Thyroid Test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:23 PM on 4/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
what is the first endocrine gland to develop in the human embryo?
the thyroid gland
2
New cards
what does the thyroid develop from?
the floor of the primitive pharynx/base of the tongue, then it migrates inferiorly
3
New cards
where is the thyroid gland located?
on the anterior, inferior neck on either side of the trachea
4
New cards
what does the thyroid maintain?
metabolism, growth, and development
5
New cards
what is the thyroid regulated by?
the pituitary gland and hypothalamus
6
New cards
what sits just superior to the thyroid on the anterior neck?
the thyroid cartilage (adam’s apple)
7
New cards
what connects the right and left lobes of the thyroid?
a central bridge of tissue called the isthmus
8
New cards
what is the normal LONG measurement of the thyroid?
4-6cm
9
New cards
what is the normal AP measurement of the thyroid?
1\.5-3cm
10
New cards
what is the normal TRV measurement of the thyroid?
1-2cm
11
New cards
what is the normal measurement of the isthmus?
0\.4-0.6cm
12
New cards
AKA false thyroid capsule-contains more than just the thyroid itself and assists in forming the carotid sheath
pre-tracheal fascia
13
New cards
adheres directly to the surface of the thyroid tissue itself
true thyroid capsule
14
New cards
what are the two types of tissue that the thyroid is made of?
follicular cells and c cells
15
New cards
make up the majority of the thyroid tissue and secretes T3 and T4; these cells require iodine to produce T3 and T4
follicular cells
16
New cards
AKA parafollicular cells; secrete calcitonin
c cells
17
New cards
the main nerves of your parasympathetic nervous system; this system controls specific body functions such as your digestion, heart rate, and immune system; these functions are involuntary meaning you can’t consciously control them; AKA vagal nerves
vagus nerve
18
New cards
what are the anterior muscles also known as the strap muscles that surround the thyroid?
1\.) sternohyoid
2\.) omohyoid
3\.) sternothyroid
2\.) omohyoid
3\.) sternothyroid
19
New cards
this is present in 10-40% of the population; it is a superior extension of the thyroid isthmus and is more common in the LT lobe
accessory or pyramidal lobe
20
New cards
the recurrent laryngeal nerve creates a pseudotumor along the posterior of the thyroid; not a nodule, normal thyroid tissue
zuckerkandl’s tubercle
21
New cards
the rate at which the body uses energy while at rest to maintain vital functions such as breathing and keeping warm
basal metabolism
22
New cards
what are thyroid secretions controlled by?
TSH
23
New cards
what is TSH and what is it secreted by?
thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) and it is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland
24
New cards
what is the level of TSH regulated by?
the basal metabolic rate (BMR)
25
New cards
this results from a low concentration of thyroid hormones; triggers the hypothalamus to tell the pituitary gland to release TSH into the blood stream
decrease in BMR
26
New cards
what is the primary hormone secreted by the thyroid? (90%)
T4 (thyroxine)
27
New cards
what is the secondary hormone secreted by the thyroid? (10%)
T3 (triiodothyronine)
28
New cards
what is the primary function of the calcitonin secreted by the c cells?
to decrease the blood calcium levels, preventing hypercalcemia
29
New cards
what is the thyroid composed of?
follicles filled with colloid
30
New cards
small secretory cavity, sac, or gland
follicle
31
New cards
a gelatinous or mucinous substance found normally in the thyroid
colloid
32
New cards
a thyroid that is functioning normally and producing the correct amount of thyroid hormones
euthyroid
33
New cards
undersecretion of thyroid hormone; the most common thyroid disorder; most commonly caused by a chronic thyroid inflammatory process called Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
hypothyroidism
34
New cards
a rare, more severe complication of hypothyroidism that could lead to a life-threatening coma
myxedema
35
New cards
oversecretion of thyroid hormones; occurs when the thyroid is not functioning from Grave’s disease, overall thyroid enlargement, or localized adenoma causing oversecretion of thyroid hormones
hyperthyroidism
36
New cards
an extreme form of hyperthyroidism
thyrotoxicosis
37
New cards
congenital absence of the thyroid gland; may affect one lobe, the isthmus, or the entire gland; this has a severe affect on physical and mental development
aplasia
38
New cards
underdevelopment of any part of the thyroid gland; may be associated with congenital hypothyroidism
hypoplasia
39
New cards
may be present along embryologic descent if the thyroid migrates too little or too far; ectopic thyroid tissue locations include: posterior to the tongue, near the larynx, and mediastinal area; scintigraphy is ideal to visualize this
ectopic thyroid tissue
40
New cards
what are two tests used to determine thyroid function?
