Osteology Exam
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Directional Terms, Osteology, Body Planes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Osteology
The study of bone structure and the treatment of bone disorders
Functions of the Bone
Support, Protection of internal Organs, Movement, Mineral Storage, Storage of energy + lipid in yellow marrow, blood cells production in red marrow
Bone Matrix consist of:
25% Water, 25% protein fibers, 50% mineral salts, bone cells
Characteristics of Bone Matrix
Hardness and Tensile Strength
Calcification
Mineral Salts (Calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate) crystallizes around collagen fibers, hardening the matrix
Tensile Strength
Collagen fibers reinforces the matrix, making the bone flexible and brittle
Osteoprogenitor Cells
Unspecialized precursor cells that form osteoblasts; found in periosteum and endosteum
Osteoblasts
Immature bud cells that form bone; build bone tissue matrix (collagen and minerals)
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells; maintain daily cell activities of bone tissues
Osteoclasts
Develop from white blood cells; aid in the destruction of the matrix (collagen and minerals)
Cancellous Bone
Make up tissue in short, flat, irregularly shaped bones and Epiphysis of long Bone; stores red bone marrow and provides support; made up of trabeculae
Structure of Trabeculae
Arranged in an irregular latticework of thin columns of bone, spaces between are filled with red marrow, canaliculi connect to the periosteum, osteocytes not buried deeply- osteons are not necessary.
Compact Bone
found in external layers of all bones and make up the diaphysis of long bones; provides protection and support, helps long bone resist the stress of weight, made up of osteons.
Structure of Osteon
Consists of concentric lamellae, lacunae, canalliculi, haversian and volkmann’s canals.
Volkmann’s Canal
Runs horizontally through bone; allows the passage of blood vessels and nerves that penetrate from the periosteum.
Haversian Canal
Run vertically (longitudinally) through the bone; connects the blood vessels and nerves of the periosteum with those of the medullary cavity.
diaphysis
central shaft
epiphysis
end of long bones
metaphysis
region where diaphysis joins the epiphysis
Articular Cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the end of bones
periosteum
thick double layered membrane covering bone
outer fibrous layer
contains blood vessels, lymph, nerves
inner elastic layer
contains blood vessels and bone cells
Function of Periosteum
helps bone to grow in diameter, protects the bone, repairs, nourishes, and serves as an attachment for ligament and tendons.
Medullary Cavity
Central cavity, containing yellow marrow
Endosteum
thin membrane lining medullary cavity
