Cobalt-60 Calculation Factors
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 355 - Tx Planning and Dosimetry I. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is the calibration condition for Cobalt-60 calculations?
10 × 10 field
measured at 80 cm
measured along the beam’s central axis
Do Co-60 machines have calibration factors (CF)?
no, there is no CF because this machine uses a cobalt pellet as it’s RT source
What is used instead of a calibration factor for Co-60?
Output factor
the dose rate to a small mass of tissue at the isocentre for a 10×10 cm field
What is the output of a Co-60 treatment machine related to?
the source’s activity
source’s dose rate at different points in time due to decay
Why does the Co-60 machine’s output change over time?
due to the decaying source
half-life
time for the radioactive source to decay to half of it’s original intensity
what is Co-60 half-life?
5.26 years
decays ~1% per month
Why is the mid-point date of treatment used to calculate the source’s output?
the output needs to reflect the average dose rate over the course of the patient’s treatment
What is the decay factor formula
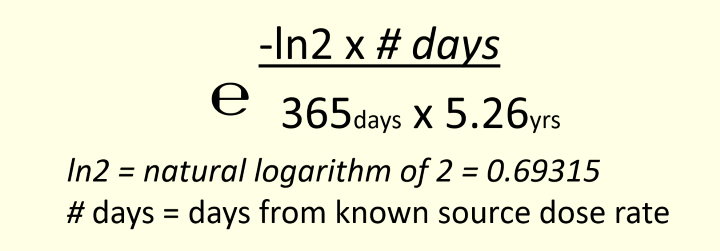
in treatment timer calculations, the dose rates in cobalt tables need to be adjusted to reflect…
the average dose rate over the patient’s treatment course
what are the three steps to finding the midpoint date
take the # of fractions from the dose prescription and count out the actual treatment days for the patient starting from the first treatment to the last treatment (don’t count weekends or stat holidays)
count the total days within the treatment course range including weekends and holidays and divide this number by two to get half of the treatment course length
starting on the patient’s start date, count out this half-way point number on the calendar
How does collimater scatter factor (Sc) differ between Cobalt and LINAC?
the concept is the same, but the measurement is at 80 cm along the central axis and not 100 cm
Is phantom scatter factor (Sp) used in Co-60 machines?
No!, TAR @ dmax will account for scatter at dmax depth
What is TAR
the ratio of absorbed dose at depth in a tissue to the absorbed dose at the same point in air within a build-up cap
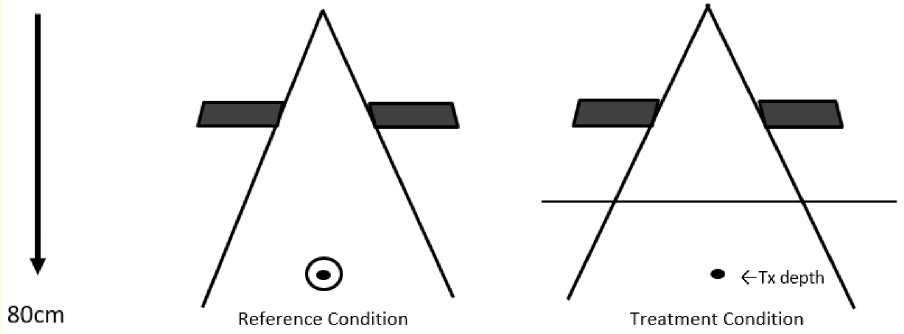
what does TAR take into account
scatter in the patient at the depth of treatment
in Cobalt-60 unit calcs only
what is a build up cap?
a probe that is covered with enough material to ensure the establishment of EE in the reference measurement
three factors that affect TAR
field size
depth
energy
is TAR independent of SSD?
yes
list 5 other factors that may be used alongside TAR in Co-60 calculations
ISL
PDD
Physical Wedge Factors
Perspex Tray Factors (to hold shielding blocks)
physical compensator factors
what is the formula for dose rate in a cobalt machine?
DR = midpoint output x ISL x Sc x TAR x other factors
What is a Co-60 timer setting
a measure of how long the beam is on for each treatment field, measured in minutes
used because the source decays over time
What is the formula for Tx time
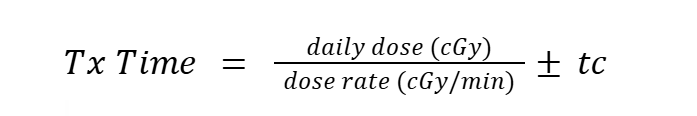
what is a time correction (tc)?
a factor that accounts for when the treatment time starts relative to the movement of the cobalt source from the source drawer to the ‘On’ position at the collimator opening
Describe a positive timer correction
the timer starts once the source starts moving, but the source is not fully in the ‘on’ position yet. Thus the full dose won’t reach the patient by the time the time stops
time must be added to account for this shortage!
typically +0.01-0.02 minutes

Describe a negative time correction
the timer starts once the source is in the fully ‘on’ position, however some dose will exit the collimators and reach the patient before the timer starts. Thus time must be subtracted to account for dose overage
typically -0.01 - 0.02 minutes
