PHYS237-Experiments
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
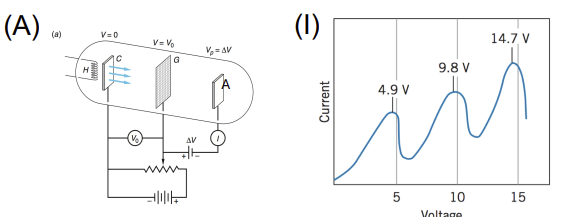
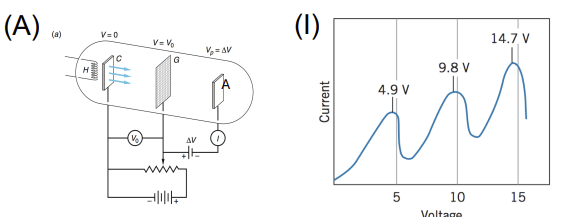
Franck–Hertz Experiment
Apparatus: Electron gun, mercury vapor tube, collector electrode, adjustable voltage
Data Collected: Current vs. accelerating voltage
Results: Drop in current at specific voltages corresponding to energy absorbed by atoms
Significance: Provided evidence for quantized atomic energy levels
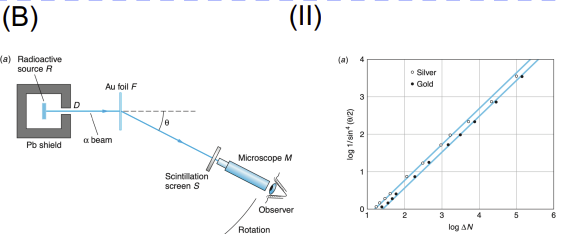
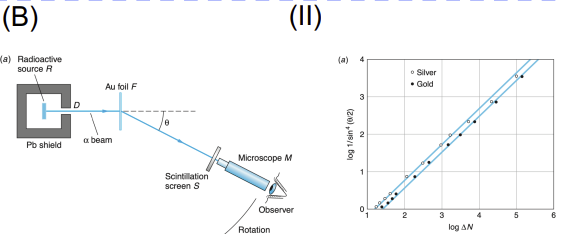
Rutherford Scattering
Apparatus: Alpha particle source, thin gold foil, circular zinc sulfide screen/detector
Data Collected: Angle and frequency of alpha particle deflections
Results: Most passed through, but some deflected sharply
Significance: Disproved plum pudding model; led to nuclear model of atom (dense, positive nucleus)
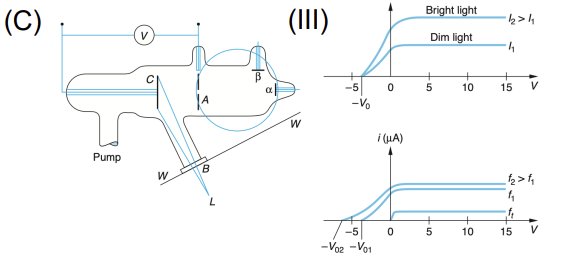
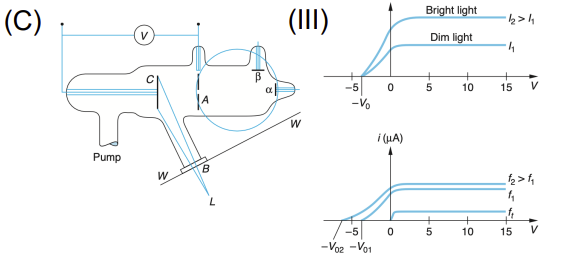
Hertz/Lenard Experiments (Photoelectric Effect)
Apparatus: Ultraviolet light source, metal cathode, anode, vacuum tube, and voltage source
Data Collected: Current vs. light intensity/frequency/voltage
Results: Emission of electrons only above a threshold frequency, independent of intensity
Significance: Supported quantization of light (photons); led Einstein to propose photoelectric equation, showing light's particle nature
