Past Echo Exams
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Old echo test questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
when stage 1 (mild) diastolic dysfunction is present, the mitral inflow e/a ratio will:
b. decrease
with mild diastolic dysfunction (impaired relaxation of the ventricle), the deceleration time of the e wave of mitral inflow will be:
a. prolonged
tachycadia may cause the doppler signal of the left ventricular inflow to:
c. have a fused e/a velocity
all of the following echo features are consistent with diastolic dysfunction except:
b. pulmonary s wave greater than d wave
the valsalva maneuver can be utilized in evaluation of diastolic dysfunction to:
c, differentiate normal mitral inflow from a pseudonormalization pattern
pulmonary venous doppler tracing should be obtained from which view?
a. apical four chamber
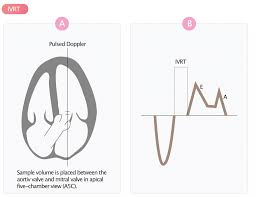
this image demonstrates how to obtain and measure what diastolic parameter:
d. isovolumic relaxation time
to measure peak early diastolic myocardial velocity the doppler gate should be placed:
b. at the lateral or septal mitral valve annulus (tdi)
all the following conditions are associated with diastolic dysfunction except:
d. aortic dissection
a normal mitral annulus tissue doppler spectral waveform is:
d. negative and below the baseline
in the presence of severe diastolc dysfunction, we expect the isovolumic relaxtion time to be:
b. shortend
grade 3, severe diastolic dysfunction is characterized by:
a. e/a greater than 2
true or false: patients with diastolic dysfunction will always have systolic dysfunction.
false
diastolic function is difficult to accurately assess in a patient with which coexisting condition:
b. mitral stenosis
a secondary finding in a patient with grade 3 (severe) diastolic dysfunction may be:
a. left atrial enlargement
all of the following parameters are important for the assesment of diastolic dysfunction except:
b. left ventricular outflow tract velocity
diastolic function assesment should be conducted during what segment of the ecg?
d. from the end of the t wave to the onset of the qrs complex
diastole is the interval from aortic valve ____ to mitral valve ____.
b. closure, closure
true or false: diastolic heart failure causes patients to be symptomatic .
true
the period of diastole most effected by heart rate is:
c. diastasis
the number one cause of diastolic dysfunction is:
b. increased age
diastasis end when:
c. the left atrium contracts
_____is the term that describes the elasticity of the ventricle:
c. compliance
during rapid filling phase of diastole ventricular volume increases, ventricular pressure :
c. remains the same
as a ventricle becomes stiffer, filling pressure ____ and stroke volume _____
a. increases, decreases
diastolic dysfunction will always ____ systolic dysfunction
b. precede
by dividing peak e wave velocity and peak e’ velocity the lv edp can be estimated. values of e/e’ ____suggested elevated lvedp.
d. greater than 15
true or false: left atrial dilation always indicates diastolic dysfunction.
false
true or false: the left atrial appendage should be included in the left atrial volume measurement.
false
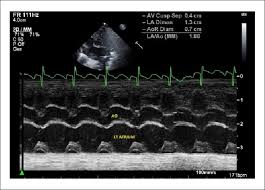
the following m-mode tracing:
d. provides no info regarding diastolic function status
true or false: an x-ray finding of cardiomegaly & pulmonary venous congestion indicates systolic dysfunction rather than diastolic dysfunction.
