Chemistry of Life (Ware)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:08 PM on 9/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
1
New cards
Scientific Method
Process of systematic observation, measurement, and experimentation to test a hypothesis
2
New cards
Hypothesis
A proposed explanation requiring further investigation
- "If (independent variable)....then (dependent variable)"
- "If (independent variable)....then (dependent variable)"
3
New cards
Independent Variable
- 1 variable that is changed in experiment
- the "cause"
- x-axis
- isn't changed by the other variables you are trying to measure
- the "cause"
- x-axis
- isn't changed by the other variables you are trying to measure
4
New cards
Dependent Variable
- dependent on the independent variable
- the "effect"
- y axis
- the "effect"
- y axis
5
New cards
Controlled Variable
- Variables that stay CONSISTENT to ensure it doesn't influence results
6
New cards
Control
Without the independent/manipulated variable
7
New cards
Scientific Theory
- throughly tested
- reasoning that groups many different observation
- unlike scientific hypothesis (not fully tested yet)
- reasoning that groups many different observation
- unlike scientific hypothesis (not fully tested yet)
8
New cards
Steps of Origin of Life
1. formation of the earth (4.5 billion), acquired organic chemicals by the collision with other comets/meteorites
2. Prebiotic synthesis & Accumulation of amino acids, sugars, lipids, etc in the environment
3. Prebiotic condensation & reactions with polymers of proteins and nucleic acids (RNA)
4. Synthesis of lipids - self-assembly into membranes/liposome capturing prebiotic molecules
5. Protobiont Formation- first living systems with cooperative interactions
2. Prebiotic synthesis & Accumulation of amino acids, sugars, lipids, etc in the environment
3. Prebiotic condensation & reactions with polymers of proteins and nucleic acids (RNA)
4. Synthesis of lipids - self-assembly into membranes/liposome capturing prebiotic molecules
5. Protobiont Formation- first living systems with cooperative interactions
9
New cards
Early Atmosphere Gases
Hydrogen sulfide (toxic gas) and carbon dioxide
10
New cards
Common Elements of Life
Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, sulfur
11
New cards
Chemosynthesis
- bacteria use hydrogen sulfide to make sugar
(early life in deep ocean vents)
(early life in deep ocean vents)
12
New cards
Life Moving to Earth's Surface
- energy = sun
- chlorophyll - traps sunlight, turns co2 and oxygen into food
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS CAUSES LIFE TO SPREAD
- chlorophyll - traps sunlight, turns co2 and oxygen into food
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS CAUSES LIFE TO SPREAD
13
New cards
Stromatolites (Cyanobacteria on Top)
- oldest fossil
- bacteria's waste gas with iron to ocean floor: rusts earth, makes iron ore
- cynaobacteria makes oxygen, got rid of toxic gases - made ozone layer
- bacteria's waste gas with iron to ocean floor: rusts earth, makes iron ore
- cynaobacteria makes oxygen, got rid of toxic gases - made ozone layer
14
New cards
Microbes
Ruled earth for 3 billion years
15
New cards
RNA
- ribonucleic acid
- contains sugar ribose
- solves "chicken and egg" problem" (genes need enzymes to form, enzymes need genes to form)
- RNA acts both as genes and enzymes
- contains sugar ribose
- solves "chicken and egg" problem" (genes need enzymes to form, enzymes need genes to form)
- RNA acts both as genes and enzymes
16
New cards
DNA
- deoxyribonucleic acid
- contains sugar deoxyribose
- contains sugar deoxyribose
17
New cards
A) Ocean Surface
- began near tide pool, pond, moist clay
- gas from volcano mixed with UV light/electric discharges makes PREBIOTIC MOLECULES
- gas from volcano mixed with UV light/electric discharges makes PREBIOTIC MOLECULES
18
New cards
B) Panspermia
- comets and meteors carried living organisms onto earth when it landed
- organisms will need to survive the heat of landing
- organisms will need to survive the heat of landing
19
New cards
C) Undersea Thermal Vents
