Amplify - Evolutionary History
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
Adaptive Trait
A trait that makes it more likely that an individual will survive in a specific environment.
2
New cards
Body Structure
Any part of an organism.
3
New cards
Ancestor Population
An older population from which two or more newer species descended or evolved from.
4
New cards
Shared Structure
A body structure in two or more species that has the same parts (for example, the same bones).
5
New cards
Paleontologists
Scientists who study fossils in order to understand the ancient history of life on earth.
6
New cards
Evolution
The process by which species adapt to changes in the environment over a very long time.
7
New cards
Organisms
Living things, such as plants, animals, and bacteria.
8
New cards
Speciation
The process by which one population evolves into two or more different species.
9
New cards
Species
A group of organisms of the same kind that can successfully reproduce with their own kid.
10
New cards
Stability
When something stays mostly the same over time.
11
New cards
Change of Environment
What causes organisms or species that have certain body structures to change?
12
New cards
Sharing of the Same Ancestry Population.
How do two different species share the same bone structure?
13
New cards
Sharing of the Same Ancestry Population but Said Population Separated into different environments that required different types of said thing.
What causes different species to have the same body part but for different benefits?
14
New cards
Shared Ancestor Population
What causes two or more species to share something?
15
New cards
Limb
An organism’s arm, leg, or wing
16
New cards
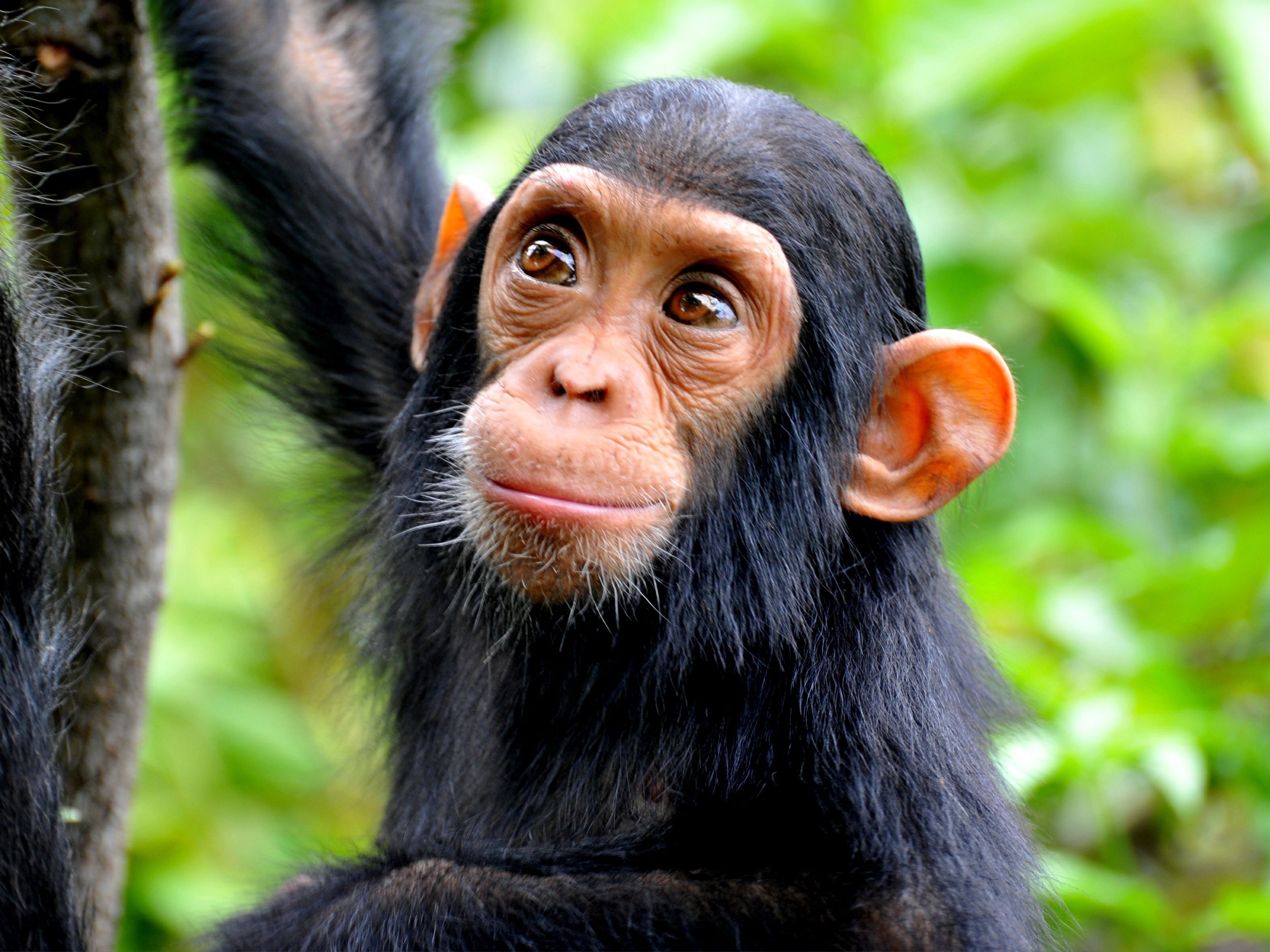

Their environment must have changed.
