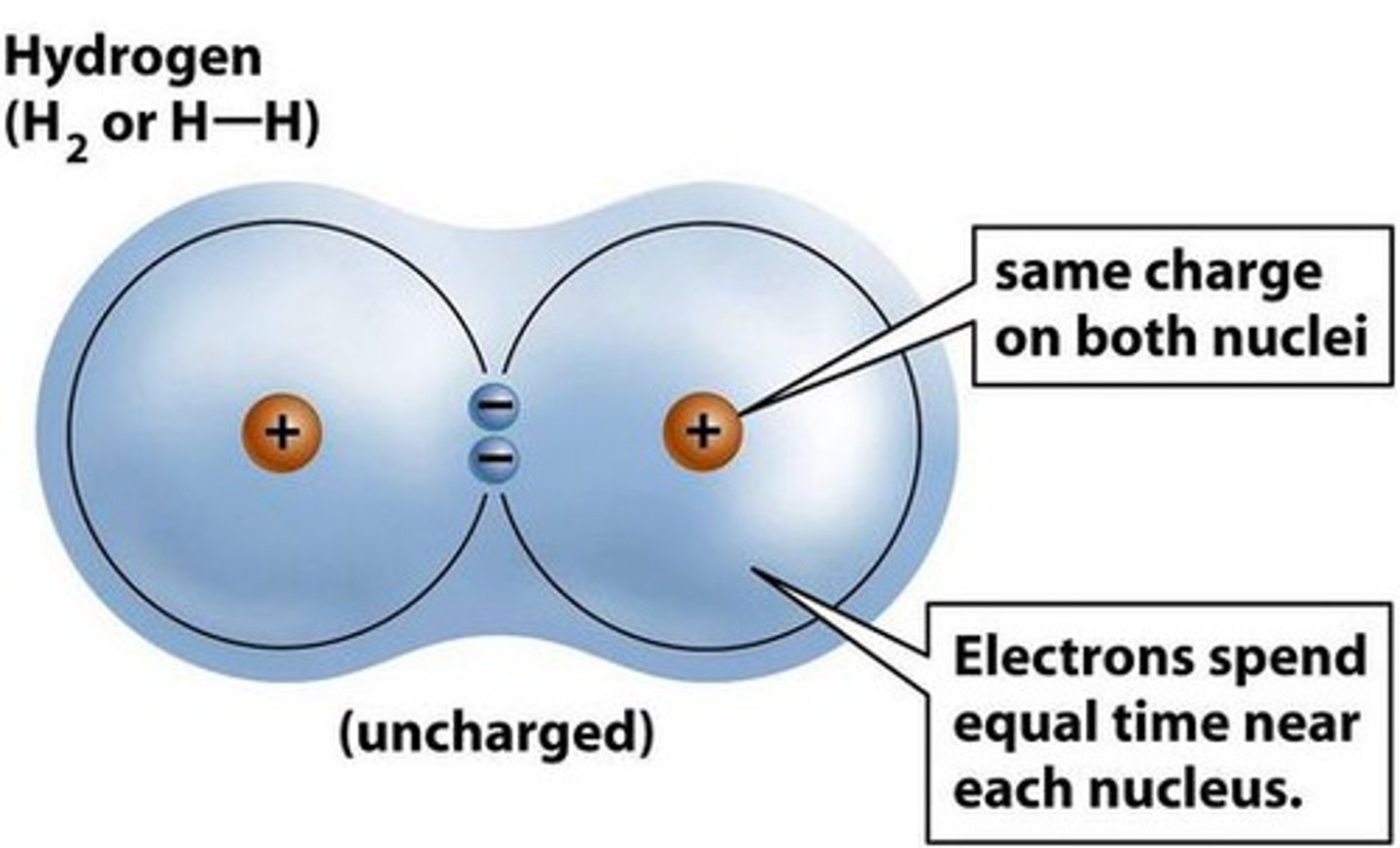
USC 11 Chemistry Quizlet for SAT 2 2025
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Use minimisation of repulsion around central atom to find shape
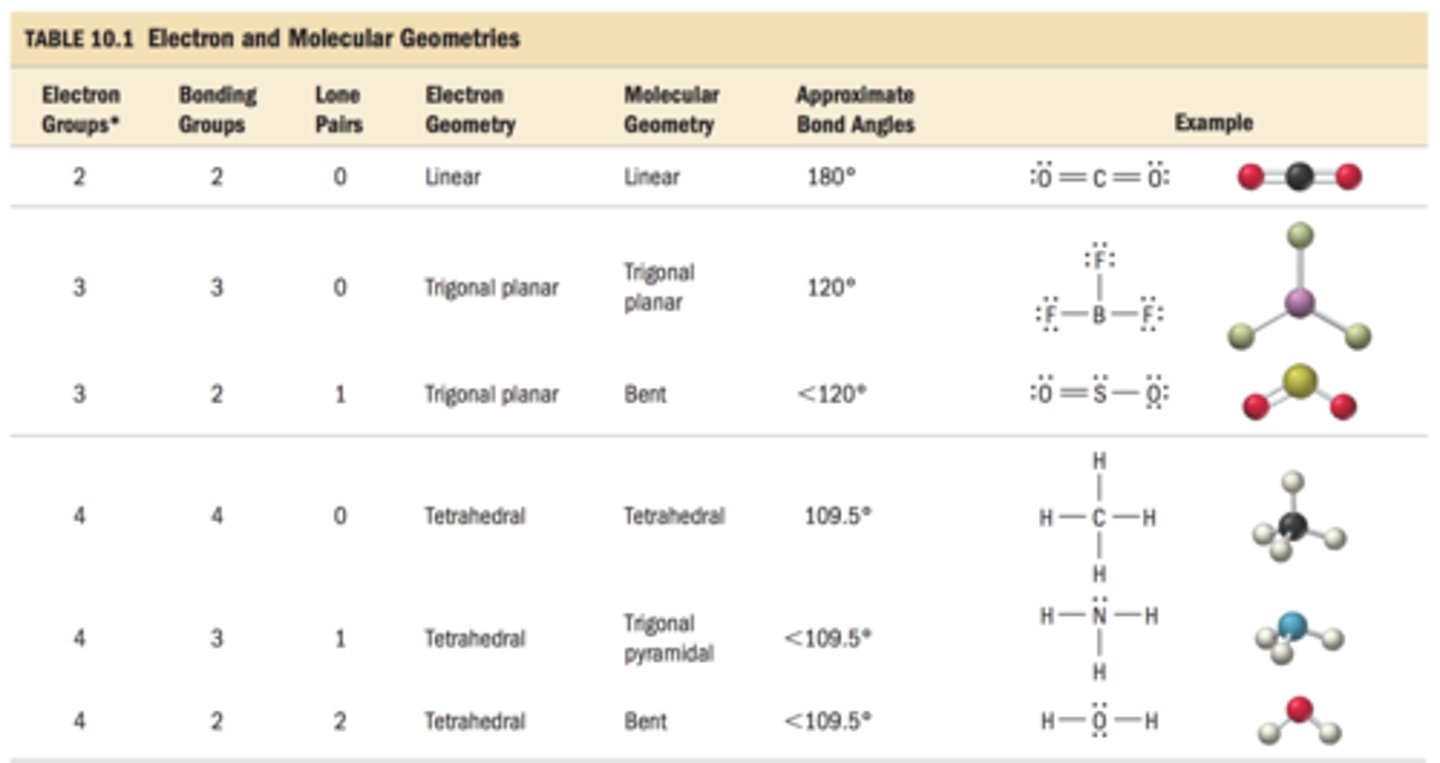
tetrahedral molecule
A molecular shape formed when there are four atoms attached to the central atom and four electron dense regions around the central atom
