Blood, cell identification
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Blood is _____________________tissue
connective
2 components of blood
cells and plasma
cells in blood
red blood cells(erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), platelets (thrombocytes)
composition of plasma
92% water, proteins, amino acids, hormones, electrolytes
hematocrit
volume of blood cells in a sample. Should be 45%
Description of Red blood cells term-12(erythrocytes)
bioconcave discs, lack nuclei, has hemoglobin molecules
Function of red blood cells (erythrocytes)
transports oxygen to cells, carries away CO2, hemoglobin carries oxygen
formation of red blood cells in bone marrow
hematopoeisis
phagocytosis
breakdown of red blood cells in liver and spleen
white blood cells
leukocytes
Function of White blood cells (leukocytes)
protect agains disease
agranular and granular
2 Categories of Leukocytes/White blood cells
2 kinds of agranular leukocytes/white blood cells
lymphocytes (t-cells, b-cells, nk-cells) (20-25%)
monocytes (3-8%)
3 kinds of granular leukocytes/white blood cells
basophils (0.5-1%)
neutrophils (60-70%)
eosinophils (2-4%)
Neutrophils description
nucleus has several lobes. Make up 60% of WBCs. Present in pus of wounds.
basophils description
produces heparin and histamines. Make up 1% of WBCs. Important for inflammatory reactions.
eosinophils description
attack parasites. Make up 2% of WBCs.
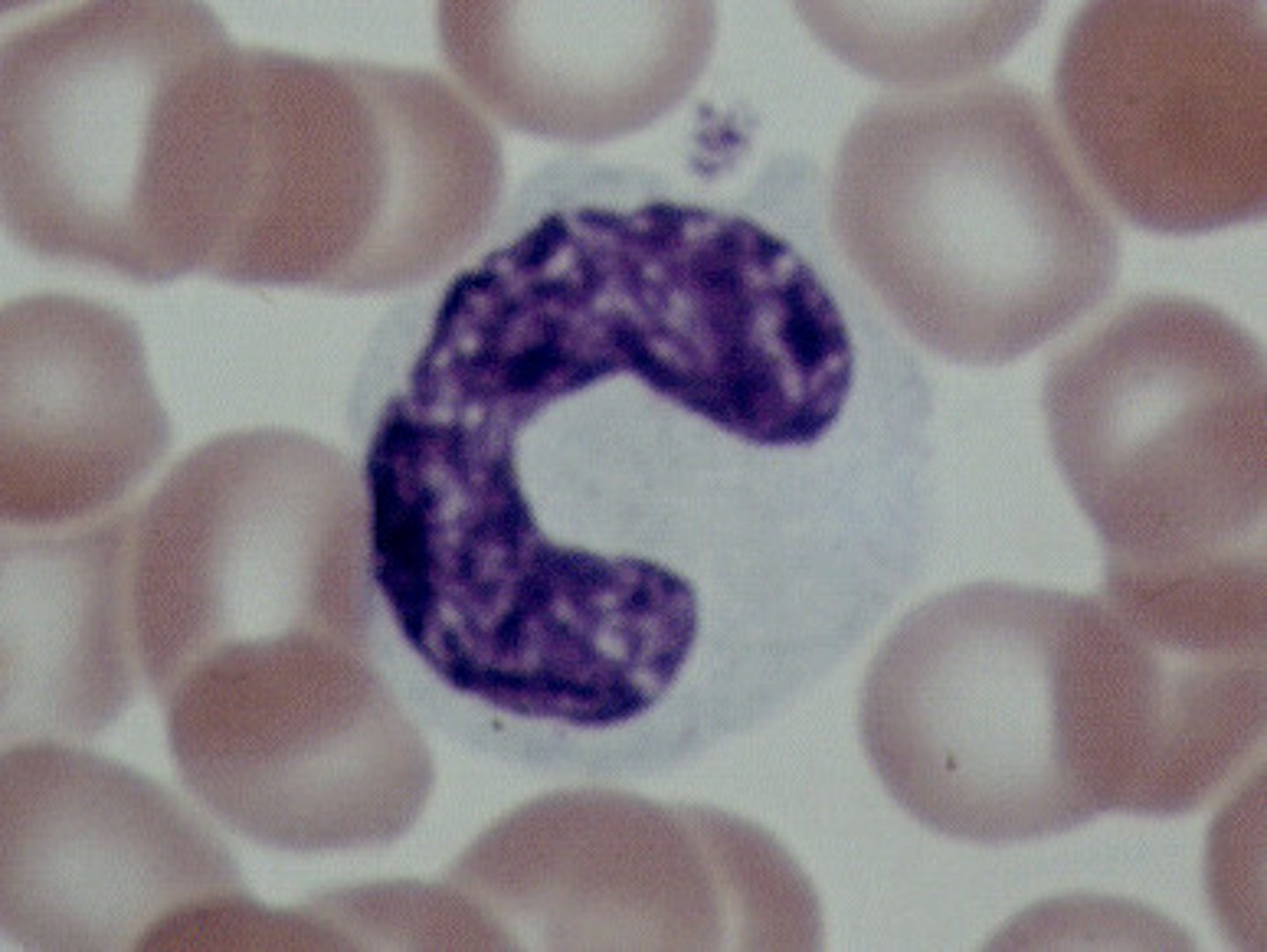
Monocyte description
larger cell, horseshoe shaped nucleus, become macrophages (engulf invader cells)
lymphocytes description
dark nucleus takes up whole cell. Defends against invaders. Yields antibodies. Makes up 30% of WBCs.