iodine uptake and thyroid scan
41
New cards
what shows more uptake of the tracer?
hyperactivity
42
New cards
what shows less uptake of the tracer?
hypothyroidism
43
New cards
a reporting system for thyroid nodules on ultrasound proposed by the american college of radiology
ti-rads
44
New cards
a general enlargement of the thyroid gland; longer than 6cm in length or thyroid parenchyma extending over the CCA in TRV
goiter
45
New cards
multiple nodules causing the thyroid to become enlarged
multinodular goiter
46
New cards
may affect large groups of people in a geographical area where iodine levels in the soil, food, and water are low; iodized salt usually corrects iodine insufficiency
endemic goiter
47
New cards
when enlargement of the gland is not associated with abnormal thyroid function
nontoxic goiter
48
New cards
when enlargement of the thyroid causes hyperthyroidism
toxic goiter
49
New cards
a true epithelial cyst in the thyroid is benign and uncommon
simple cyst
50
New cards
a cyst with a tiny echogenic focus; commonly has a comet tail artifact posterior to the echogenic focus; may be multiple
colloid cyst
51
New cards
a cyst that may have low-level echoes with debris present, wall irregularities, and internal septations
hemorrhagic cyst
52
New cards
a solitary, slow growing benign neoplasm
thyroid adenoma
53
New cards
a benign thyroid neoplasm that represents 5-10% of all thyroid nodules; 7x more likely in females
follicular adenoma
54
New cards
rare type of adenoma that have malignant cancer cells found after extraction
hurthle cell adenoma
55
New cards
a group of disorders that include inflammation of the thyroid gland with several causes including bacterial/viral infections, postpartum, post-radiation ablation technique, drug-induced, or autoimmune-related abnormalities
thyroiditis
56
New cards
typically caused secondary to a viral infection; diffuse inflammation of the thyroid with significant pain on thyroid palpitation, dysphagia, fever, thyroid enlargement, and malaise
de Quervians’s thyroiditis
57
New cards
an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the thyroid and the thyroid responds by creating excessive thyroid hormones; the most common cause of hyperthyroidism; 5-8x more common in women after 30 years of age
grave’s disease
58
New cards
the most common form of thyroiditis caused by a destructive autoimmune disorder which leads to chronic inflammation of the thyroid
hashiomoto’s thyroiditis
59
New cards
rare cancer of the thyroid; there are 4 types: papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic
thyroid carcinoma
60
New cards
most common thyroid cancer; considered the least aggressive type of tumor; females are affected more than males at age 20-40; major spread of this is through lymphatic channels
papillary carcinoma
61
New cards
second most common thyroid cancer; more aggressive than papillary carcinoma with a 20-year mortality rate of 20%; 3x more likely in females and seen between the ages of 40-60; NOT associated with radiation; there are 2 types: minimally invasive and widely invasive; spreads through the bloodstream
follicular carcinoma
62
New cards
accounts for 5-10% of thyroid cancers; develops from the c cells that secrete calcitonin; slightly higher female to male incidence (3-2) NOT associated with radiation
medullary carcinoma
63
New cards
rare thyroid cancer; considered the most deadly; 2x more likely in men after age 60; may be associated with radiation; usually diagnosed at stage 4 when found; this cancer grows quickly; typically causes death by asphyxiation due to invasion of the trachea
anaplastic carcinoma
64
New cards
what does anaplastic mean?
undifferentiated
65
New cards
term used to describe cells or tissues that do not have specialized structures or functions; these often grow and spread quickly
undifferentiated
66
New cards
the space remaining after a thyroid has been removed
the thyroid fossa
67
New cards
what are the parathyroids derived from?
endoderm cells
68
New cards
the stalk between the thyroid and the tongue
the thyroglossal duct
69
New cards
small, encapsulated, oval structures attached to the posterolateral surface of the thyroid glands; typically oval/bean shaped
parathyroid glands
70
New cards
what do parathyroids secrete?
PTH (parathyroid hormone)
71
New cards
what does PTH do?
maintains blood levels of calcium and phosphorus
72
New cards
where are the parathyroid glands located?
on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland
73
New cards
what is the approximate normal measurement of a parathyroid gland?