- life have survived and arises from ancient volcanic vents
- needs gases, energy, catalysts (metal sulfides)
- needs gases, energy, catalysts (metal sulfides)
20
New cards
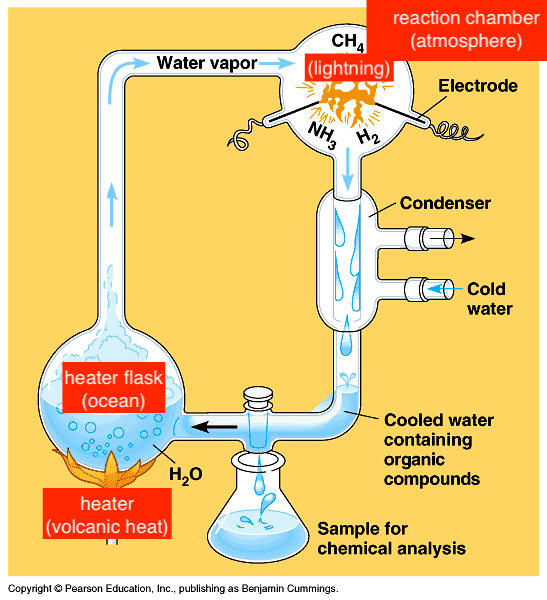
Miller-Urey Experiment
- 1950s, to recreate conditions of primitive earth to see what might given rise to molecules of first organisms
- created amino acids, nucleic acids, sugars, lipids, adenine, ATP
- created amino acids, nucleic acids, sugars, lipids, adenine, ATP
21
New cards
Endosymbiosis Theory
Origin of Eukaryotes:
- large prokaryote cells ingest free-floating prokaryotes
- organelles: mitochondria and chloroplast- dependent on the nucleus to direct metabolic processes
- large prokaryote cells ingest free-floating prokaryotes
- organelles: mitochondria and chloroplast- dependent on the nucleus to direct metabolic processes
22
New cards
Origin of Mitochondria
prokaryote cells engulfing purple bacteria
23
New cards
Origin of Chloroplasts
prokaryote cells engulfing cyanobacteria (already capable of photosynthesis)
24
New cards
2 Sequence of Evolutionary Change
1. Animal Cells diverged before leading to plant cells
2. Plant Cells to Animal Cells (plant cell evolved from plant cells and lost chloroplast)
2. Plant Cells to Animal Cells (plant cell evolved from plant cells and lost chloroplast)
25
New cards
Buildup of Free Oxygen In Atmosphere
Allows animals to develop features to turn oxygen into energy (ex photosynthesizing)
26
New cards
First Appearances
Primitive Cells: 3500 mya
Invertebrates: 550 mya
Fish (ray-finned): 400 mya
Land Plants: 375 mya
Reptiles: 260 mya
Mammals: 200 mya
Birds: 180 mya
Invertebrates: 550 mya
Fish (ray-finned): 400 mya
Land Plants: 375 mya
Reptiles: 260 mya
Mammals: 200 mya
Birds: 180 mya
27
New cards
Significance of Mass Extinctions to Biodiversity
- causes living things to compete for living resources
- most adaptable types can live
- stimulation for more complex organisms
- most adaptable types can live
- stimulation for more complex organisms
28
New cards
One or More Cells
All living things are made up of...
(unicellular/multicellular)
(unicellular/multicellular)
29
New cards
Reproduce
All living things...
sexual = two sex cells required
asexual= no gameates/sex cells used (only needs 1 parent cell)
sexual = two sex cells required
asexual= no gameates/sex cells used (only needs 1 parent cell)
30
New cards
Genetic Code
All living things contain a....
(univeral, passes down to offspring, starts as RNA but DNA rules because more stable)
(univeral, passes down to offspring, starts as RNA but DNA rules because more stable)
31
New cards
Grow and Develop
All living things __1__ and __2___...
1. Increases in size (divides repeadly)
2. Change/performs different functions
1. Increases in size (divides repeadly)
2. Change/performs different functions
32
New cards
Metabolism
All living things have a....
Combination of chemical reactions when organisms makes/breaks molecules (etc obtain and use material/energy)
Combination of chemical reactions when organisms makes/breaks molecules (etc obtain and use material/energy)
33
New cards
Autotroph
Organisms obtains energy from sun/inorganic compound (photosynthesis)
etc: the grass
etc: the grass
34
New cards
Heterotroph
Organism obtains energy from consuming nutrients (organic molecules) from environment
etc: cow
etc: cow
35
New cards
Respond
All living things ________ to their environment.
36
New cards
Stimulus
- a signal from the environment that causes internal/external reaction
37
New cards
Behavior
a complex response to stimulus
38
New cards
Homeostasis
All living this maintain....
Maintaining stable internal conditions (body tempt, blood sugar levels,etc) despite external environment changes
Maintaining stable internal conditions (body tempt, blood sugar levels,etc) despite external environment changes
39
New cards
Evolve
As a group, all living things....
- adapt to environment to survive
- small changes over millions years to big changes
- adapt to environment to survive
- small changes over millions years to big changes
40
New cards
Water
All living things need _____ to survive.