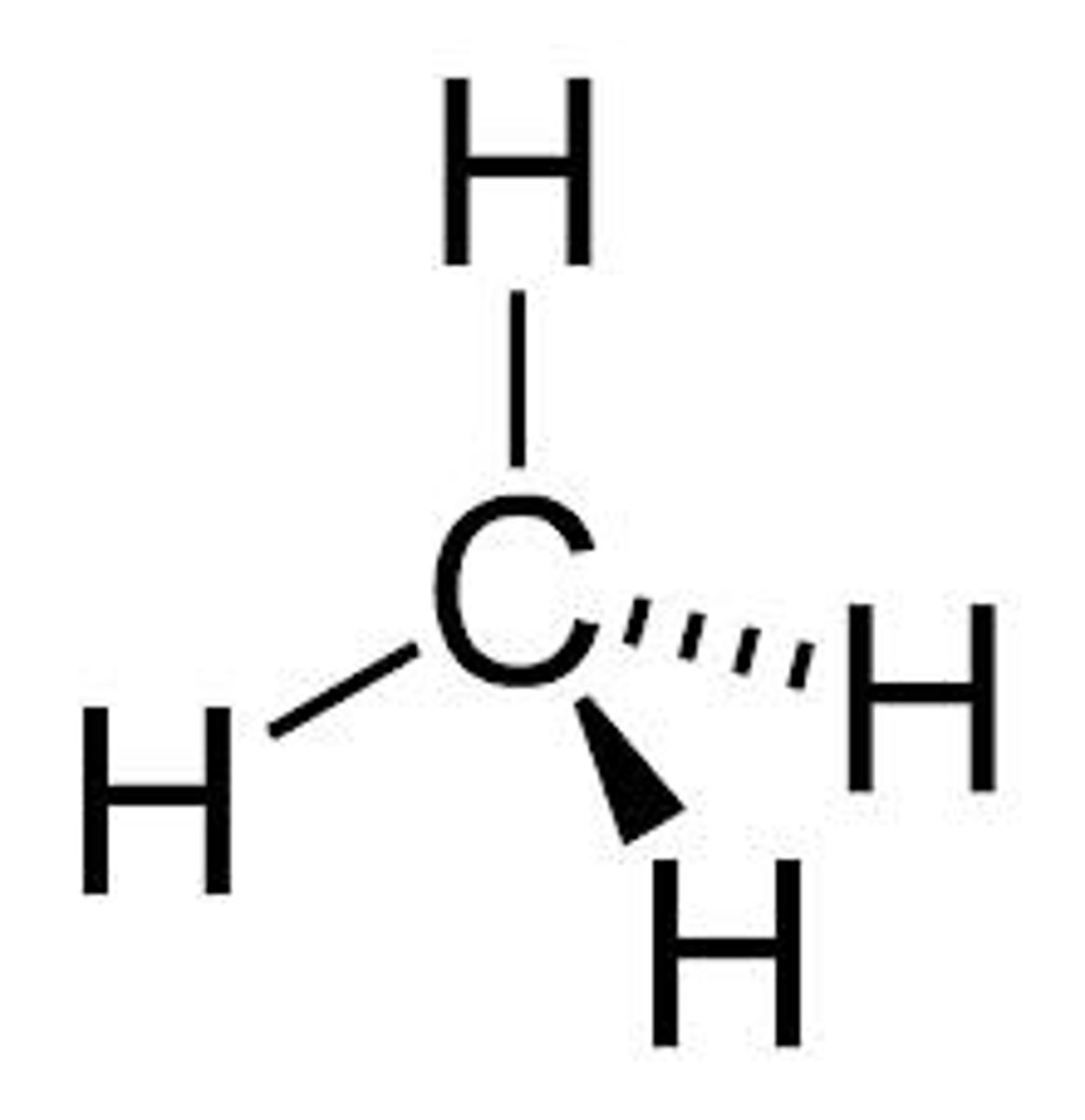
trigonal pyramidal molecule
A molecular shape formed when there are three atoms attached to the central atom and four electron dense regions around the central atom
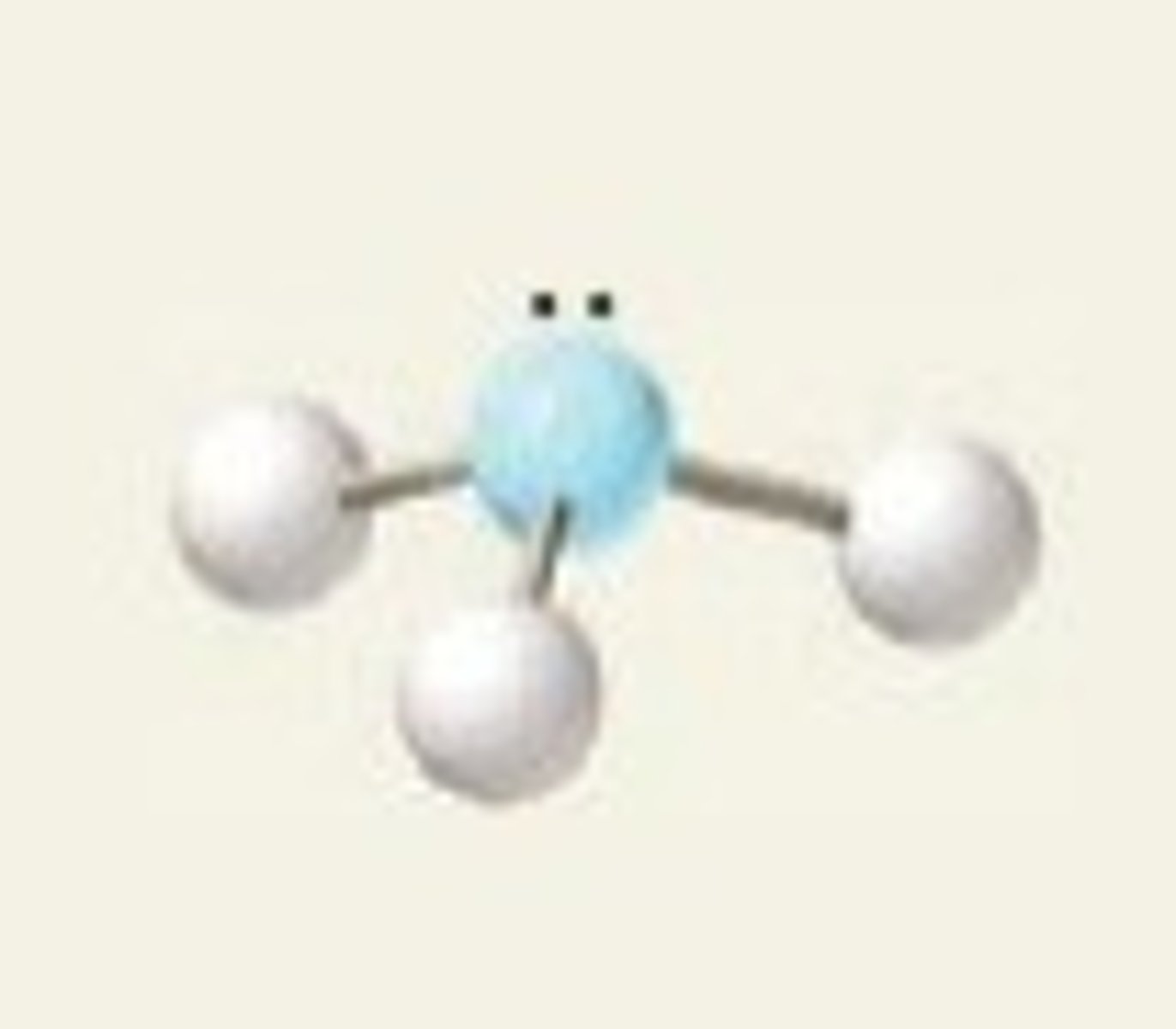

V-shaped molecule
A molecular shape formed when there are two atoms attached to the central atom and four electron dense regions around the central atom
