Unit 8
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to electricity, insulation, and charging processes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Insulator
Materials that do not conduct electricity, such as plastic.
Conductor
Materials that allow electricity to flow easily, primarily metals.
Charging by Friction
The process of charging an object through friction with another object.
Charge Neutralization
When two identical conducting spheres in contact share excess charge evenly.
Coulomb's Law
A formula expressing the force between two charges
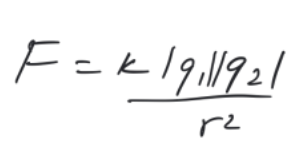
Elementary Charge (e)
The basic unit of electric charge, approximately equal to 1.6 × 10^-19 C.
The Process of Induction
charging something with either a positive or negative charge, creating a zone of electron deficiency and another of electron build-up, and then grounding the thing with a wire and removing either the deficiency or build-up
Grounding
The process of transferring excess charge to the earth to neutralize an object.
Zone of Charge
Regions of positive and negative induced charge created by the influence of a nearby charge.
Net Charge
The total charge of an object after accounting for all excess electrons and protons.
What is Coulomb's constant?
Coulomb's constant (k) is a proportionality factor in Coulomb's Law, approximately equal to 8.99 x 10^9 N m²/C², used to calculate the electric force between point charges.
What is the significance of the inverse square relationship in Coulomb's Law?
The inverse square relationship in Coulomb's Law indicates that as the distance between two charges increases, the electric force decreases rapidly, specifically with the square of the distance.
How does Coulomb's Law relate to electric fields?
Coulomb's Law provides the basis for understanding electric fields, as the electric field (E) created by a point charge can be derived from the force it exerts on a test charge placed in its vicinity.
What are the limitations of Coulomb's Law?
Coulomb's Law applies only to point charges and assumes that the charges are static
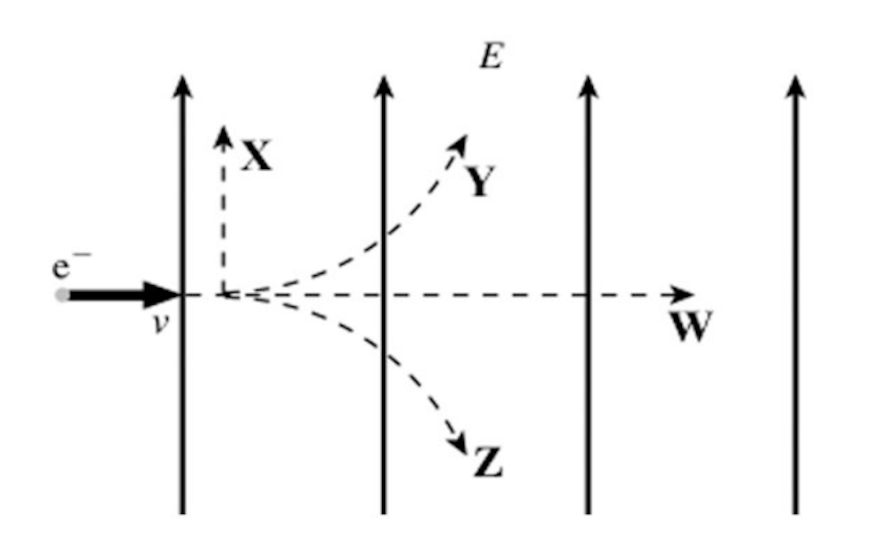
An electron is initially moving to the right when it enters a uniform electric field directed upwards, as shown in the figure. Which trajectory (X, Y, Z, or W) will the electron follow in the field?