false
the gold standard test for diagnosis of elevated filling pressures is:
c. cardiac catheterization
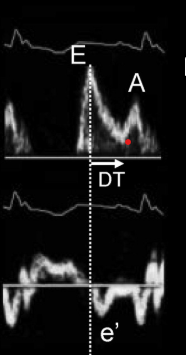
the following mitral inflow and tissue doppler waveforms most likely indicate:
c. grade 2 moderate diastolic dysfunction (pseudonormal)
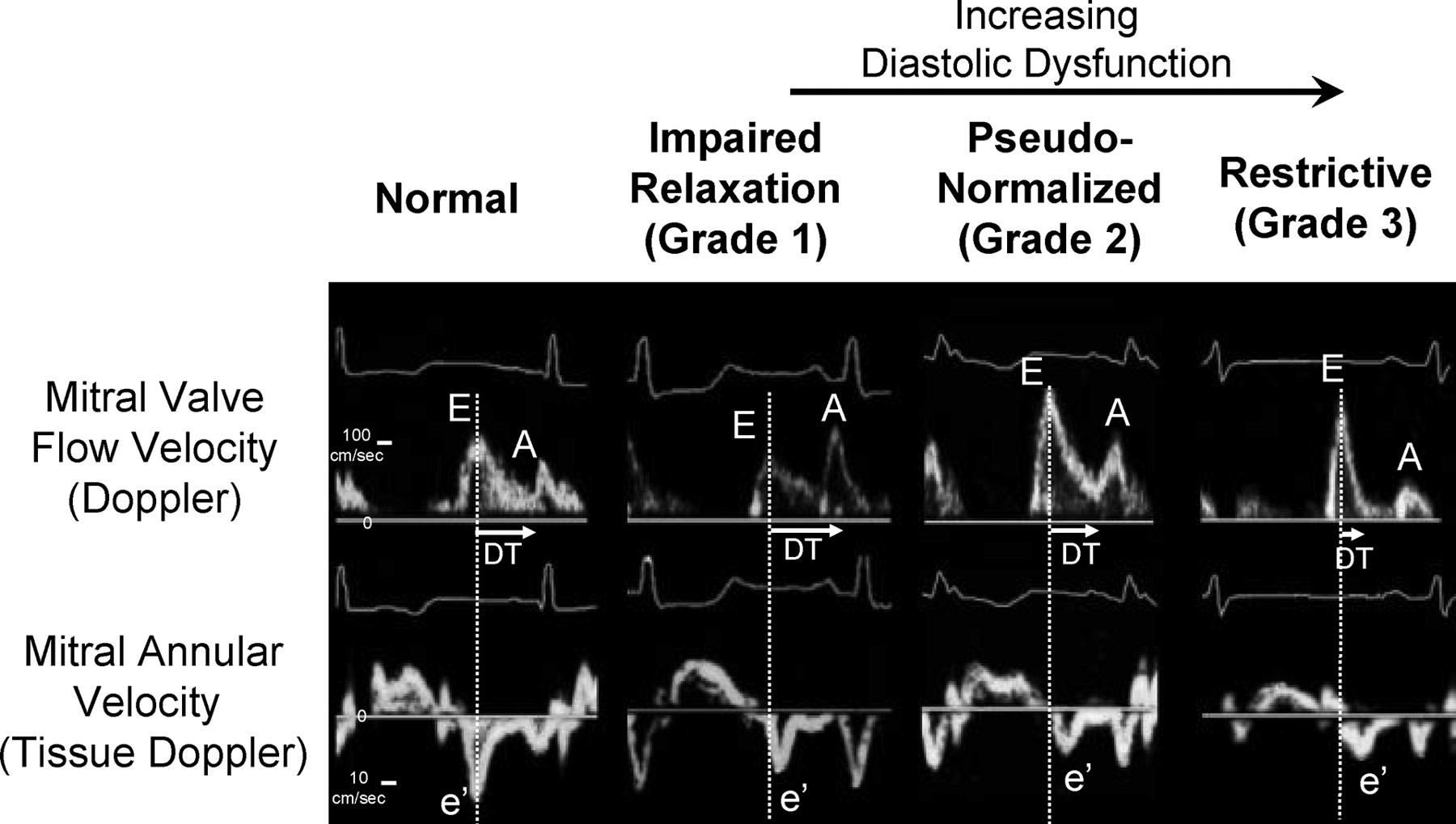
true or false: an e/a ration of greater than or equal to 2 always indicates severe diastolic dysfunction.
false
in a patient with mitral stenosis a continuous wave doppler study measures a peak diastolic velocity if 2.0m/s. what is the peak pressure gradient across the mitral valve?
a. 16 mmhg
*4(2.0)² = 16
aortic stenosis is example of something that would cause:
b. increased afterload
which of the following is not a cause of increased left ventricular mass?
d. long term use of oxygen
what is the name for the external layer of the left ventricle?
d. epicardium
the longer the length and higher the tension of the muscle fibers at end diastole, the stronger the resulting contraction will be. this known as:
c. the frank starling law
blood will always flow from:
b. high pressure to low pressure
the period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into ciruculation is called:
a. systole
during the qt interval on the ecq:
b. the atria are filling
which of the following would indicate normal lv systolic function by strain:
c. -25%
in a normal individual, during isovolumic contraction the:
c. pressure in the left ventricle increases, no valves are open
_____ is defined as the weight of the left ventricle, which has been found to be an important predictor of adverse cardiovascular events and premature death.
d. left ventricular mass
when sound waves hit an object moving towards the sound source, the reflected frequency will be _____ the transmitted frequency.