The body structures for a population of chimpanzees were stable for a long time. Then, their body structures changed, making the chimpanzees stronger. Why did this happen?
17
New cards
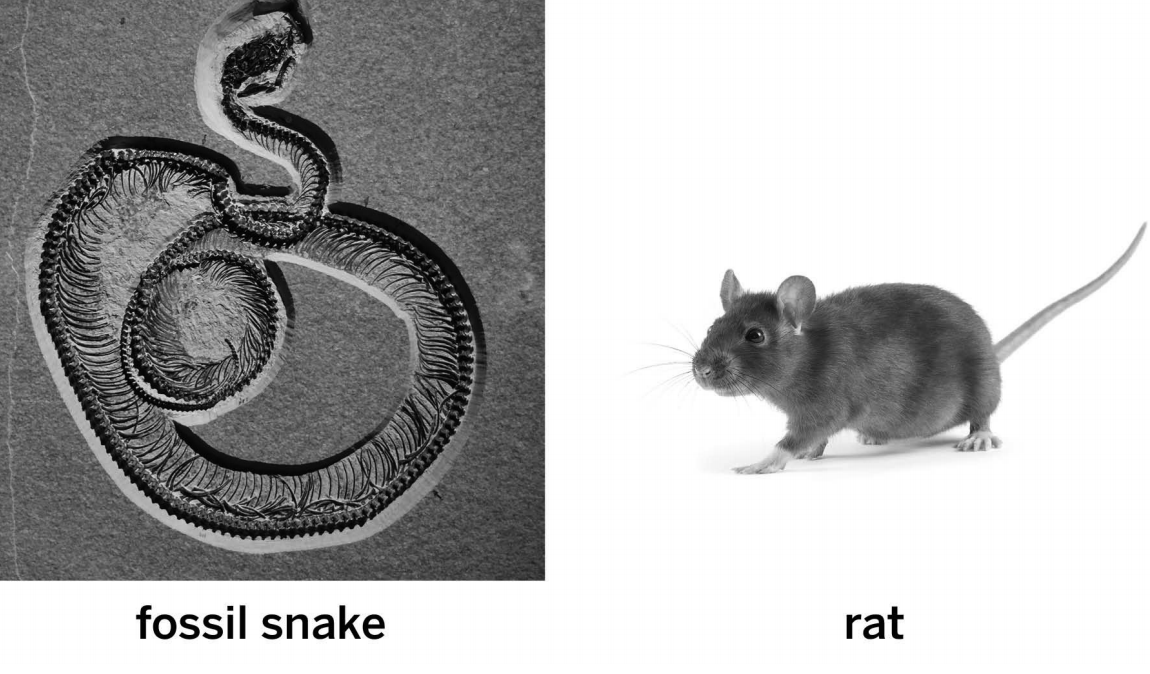
The snake and rat both share the same ancestor population that had a quadrate bone.
This fossil snake and this living rat both have a structure in their skull called the quadrate bone. How did this happen?