trajectory z
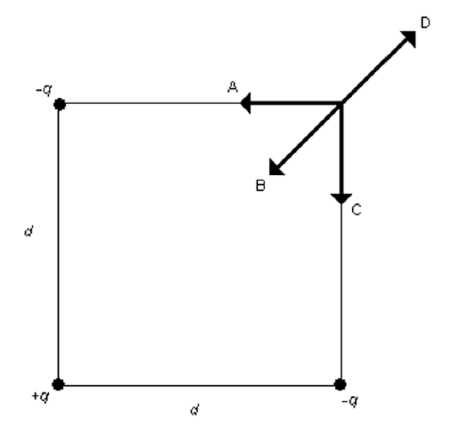
Three equal-magnitude point charges of varying signs are placed at three of the corners of a square of side d as shown in the figure. Which one of the arrows shown represents the direction of the net electric field at the vacant corner of the square?
B
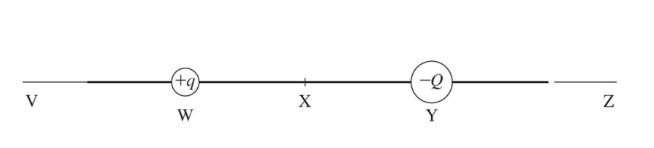
The figure shows two unequal charges, +q and -Q. Charge -Q has greater magnitude than charge +q. Point X is midway between the charges. In what section of the line will there be a point where the resultant electric field is zero?
VW
The electric field at point P due to a point charge Q a distance R away from P has magnitude E. In order to double the magnitude of the field at P, you could
double the charge to 2Q
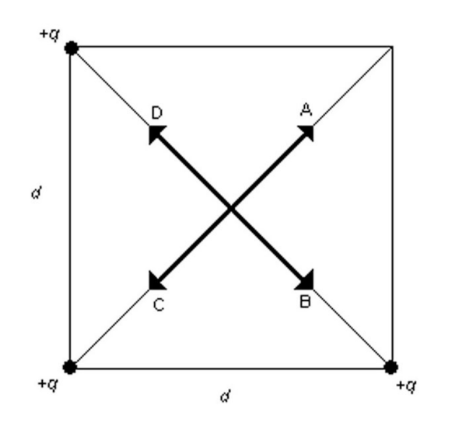
Three equal positive point charges +q are placed at the corners of a square of side d as shown in the figure. Which one of the arrows shown represents the direction of the net electric field at the center of the square?
A
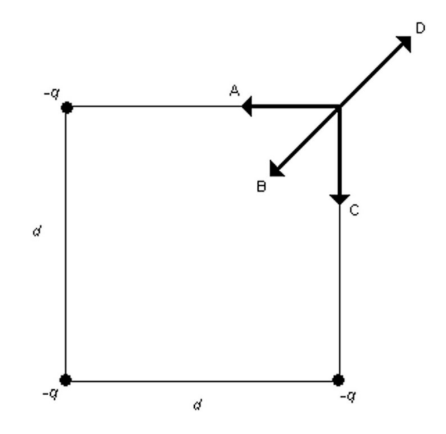
Three equal negative point charges -q are placed at three of the corners of a square of side d as shown in the figure. Which one of the arrows shown represents the direction of the net electric field at the vacant corner of the square?
B
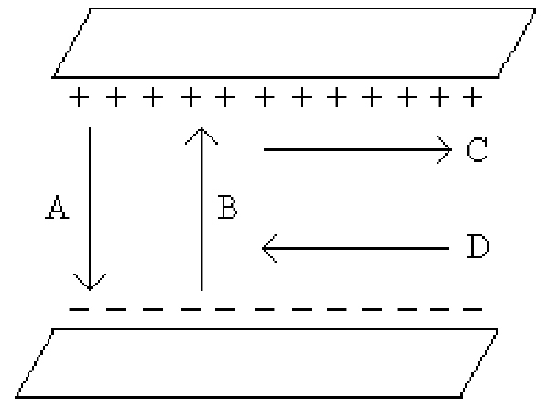
Which one of the arrows shown in the figure best represents the direction of the electric field between the two uniformly charged metal plates?