Linear shaped molecule
A molecular shape formed when there are two atoms attached to the central atom and two electron dense regions around the central atom
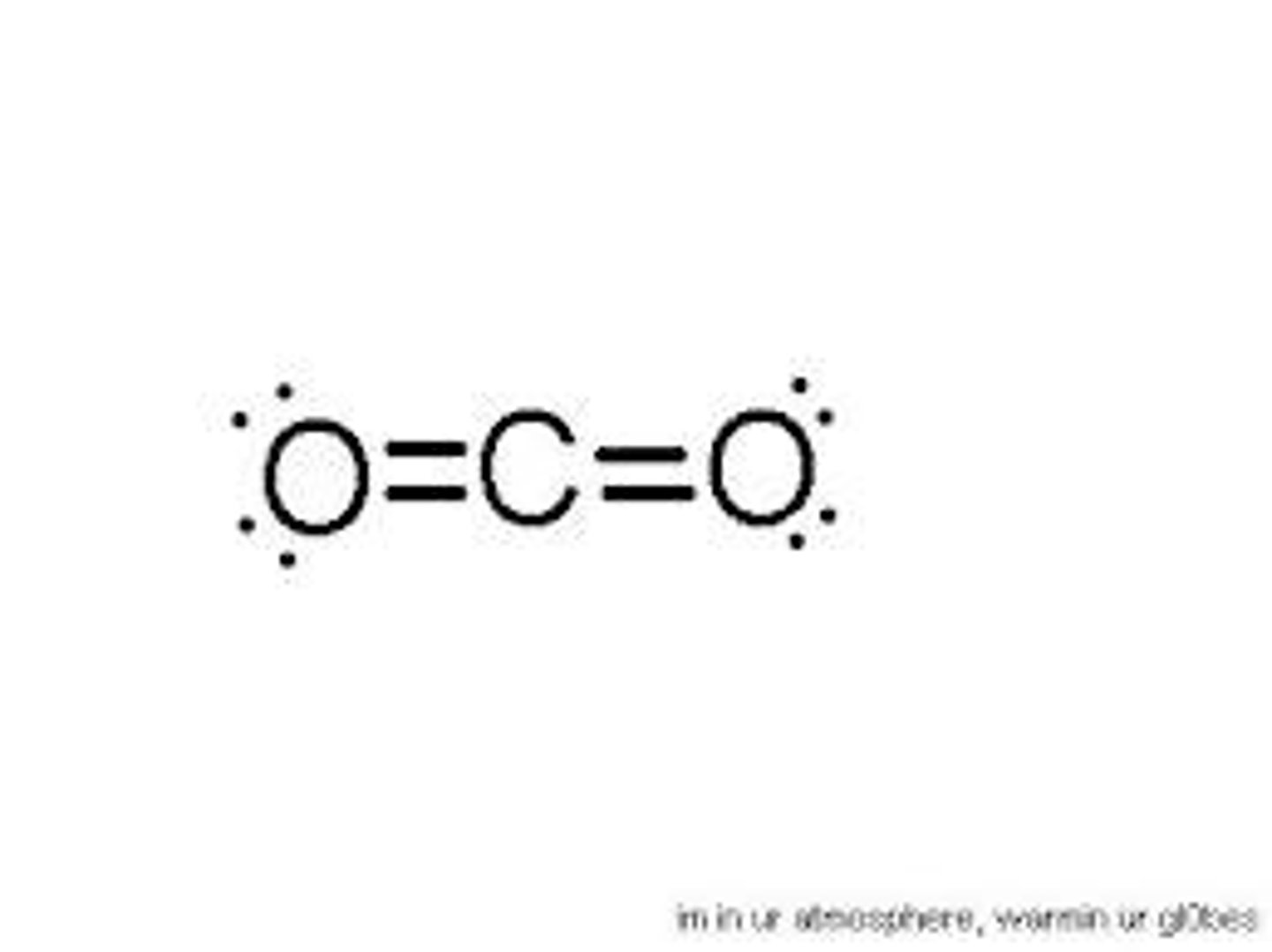
Trigonal planar molecule
A molecular shape formed when there are three atoms attached to the central atom and three electron dense regions around the central atom