Ossification
embryonic connective tissue (fibrous and cartilage) hardens into bone; begins the 6th week into utero and continues into adulthood
Intramembranous Ossification
occurs directly within fibrous connective tissue; osteoprogenitor cells develop into osteoblasts; occurs in flat bones of skull and lower jaw
Endochondral Ossification
occurs within hyaline cartilage tissue; cartilage becomes calcified from inside out, remains on articular surfaces; occurs in most bones and long bones
Nutrient Artery
blood vessels that enter the bone threw the periosteum
Remodeling
the replacement of old, worn, or injured bone tissue
Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesiums; Vitamins A, B12, C, and D; Hormones: Human Growth Hormone, Testosterone, Insulin, Thyroxine
Normal bone growth requirements
Mechanical Stress
Affected by muscle work and gravity
Weakened bone and reduced denisty
Removal of stress causes:
Increased bone density
Exercises such as walking and weight lifting will:
Mechanical stress, increasing mineral deposition, and production of collagen fibers
Bone strength depends on
Demineralization
loss of calcium and other minerals from matrix
30; accelerates at around 45 while estrogen levels decrease
beginning of demineralization in females:
45
beginning of demineralization in males:
Decrease in protein synthesis
reduces collagen production; bone loses tensile strength, causing it to become more brittle
Osteoporosis
loss of calcium, bone becomes less dense
Ricketts
bone becomes too flexible; vitamin D deficiency
Paget’s Disease
abnormal acceleration of the remodeling process
Osteosarcoma
bone cancer; this makes bone more brittle
Scoliosis
sideways curvature of the spine that occurs mostly during growth spurts
Superior (cranial)
toward the head/upper part of the structure of the body; above
inferior (caudal)
away from the end/toward the lower part of the body; below
anterior (ventral)
toward the front of the body; in front of
posterior (dorsal)
toward the back of the body; behind
medial
toward the midline of the body
lateral
away from the midline of the body
proximal; for limbs
closer to the origin (point of attachment) of the trunk of the body
distal; for limbs
farther from the origin (point of attachment) of the trunk of the body
superficial
toward the body surface
deep
away from the body surface; internal
transverse section
1
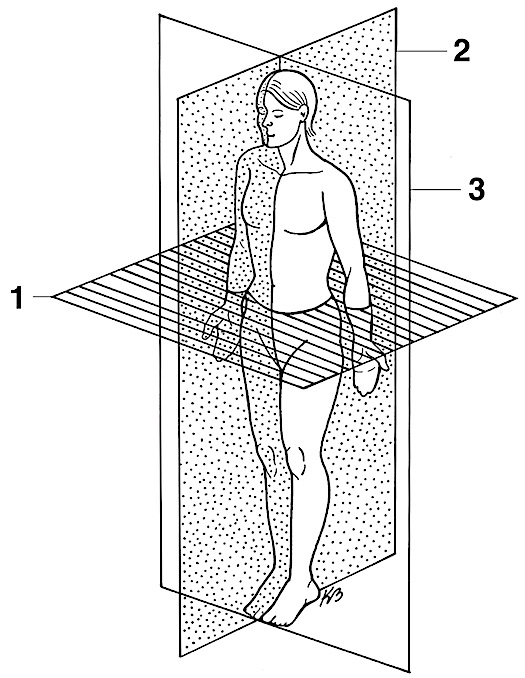
(mid) sagittal section
2
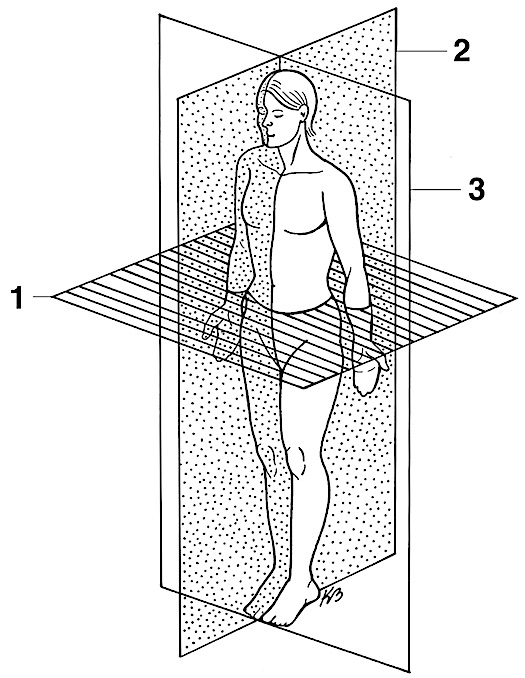
coronal section
3
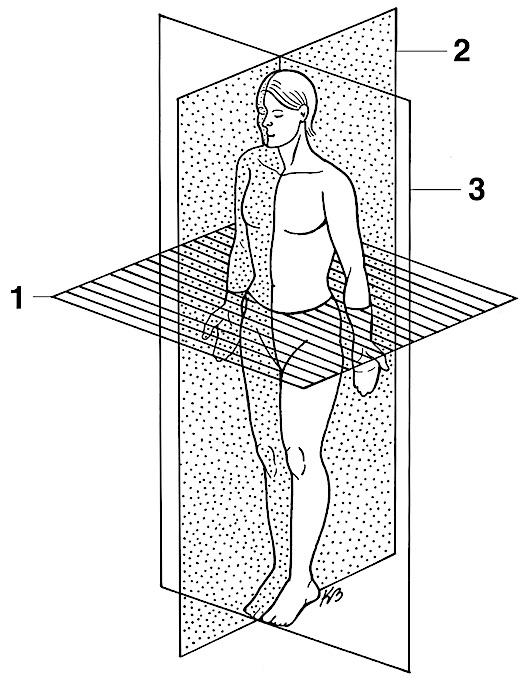
oblique
diagonal cut -no pic :(-
Axial
Division of skeletal system containing skull, vertebrae, and thorax (chest)
Appendicular
Division of skeletal system containing bones, upper & lower extremities, including the shoulder and pelvic girdle