Posterior Leg
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
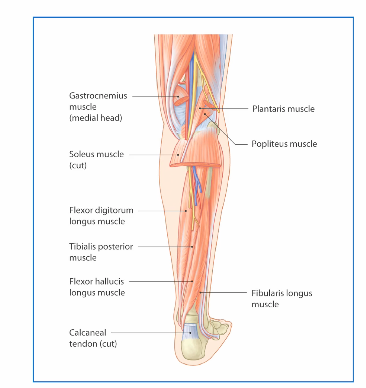
overview of posterior leg muscles in terms of actions
plantar flexors, inverters, toeflexors
superficial compartment muscles
gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris
deep posterior leg muscles
popliteus
tib post
flexor digitorum longus
flexor hallucis longus
what are all muscles in posterior leg innervated by
tibial nerve (L4-S3)
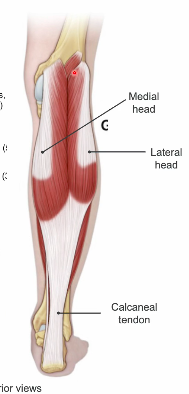
gastrocnemius O I A
LH: LATERAL FEMORAL CONDYLE
MH: medial femoral condyle
A: plantar flexor, knee flexion
gastrocnemius innervated by what
tibial nerve
Soleus
deep to gastroc
O: HEAD OF FIBULA, SOLEAL LINE OF TIBIA
I: CALCANEAL TENDON
A: PLANTAR FLEXION
soleus innervation
tibial nerve
two heads of gastrocnemius, and soleus coming together at calcaneal tendon is called what
triceps surae
where is calcaneal tendon inserting
calcaneal tuberosity
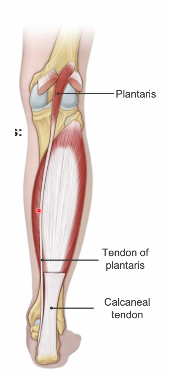
plantaris
O: lateral supracondylar line
I: calcaneal tendon
A: weakly assists plantar flexion
innervated by tibial nerve
what muscles are found in deep posterior leg region
popliteus
flexor digitorum longus
tibialis posterior
flexor hallucis longus
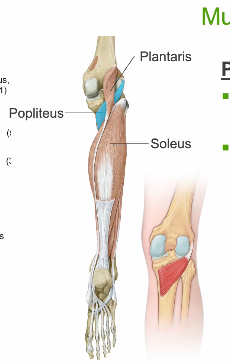
popliteus
Popliteus
▪ O: lateral femoral condyle +
lateral meniscus
▪ I: Posterior surface tibia
superior to Soleal line
▪ Action
– Rotates femur laterally to
unlock the knee (fixed tibia)
▪ Innervation
– Tibial n. (L4-S3)
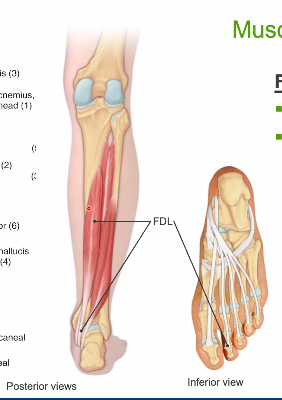
flexor digitorum longus
O: distal posterior tibia
▪ I: distal phalanges 2-4
– Passes posterior to medial
malleolus to plantar surface
▪ Action
– Plantar flexion
– Flex digits 2-4 (MTP, PIP,
DIP)
– Inversion
▪ Innervation
– Tibial n. (L4-S3)
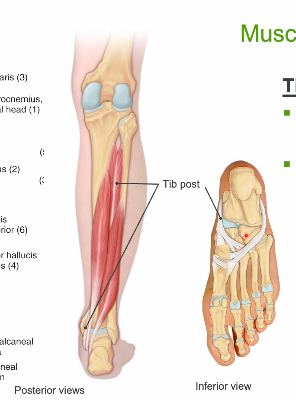
Tibialis posterior
O: tibia, interosseus
membrane, fibula