For metabolic processes, homeostasis, chemical reactions
For metabolic processes, homeostasis, chemical reactions
41
New cards
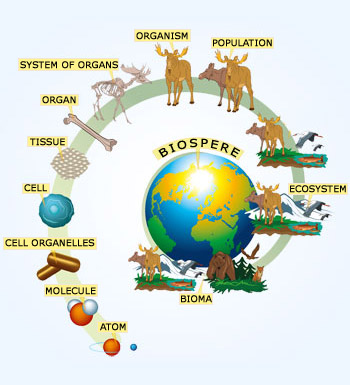
Hierarchy
Structural Organization of cellular organisms
Each level is part of next, higher level
Each level is part of next, higher level
42
New cards
Carbon
- #6, solid at room temp
- found everywhere (atmosphere oceans, living things/ores, minerals)
- oxygen for photosynthesis, energy production
- gas absorbed by organism
- found everywhere (atmosphere oceans, living things/ores, minerals)
- oxygen for photosynthesis, energy production
- gas absorbed by organism
43
New cards
Oxygen
- #8, gas at room temp
- found in atmosphere/waters
- absorbed through lungs/gills
- ozone layer - protects organism, cellular respiration
- found in atmosphere/waters
- absorbed through lungs/gills
- ozone layer - protects organism, cellular respiration
44
New cards
Hydrogen
- #1, gas in room temp
- gases, stars, water, microorganisms
- absorbed mainly through water
- producing energy, fuels sun, main part of water
- gases, stars, water, microorganisms
- absorbed mainly through water
- producing energy, fuels sun, main part of water
45
New cards
Nitrogen
- #7, commonly a gas, very stable
- soil/plants, water, amino acids/proteins
- bacteria convert it to ammonia - absorbed
- animo acids - proteins, nucleic acid
- soil/plants, water, amino acids/proteins
- bacteria convert it to ammonia - absorbed
- animo acids - proteins, nucleic acid
46
New cards
Sulfur
#16, commonly a solid
- volcanic areas/ hot springs/underground
- plants get it from soil, animals from eating plant
- growth of plants, metabolism, photosynthesis, builds and fixes DNA
- volcanic areas/ hot springs/underground
- plants get it from soil, animals from eating plant
- growth of plants, metabolism, photosynthesis, builds and fixes DNA
47
New cards
Phosphorus
#15, mostly as a solid, flammable when exposed to air
- erosion from rocks, soil
- eating plants, or plant-eating animals
- holds dna together
- erosion from rocks, soil
- eating plants, or plant-eating animals
- holds dna together
48
New cards
Calcium
- #20, solid at room temp
- limestone deposit
- muscle contraction, human skeleton, good for shells
- limestone deposit
- muscle contraction, human skeleton, good for shells
49
New cards
Sodium
#11, solid when pure, highly reactive
- seawater, earths crust
consume sodium (salt) plants get from roots (not required to live)
- holds water in blood/helps blood pressure
- seawater, earths crust
consume sodium (salt) plants get from roots (not required to live)
- holds water in blood/helps blood pressure
50
New cards
Potassium
#19, solid when pure
- earth's crust, salty water, foods
- plants get it, animals eat these plants
- normal levels of fluid in living cells
- earth's crust, salty water, foods
- plants get it, animals eat these plants
- normal levels of fluid in living cells
51
New cards
Magnesium
#12, commonly solid
- minerals (magnesite/dolomite), in the sea, foods
- chlorophyll in plants, nerve/muscle function, steady heartbeat
- minerals (magnesite/dolomite), in the sea, foods
- chlorophyll in plants, nerve/muscle function, steady heartbeat
52
New cards
Chlorine
#17, commonly a gas
- salt, ocean algae
- acquired by touching, eating, breathing
- concentrates in chloroplasts, excretion, acid balance of body
- salt, ocean algae
- acquired by touching, eating, breathing
- concentrates in chloroplasts, excretion, acid balance of body
53
New cards
Iron
#26, solid in pure state
- in many stars, earth's core, ores
- acquired through food
- transports oxygen, produces energy
- in many stars, earth's core, ores
- acquired through food
- transports oxygen, produces energy
54
New cards
Atoms
- basic building blocks of life
- incredibly small
- electrically neutral (same # of proton/electron)
- # of protons is atom's number
- incredibly small
- electrically neutral (same # of proton/electron)
- # of protons is atom's number
55
New cards
Isotopes
- forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but DIFFERENT numbers of NEUTRONS in their nuclei
- different in relative atomic mass but not in chemical properties (same number of electrons)
- radioactive isotopes: unstable nuclei that break down at a constant rate
- different in relative atomic mass but not in chemical properties (same number of electrons)
- radioactive isotopes: unstable nuclei that break down at a constant rate
56
New cards
Ions
- when atoms gain/lose electrons
- positively or negatively charged
- different # of protons/electrons
- positively or negatively charged
- different # of protons/electrons
57
New cards
Ionic Bonds
- formed when one or more electrons are transferred
from one atom to another.
from one atom to another.