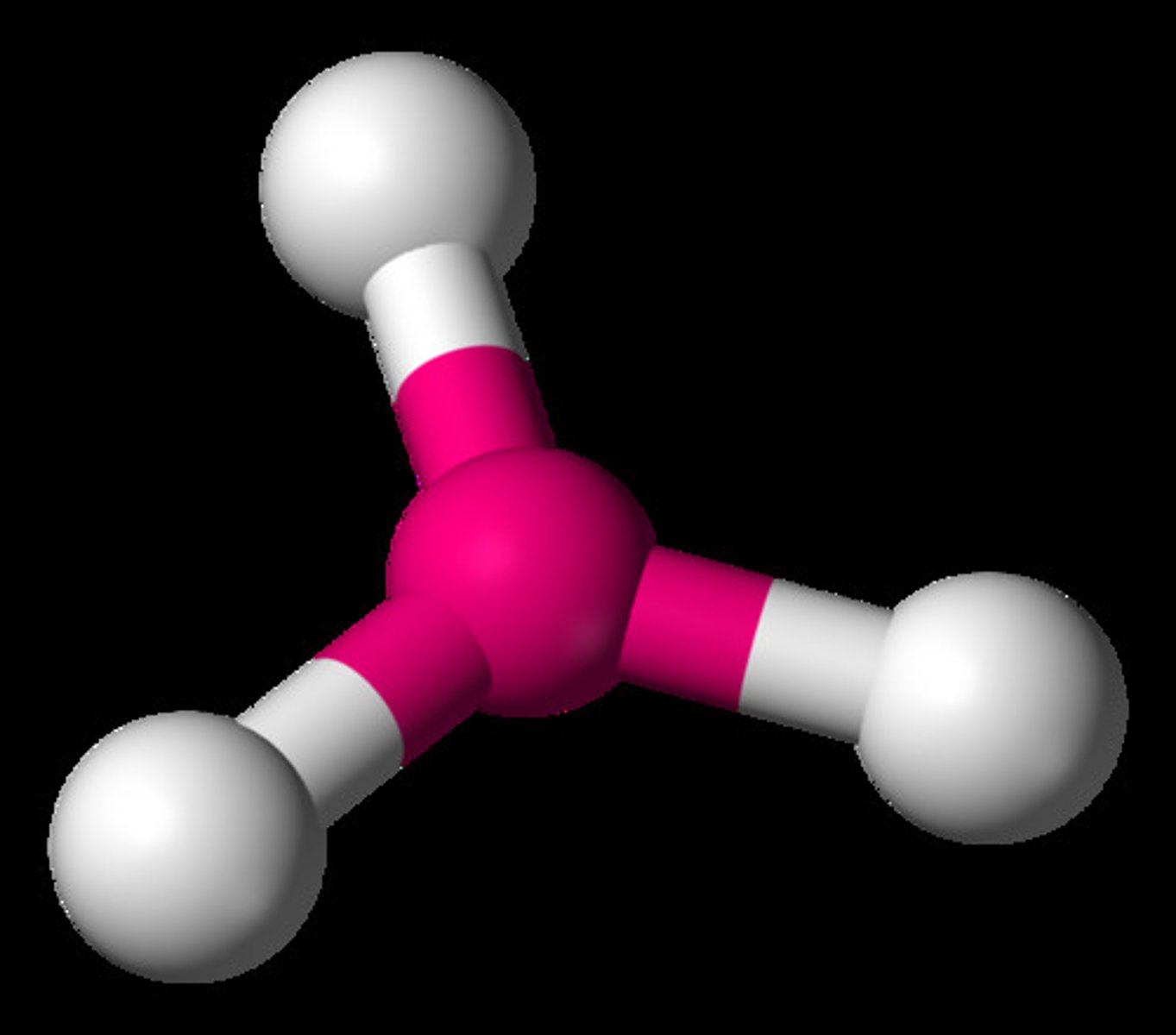
Dipole
A bond in a molecule that has two poles, or regions, with opposite partial charges
Dispersion forces
Weak forces between particles that result from random shifts in the density of electrons around a nucleus, forming temporary dipoles
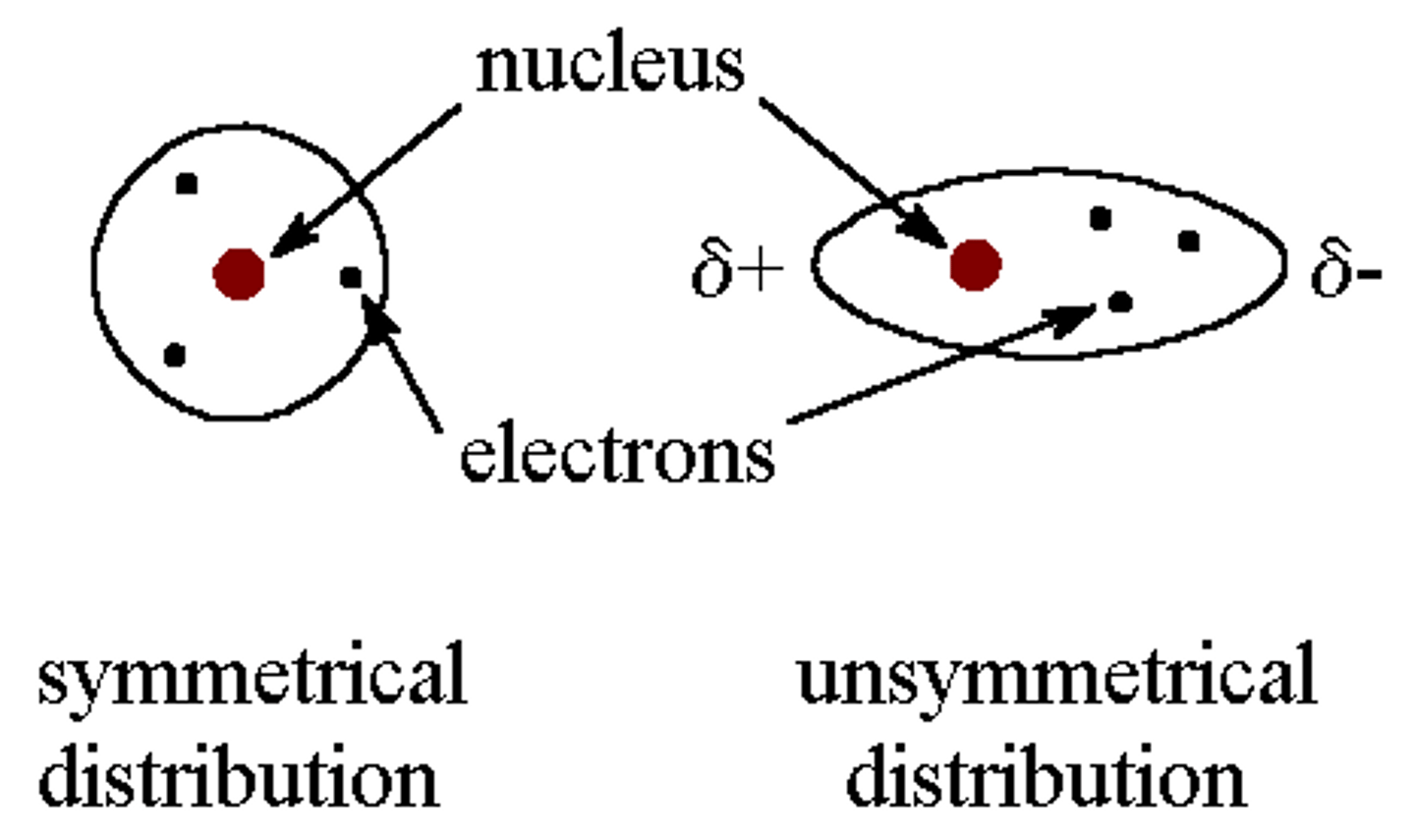
Temporary dipole