thrombocytes/platelets
Clotting cells
coagulation
thickening of blood to form a clot/hematoma
lymphocyte
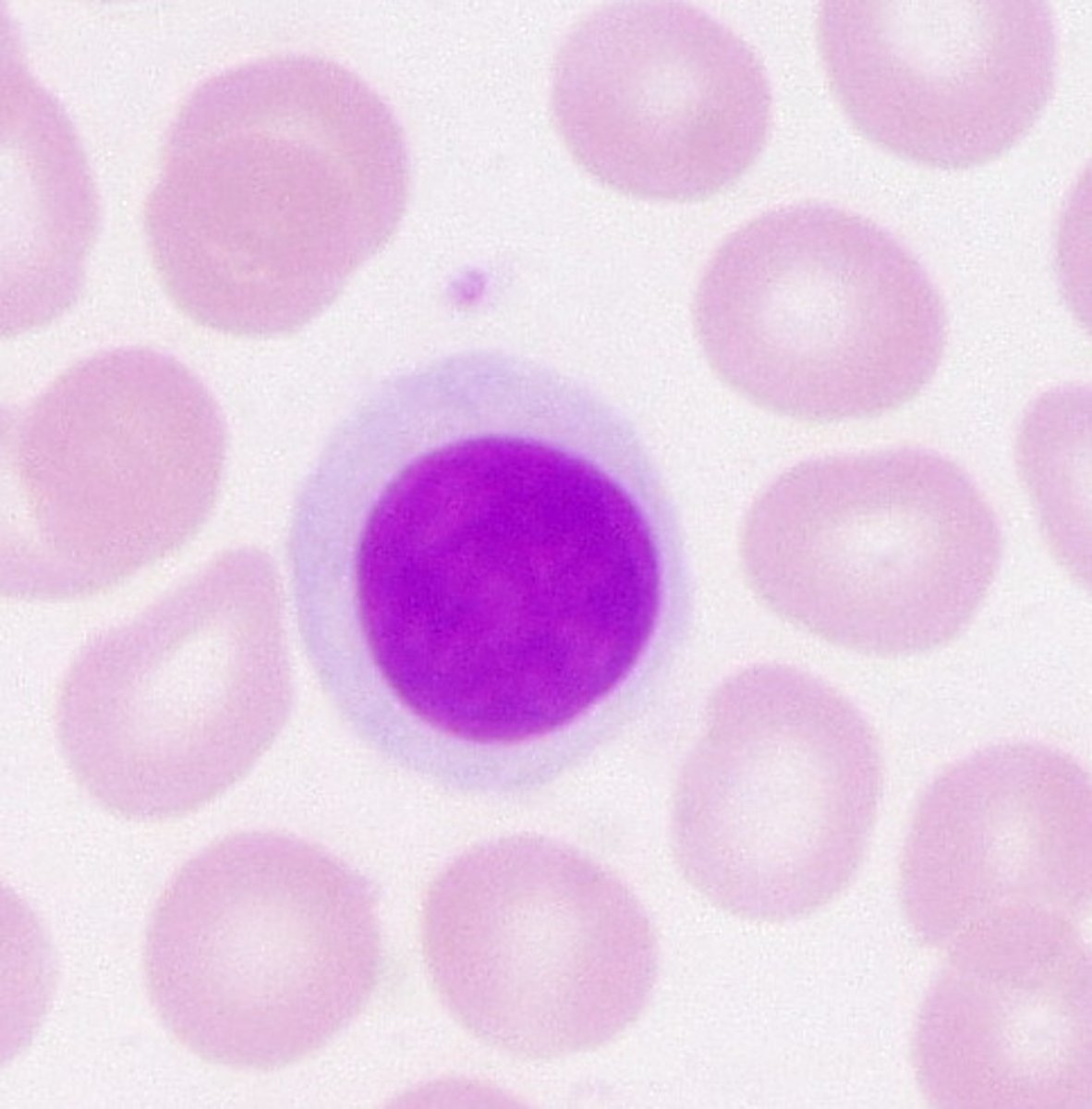
basophil