58
New cards
Covalent Bonds
- forms when electrons are shared between
atoms
atoms
59
New cards
Protons
- positively charged particles (+)
- about same mass as neutrons
- about same mass as neutrons
60
New cards
Neutrons
- carry no charge
- protons and neutrons together form the nucleus
- protons and neutrons together form the nucleus
61
New cards
Electrons
- negatively charged particle
- atoms have same number of protons electrons so atoms do not have a charge
- atoms have same number of protons electrons so atoms do not have a charge
62
New cards
Molecules
the structure that results when atoms are joined together by covalent bonds
- unequal electron sharing = regions of positive/negative charges
- unequal electron sharing = regions of positive/negative charges
63
New cards
van der Waals forces
- Slight attraction between the oppositely Charged regions of nearby molecules
64
New cards
Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
1) pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom
2) a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions
3) material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are PHYSICALLY mixed together (NOT chemically)
2) a substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions
3) material composed of two or more elements or compounds that are PHYSICALLY mixed together (NOT chemically)
65
New cards
Solution
mixture in which all the components are evenly distributed throughout the mixture
solute = (like salt)
solvent = (like water)
solute = (like salt)
solvent = (like water)
66
New cards
Acid
- compound that forms H+ HYDROGEN ions in solution
- lower than 7 on pH scale
- lower than 7 on pH scale
67
New cards
Bases
- compound that produces OH- HYDROXIDE ions in solution
- higher than 7 on pH scale
- higher than 7 on pH scale
68
New cards
Valance Electrons
- electrons at the highest level for that element
(non full levels will bond with other elements)
first level = 2
second level = 8
HYDROGEN VALENCE: 2-1=1
CARBON VALENCE: 6-2=4
NITROGEN VALENCE: 7-2=5
OXYGEN VALENCE: 8-2=6
(non full levels will bond with other elements)
first level = 2
second level = 8
HYDROGEN VALENCE: 2-1=1
CARBON VALENCE: 6-2=4
NITROGEN VALENCE: 7-2=5
OXYGEN VALENCE: 8-2=6
69
New cards
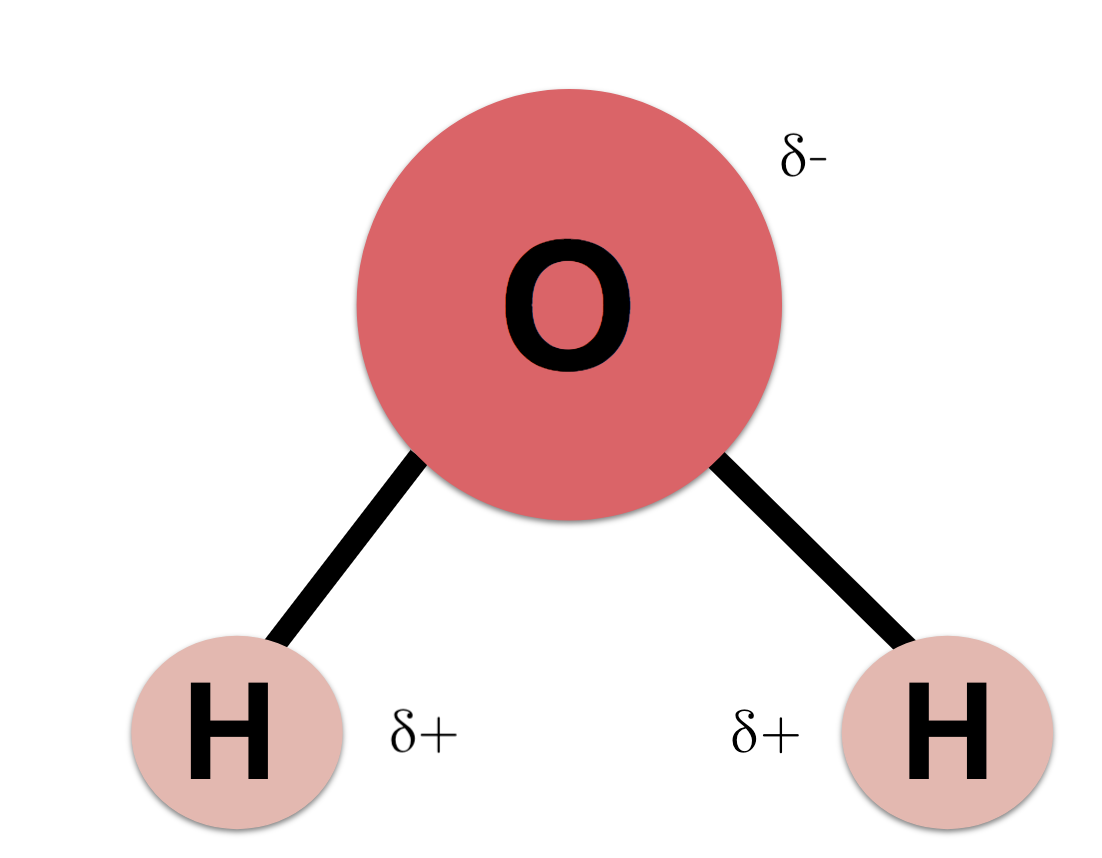
Water Molecule
- consists of 2 hydrogens, 1 oxygen
- neutral
- oxygen end has slight - charge, hydrogen end has slight + charge
- neutral
- oxygen end has slight - charge, hydrogen end has slight + charge
70
New cards
Hydrogen Bonding
- the attraction between the hydrogen atom on one water molecule and the oxygen atom on another water molecule
- affected by polarity
- water molecule: 4 hydrogen bonds
- affected by polarity
- water molecule: 4 hydrogen bonds
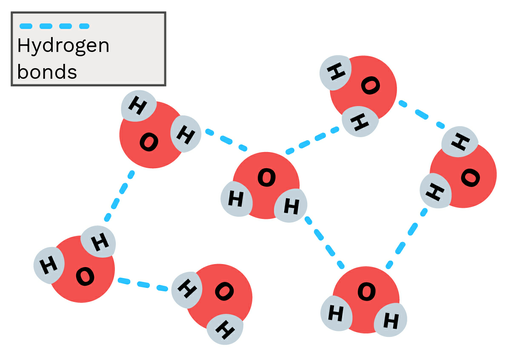
71
New cards
Adhesion
- attraction between molecules of different substances
- etc: water molecules attached to tube - meniscus
- etc: water molecules attached to tube - meniscus
72
New cards
Cohesion
- attraction between molecules of the same substance
- etc: surface tension of water
- etc: surface tension of water
73
New cards
Surface Tension
- created by hydrogen bonds/property of cohesion
- allows insects to walk on water
- allows insects to walk on water
74
New cards
High Specific Heat
Specific heat: amount of energy required to change 1 gram of a substance 1 C
Water RESISTS change in temperature (thermal inertia) because of hydrogen bonds
Moderates Earth's climate/ocean temperature - sweat to cool down skin from overheating
Water RESISTS change in temperature (thermal inertia) because of hydrogen bonds
Moderates Earth's climate/ocean temperature - sweat to cool down skin from overheating
75
New cards
Less Dense as a solid
Water is......
