Genetics E1- Review
1/91
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What symbol indicates an affected individual on a pedigree?
Shaded in shape
What symbol indicates a male on a pedigree?
Square
What symbol indicates a female on a pedigree?
Circle
What does an arrow indicate on a pedigree?
Proband
What does a horizontal line indicate on a pedigree?
Mating
What does a vertical line indicate on a pedigree?
Offspring
What do roman numerals mean on pedigrees?
Generations
What is the p-arm (“petit”)?
Shorter arm
What is the q-arm (“queue”)?
Longer arm
What divides the chromosomal arms?
Centromere
How are bands numbered?
From centromere outward
How do you read the following chromosome nomenclature: 15q11.2
Chromosome 15, q-arm, region 11, band 2
What is transcription?
DNA to mRNA
What is translation?
mRNA to protein
What are the DNA bases?
A, T, G, C
What are the RNA bases?
A, U, G, C
What type of substitution mutation results in no amino acid change?
Silent
What type of substitution mutation results in a different amino acid?
*ex- sickle cell
Missense
What type of substitution mutation results in a premature stop codon?
Nonsense
What is the most common type of mutation?
Substitution
What is an insertion or deletion mutation that is not a multiple of 3 and changes the entire downstream sequence of amino acids?
Frameshift
List the types of mutation from least severe impact to most severe impact.
Silent < Missense < Nonsense < Frameshift
What is a reading frame?
The order of triplet codons
A single nucleotide deletion in the middle of a gene would most likely result in:
A frame-shift mutation affecting the entire downstream protein
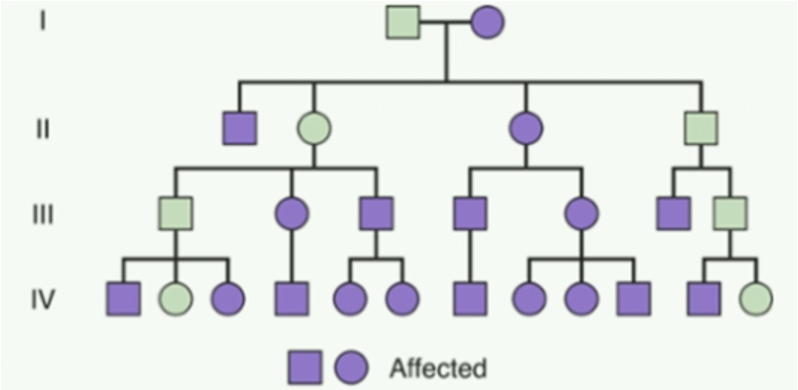
What type of inheritance pattern has vertical transmission, affecting multiple generations with male-male transmission being possible?
Autosomal dominant
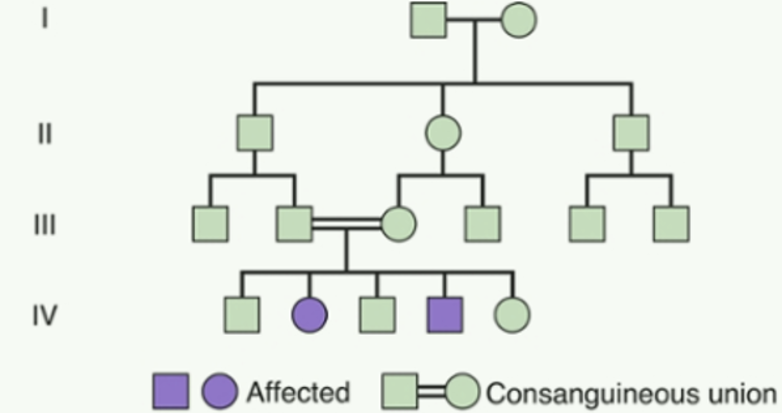
What type of inheritance pattern has horizontal transmission, occurring usually from heterozygous parents & typically affects only a single generation?
Autosomal recessive
What chance does each offspring have of inheriting the affected phenotype of an autosomal dominant condition if a heterozygous person mates with an unaffected person?
50%
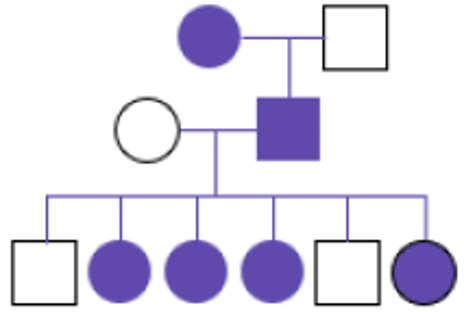
What type of inheritance pattern affects both sexes, but females MC, with affected fathers passing to 100% of daughters, and often is lethal in males?