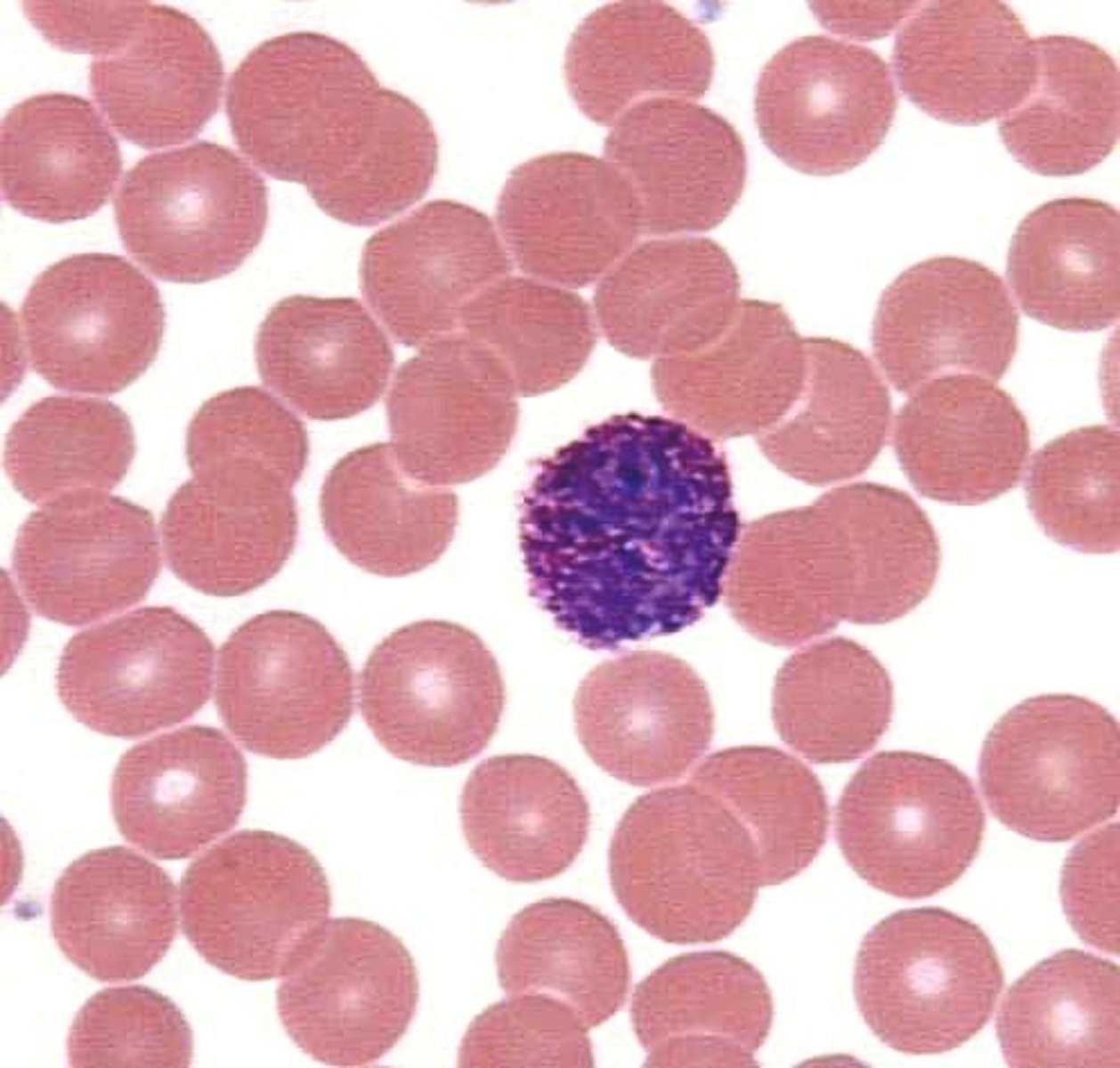
neutrophil
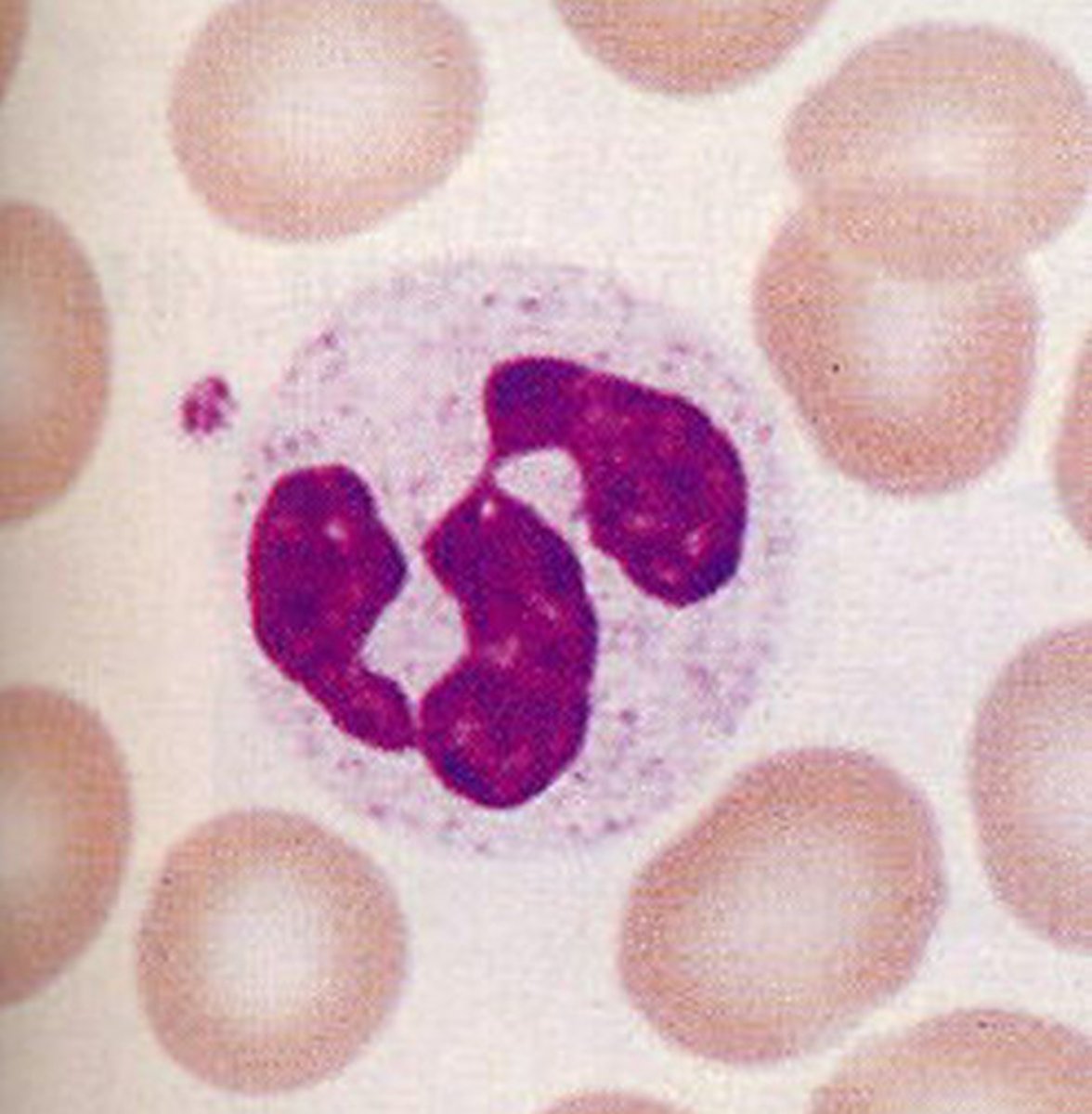
eosinophil
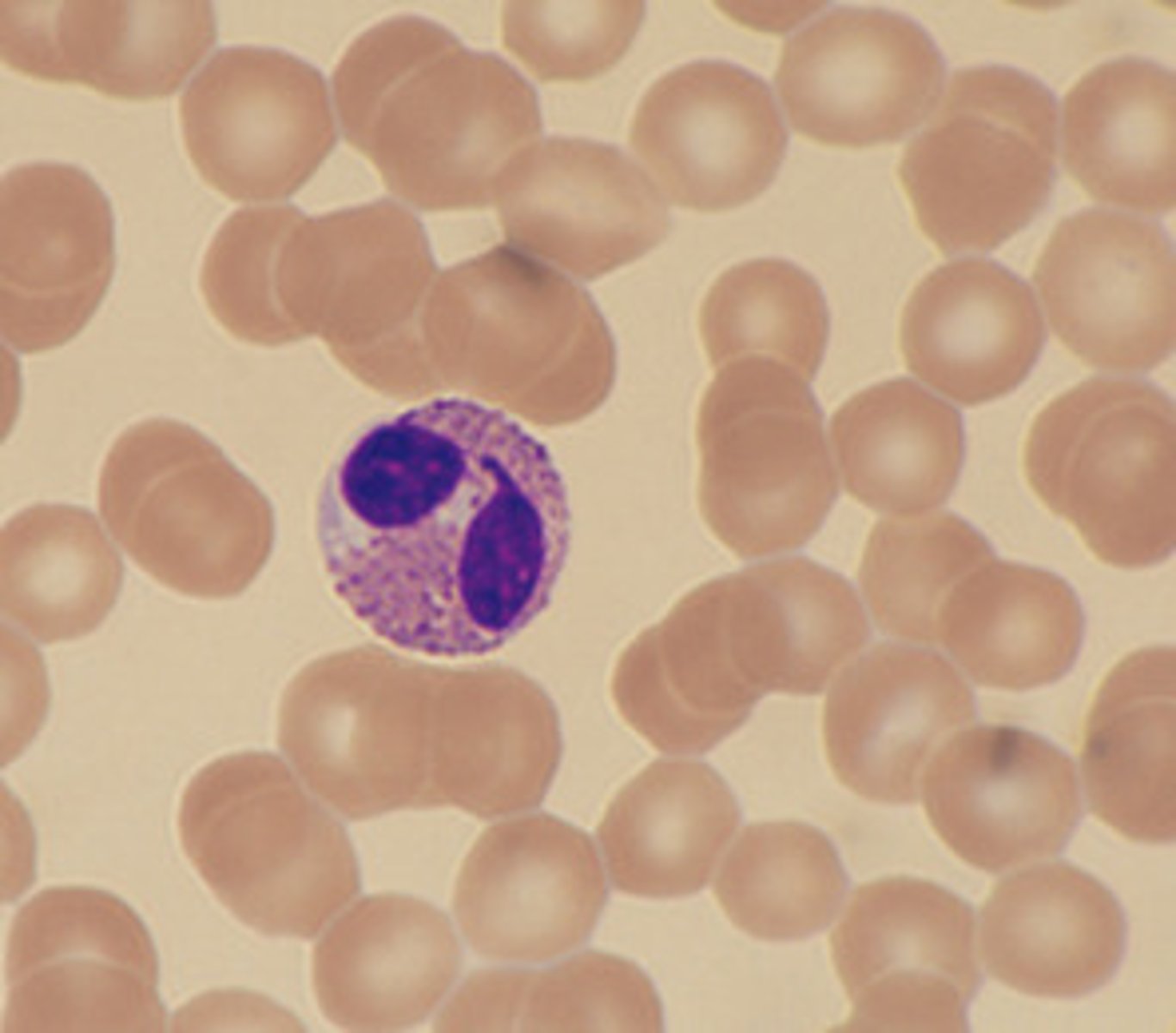