A dipole caused by a temporary imbalance in the electron cloud that causes a momentary imbalance of charge.
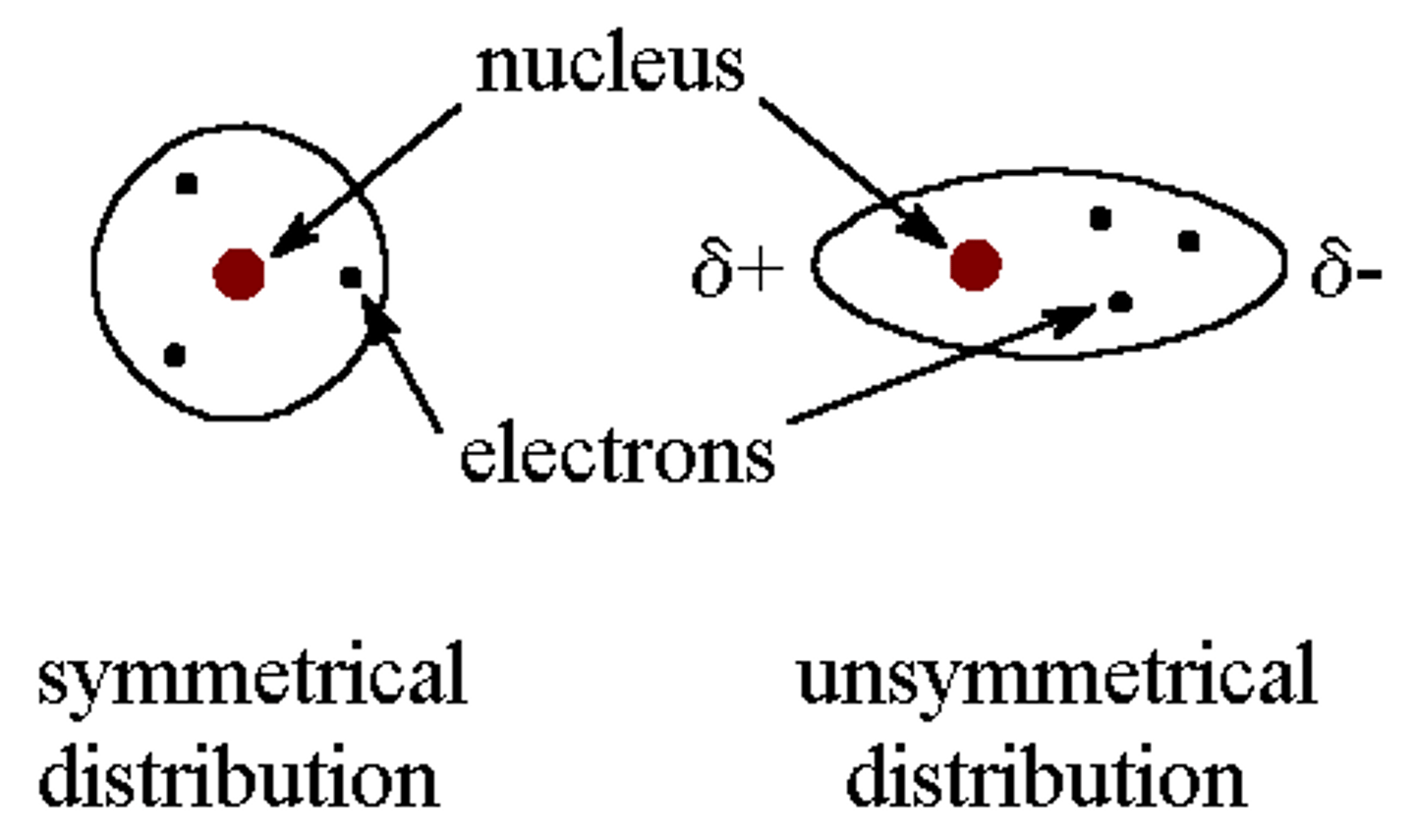
Polar molecule
A molecule with an unequal distribution of charge due to differences in electronegativity between bonded atoms, resulting in the molecule having a partially positive end and a partially negative end
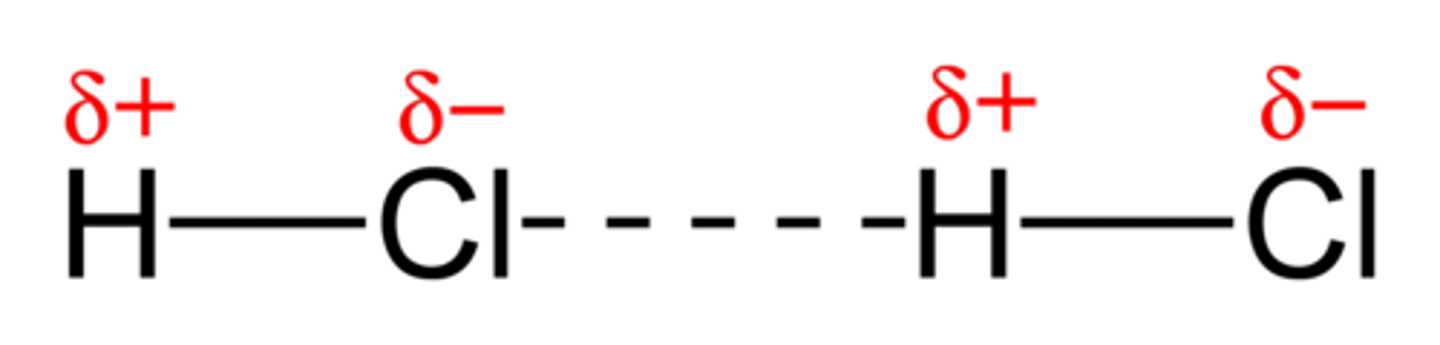
Dipole-dipole forces
