Bio Exam Study Guide
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
what is biology
the study of life
what might a biologist do
study the diversity of life, research diseases, develop technologies, improve agriculture, preserve the enviornment
what are the 8 characteristics of life
made up of one or more cell
displays organization
grows and develops
reproduces
responds to stimuli
require energy
maintains homeostasis
adaptations evolve over time
what does each characteristic of life mean
made up of one or more cell- unicellular or multicellular
displays organization- arranged in an orderly way
grows and develops- addition to mass(growth) process of natural changes over the lifetime(development)
reproduces- production of offspring
responds to stimuli- the behavior that is manifested by a living organism which is the result if an external or internal stimulus
requires energy- need food and energy to live
maintains homeostasis- regulation of an organism’s internal conditions to maintain life
adaptations evolve over time- enable the species to survive and pas on their genes to the next generation
what is the difference between growth and development
growth- increase in size
development- natural changes over lifetime
what is an example of homeostasis
sweating
what is an observation
direct method of gathering information in an orderly way
what is an inference
process of combining what you know with what you have learned to draw logical conclusions
what are examples of observations and inferences
observation- the sky is blue
inference- since the leaves changed colors, it is fall
what is a hypothesis
testable explanation of a situation
what is an experiment
investigation of a phenomenon in a controlled setting to test a hypothesis
what is an independent variable in an experiment
the tested factor that might affect the outcome of the experiment
what is a dependent variable
results from or depends on changes to the independent variable
what is a control group and what is an experimental group
control- group used for comparison
experimental- group exposes to the factor being tested
what is the point of collecting and graphing data
to see if your hypothesis was proven wrong or right
what is quantitative data
collected as numbers, such as measurements of time, temperature, length, mass, etc.
what is qualitative data
descriptions of what our senses detect
who invented the microscope
robert hooke
what is a microscope used for
magnify small objects
which scientist are responsible for early discoveries in microbiology
leeuwenhoek- single-celled living organisms
schwann- animal tissue also contained cells
virchow- all cells are produced from the division of existing cells
what is a cell
basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms
what is cell theory
all living organisms are composed of one or more cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and organization of all living organisms, cells arise from only from previously existing cells, with cells passing copies of their genetic material on to their daughter cells
what is the difference between a compound light microscope and electron microscope
compound light- use a series of glass lenses and visible light to magnify images, 1000x
electron- create an image by illuminating a sample with a beam of electrons and collecting the electrons that are reflected back from the sample, 500,000x
how can you calculate magnification on a compound light microscope
4x, 10x, 100x
what are things all cells have in common
plasma membrane
what is a prokaryote
cells without a nucleus or other membrane cound-organelles
what are examples of prokaryotes
bacteria, salmonella, EColi
what are eukaryotes?
contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
examples of eukaryotes
plants, animals, and fungi
differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are smaller and simpler cells that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They include bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, do have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, which help organize and compartmentalize functions in the cell.
analogies to describe either prokaryote or eukaryote
prokaryote- shack
eukaryote- mansion
what is selective permeablitity
the cell membrane can allow things to pass through or not allow
what is the plasma membrane made of
phospholipid bilayers
what is polarity
farthest away from neutral, very positive, or very negative
why does the plasma membrane have polar heads facing outward on each side of the bi-layer?
so the plasma membrane could exist around polar molecules
polar or nonpolar, which one like to be around water
polar
which molecules can diffuses through the membrane and why?
nonpolar, hydrophobic
what is the role of transport protein
it is a way for polar molecules to get through the membrane
what type of molecule would most likely use a transport protein channel
polar
what is cholesterol used for in the cell membrane
separate the nonpolar tails
what are carbohydrates used for
defines the cell’s characteristics, receiving signals from other cells
explain the fluid mosaic model
when you look at the cell from the top it looks like a mosaic pattern, it has a fluid movement.