thrombocyte
NOTICE THE ARROWS
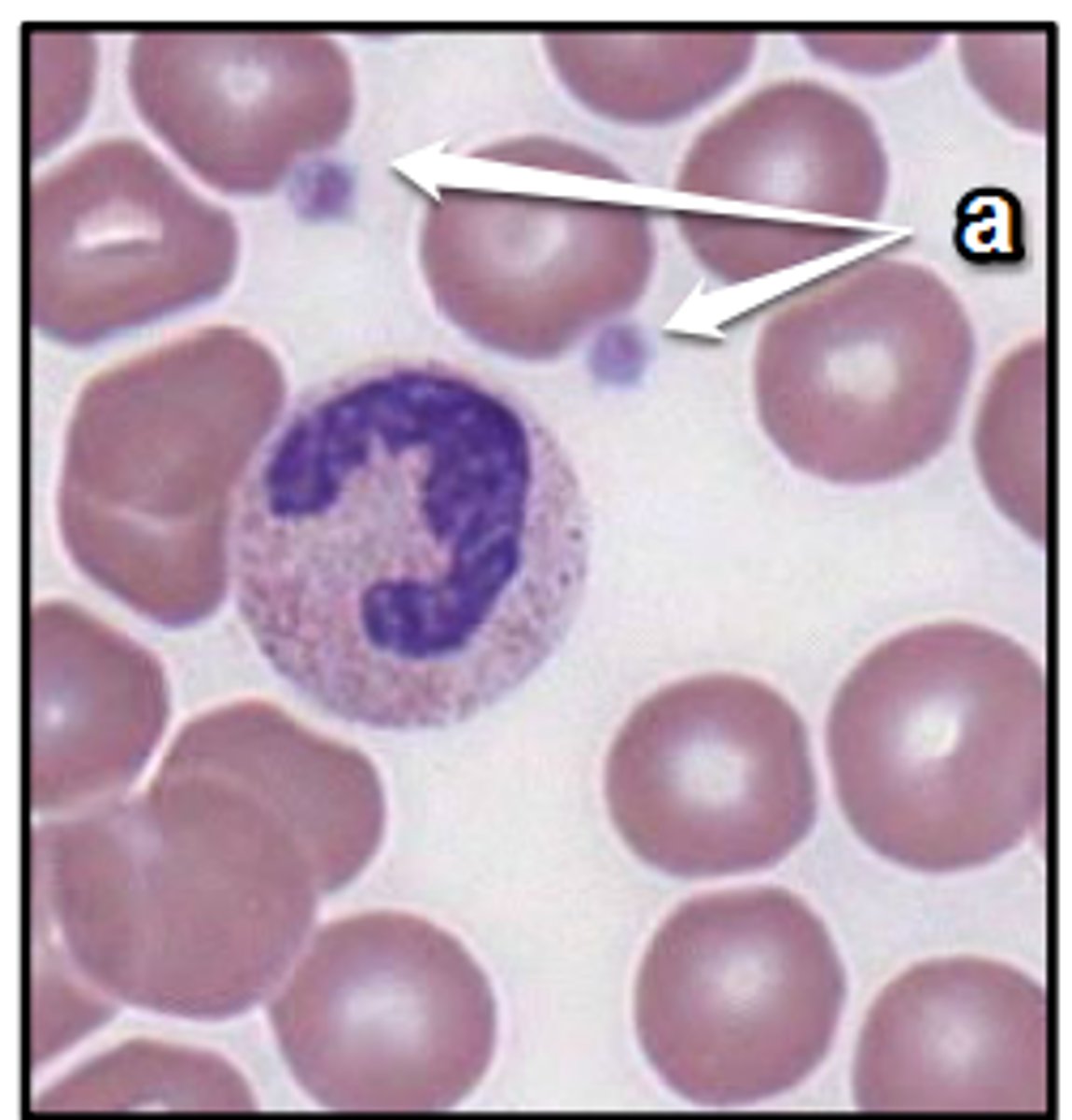
red blood cells
monocyte
Erythrocytes
red blood cells
37-52% of the total blood volume
Functions of erythrocytes
Pick up oxygen from the lungs and deliver it to tissues elsewhere
Pick up carbon dioxide from tissues and bring it to lungs for expulsion
Spectrin and actin
What proteins give RBCs flexibilty and durability?
It binds to the iron carried on the heme
How does a RBC carry oxygen?