density because of hydrogen bonds
density because of hydrogen bonds
76
New cards
Many substances
Water dissolves...
Water is polar molecule - can dissolve ionic compounds/polar molecules
Water is polar molecule - can dissolve ionic compounds/polar molecules
77
New cards
Capillary Action
- liquid can flow through narrow spaces from cohesion (water attracted to each other) and adhesion (water attracted to walls of the tube)
- etc: plant absorbing water in soil up its roots
vessels thinner - stick to the wall better
- etc: plant absorbing water in soil up its roots
vessels thinner - stick to the wall better
78
New cards
Polar Molecules
- A molecule in which the charges are unevenly distributed
- 1 atom is not shared equally with another atom "hogging the electrons" (partial negative)
- can attract each other
- 1 atom is not shared equally with another atom "hogging the electrons" (partial negative)
- can attract each other
79
New cards
Boiling Water
- heated water molecules break free from the hydrogen bonds
- liquid to gas
- as gas leaves, it remove thermal energy from the liquid with it SO temperature of the liquid remains CONSTANT during boiling
- liquid to gas
- as gas leaves, it remove thermal energy from the liquid with it SO temperature of the liquid remains CONSTANT during boiling
80
New cards
Carbohydrate
Macromolecule
C,H,O in a carbon-ring form
General Formula: (CH2O)x
Role: short/ long term energy, fuel for cellular respiration (glucose), component of cells
Monomer: monosaccharide (simple sugar): glucose, fructose
Polymer: polysaccharides (starches like glycogen for animal, cellulose)
C,H,O in a carbon-ring form
General Formula: (CH2O)x
Role: short/ long term energy, fuel for cellular respiration (glucose), component of cells
Monomer: monosaccharide (simple sugar): glucose, fructose
Polymer: polysaccharides (starches like glycogen for animal, cellulose)
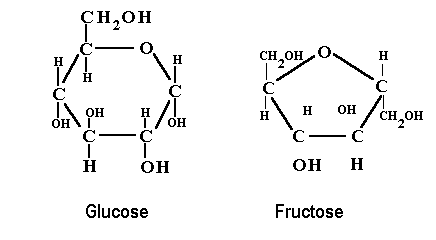
81
New cards
Lipid
Macromolecule
Glycerol with 3 fatty acid tails
lots of C, lot ofs H, some O
General Formula: CH3(CH2)nCOOH
- HYDROPHOBIC so waterproofing of surfaces, insulation in animals, steroid hormones, long-term energy storage
Saturated: carbons in chain have 4 single bonds ("saturated" with H)
Unsaturated: some carbon atoms in bond has double bonds, less H
Glycerol with 3 fatty acid tails
lots of C, lot ofs H, some O
General Formula: CH3(CH2)nCOOH
- HYDROPHOBIC so waterproofing of surfaces, insulation in animals, steroid hormones, long-term energy storage
Saturated: carbons in chain have 4 single bonds ("saturated" with H)
Unsaturated: some carbon atoms in bond has double bonds, less H
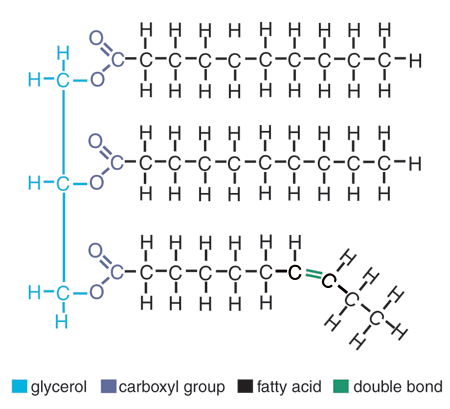
82
New cards
Nucleic Acid
Macromolecule
Made of C, H, O, N and P
(5 c sugar, nitrogenous base a,t,g,c,u, phosphate group)
Monomers: nucleotides
Polymers: nucleic acid (DNA/RNA)
control and regulate life’s processes; transcribes & translates genetic information into proteins.
Made of C, H, O, N and P
(5 c sugar, nitrogenous base a,t,g,c,u, phosphate group)
Monomers: nucleotides
Polymers: nucleic acid (DNA/RNA)
control and regulate life’s processes; transcribes & translates genetic information into proteins.