A
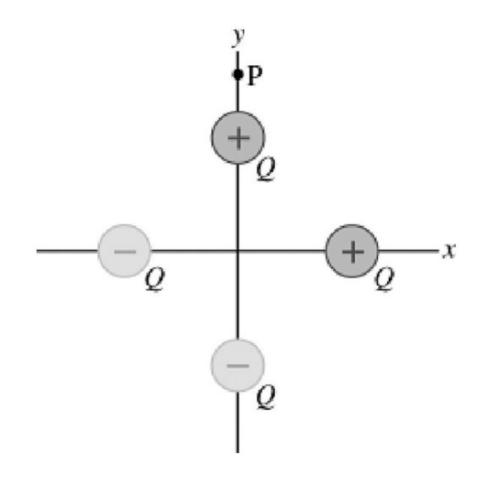
Four tiny charged particles (two having a charge +Q and two having a charge -Q) are distributed on the x- and y-axes as shown in the figure. Each charge is equidistant from the origin. In which direction is the net electric field at the point P on the y-axis?
upwards and towards the right
A plastic rod is charged up by rubbing a wool cloth, and brought to an initially neutral metallic sphere that is insulated from ground. It is allowed to touch the sphere for a few seconds, and then is separated from the sphere by a small distance. After the rod is separated, the rod
is repelled by the sphere
A negatively-charged plastic rod is brought close to (but does not touch) a neutral metal sphere that is connected to ground. After waiting a few seconds, the ground connection is removed (without touching the sphere), and after that the rod is also removed. The sphere is now
positively charged
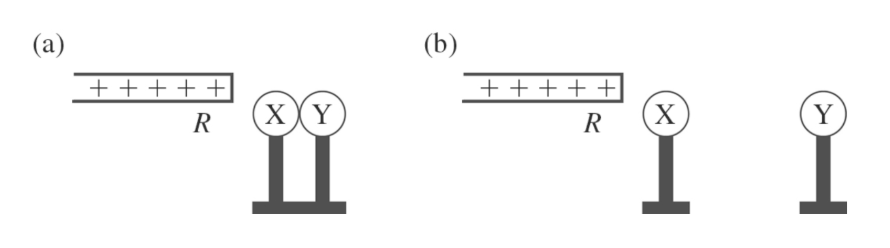
X and Y are two initially uncharged metal spheres on insulating stands, and they are in contact with each other. A positively charged rod R is brought close to X as shown in part (a) of the figure. Sphere Y is now moved away from X, as shown in part (b). What are the final charge states of X and Y?
X is negative and Y is positive
A hydrogen nucleus, which has a charge +e, is situated to the left of a carbon nucleus, which has a charge +6e. Which statement is true?
The electrical force experienced by the hydrogen nucleus is to the left, and the magnitude is equal to the force exerted on the carbon nucleus
Two point charges, Q1 and Q2, are separated by a distance R. If the magnitudes of both charges are doubled and their separation is also doubled, what happens to the electrical force that each charge exerts on the other one?
It remains the same
An electron and a proton are released simultaneously from rest and start moving toward each other due to their electrostatic attraction, with no other forces present. Which of the following statements are true just before they are about to collide?
They are closer to the to the initial position of the proton that to the initial position of the electron
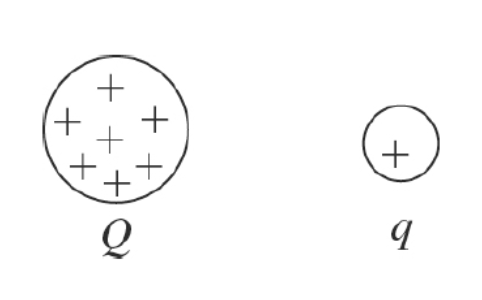
In outer space, a positive charge q is released near a positive fixed charge Q, as shown in the figure. As q moves away from Q, what is true about the motion of q?
It will move with increasing speed