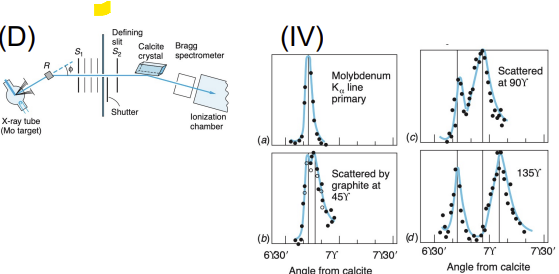
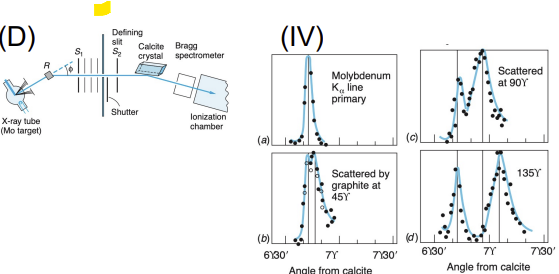
Compton Scattering
Apparatus: X-ray source, target (usually graphite), X-ray detector at various angles
Data Collected: Wavelength of scattered X-rays vs. angle
Results: X-rays scattered with increased wavelength (energy loss)
Significance: Confirmed that photons carry momentum, further evidence of light as particles
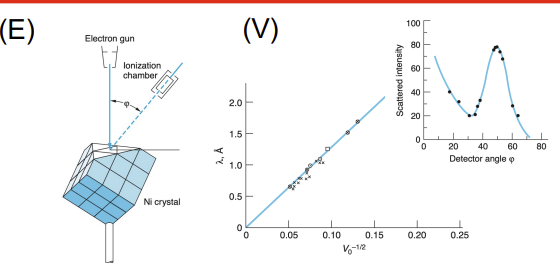
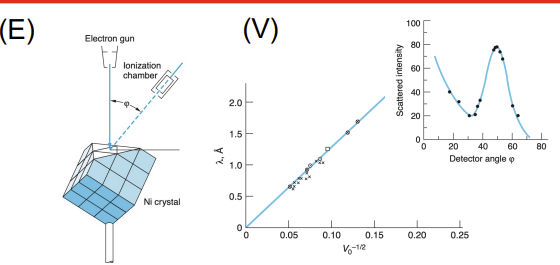
Davisson–Germer Experiment
Apparatus: Electron gun, nickel crystal, detector (movable to measure angle)
Data Collected: Intensity of scattered electrons vs. angle
Results: Peak intensities occurred at specific angles, showing electron diffraction
Significance: Demonstrated wave nature of electrons (electron diffraction), confirming de Broglie hypothesis and wave-particle duality
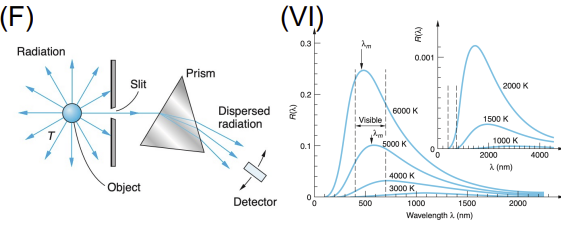
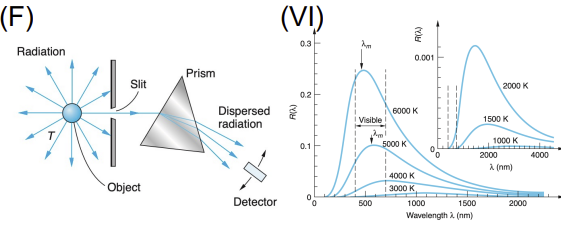
Blackbody Radiation
Apparatus: Heated cavity with small hole; measured emitted spectrum
Data Collected: Intensity vs. wavelength at various temperatures
Results: Classical physics failed (ultraviolet catastrophe); Planck's formula fit the data
Significance: Planck introduced energy quantization, foundational to quantum theory