X-linked dominant
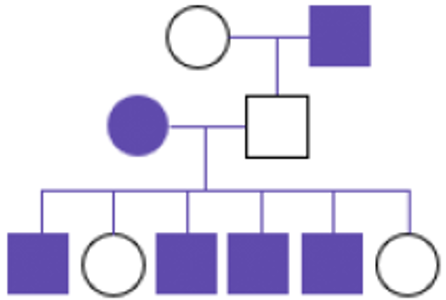
What type of inheritance pattern primarily affects males through carrier mothers and has no father-to-son transmission?
X-linked recessive
A 25-year-old woman is concerned about her family history. Her father and paternal grandfather both developed symptoms in their 40s including progressive movement problems and cognitive decline. What inheritance pattern is most likely?
Autosomal dominant
A couple comes for preconception counseling. They are first cousins and want to know about genetic risks. What would you tell them about their increased risk?
They have an increased risk for autosomal recessive conditions
What does consanguinity increase the risk for?
Rare autosomal recessive conditions
How are the offspring affected if both parents are carriers of an autosomal recessive condition?
25% affected, 50% carriers, 25% normal
How are the offspring affected if the mother is a carrier of an X-linked recessive condition?
50% of sons affected, 50% of daughters carriers
What is Mendel’s law of segregation?
Each person possesses 2 genes for a particular characteristic, only one of which can be transmitted at any one time
What are Robertsonian translocations?
2 acrocentric chromosomes (13, 14, 15, 21, 22) join at centromeres → results in 45 chromosomes but normal phenotype
What is trisomy?
Extra chromosome
What is aneuploidy?
Gain or loss of chromosomes
What is monosomy?
Missing single chromosome from a diploid pair
What is the MC viable autosomal trisomy?
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
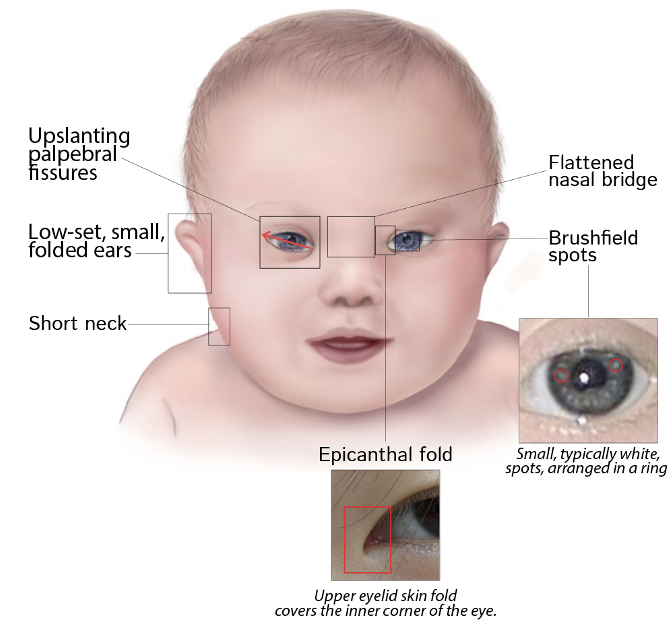
The following characteristics are seen in what condition?
heart defects
intellectual disability
up slanting palpebral fissures
flattened nasal bridge
brush field spots
epicanthal fold
increased risk of leukemia
Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)
The following characteristics are seen in what condition?
short stature
webbed neck
broad chest, widely spaced nipples
CoA
normal intelligence
primary amenorrhea (streak ovaries)
lymphedema
Turner Syndrome (45, X)
The following characteristics are seen in what condition?
tall stature
gynecomastia
hypogonadism
infertility
learning difficulties
Klinefelter syndrome (47, XXY)
A 16 y/o girl is brought to the physician by her mother due to concerns that she has not yet started menstruating. She has always been significantly shorter than her peers. She is performing well academically in the 10th grade & has good social relationships. On PE, her height is below the 3rd percentile. She has a low posterior hairline, a webbed neck and a broad, shield-like chest with widely spaced nipples. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Turner Syndrome (45, X)
What is the management for Turner Syndrome (45, X)?
Exogenous estrogen-progestin & echo to r/o CoA
The following characteristics are seen in what condition?
intellectual disability
large/prominent ears
autism spectrum behaviors
macroorchidism
Xq27.3; FMR1 gene
Fragile X Syndrome
The following characteristics are seen in what condition?
“cocktail party” personality
supravalvular AS
elfin facial features
hypercalcemia
7q11.23 deletion
Williams Syndrome
The following characteristics are seen in what condition?
CHD
immunodeficiency
cleft palate
hypocalcemia
22q11.2 deletion
DiGeorge Syndrome
What condition is a maternal deletion of 15q11.2?
Angelman Syndrome
What condition is a paternal deletion of 15q11.2?
Prader-Willi Syndrome
What features are seen with a 1p36 deletion?
Intellectual disability, seizures, & growth problems
Two unrelated children present with deletions affecting the same region of chromosome 15 (15q11.2–q13), yet they have dramatically different clinical features. What syndrome does each child have?
