Fungi
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Main Characteristics of Fungus
Bodies have a unique structural composition
They get their nutrients from other organisms
seen has decomposers
They reproduce asexually and sexually (+,-)
A group of fungi - Chytrids
Predominantly aquatic
Most are scavengers
One specie is a frog killer
Some frogs are resistant, others aren’t
Invaded the frog’s skin surface layer causing damage to the keratin layer and disrupting moisture balance
Have photosynthesis capacity
Eukarya
have nuclei
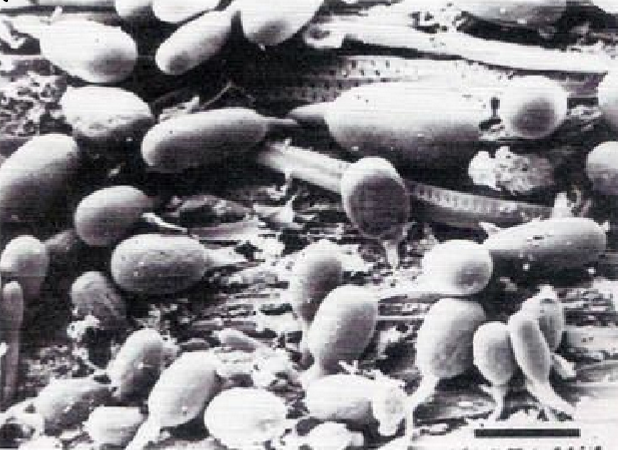

A group of fungi - Rumen
Anaerobic - don’t need air to survive
Symbiotic relationship with ruminants (animals = cow, sheep, deer)
Can hangout in the stomach of animals
Allows cows to chop and survive on grass because it allow them to digest the cellulose and the plant proteins
A group of fungi - Basidiomycetes
classic moldy bread
Mycorrhiza
need in plant roots
Process/fix the byproducts of plants allowing for the plants to get nitrogen back (nitrogen fixing)
reason for crop rotation occurring
excessive nitrogen are taken care of in plants don’t need as much and give to other plants that need it
Endophytes
In plant leaves
Good for the plant
makes the plant taste bad so animals won’t eat it
Allowing plants to stay alive and reproducing
Truffles
Underground mushrooms
Hard to cultivate
Stinky Cheese
Fungus injected into the cheese and grow within it for the taste
Basidiomycete ‘rusts’
Stop crop growth
Powdery Mildew
Doesn’t kill the plant but sucks the life out the plant by sucking out its nutrients
Dutch Elm Disease
Major issue in forsest in the west
Kills the Elm trees
Impacts of fungi on humans
Ringworm & Athletes foot
Lung Diseases
Inhaling a fungal spore
fungi grow in lungs