83
New cards
Amino Acids/Proteins
Macromolecule
Made of C, H, O and N
Monomer: Amino Acids
Polymers: Polypeptides (2 amino acids bonded by PEPTIDE BOND)
Protein is 1+ polypeptide strand is folded/coiled/arranged into shape
Amino acids:
- Carboxyl group
- Amino group
- R group (different) 20 different types - forms shape
Major structural component in body part, regulate body proccesses, aid in movement, transports molecules
Made of C, H, O and N
Monomer: Amino Acids
Polymers: Polypeptides (2 amino acids bonded by PEPTIDE BOND)
Protein is 1+ polypeptide strand is folded/coiled/arranged into shape
Amino acids:
- Carboxyl group
- Amino group
- R group (different) 20 different types - forms shape
Major structural component in body part, regulate body proccesses, aid in movement, transports molecules
84
New cards
Monomer
- smaller units that joins together to form polymers/macromolecules
85
New cards
Polymer
a naturally occurring or synthetic compound consisting of large molecules made up of a linked series of repeated simple monomers
86
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
a chemical reaction that BONDS two monomers together
by removing 2H and 1O (1 H2O) in the process
Absorbs energy
by removing 2H and 1O (1 H2O) in the process
Absorbs energy
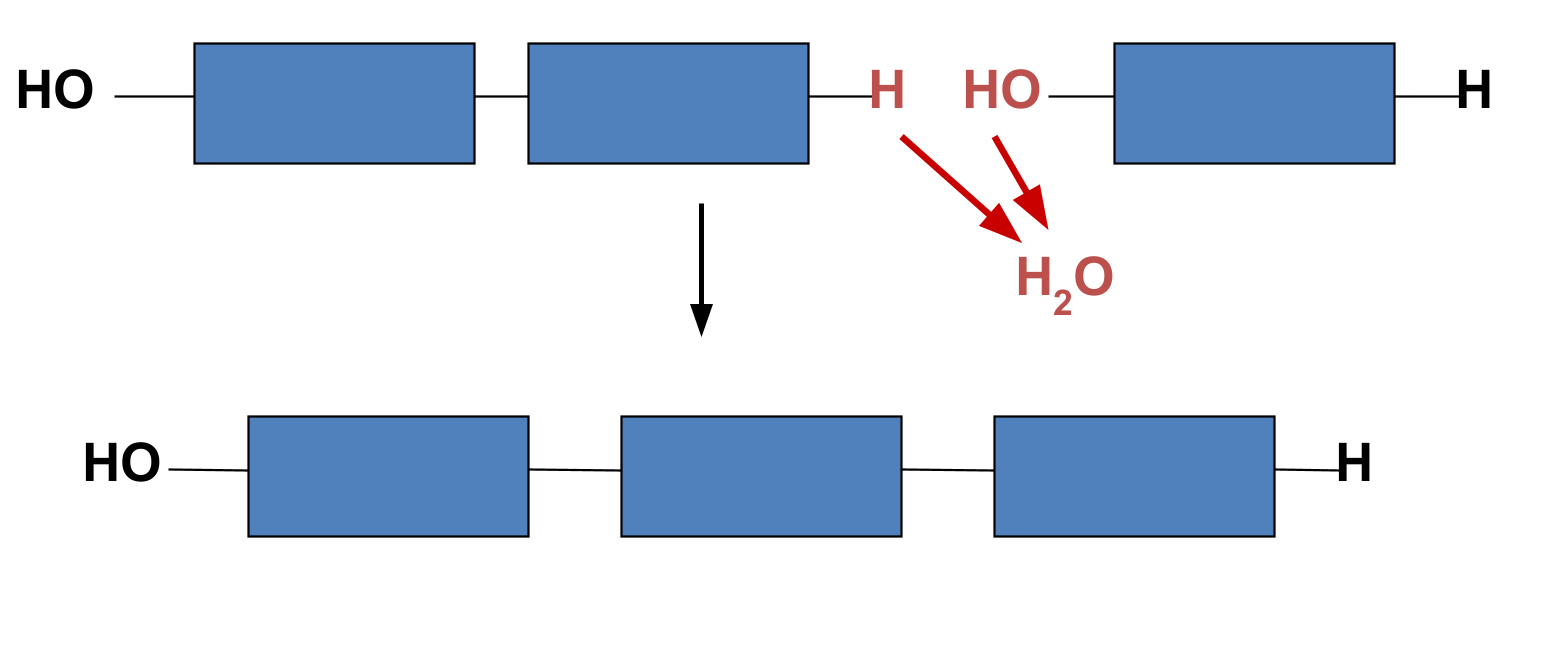
87
New cards