0\.5 x 0.3 x 0.1cm
74
New cards
what is the primary function of the parathyroid glands?
to help maintain homeostasis of blood calcium concentration
75
New cards
in the bones, what is calcium stored as?
phosphate
76
New cards
what decreases the concentration of calcium in the blood?
calcitonin
77
New cards
an endocrine disorder caused by increased function of the parathyroid gland; more common in women after age 40; characterized by abnormal secretion of PTH, which elevates calcium in the blood
primary hyperparathyroidism
78
New cards
a benign, solid mass and the most common cause of hyperparathyroidism; usually oval and solitary and can involve 1 or more parathyroid
parathyroid adenoma (PTA)
79
New cards
enlargement and hyperfunction of the parathyroid gland with no apparent cause
parathyroid hyperplasia
80
New cards
1% of pts with primary hyperparathyroidism have this
parathyroid carcinoma
81
New cards
occurs when the serum PTH level is increased due to chronic hypocalcemia
secondary hyperparathyroidism
82
New cards
most common congenital anomaly; 90% are found before age 10 in the pediatric pt
thyroglossal duct cyst
83
New cards
congenital cystic mass in the lateral neck in the submandibular region
branchial cleft cyst
84
New cards
localized or generalized enlargement of the lymph nodes
cervical lymphadenopathy (lymphomegaly)
85
New cards
identifies stiffness of tissues
elastography
86
New cards
what color do cold nodules appear to be in nuc med imaging? (scintigraphy)
lighter/white
87
New cards
what color do hot nodules appear to be in nuc med imaging? (scintigraphy)
darker/black
88
New cards
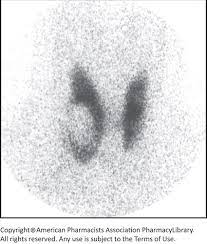
is this nodule hot or cold?
cold
89
New cards
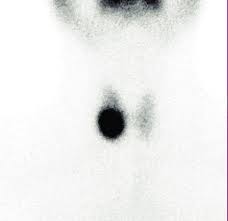
is this nodule hot or cold?
hot
90
New cards
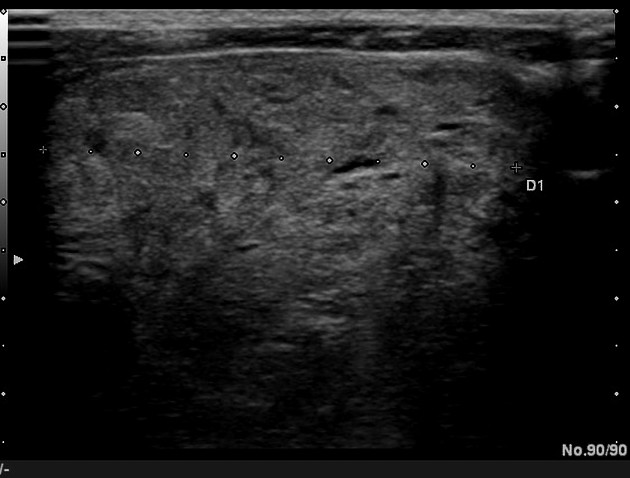
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
multinodular goiter
91
New cards
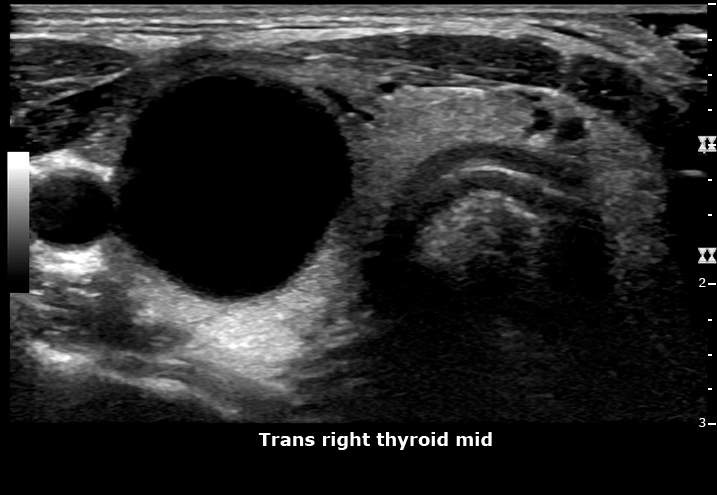
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
simple thyroid cyst
92
New cards
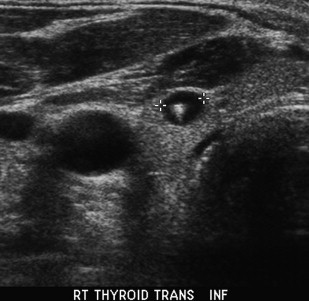
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
colloid cyst
93
New cards
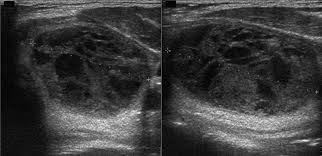
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
hemorrhagic thyroid cyst
94
New cards
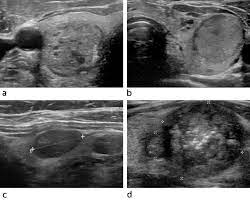