18
New cards
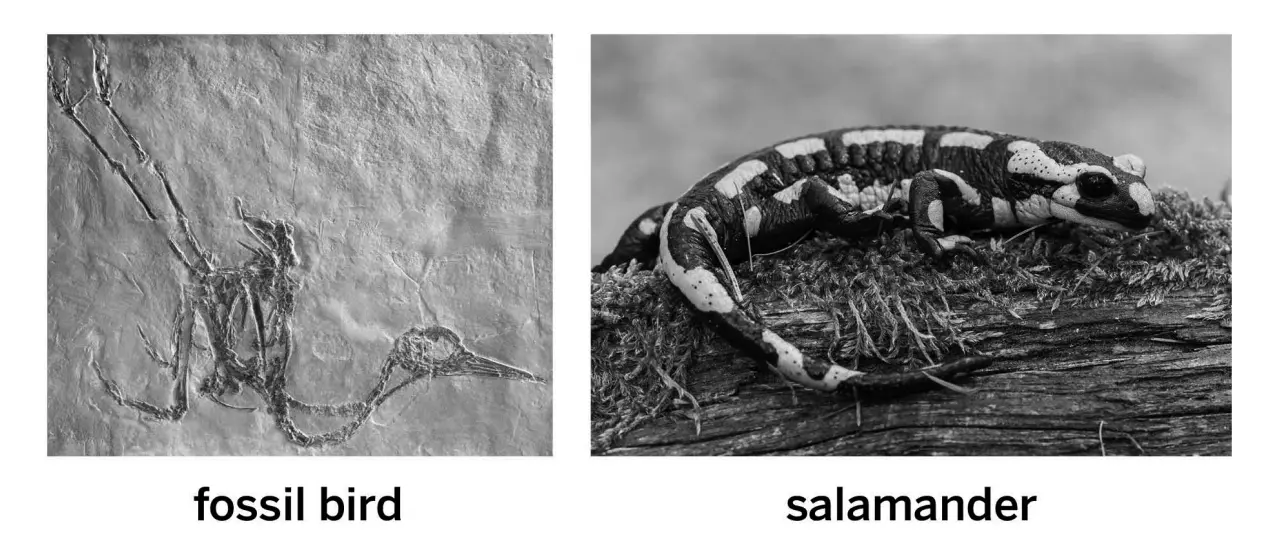

The salamander and bird both inherited tails from a shared ancestor population. But the population separated into different environments where different types of tails evolved.
This fossil bird and this living salamander both have tails. However, the bird has a very short tail that helps it have a light skeleton for flying. The salamander has a long tail that helps it balance while it runs. Why did this happen?
19
New cards
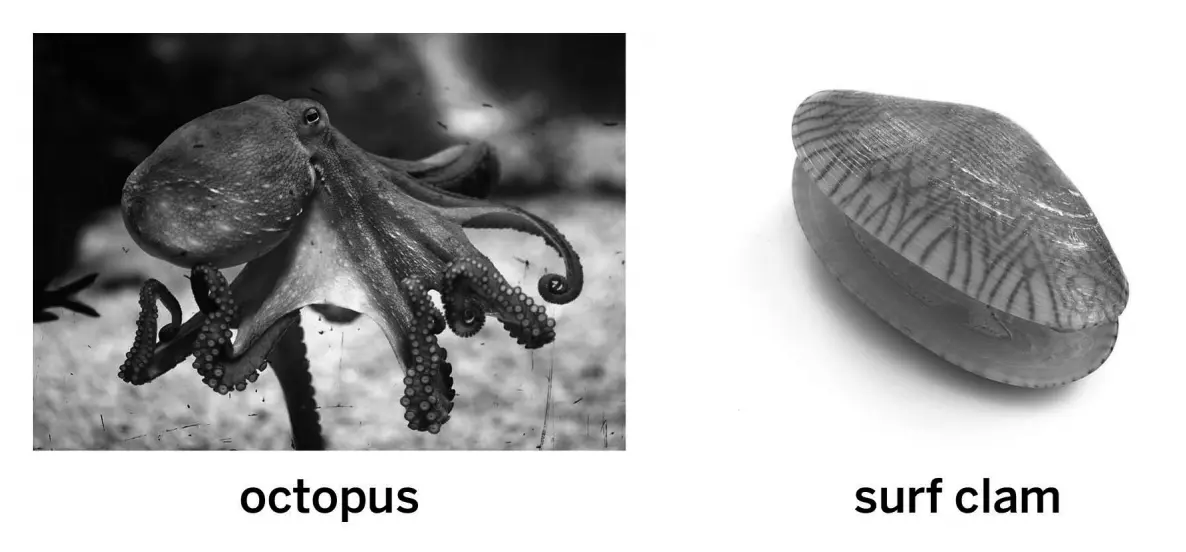

The octopus and surf clam both inherited the mantle structure from a shared ancestor population.
