Peripheral Nervous System
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
peripheral nervous system
links that connect the outside world to the CNS
includes all neural structures outside the brain and spinal cord
sensory receptors
peripheral nerves
ganglia
efferent motor ending
sensory receptors
dendritic end organs, or parts of other cell types, specialized to respond to a stimulus
classification
stimulus type
location in the body
structural complexity
stimulus type, location in the body, and structural complexity
What are the classifications of sensory receptors?
mechanoreceptors
generate impulses when deformed by a mechanical force
touch
pressure
vibration
stretch
thermoreceptors
sensitive to temperature changes
photoreceptor
respond to light energy
chemoreceptor
respond to chemicals in solution and concentrations of chemicals
molecules that are smelled or tasted
changes in blood or interstitial fluid
nociceptors
pain receptors
respond to potentially damaging stimuli
dermis: glass, sunburn, stab, splinter
exteroceptors
respond to a stimuli which arise outside the body
most are at or near the body
touch, pressure, pain, temperature receptors in the skin
most of the receptors are found in the special senses - vision, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium
interceptors
aka viseroceptors
respond to stimuli which arise within the body
located within the visceral organs and blood vessels
monitor a variety of stimuli including chemical changes, tissue stretch, and temperature
proprioceptors
provide info regarding the position of the body in space
monitor how much organs containing these receptors are stretched
located in muscles, tendons, and joints (bladder & intestines)
golgi tendon organ
proprioceptor
happens at tendon site
muscle spindle
proprioceptors
helps at the site of muscle
simple
What kind of structural complexity?
modified dendritic nerve endings of sensory neurons
located throughout the body
monitor most types of general sensory information
widely distributed
complex
What kind of structural complexity?
sense organs
localized collections of many types of cells
eyes, taste buds
structural complexity
Sensory receptors are classified according to stimulus type, body location, and ….
pain
Nociceptors are …. receptors
proprioceptors
Receptors that provide information about the position of the body in space are called….
exteroceptors
Vision, hearing, taste and smell are all stimuli monitored by the…..
proprioceptors
Changes in tension in muscles and tendons are monitored by…
nerves
bundles of neuron fibers (processes) found outside the CNS
31 pairs of spinal
12 pairs of cranial
types
sensory
motor
mixed
sensory nerve
contains sensory fibers only
motor nerves
contain motor nerves only
mixed nerves
contains both motor and sensory fibers
12
How many cranial nerves are there?
31
How many spinal nerves are there?
Spinal nerves
attached to the spinal cord
all are mixed
named for their association with the vertebrae's
occur in pairs
cervical
thoracic
lumbar
sacral
coccygeal
cervical
8 pairs of spinal nerve
thoracic
12 pairs of spinal nerves
lumbar
5 pairs of spinal nerves
sacral
5 pairs of spinal nerves
coccygeal
1 pair of spinal nerve
roots
sites of attachment to the spinal cord
dorsal
ventral
ventral root
contains motor fibers which exit the anterior horn
dorsal root
contains sensory fibers that access the posterior horn
dorsal root ganglia
contains the cell bodies of the sensory neurons
rami
branches
posterior (dorsal)
anterior (ventral)
posterior (dorsal) ramus
provides sensory and motor intervention to the skin and muscle of the back
anterior (ventral) ramus
innervates the ventrolateral surface (skin), structures in the body wall, and the extremities
dermatomes
specific areas of the skin monitored by each spinal nerve
plexuses
interlacing nerve networks, formed by the joining of the anterior ramus (rami) of certain spinal nerves
located in the cervical, lumbar, sacral regions of the cord
none between T2 - T12
named for the area supplied
cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral
plexus names
cervical plexus
supply the muscles of the neck & diaphragm
C1-C5
brachial plexus
supply the shoulder girdle & arm
C5-T1
lumbar plexus
supplies the pelvic girdle & thigh
L1-L4
sacral plexus
supplies the muscles of the leg
L4-S4
solar and celiac
What are the sympathetic NS plexus?
solar plexus
top of gut
nerves radiate in sun beam look
boxers, wrestlers
celiac plexus
ganglion and radiating nerves of the sympathetic system in the pit of stomach
plexuses
fibers travel to the periphery via different routes
each muscle receives innervation from more than one spinal nerve
damage to one spinal root or segment can not completely paralyze a muscle
cranial nerves
arise from the brain
primarily serve the head and neck
some sensory only
some motor only
some mixed
naming
function
roman numeral
according to the position on the brain (anterior to posterior)
wandering
What does vagus mean in latin?