what thyroid pathology is shown here? note: these have a broad range of appearances and most often appear as solitary and homogeneous
thyroid adenoma
95
New cards
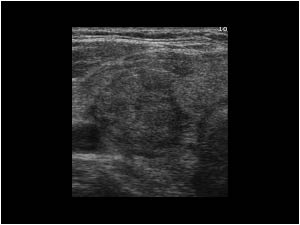
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
symptoms vary but may include mild-severe swelling, tenderness of the thyroid, symptoms of hypothyroidism
symptoms vary but may include mild-severe swelling, tenderness of the thyroid, symptoms of hypothyroidism
thyroiditis
96
New cards
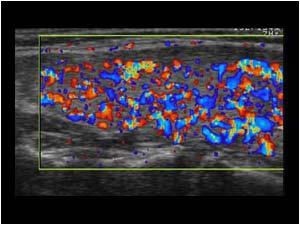
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
characterized by three clinical findings: hypermetabolism, diffuse toxic goiter, and exophthalmos. Other symptoms include enlarged thyroid, thickening of the skin in the legs/feet, elevated T3/T4, and very low TSH
characterized by three clinical findings: hypermetabolism, diffuse toxic goiter, and exophthalmos. Other symptoms include enlarged thyroid, thickening of the skin in the legs/feet, elevated T3/T4, and very low TSH
grave’s disease
97
New cards
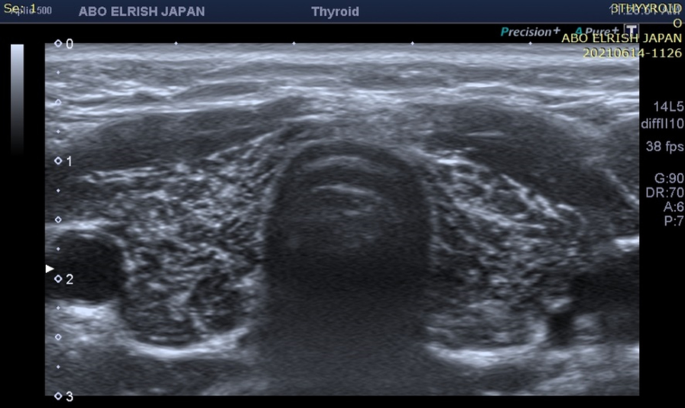
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
young middle-aged woman; painless, diffusely enlarged thyroid; low serum T3/T4 and elevated TSH
young middle-aged woman; painless, diffusely enlarged thyroid; low serum T3/T4 and elevated TSH
hashimoto’s thyroiditis
98
New cards
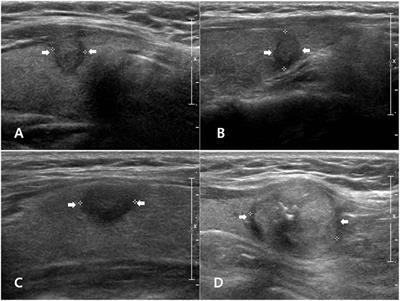
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
palpable, firm, painless, solitary nodule in the thyroid; pt may present with cough, hoarseness, dysphagia, or dyspnea due to compression of adjacent neck anatomy
palpable, firm, painless, solitary nodule in the thyroid; pt may present with cough, hoarseness, dysphagia, or dyspnea due to compression of adjacent neck anatomy
thyroid carcinoma
99
New cards
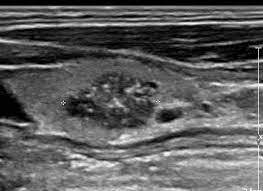
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
pts with hx of radiation are at increased risk; major spread is through lymphatic channels
pts with hx of radiation are at increased risk; major spread is through lymphatic channels
papillary carcinoma
100
New cards
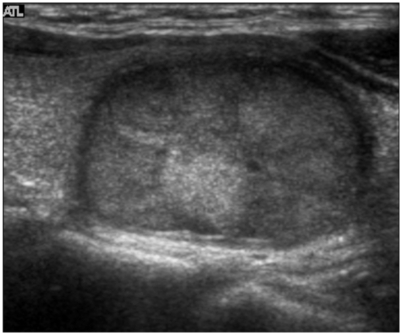
what thyroid pathology is shown here?
not associated with hx of radiation; spreads through bloodstream
not associated with hx of radiation; spreads through bloodstream
follicular carcinoma