Attractions between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules
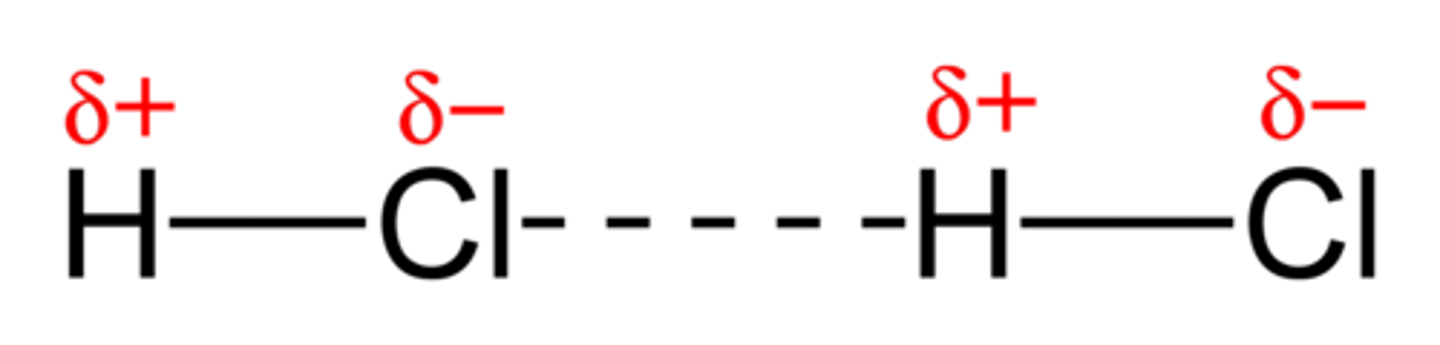
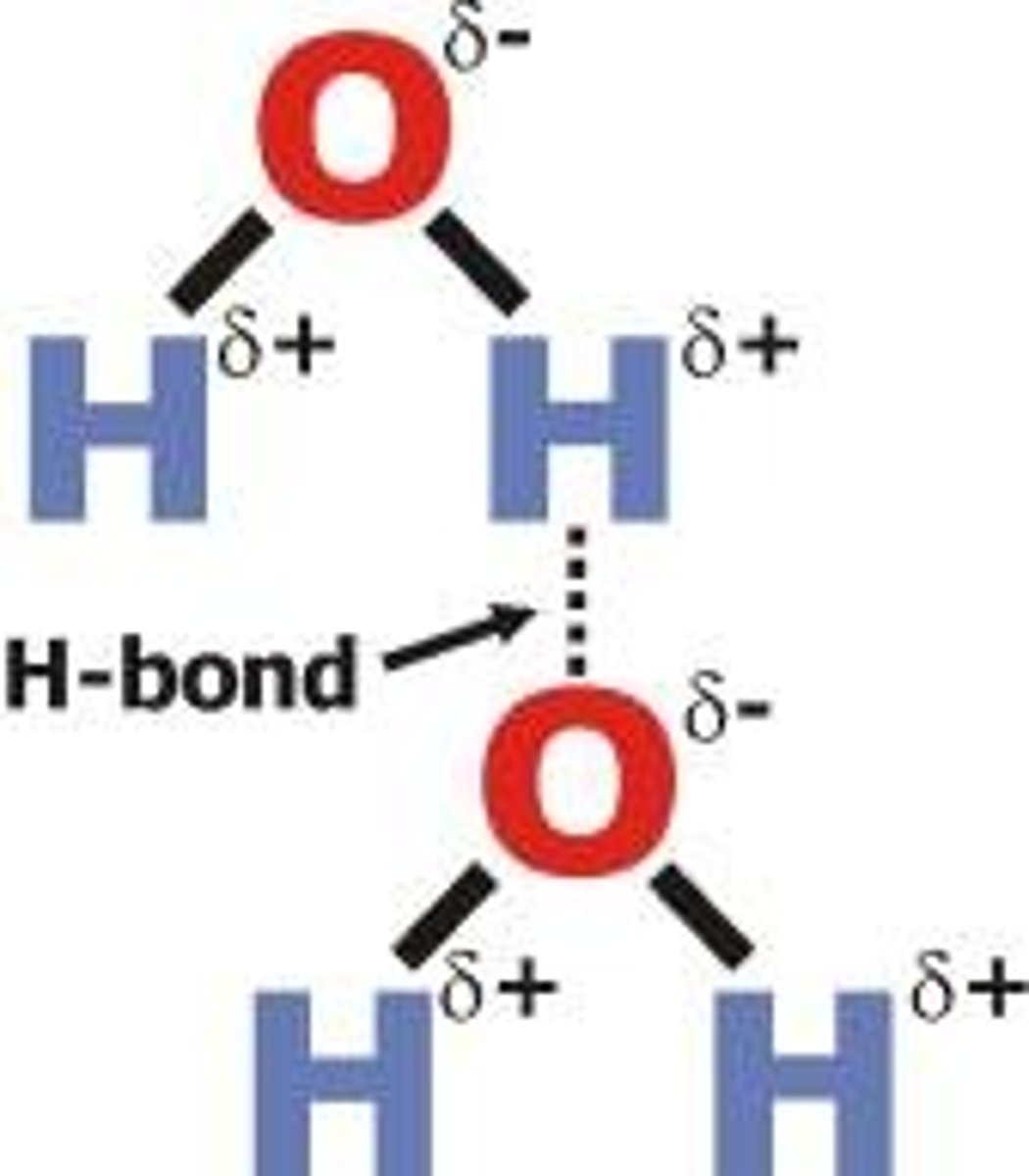
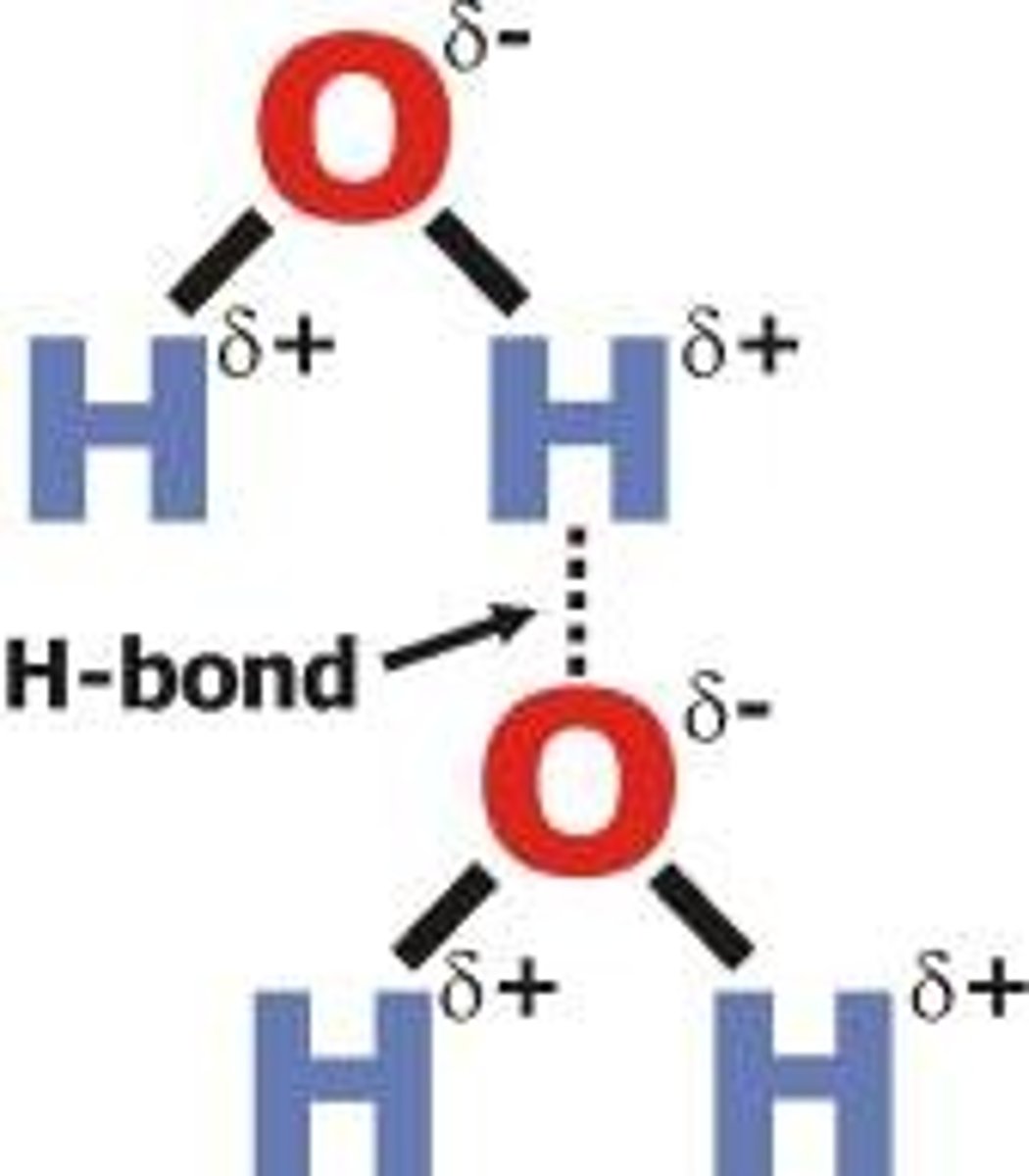
Hydrogen bonding
A strong type of intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction. Occurs between molecules that have H bonded to F, O or N
Hydrocarbon
An organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen
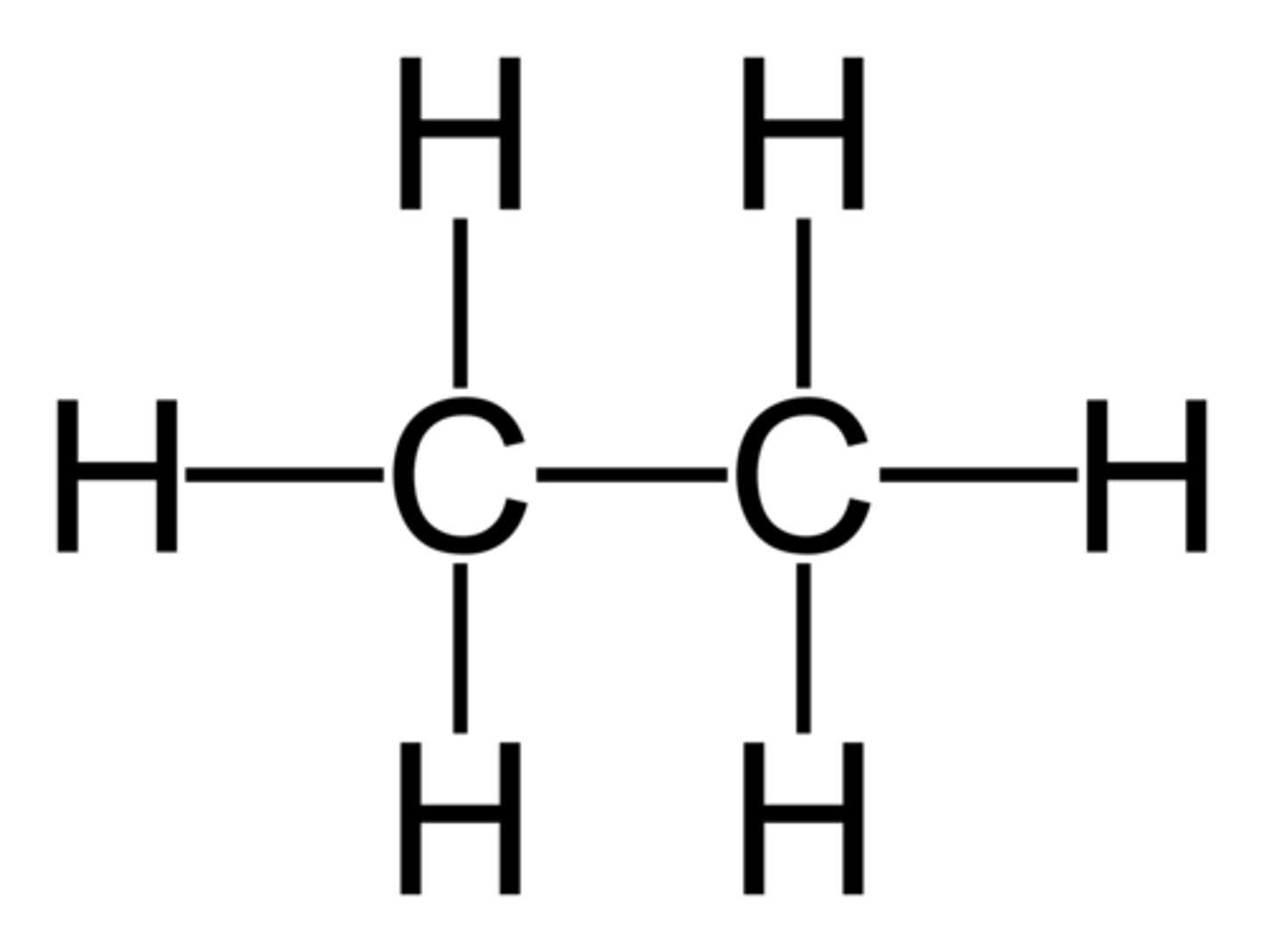
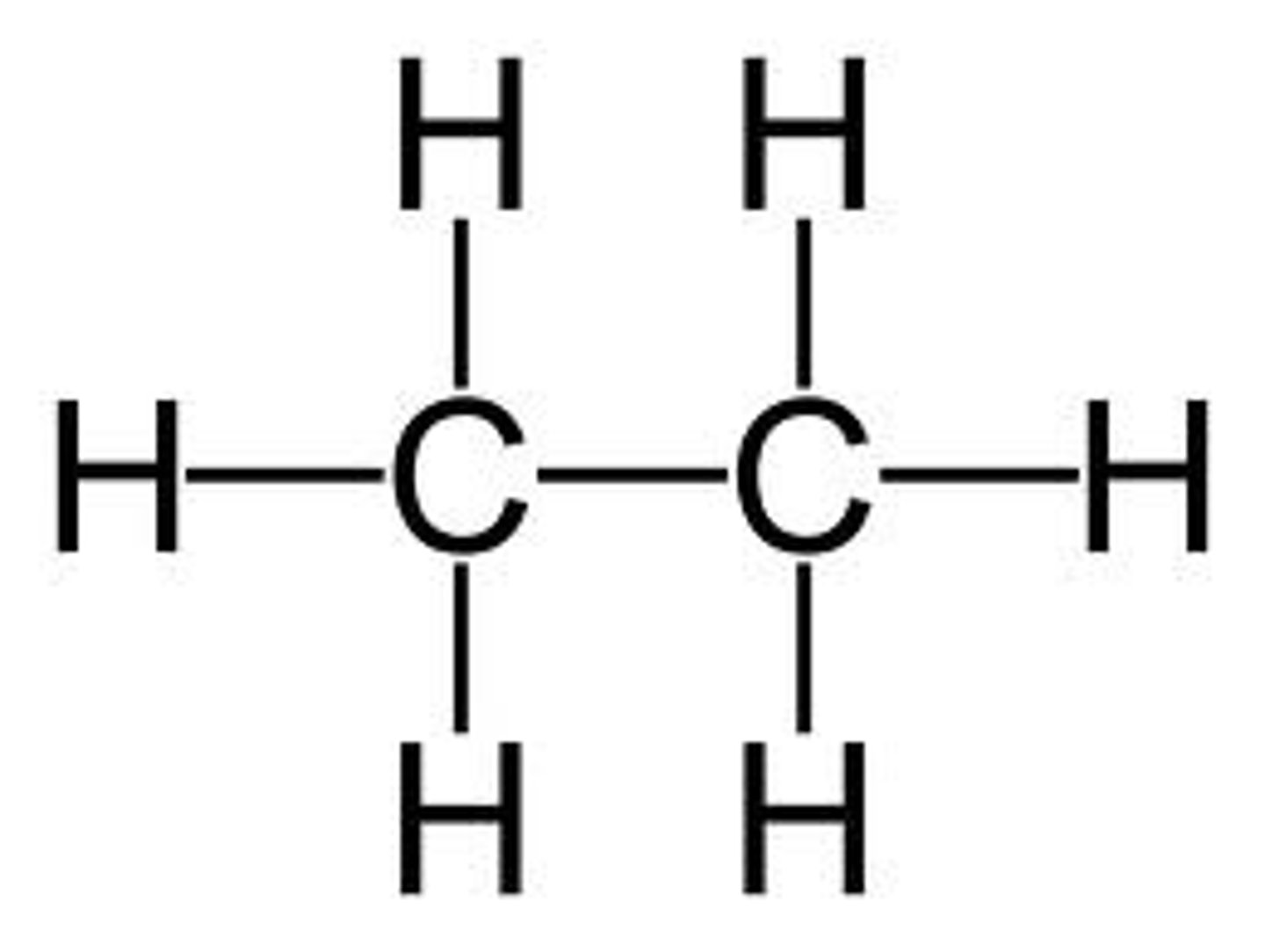
Alkane
A hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds
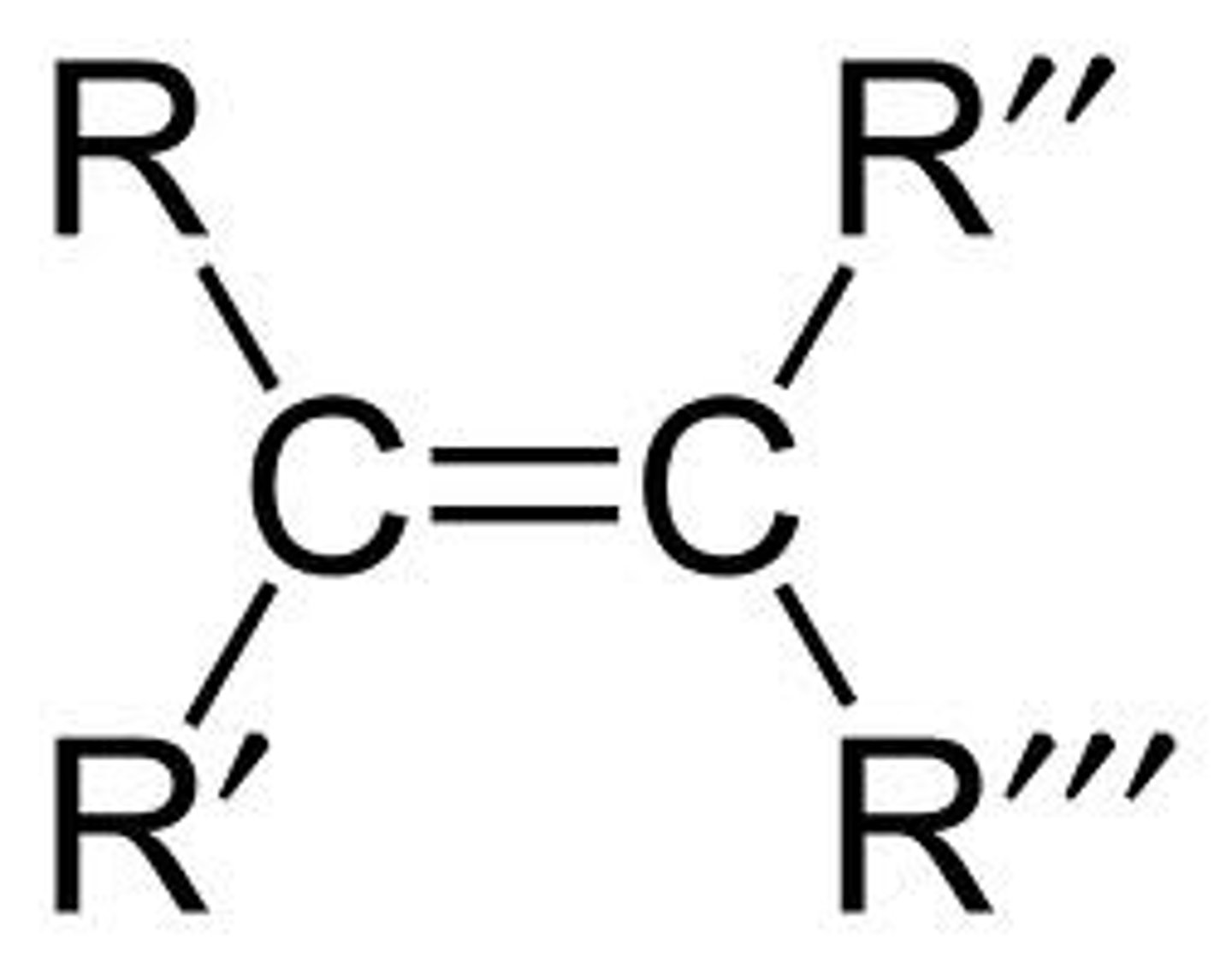
Alkene
A hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond
Functional group
A specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions.