olfactory
sensory
smell
I
optic
sensory
vision
II
oculomotor
motor
contraction of eye muscles
III
trochlear
motor
contraction of one eye muscle (vertical)
IV
trigeminal
mixed
sensory - from face
motor - chewing muscles
V
abducens
motor
contraction of one eye muscle (horizontal)
VI
facial
mixed
motor - facial expressions, salivary & lacrimal glands
sensory - taste
VII
auditory (vestibulocoochlear)
sensory
balance and hearing
VIII
glossopharyngeal
mixed
motor - swallowing & salvia production
sensory - taste
IX
vagus
mixed
sensory & motor - pharynx, larynx, & viscera
X
spinal accessory
motor
activates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscle
XI
hypoglossal
motor
control of tongue movements
XII
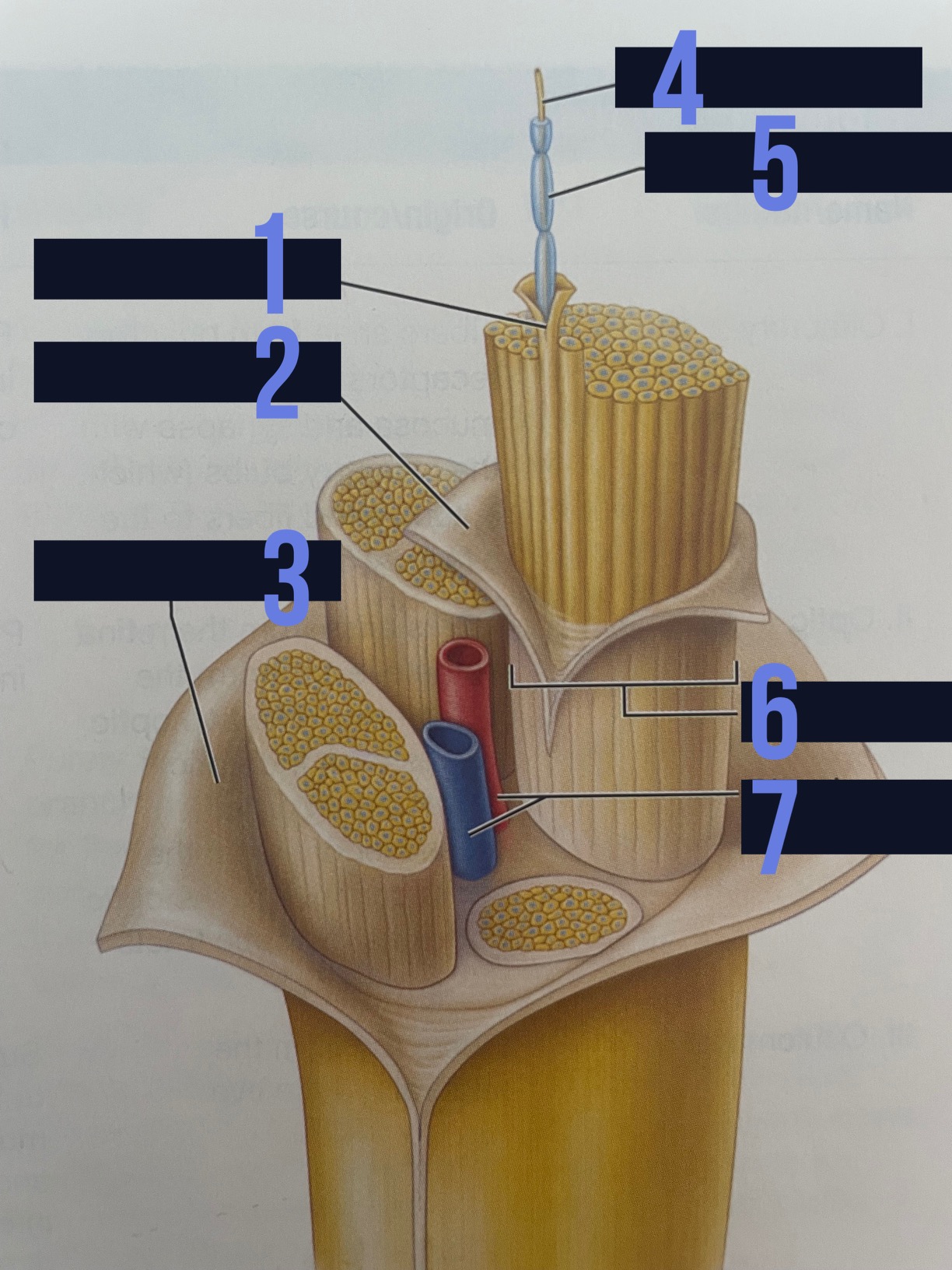
endoneurium
identify 1
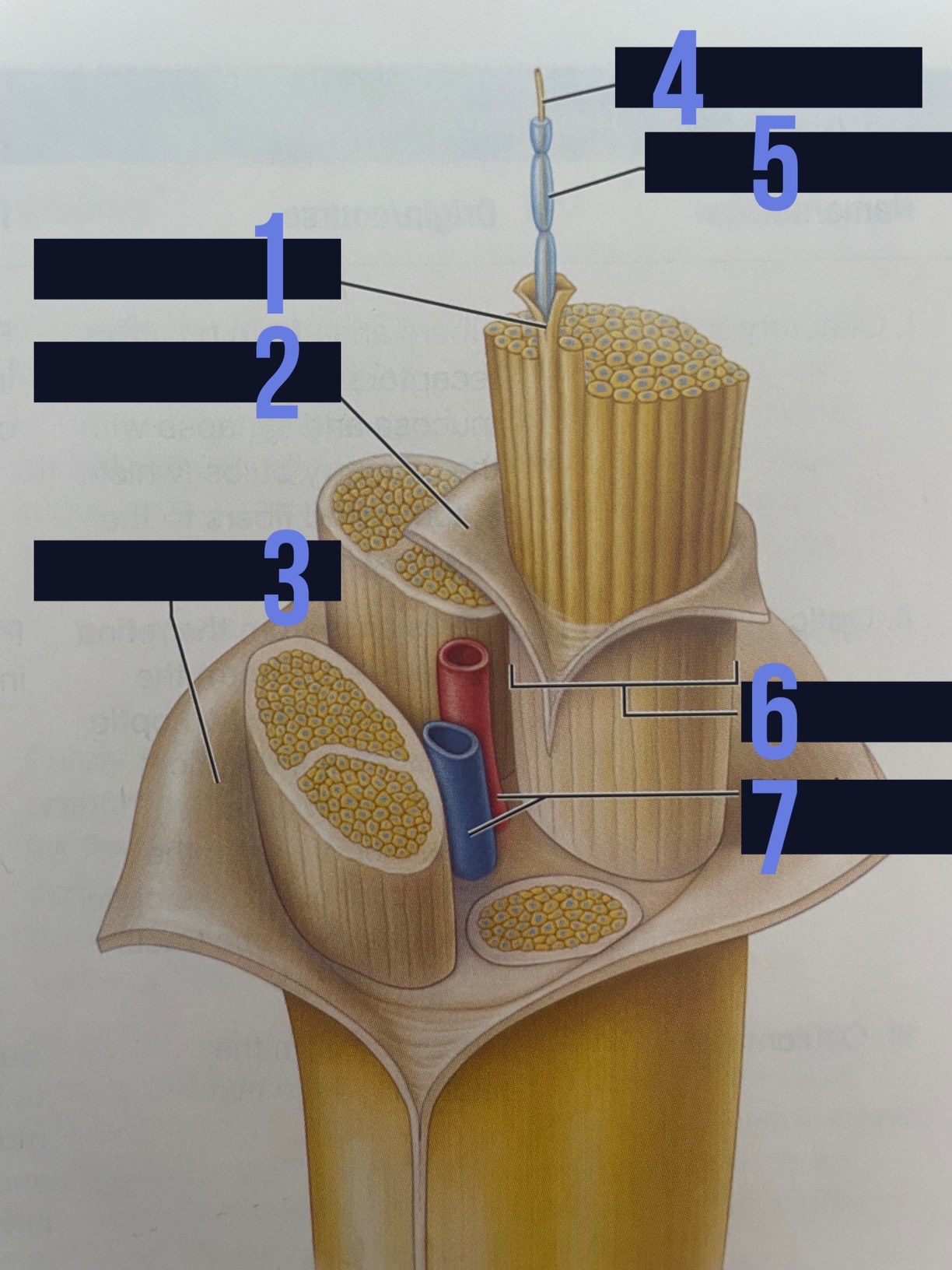
perineurium
identify 2