a. higher than
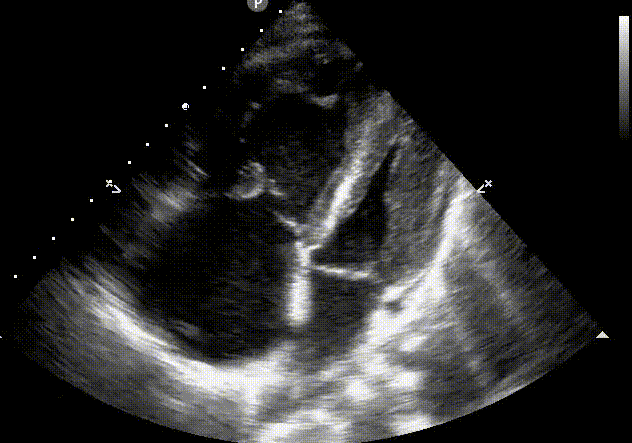
given the following image, what is your qualitative assessment of the right ventricle size?
c. dilated
akinesis of the anterior left ventricular wall is most likely to indicate obstruction of the:
c. left anterior descending artery
which of the following is associated with a psuedoaneurism?
d. has a narrow neck
a segment of the left ventricle that lacks systolic wall thickening and motion is best described as:
b. akinetic
the echocardiogram of a patient with a ruptured papillary muscle wall will exhibit all of the following except:
c. some degree of aortic regurge
what is the term that describes a regional wall motion abnormality that occurs after a brief period of ischemia that has not caused permanent damage?
b. stunning
a pericardial effusion occuring 6-10 days after a myocardial infarction that is accompanied by a fever may represent:
a. dressler’s syndrome
the right ventricle may be involved up to 50% of the time in patients with infarctions of the:
c. inferior wall
when a segment of the heart wall bulges in systole, appears thinned and moves paradoxically compared to the surrounding myocardium, it is termed:
b. dyskinetic
disease in the left anterior descending artery affects all of the following areas except:
b. right ventricle free wall
which of the following is the earliest manifestation of myocardial ischemia detectable during stress echo?
d. regional diastolic dysfunction
what is the purpose of stress echocardiography?
b. used to evaluate change in myocardial performace and valvular hemodynamics
true or false: st elevation on ecg always indicates acute myocardial infarction (MI).
false
in exercise stress echocardiography, inital images should be acquired within how many seconds from the time the patient ceases exercise?
a. 60 seconds
after stress echocardiography, reduced wall thickening and motion, dilation of the lv, and reduction in ejection fraction may indicate:
c. multiple vessel disease
if a patient can’t achieve target heart rate, this may produce:
b. false negatives
in addition to apical four and two chamber views, what other views are used during stress testing?
a. parasternal long and parasternal short axis
if collateral vessels are well established in the coronary artery system, then the echo findings may present as:
b. false negative
in stress echo, hypertension may result in which one of the following:
a. false positive
put the folloiwng events in order from the first to occur to the last to occur following the ischemic cascade:
ischemic ecg changes, regional diastolic dysfunction, regional systolic dysfunction, perfusion abnormality, and angina/symptoms
perfusion abnormality
regional diastolic dysfunction
regional systolic dysfunction
ischemic ecg changes
angina/symptoms
in the parasternal short axis view at the chordal level, which segments are seen?
a. base
the apical long axis and parasternal long axis demonstrate which two walls?
a. inferolateral and anteroseptal
what type of stress echocardiogram is most sensitive for detection of cad?
b. exercise
a flail mitral valve leaflet will result in ____ mitral regurge.
a. severe
the normal response of the left ventricle end systolic cavity size during exercise is:
b. reduced
true or false: the apex should be seen in the parasternal long axis view.
false
all of following are indications for a stress echo except:
c. acute MI
what is a common secondary pathology that should be evaluated for in a patient with this condition?
c. apical thrombus
true or false: a patient had a resting echo that demonstrated hypokinesis of the anterior wall. on the echo performed 24 hours following reperfusion of a coronary artery that was 98% occluded we should expect to see a normal lv, with normal global and regional wall motion in all segments.
false
papillary muscle rupture can occur in rare cases of inferior wall myocardial infarctions. the coronary artery most often responsibility for this ischemic event is the:
c. right coronary artery
a thrombus described as mobile, and attached to the left ventricle wall by a stalk would be classified as:
a. pedunculated
all of the following are treatment options for myocardial infarction except:
d. direct current cardioversion (dccv)
the _____ artery branches off of the left main coronary artery and continues laterally in the atrioventricular groove to supply the inferolateral lv wall.
b. left circumflex artery
myocardial perfusion occurs from:
c. epicardium to endocardium