macro sec 1: basics of market system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
macroeconomics
studys overall economy
microeconomics
studies the decision-making of individual units (households, firms, etc.)
circular flow model
a visual representation of how money, goods, and services move through the economy, illustrating the interactions between households and firms.
broken window fallacy
a concept that argues against the idea that economic activity is boosted by destruction, as it ignores the unseen costs and lost opportunities.
basaits writings
economists must focus on what is seen and what is not seen (ppl tend to focus on what they can see)
economics is study of
how decisions are made when scarcity exists
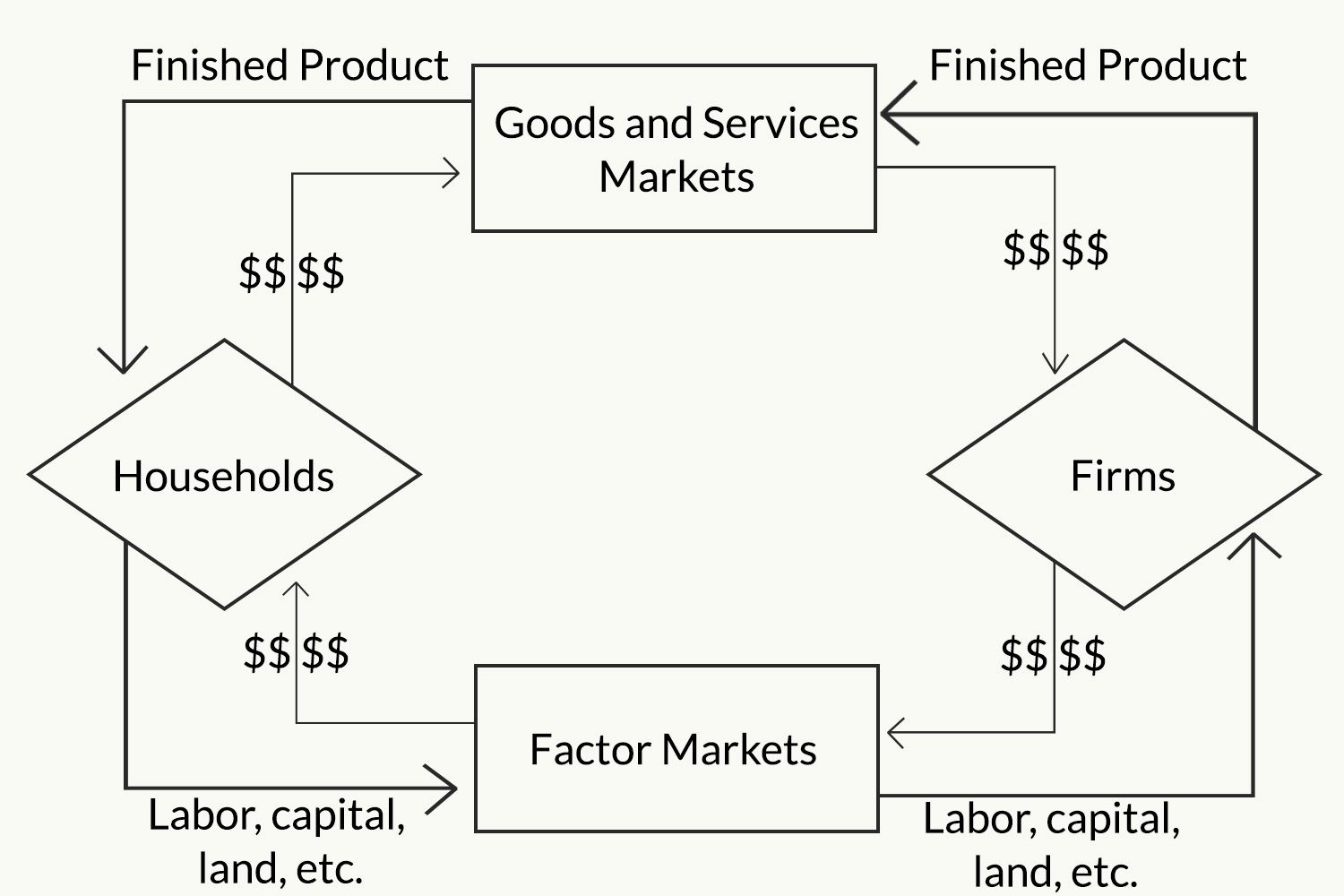
what model
circular flow model
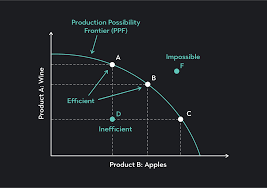
what graph
production possibilities frontier (shows various combinations of outputs the economy can produce)
normative statement
opinion based ; statement about how the world OUGHT to be
positive statement
descripive / factual ; makes measurable claim about how world is
absolute advantage
ability to produce good using fewer inputs than other producers
comparative advantage
ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost as another producer
adam smith in wealth of nations
rejected mercantilism, recommended using absolute advantage as the basis of trade,
imports
goods produced abroad and sold domestically
exports
goods produced domestically and sold abroad.
that which is seen, that which is not seen
is a concept introduced by Adam Smith that distinguishes between the visible effects and the hidden consequences of economic actions and policies
smooth haley tariff act of 1930
is a U.S. law that raised tariffs on imported goods, aiming to protect American industry but resulted in retaliatory measures and worsened the Great Depression.
law of demand
amount demanded for good falls when price of good rises
shifts in demand curve
price expectations, changes in individual tastes, price of related goods, changes in income
normal good
demand falls when income falls and rises when income rises, reflecting consumer preferences for higher quality or non-essential items (luxury car)
inferior good
demand rises when incomes falls and demand falls when income rises (taking the bus)reflects consumer preference for lower quality or essential items.
subsitutes
goods that can replace each other, leading to an increase in demand for one when the price of the other rises. Examples include butter and margarine.
complements
fall in price in one good increases demand for another (ice cream and hot fudge)
law of supply
the higher the price the greater the quality supplied
shifts in supply curve
new technology, input prices, # of sellers
surplus
quantity supplied greater than quanity demanded
shortage
quanity supplied less than quanity demanded
invisible hand
adam smith ; market forces that push price to equalibrium