This octopus and this surf clam both have a body structure called a mantle, which covers their soft bodies. However, the octopus’s mantle has muscles that help the octopus swim. The surf clam’s mantle helps the clam build its shell. Why are the mantles different?
20
New cards
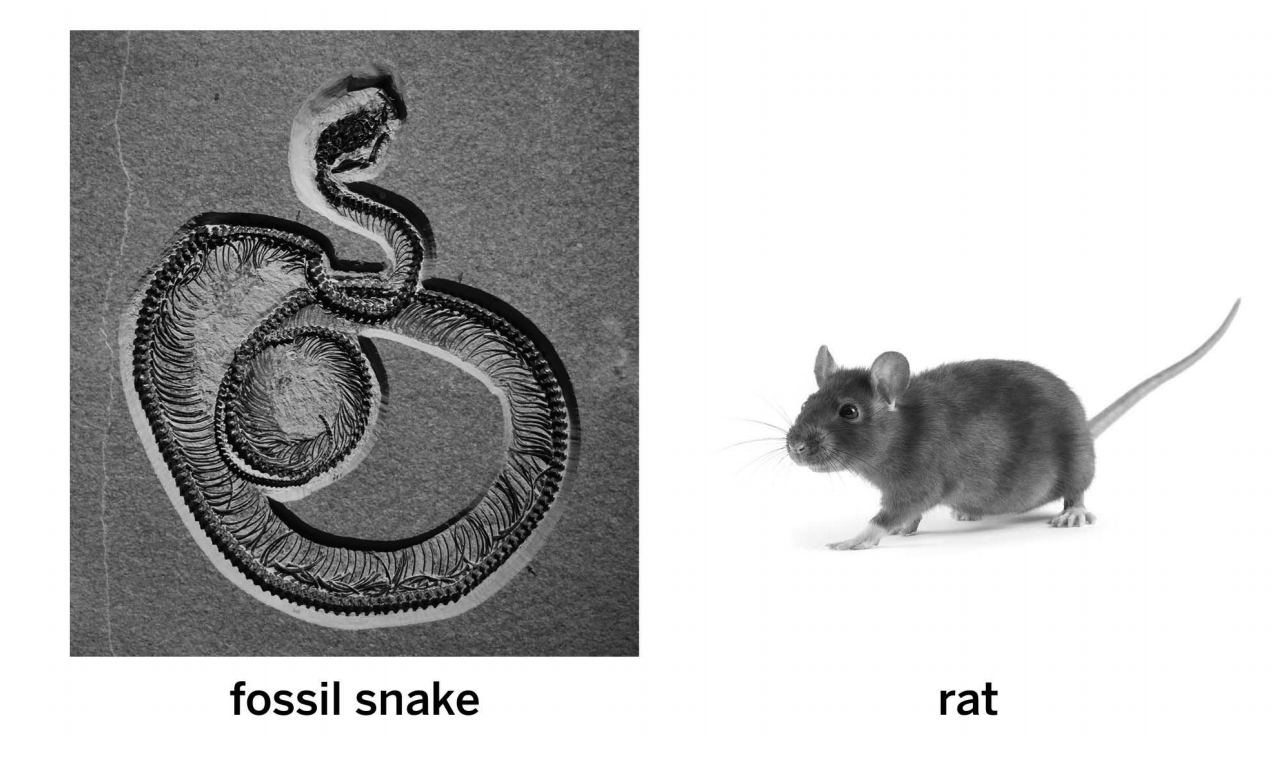
The snake and mouse both inherited the mantle structure from a shared ancestor population
This fossil snake and this living rat both have a structure in their skull called the quadrate bone. What best explains why both species have a quadrate bone?