know how to label the whole membrane
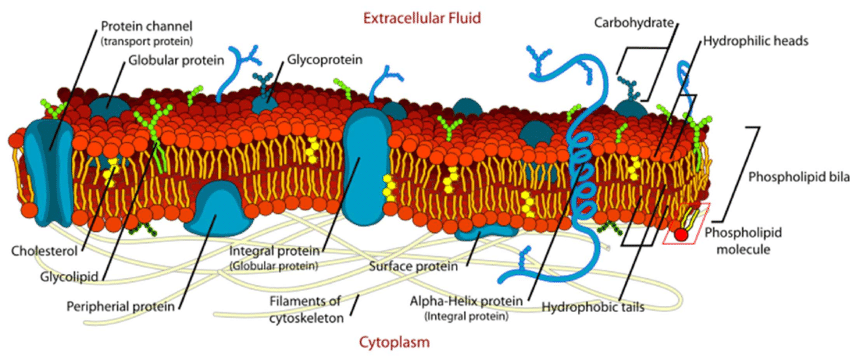
cytoplasm
fluid in the membrane
cytoskeleton
supporting network of long, thin protein fibers that form a frame work for the cell
microtubules
long, hollow protein cylinders that form a rigid skeleton for the cell and assist in moving substances within the cell
microfilaments
thin protein threads that help give the cell shape and enable the part of the entire cell move
nucleus
contains DNA
ribosomes
organelles that manufacture proteins
endoplasmic reticulum(ER)
membrane system of folded sacs and interconnected channels that serves as the site for protein and lipid synthesis
golgi apparatus
flattened stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins,
vacuole
temporary storage, plant cells only
lysosomes
vesicles that contain substances that digest excess or worn-out organelles and food particles, animal cells only
centrioles
organelles made of microtubules that function during cell division
mitochondria
concert fuel particles into usable energy, powerhouse of the cell
chloroplast
capture light and convert it into chemical energy in process called photosynthesis, plant cells only
cell wall
thick, rigid, mesh of fibers that surround the outside of the plasma membrane
cilia
short, numerous projections that look like hair
flagella
longer and less numerous than cilia, move in a whip-like motion
similarities between plant and animals cells
Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic and contain several diverse organelles that are not found in prokaryotic cells.
differences between plant and animal cells
Plant cells have a cell wall in addition to a cell membrane, whereas animal cells have only a cell membrane
similarities/differences between bacteria and animal cells
similarities: Both bacterial cells and animal cells are composed of a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material
differences: Bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus or membrane bound organelles, whereas animal cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
similarities/differences between bacteria and plant
They both have a cell wall but a bacterias cell wall isn't made from cellulose.
process of protein production inside the cell
ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, then is sent to the ER where the ribosomes stick and then create those proteins, they are then sent to the golgi apparatus which packages and sends it off the the cell
diffusion
the net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration(high to low) no energy
dynamic equilibrium
when diffusion occurs over a long enough time, concentrations will become uniform
facilitated diffusion
uses transport proteins to move ions and small molecules across the plasma membrane
osmosis
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane( opposite of diffusion) with no energy
trend of movement for osmosis
low solute concentration to high solute concentration
hypotonic solution
lower concentration of solutes than the cytoplasm of the cell
what will happen to a cell in a hypotonic solution
animal cells can burst when placed in extremely hypotonic solutions
hypertonic solution
higher concentration of solutes than the cytoplasm of the cell
what will happen in a hypertonic solution
cause wilting in plants
isotonic solution
the same concentration of water and solutes as the cytoplasm of the cell
what will happen in an isotonic solution
there will be no net movement of water
passive transport
does not require energy
active transport
The movement of particles across the cell membrane, against the concentration gradient, requires energy
how does the Na+/K+ ATPase pump work
to maintain levels of sodium (Na+) and Potassium (K+) inside/outside the cell
how does coupled transport work? what molecules are involved
sugar can pair with Na+ ions and enter the cell through facilitated diffusion-saving energy- sugar and sodium
endocytosis
the process by which a cell surrounds an object in the outside environment in a portion of the plasma membrane
exocytosis
the excretion of materials at the plasma membrane
catabolic reaction
releases energy by breaking down larger molecules
anabolic reaction
use energy to build larger molecules
what type of reaction is photosynthesis
anabolic
what type of reaction is cellular respiration
catabolic
how are cellular respiration and phtotsynthesis related to one another
Photosynthesis makes the glucose that is used in cellular respiration to make ATP
what is the arrangement of the ATP molecule
nucleotide made of an adenine base, ribose sugar, and 3 phosphate group
how do you release energy from the ATP molecule
when the bond between the second and third phosphate groups is broken
what is the chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O = C6H12O6 + 6O2
thylakoid
flattened saclike membranes
grana
stacks of thylakoids
stroma
the fluid-filled space outside the grana
most common pigment found in plants
green
what colors does chlorophyll absorb? reflect?
absorb- red and blue
reflect-green
how do leaves change color in autumn
chlorophyll dies so other pigments are more abundant and other colors of light are reflected
explain how light energy begins the phase of photosynthesis
chlorophyll absorbs light energy, which excites some electrons in the pigment molecules to higher energy levels
what are the products of photosynthesis
ATP, NADPH, Oxygen
how does a plant make NADPH
ferredoxin transfers the electron to the carrier molecule NADP
how does the plant make ATP in phase one
hydrogen ions diffuse through ATP synthase when they diffuse through it , it allows it to join ADP
what is the ATP molecule used for
provides chemical energy