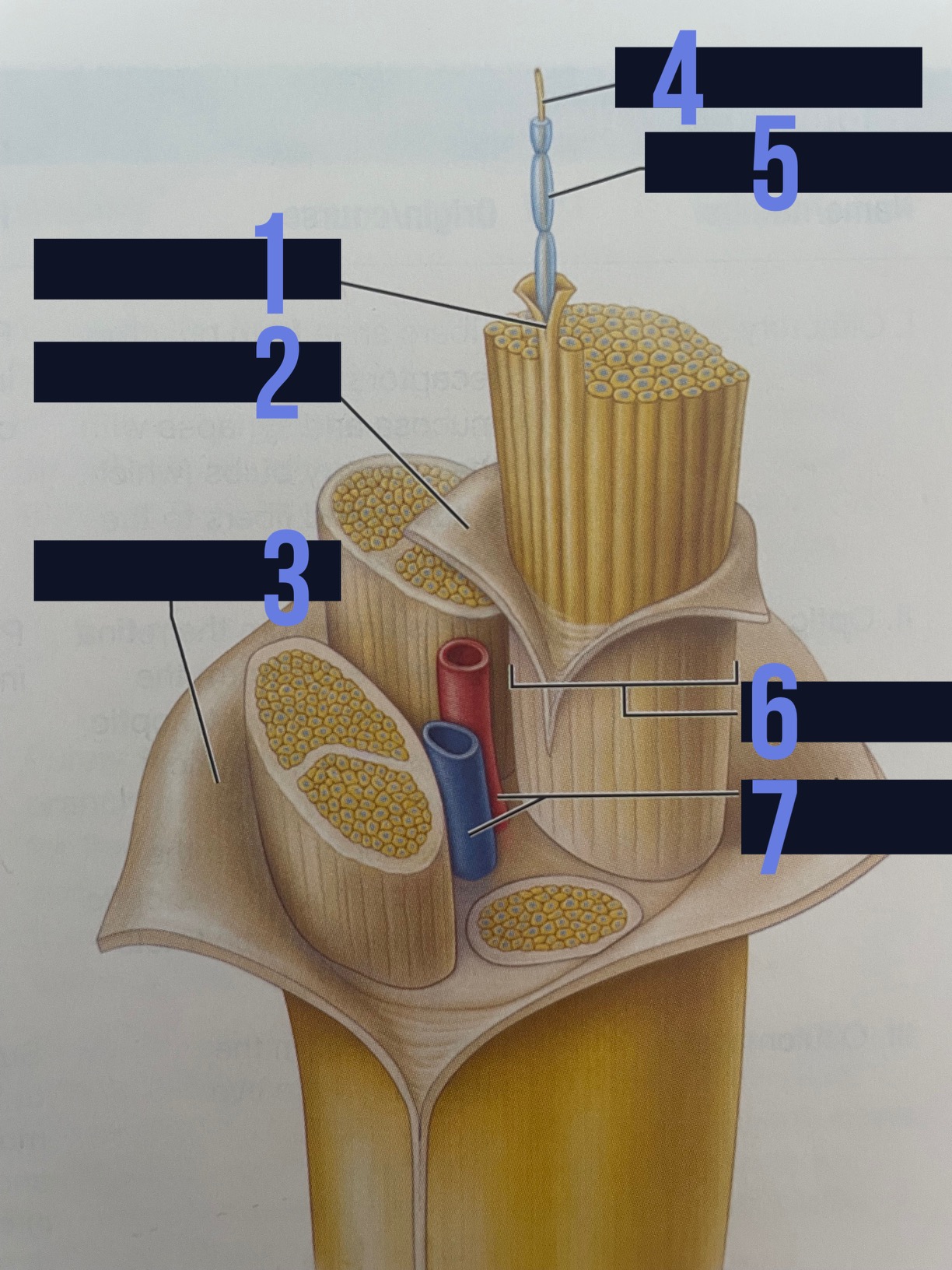
epineurium
identify 3
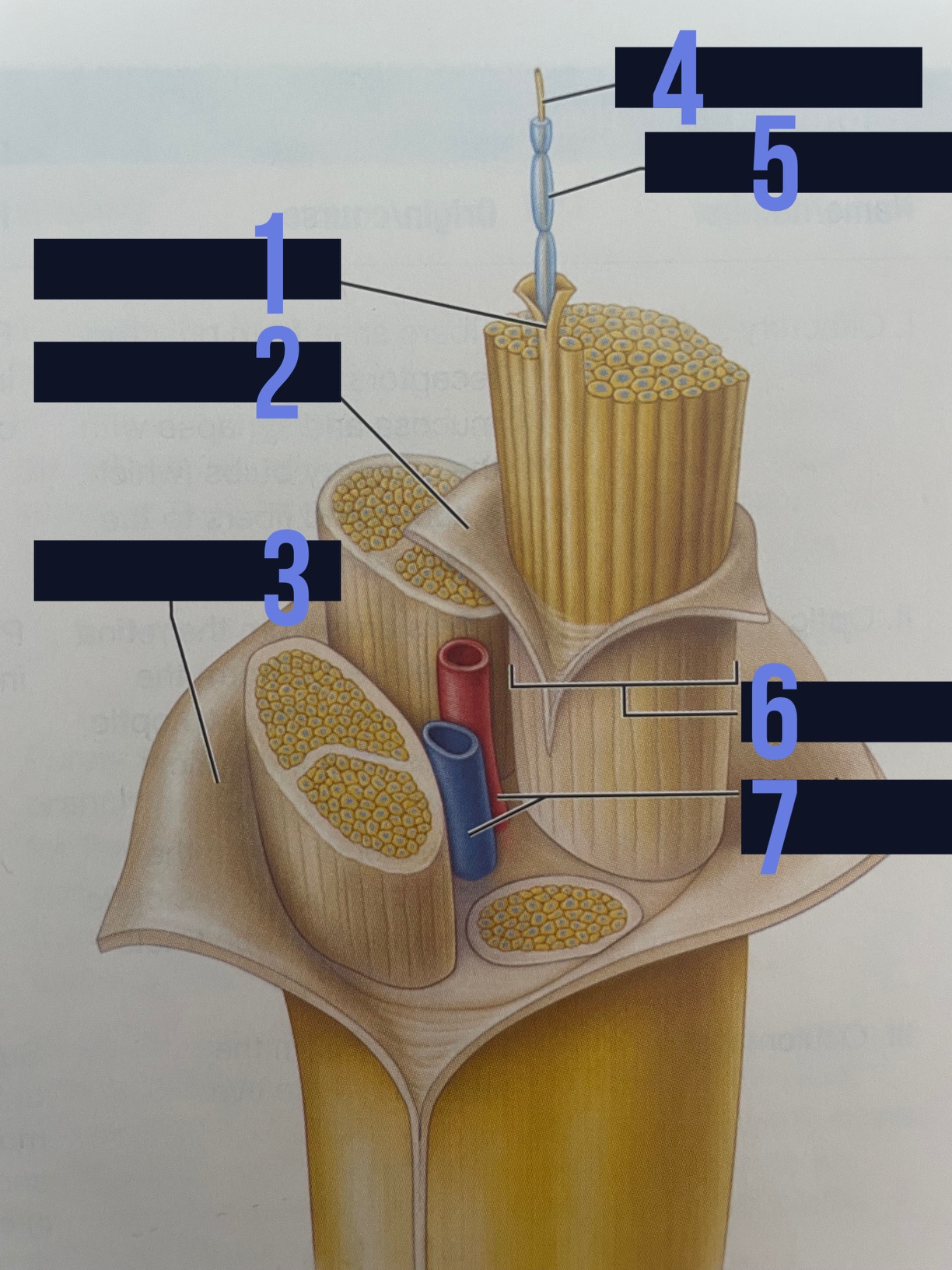
axon
identify 4
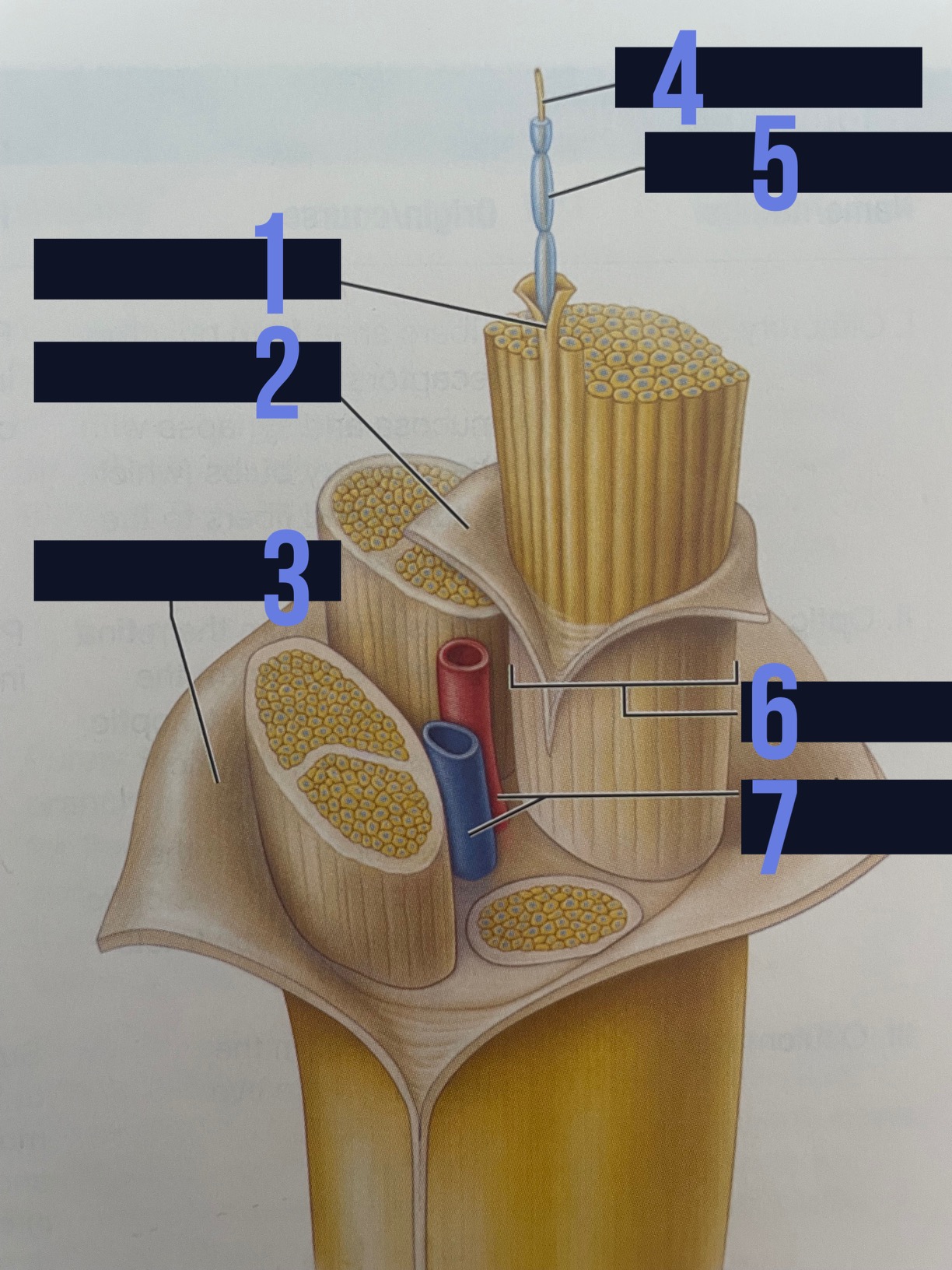
myelin sheath
identify 5
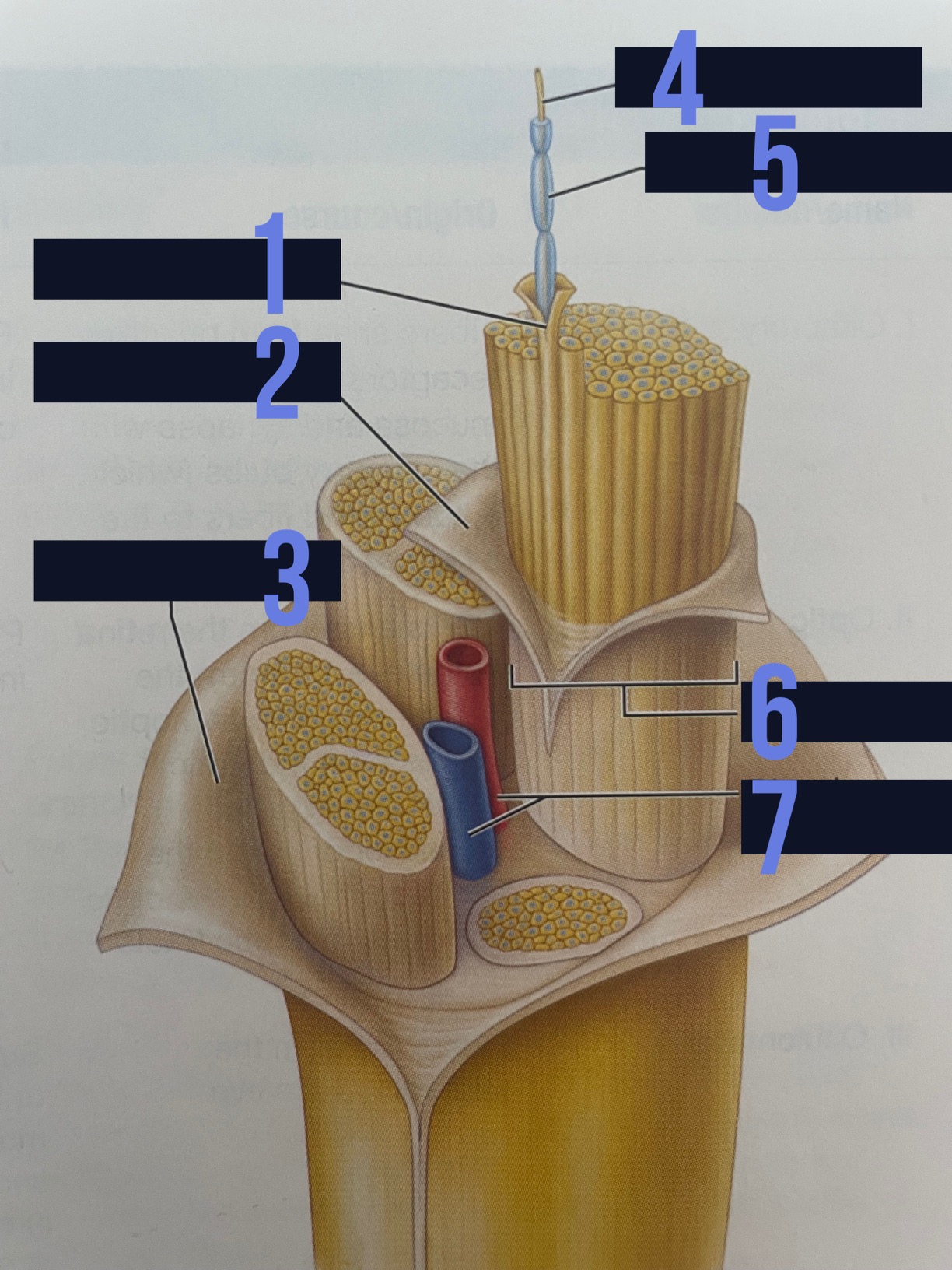
fascicle
identify 6
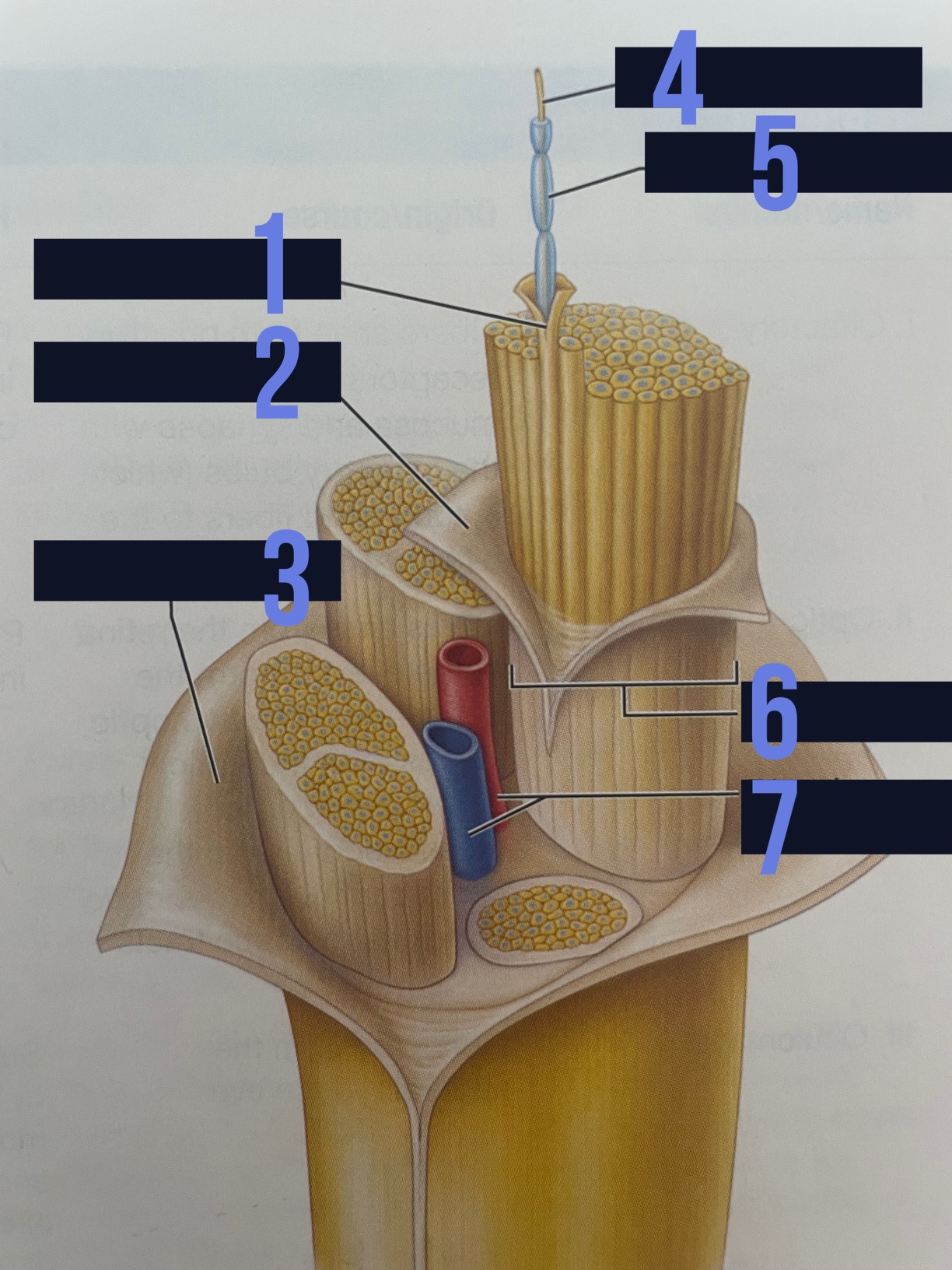