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction in which a bond between two monomers is BROKEN by using a water molecule (1 H2O)
Release energy
Release energy
88
New cards
Four Levels of Protein
Primary: long single strand of a.a.'s (polypeptide)
- not yet a protein
Secondary: Alpha Helix and beta pleated sheet (back and forth)
Tertiary: has many interactions (H-bonds, Disulfide bridges, Ionic bonds, Hydrophobic interactions) between R-groups along
the same polypeptide chain, forming a unique globular
shape
Quaternary: More than 1 polypeptide chain interacting together in any way (mentioned previously) to make one protein molecule
- not yet a protein
Secondary: Alpha Helix and beta pleated sheet (back and forth)
Tertiary: has many interactions (H-bonds, Disulfide bridges, Ionic bonds, Hydrophobic interactions) between R-groups along
the same polypeptide chain, forming a unique globular
shape
Quaternary: More than 1 polypeptide chain interacting together in any way (mentioned previously) to make one protein molecule
89
New cards
Chemical Reaction
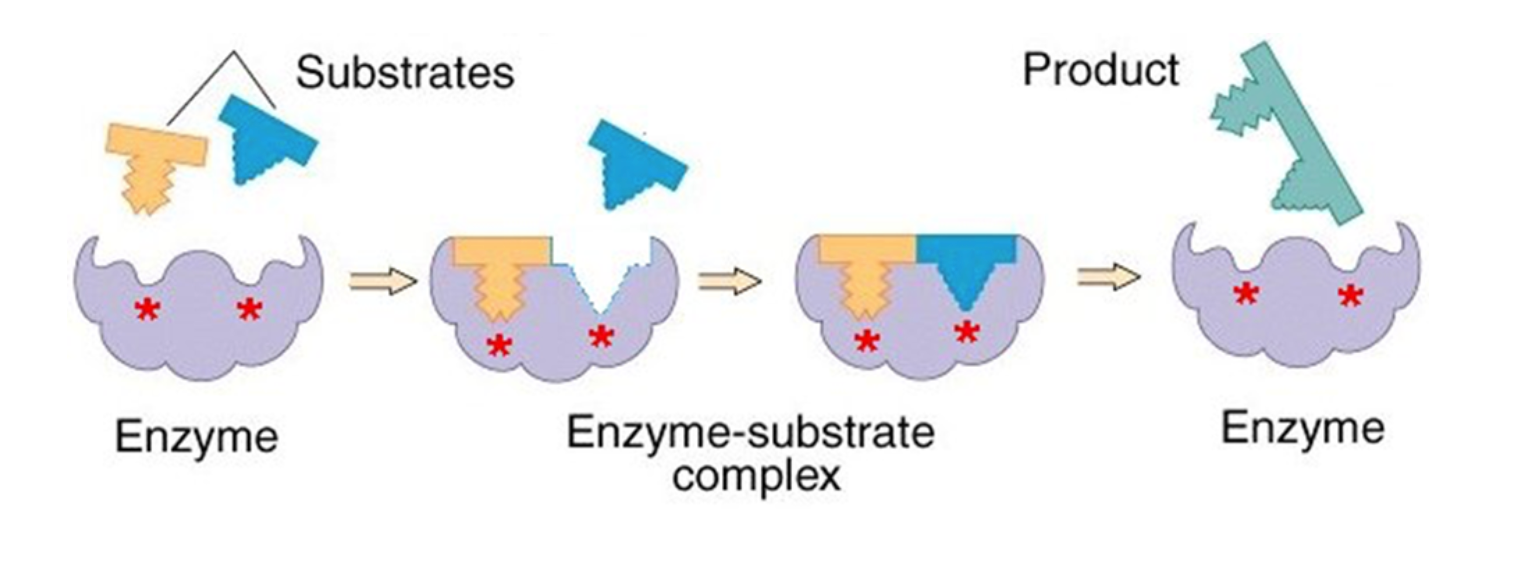
Turns Substrates into Products (one set of chemicals into another)
mass/energy is CONSERVED
mass/energy is CONSERVED
90
New cards
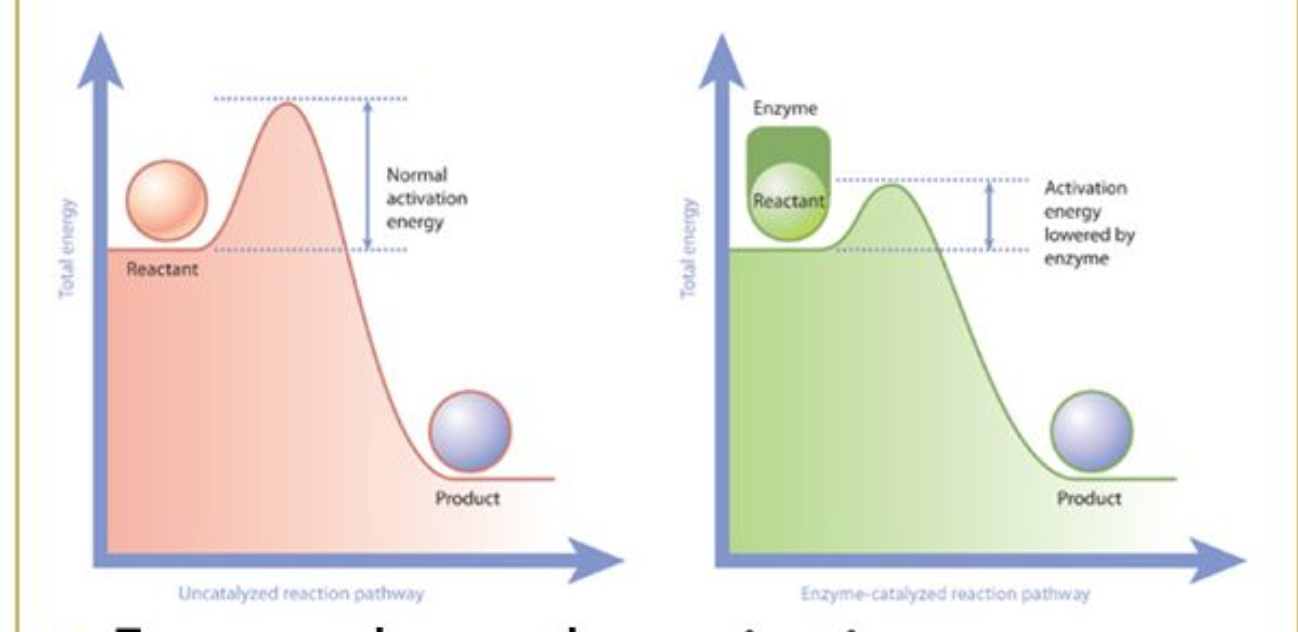
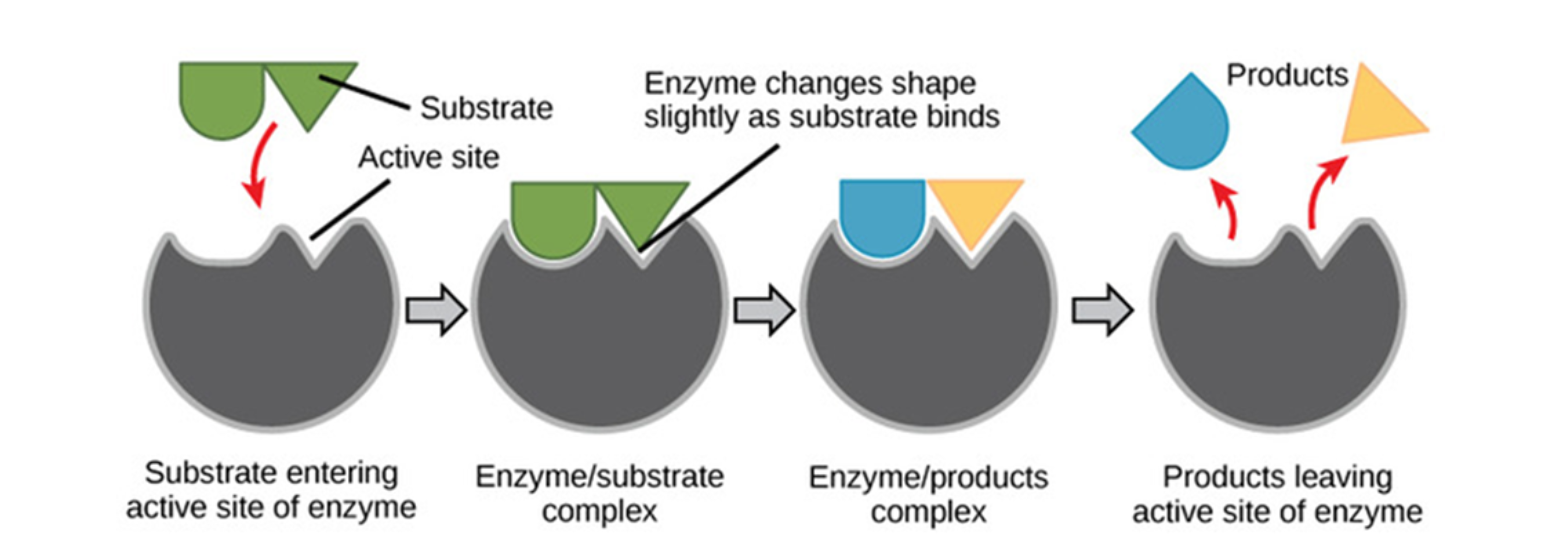
Enzymes
proteins that act as biological CATALYST - lower's reaction activation energy to speed up rate of chemical reaction