▪ I: tarsals, base of MT 2-4
– Passes posterior to medial
malleolus to plantar surface
▪ Action
– Inversion
– Plantar flexion
– Support arches
▪ Innervation
– Tibial n. (L4-S3)
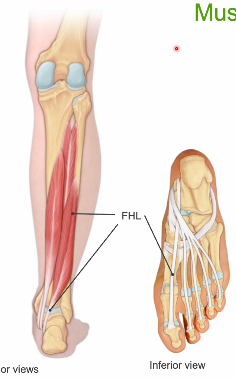
flexor hallicus longus
Flexor hallucis longus
▪ O: posterior fibula,
interosseus membrane
▪ I: distal phalanges 1
– Passes posterior to medial
malleolus to plantar surface
▪ Action
– Flex hallux
– Plantar flexion
▪ Innervation
– Tibial n. (L4-S3)
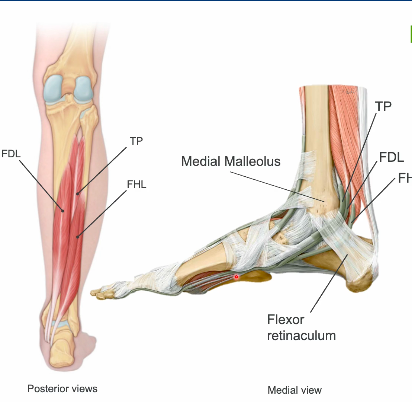
structural relationships for msucles of the posterior leg
medially to laterally
(DOWN THE HATCH)
flexordigitorum longus, tibialis posterior, flexur hallucis longus
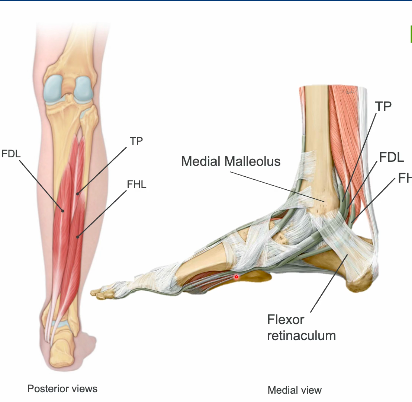
once these muscles travel posterior to the medial malleolus (tarsal tunnel) something happens, what would this structural relationship be?
TOM DICK HARRY
ant—-posterior
TP,FDL,FHL
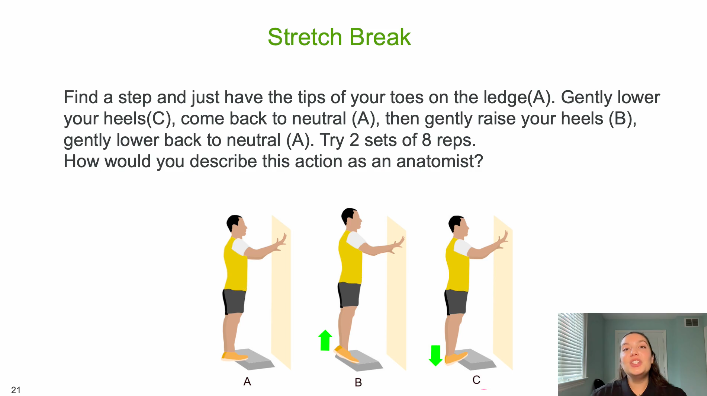
Phase A → C: Lowering the heels
This is ankle dorsiflexion, produced eccentrically by the triceps surae (gastrocnemius + soleus) as they lengthen to control the downward motion.
The Achilles tendon is also being lengthened under load.
The subtalar and midfoot joints contribute slight pronation depending on individual mechanics.
Phase C → A: Returning to neutral
Still controlled plantarflexor activity, transitioning from eccentric to isometric as the ankle returns to a neutral position on the step.
Phase A → B: Rising onto the toes
This is ankle plantarflexion, produced concentrically by the triceps surae.
The movement lifts the body vertically by shortening the calf muscles and increasing tension through the Achilles tendon.
The ankle may demonstrate slight supination as the heel rises (again depending on an individual's pattern).
Phase B → A: Lowering back to neutral
Controlled eccentric dorsiflexion action of the plantarflexors.