Child A: History of poor feeding in infancy, now obese with an insatiable appetite
Child B: Exhibits inappropriate laughter, seizures, and severe intellectual disability
Child A: Prader-Willi; Child B: Angelman
What is the percentage of people with a disease genotype who show the phenotype?
Penetrance
What term refers to the range of severity in people with the same genetic condition?
Variable expressivity
What is the MCC of inherited intellectual disability?
Fragile X Syndrome
What type of inheritance pattern does fragile X syndrome display?
X-linked dominant
Why might female carriers look different from affected males with fragile X syndrome?
Reduced penetrance & variable expressivity
What genetic testing method is best for chromosome number / structure?
*ex: Down syndrome diagnosis
Karyotype
What genetic testing method is best for small deletions / duplications?
*ex: Autism evaluation
Microarray
What genetic testing method is best for specific deletions?
*ex: DiGeorge syndrome
FISH
What genetic testing method is best for enzyme deficiencies?
*ex: PKU screening
Biochemical
FISH would be the most appropriate initial test for:
Suspected DiGeorge syndrome based on clinical features
What are clinical applications of PCR?
Mutation detection, viral load testing, paternity testing, forensic analysis, research applications
What type of genetic testing amplifies DNA for analysis & makes millions of copies from tiny samples?
PCR
What are the best applications for biochemical analysis?
IEM, enzyme deficiency diseases, newborn screening FU, monitoring treatment response
Which genetic testing method would be most appropriate for evaluating a child with multiple congenital abnormalities and unexplained intellectual disability?
Chromosome microarray
What is the most critical teratogen period?
3-16 weeks gestation (organogenesis)
What teratogen causes neural tube defects & cognitive effects?
VPA
What teratogen causes growth restriction, facial dysmorphology, & CNS effects?
Alcohol
What teratogen causes multiple malformations and requires 2 forms of contraception?
Isotretinoin
What teratogen causes renal dysplasia in the 2nd/3rd trimester?
ACE inhibitors
What matters more for teratogens— dose or timing?
Timing
What is the safety protocol for isotretinoin?
Pregnancy test before initiation & monthly during treatment, 2 forms of contraception requiring during treatment, & stop meds 1 month before attempting conception
What patients should genetic screening be offered to?
All pregnant women regardless of age
What prenatal tests are diagnostic but carry procedural risks?
CVS or amniocentesis
What is a screening test that detects trisomies 13, 18, 21 & sex chromosome aneuploidies, and has higher detection rates than traditional serum screening?
Cell-free DNA
What conditions are universally recommended to screen for carriers?
CF, spinal muscular atrophy, hemoglobinopathies
What conditions are ethnicity-specific when deciding to screen for carriers?
Tay-Sachs (Ashkenazi Jewish, French Canadian)
Sickle Cell (African American)
Thalassemias (Mediterranean, Asian)
After negative carrier screening for cystic fibrosis, a patient's residual risk of being a carrier is:
Reduced but not eliminated
What type of conditions should you think of when you see the following?
Neuro sx: seizures, developmental delay, hypotonia
GI sx: vomiting, poor feeding, hepatomegaly
Unusual odors: maple syrup, musty, fruity
Metabolic acidosis w/ hyperammonemia
FHX of early infant deaths
IEM
What is the primary goal of newborn screening?
Detect disorders before they become symptomatic
How can you prevent intellectual disability with PKU?
Dietary management
How can you prevent developmental delays with congenital hypothyroidism?
Thyroid hormone
How can you prevent infections with sickle cell disease?
Prophylactic antibiotics
The combination of metabolic acidosis and hyperammonemia in a newborn most likely suggests:
Inborn error of metabolism
What is a classic presentation of a metabolic emergency, which can cause rapid neurological damage?
Metabolic acidosis & hyperammonemia
A 32 y/o woman, currently 10 wks pregnant, presents to the clinic w/ her husband. They’re concerned bc there is a FHx of CF on her husband's side & his nephew is affected. During their prenatal visit, they ask about carrier screening, stating, “We want to know our risks.” What would you discuss with them?
Explain autosomal recessive inheritance, discuss carrier testing options, and explain residual risk even after negative testing
A 28 y/o woman presents for genetic counseling. Her father has Huntington disease, & she is now considering predictive genetic testing. She’s seeking guidance on whether to undergo testing and what the implications might be for her. What do you advise?
Huntington is autosomal dominant with complete penetrance → 50% chance the daughter inherited the gene; if she is positive, her children will have a 50% risk of being affected
What produces visible karyotypes to asses chromosomal structure?
G-banding
What is considered advanced maternal age?
35 y/o at delivery
How are mitochondrial disorders transmitted?
Exclusively through maternal line (all mitochondrial DNA is maternally inherited)
What kind of condition should you consider if there is no male-to-male transmission?
X-linked