reactants= substrates - binds with enzyme at the activation site
- either tertiary or quaternary
reactants= substrates - binds with enzyme at the activation site
- either tertiary or quaternary
91
New cards
Activation Energy
energy needed to get every chemical reaction started
- enzymes lowers
- enzymes lowers
92
New cards
Enzyme activity influences
- Environmental conditions (temp., pH, ionic concentrations such as NaCl)
- Cofactors and coenzymes: inorganic or organic
compounds needed (ex., vitamins) for proper enzyme activity
- Enzyme inhibitors: molecules that either
1) mimic the substrate SO it blocks the active site
2) bond to the enzyme so that it changes the shape of the active site
- Cofactors and coenzymes: inorganic or organic
compounds needed (ex., vitamins) for proper enzyme activity
- Enzyme inhibitors: molecules that either
1) mimic the substrate SO it blocks the active site
2) bond to the enzyme so that it changes the shape of the active site
93
New cards
Catabolic Enzyme Reaction
- takes larger structures (like proteins, fats or tissues) and breaks them down into smaller units (such as cells or fatty acid)
(digesting food)
BREAKING
(digesting food)
BREAKING
94
New cards
Anabolic Enzyme Reaction
creating bigger, complex molecules from smaller, simpler molecules for future use
BONDING
BONDING