21
New cards
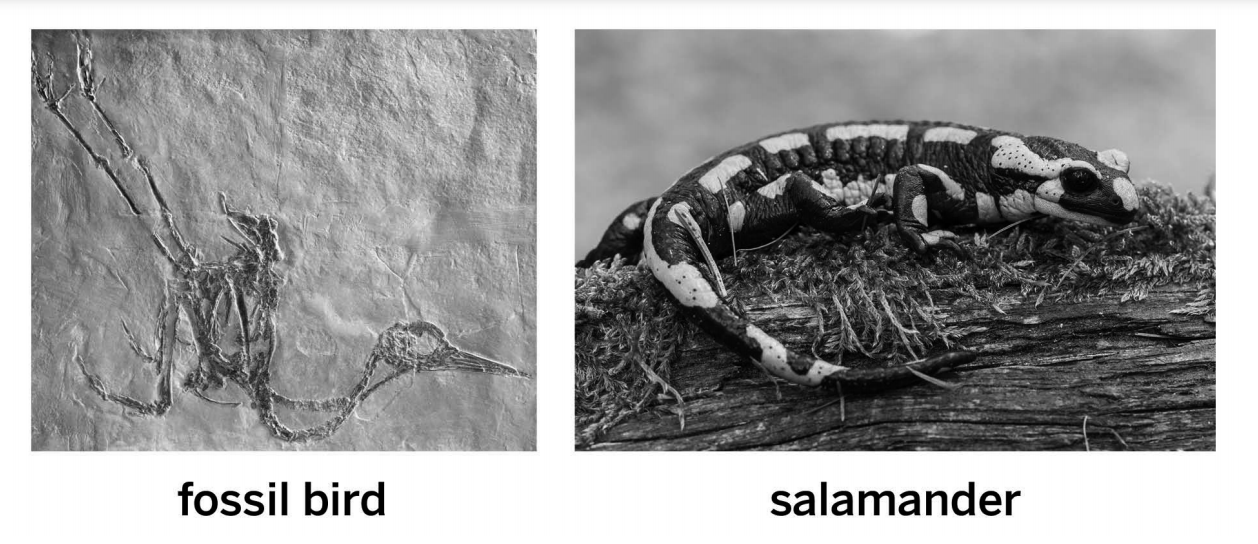

The salamander and bird both inherited tails from a shared ancestor population, but this population separated into different environments.
This fossil bird and this living salamander both have tails. However, they have different tail structures. The bird has a very short tail made of just one bone for flying. The salamander has a long tail with many bones that helps it balance while it runs. What most likely explains why they are different?
22
New cards
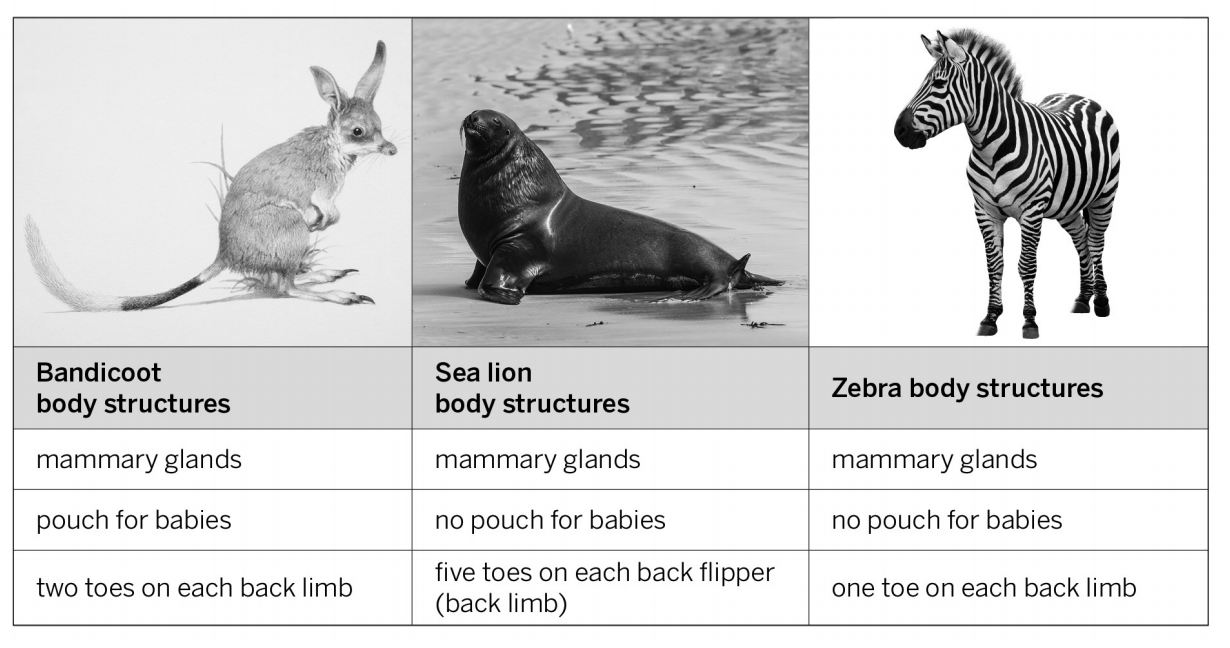
All three species share an ancestor population, but sea lions and zebras share a more recent ancestor population.