blood vessels
identify 7
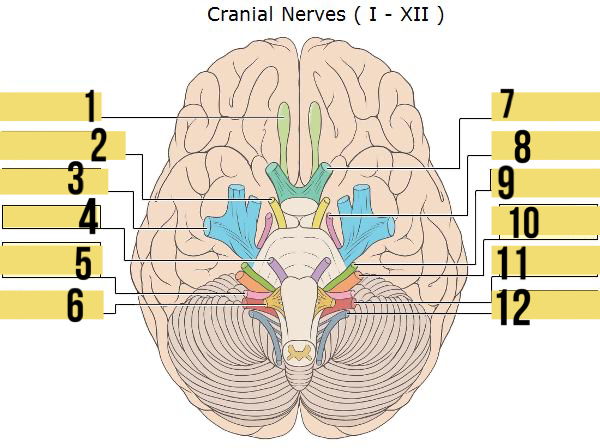
olfactory (I)
identify 1
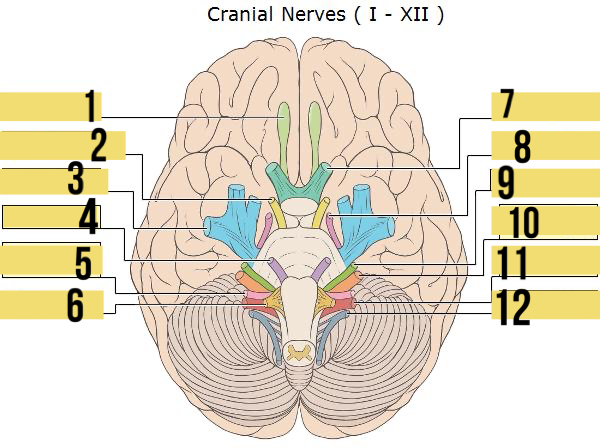
oculomotor (III)
identify 2
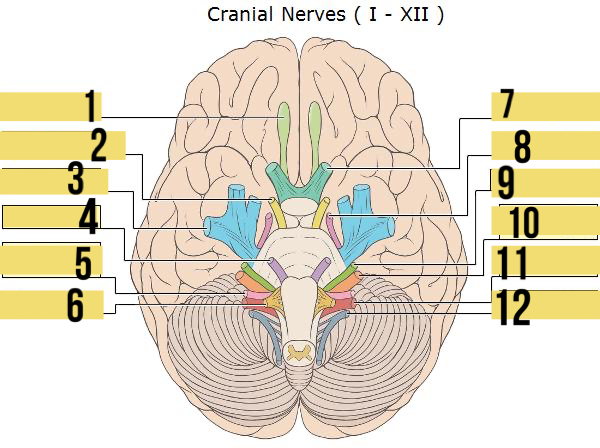
trigeminal (V)
identify 3
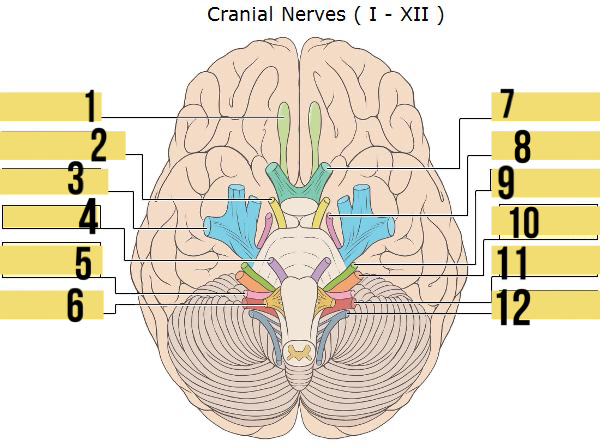
abducens (VI)