Erythropietin (EPO)
What stimulates the colonizing-forming unit (CFU) into a erythroblast
Hematopoietic stem cells, colony-unit, erythroblasts, reticulocytes, erythroctyes
Order of erythrocyte cell development
Hypoxemia
A deficiency of oxygen in the blood
Sickle-cell anemia
abnormally shaped red blood cells due to HbS
Hemolysis
the rupture of red blood cells
Polycythemia
Excess of red blood cells
Iron-deficiency anemia
Dietary iron deficiency
Characterized by small pale erythrocytes
Pernicious anemia
autoimmune disease in which antibodies destroy stomach tissue is called…?
Gastroferritin
Protein that binds to ferrous iron and transports it to the small intestine
Leukocytes
white blood cells
Platelets
create the buffy coat
heart, blood vessels, and blood
Circulatory system consists of…
Transport, protect, and regulate
Purposes of blood circulation?
Albumin
responsible for colloid osmotic pressure
major contributor to blood viscosity
Globulin
split into alpha, beta, and gamma
various roles in solute transport, clotting, and immunity
Fibrinogen
Precursor of fibrin
Fibrin
sticky protein that forms the framework of a blood clot
Plasma cells
Where is gamma globulin made?
Viscosity
the resistance of a fluid to flow
Osmolarity
total concentration of solute particles
Hematopoiesis
Production of any of the elements of blood
Charles Drew
First black person to pursue an advanced degree of doctor of science in medicine; studied blood transfusions
Antigens and antibodies
What molecules determine blood types?
Antigens
Any large molecule capable of binding to an antibody or immune cells and triggering an immune response; usually a protein, glycoprotein, or glycolipoid
Antibodies
Proteins that bind to antigens and mark them for destruction
Agglutination
Clumping of cells by antibodies
A
If you have the alpha agglutinin (anti-A) you have blood type…?
B
If you have only alpha antibodies you have blood type…?
O
If you have If you have the alpha agglutinin (anti-A) and the beta agglutinin (anti-B), you have blood type…?
Transfusion reaction
RBCs become agglutinated in the recipient’s blood plasma
Rhesus monkey (Rh factor)
Antigen D; responsible for the positive or negative association for blood types
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
Occurs when a woman has a baby with a differing blood type
Also called Erythroblastosis fetalis
Rh immune globulin
What can be given to a mother to prevent HDN?
Destroys red blood cells and creates and excess of bilirubin
What does HDN do in a baby?
They retain organelles and nucleus throughout their life
How do leukocytes and erythrocytes differ as cells?
Haptoglobulin
Transports hemoglobin released by dead erythrocytes
Ceruloplasmin
Transports copper
Prothrombin
Promotes clotting
Prothrombin, Ceruloplasmin, Haptoglobulin
Alpha Globulins
Tranferrin, Complement proteins, others
Beta Globulins
Tranferrin
Transports iron
Complement proteins
Aids in destruction of microorganisms and toxins
Fibrinogen
becomes fibrin, major component of blood clotting
Colloid osmotic pressure
The contribution of protein to blood osmotic pressure
Myeloid hematopoiesis
Blood formation in the bone marrow and lymphoid organs
Hypoplastic anemia
reduced production of (all three) RBCs, WBCs, and platelets in the bone marrow
Aplastic anemia
A severe form of bone marrow failure where there is a complete or near-complete absence of blood cell production
Systole
pumps blood
Diastole
relaxes valves
Depolarization
contracts
Repolarization
relaxes valves
Atrial systole
The first part of the cardiac cycle is called…
Atrioventricular
During atrial systole, contraction of the atria forces additional blood through…
ventricles
Atrioventricular valves into the ____ which are already mostly filled with blood
Ventricular systole
What causes rising ventricular pressure and closes the atrioventricular valve?
The atria relaxes
When does ventricular systole begin?
Isovolumetric contraction
all four valves are closed
Rising ventricular pressure
What opens the semilunar valves?
right; pulmonary trunk
Low pressure is from the ___ ventricle to the ___
left; aorta
High pressure is from the ___ ventricle to the ___
lower than arterial pressure
At the end of the ventricular systole, ventricle pressure is…
Back flow of blood
What closes the semilunar valves?
Isovolumetric relaxation
A brief interval at the start of ventricular diastole called ___ causes all four valves to close
Decreases below atrial pressure
Isovolumetric relaxation makes ventricular pressure…
Oxygenated blood that flows through the body through veins
Atrial
Deoxygenated blood flowing in arteries to lungs
Arterial
Ventricles
When the atrioventricular valves open, blood flows through the open AV valves into ___
Ventricular diastole
There is overlap between the atrial and ___