This bandicoot, this sea lion, and this zebra have similarities and differences in their body structures. What does the information about these structures tell you about the ancestors of these species?
23
New cards
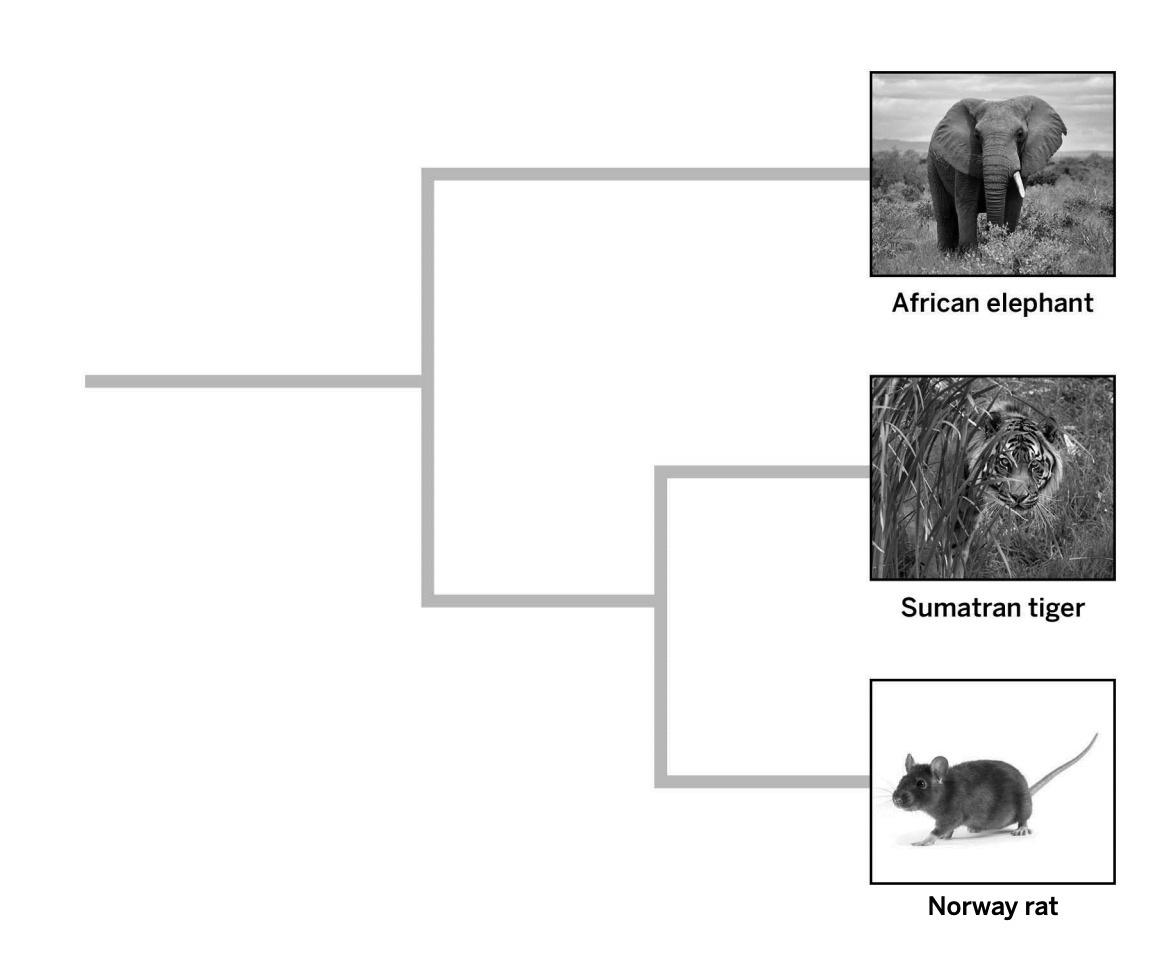
All three species share a common ancestor, but the Sumatran tiger and Norway rat are more closely related to each other.
What does this diagram show?
24
New cards
All three species share an ancestor population, but the red-eared slider and the greater flamingo share a more recent ancestor population.
This red-eared slider, this greater flamingo, and this siamang have similarities and differences in their body structures. What does the information about these structures tell you about the ancestors of these species?