identify 4
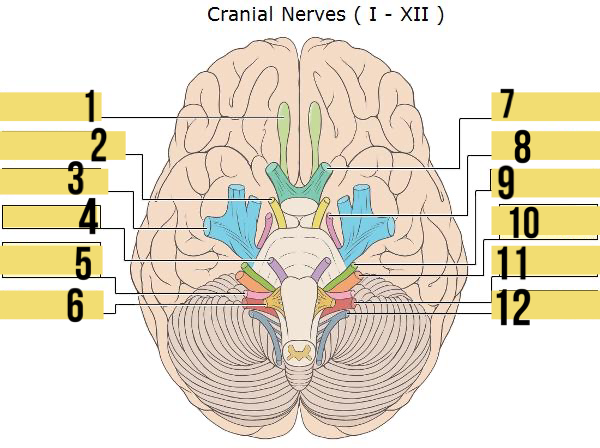
glossopharyngeal (IX)
identify 5
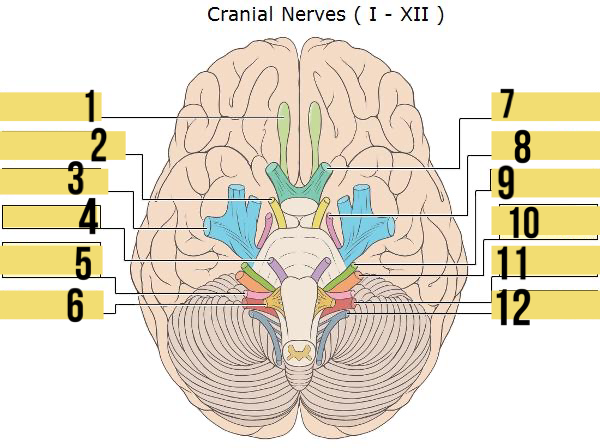
hypoglossal (XII)
identify 6
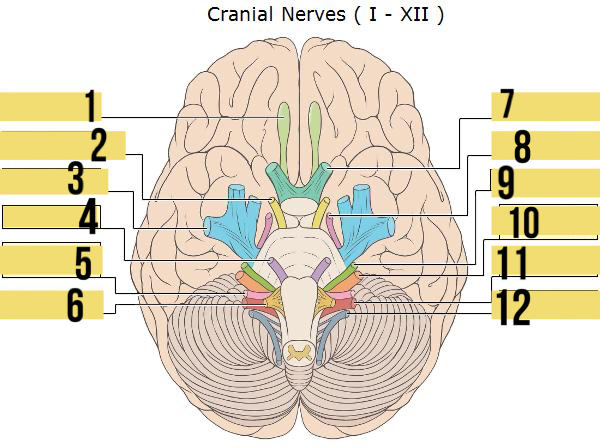
optic (II)
identify 7
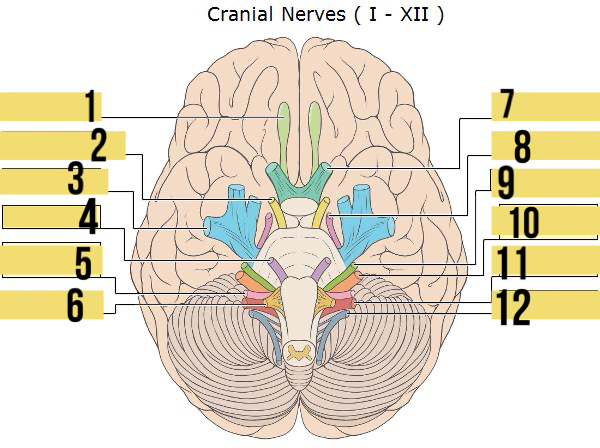
trochlear (IV)
identify 8
