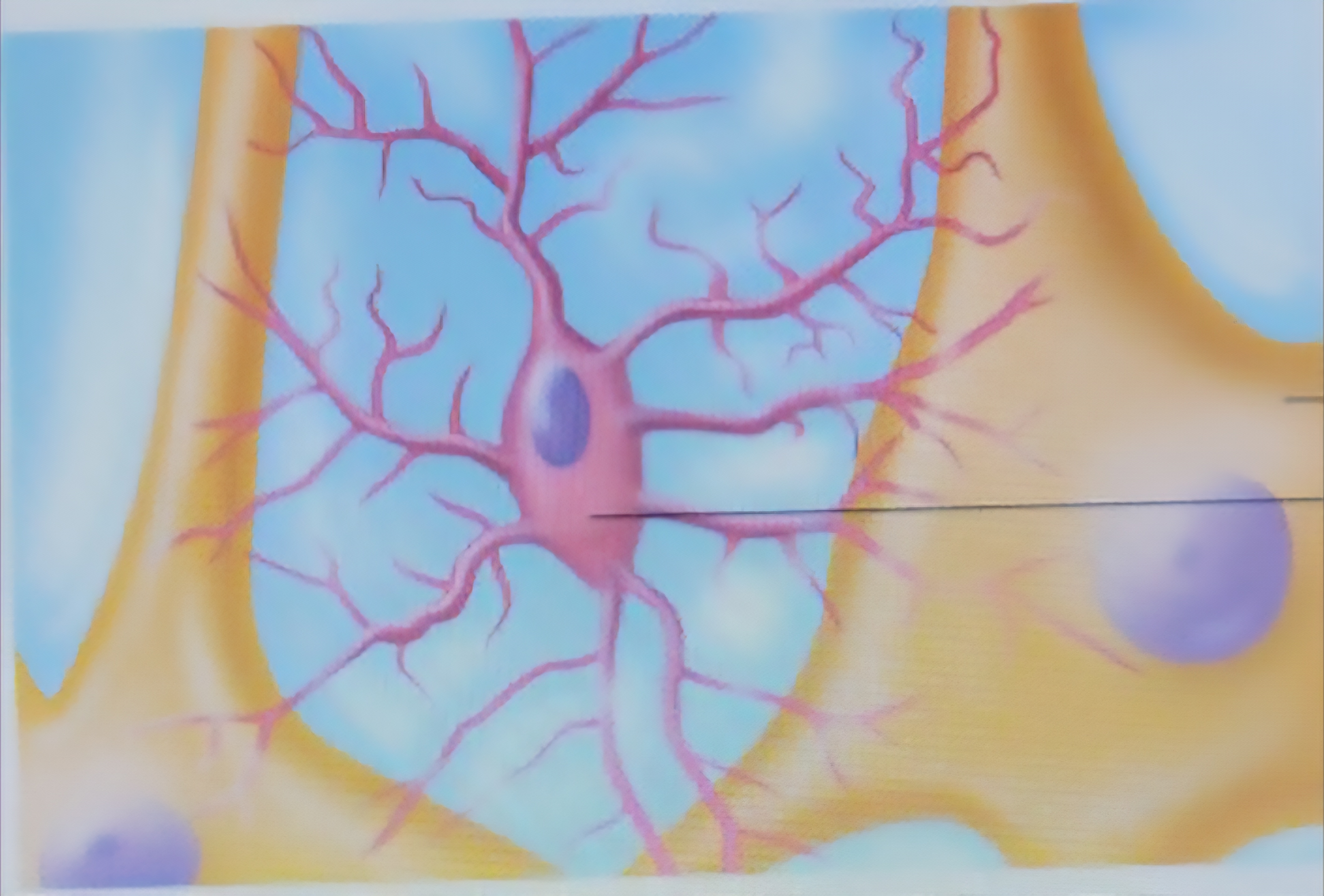
Microglia
Touch and monitor neurons, migrate towars injured neurons, can transform to phagcytize microorganisms and neuronal debris
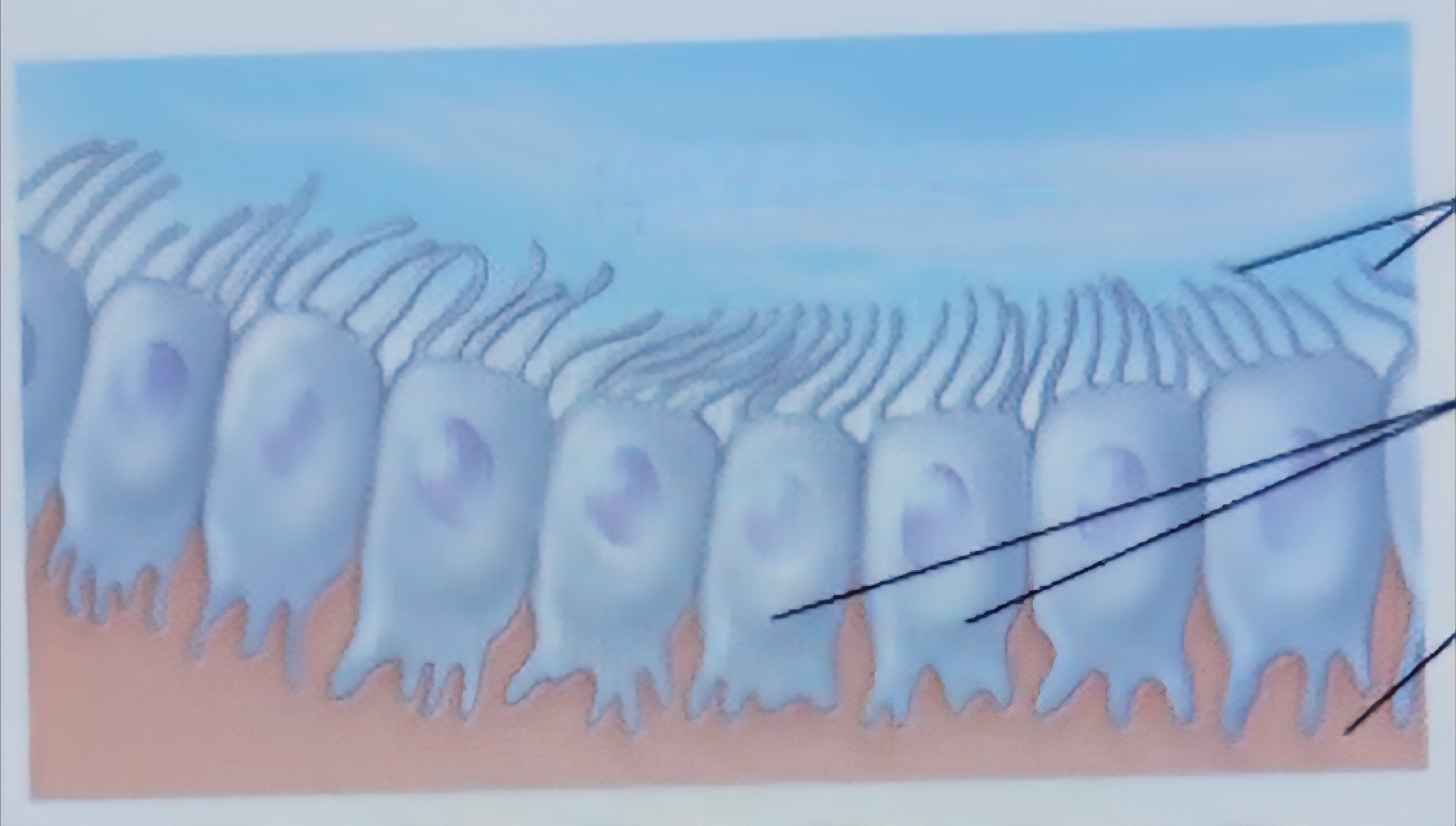
Epidymal
Line brain and spinal cavities, form permiable barriers between the CSF in cavitiea and fluid bathing CNS cells
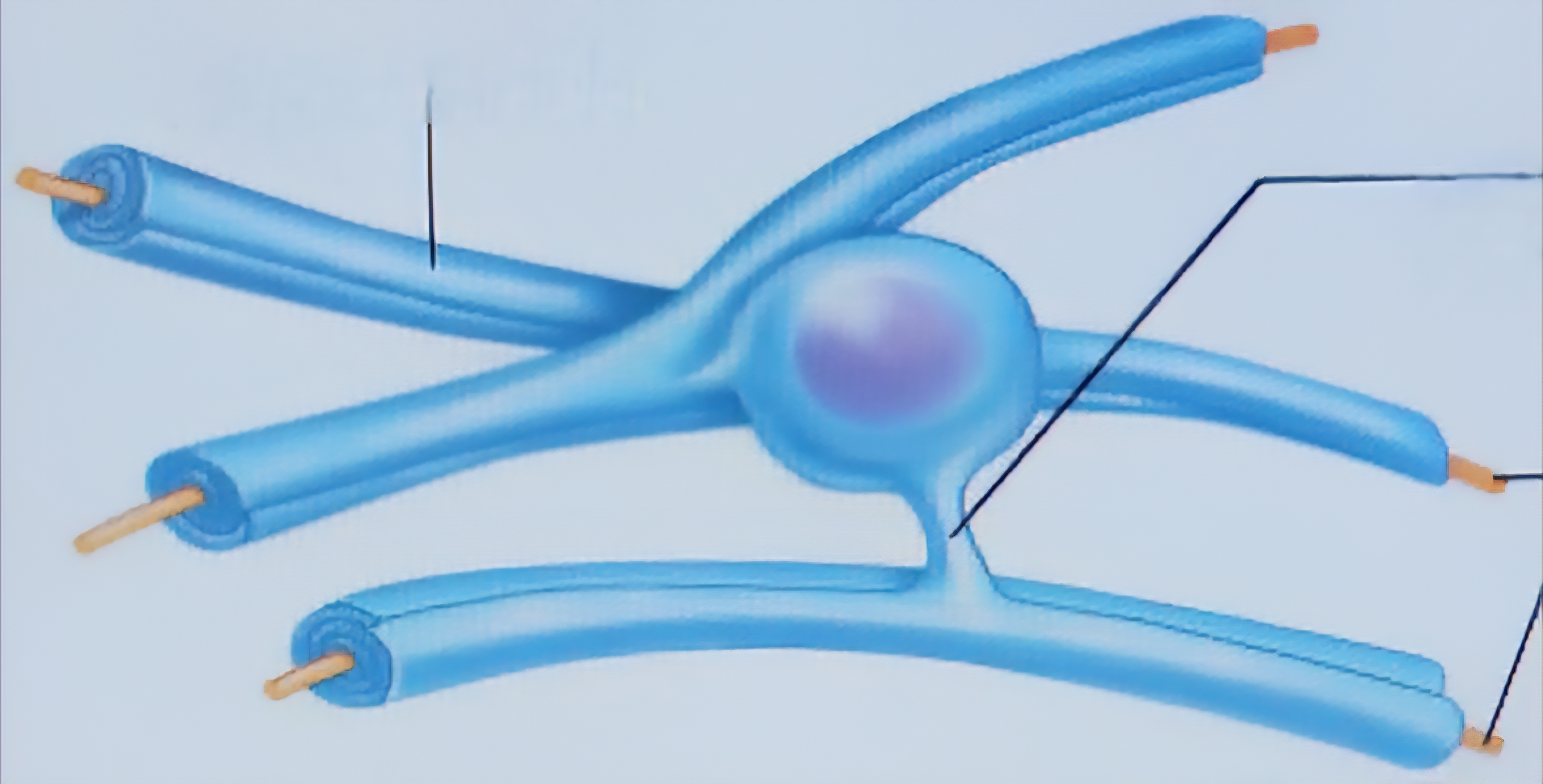
Oligodendrocyte
Wrap around the CNS nerve fibers, and form myelin sheaths
Schwann
Surround peripheral nerve fibers and form myelin sheaths, and vital to regeneration in damaged nerve fibers
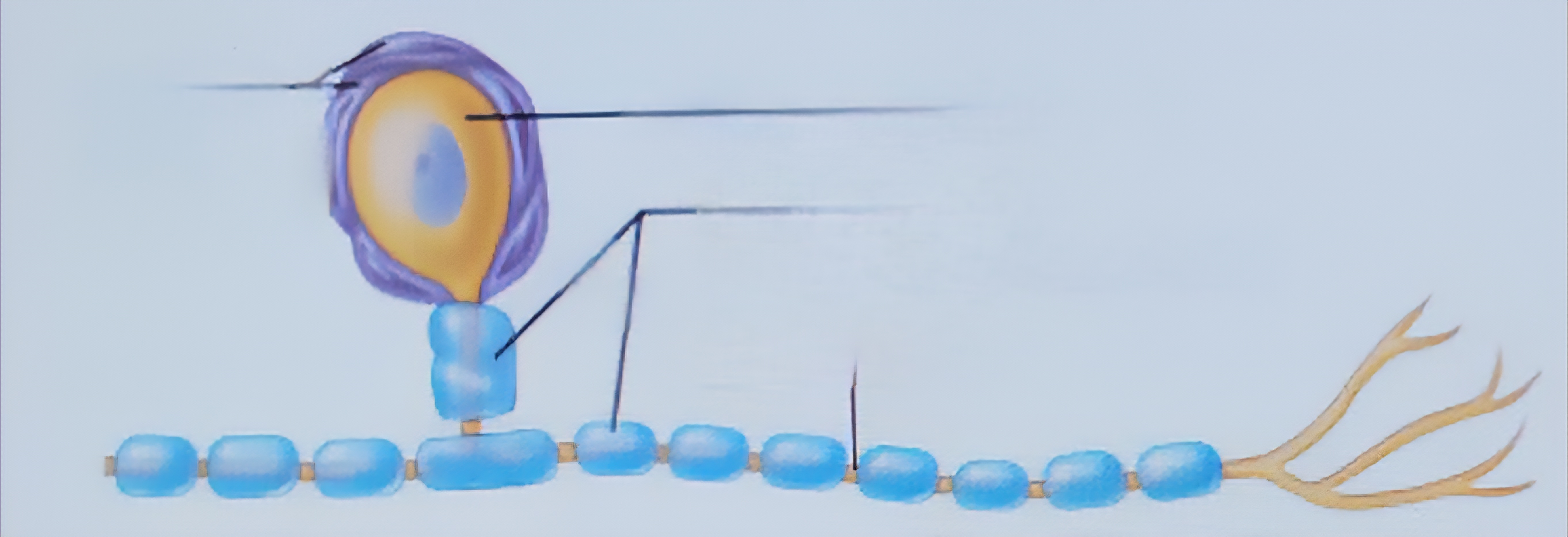
Satelite
Surround neuron cell bodies in PNS
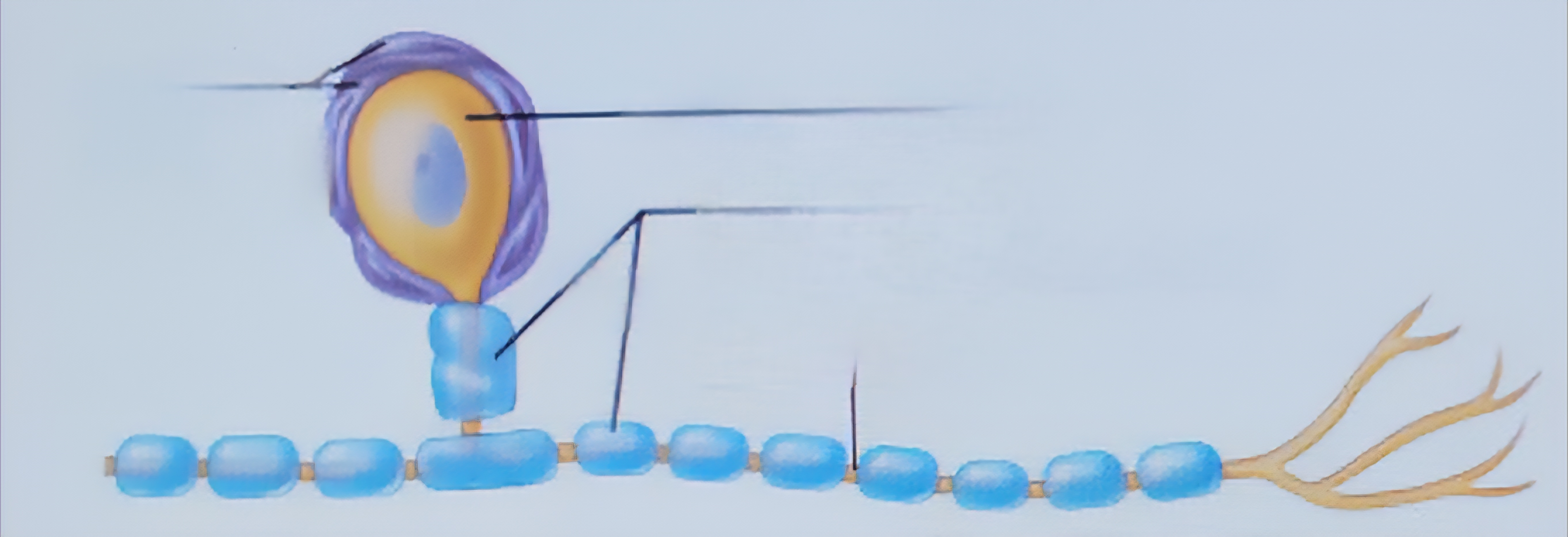
Synapse
Junctions that mediate information transfer from one neuron to another, or a neuron to an effector cell
Synaptic cleft
Fluid filled space
Chemical impulse
Uses neurotransmitters to cross the synapse between cells
Eletrical impulse
Direct flow of ions through channels connecting the cytoplasm of adjacent cells
Acetylcholine
Released at neuromuscular junctions and plays a role in memory formation
Catecholamines
Dopamine, Norepinephrine, and Epinephrine neurotransmitters
Indolamines
Serotonin and Histamine
Melatonin
Influences the release of other neurotransmitters
Epineurium
The outermost layer of connective tissue in the nerves
Perineurium
Middle layer of connective tissue in the nerves
Endoneurium
Innermost connective tissue in the nerves
Nerve
Bundle of axons in the PNS
Tract
Bundle of axons in the CNS