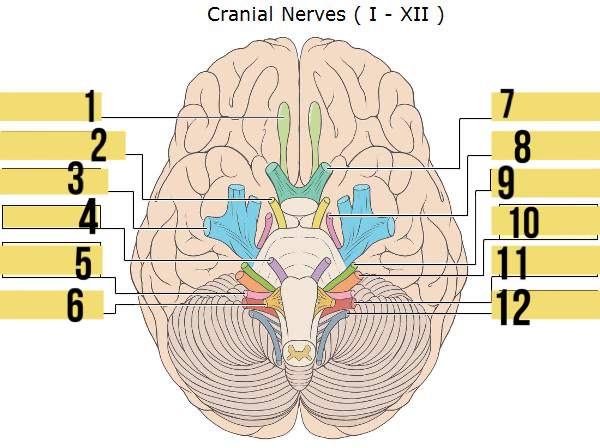
facial (VII)
identify 9
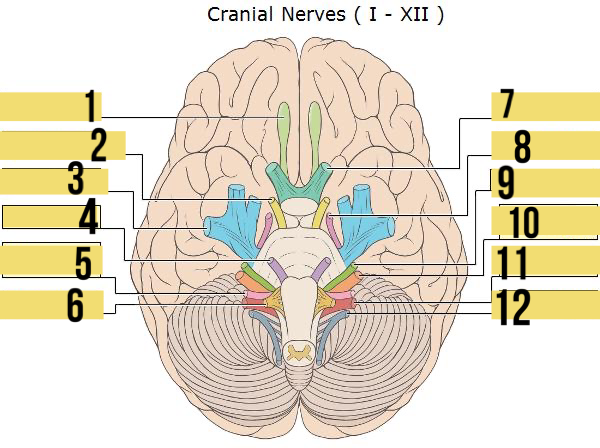
auditory/vestibulocohlear (VIII)
identify 10
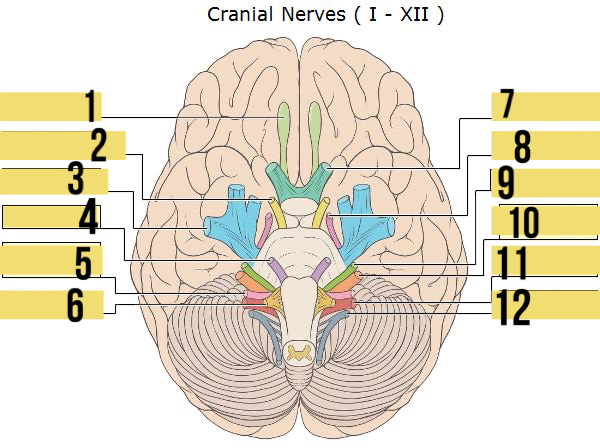
vagus (X)
identify 11
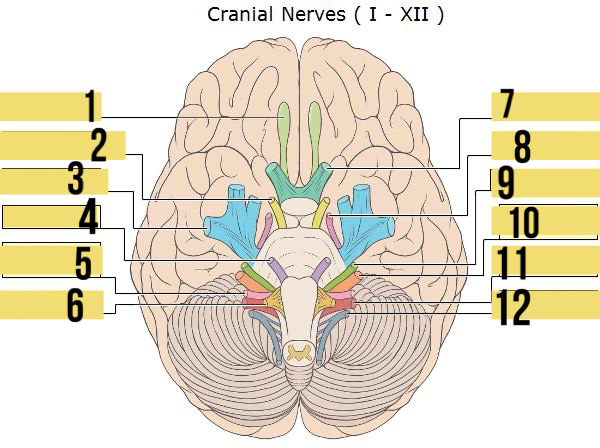
accessory (XII)
identify 12