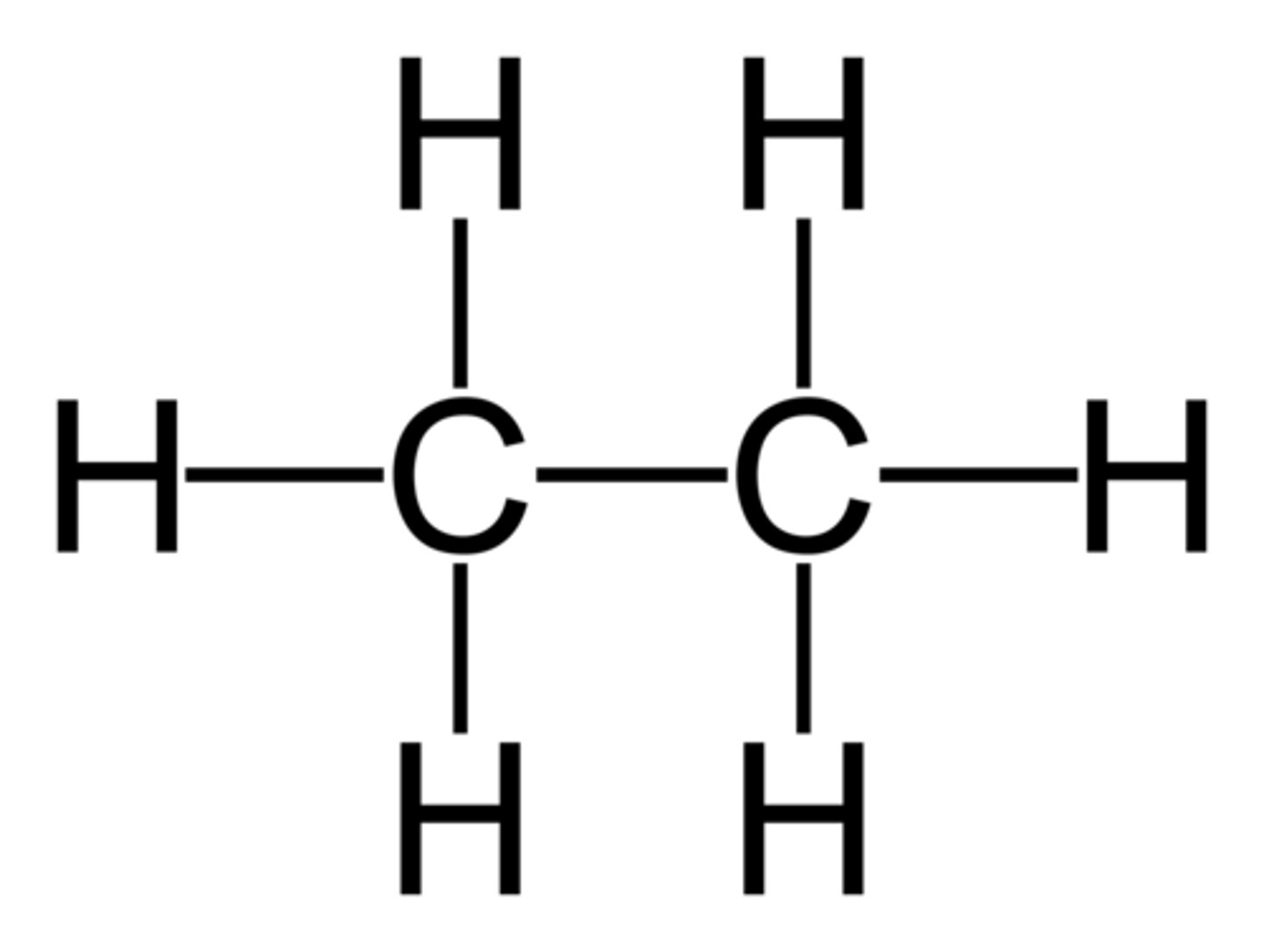
Saturated hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon in which all the bonds between carbon atoms are single bonds
Unsaturated hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon in which one or more of the bonds between carbon atoms is double or triple bond
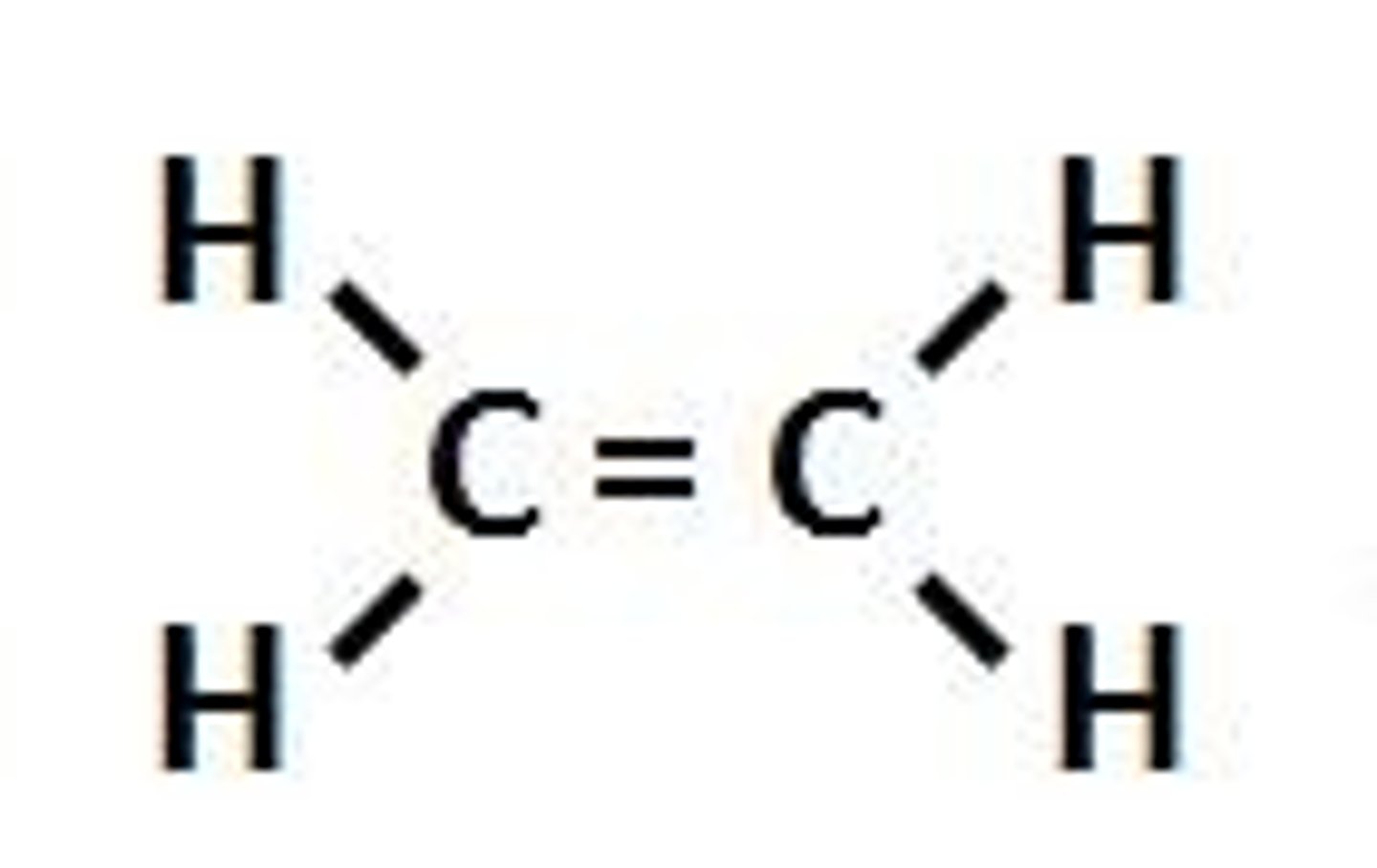
Molecular formula
A chemical formula that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a molecule, but not the arrangement of the atoms.
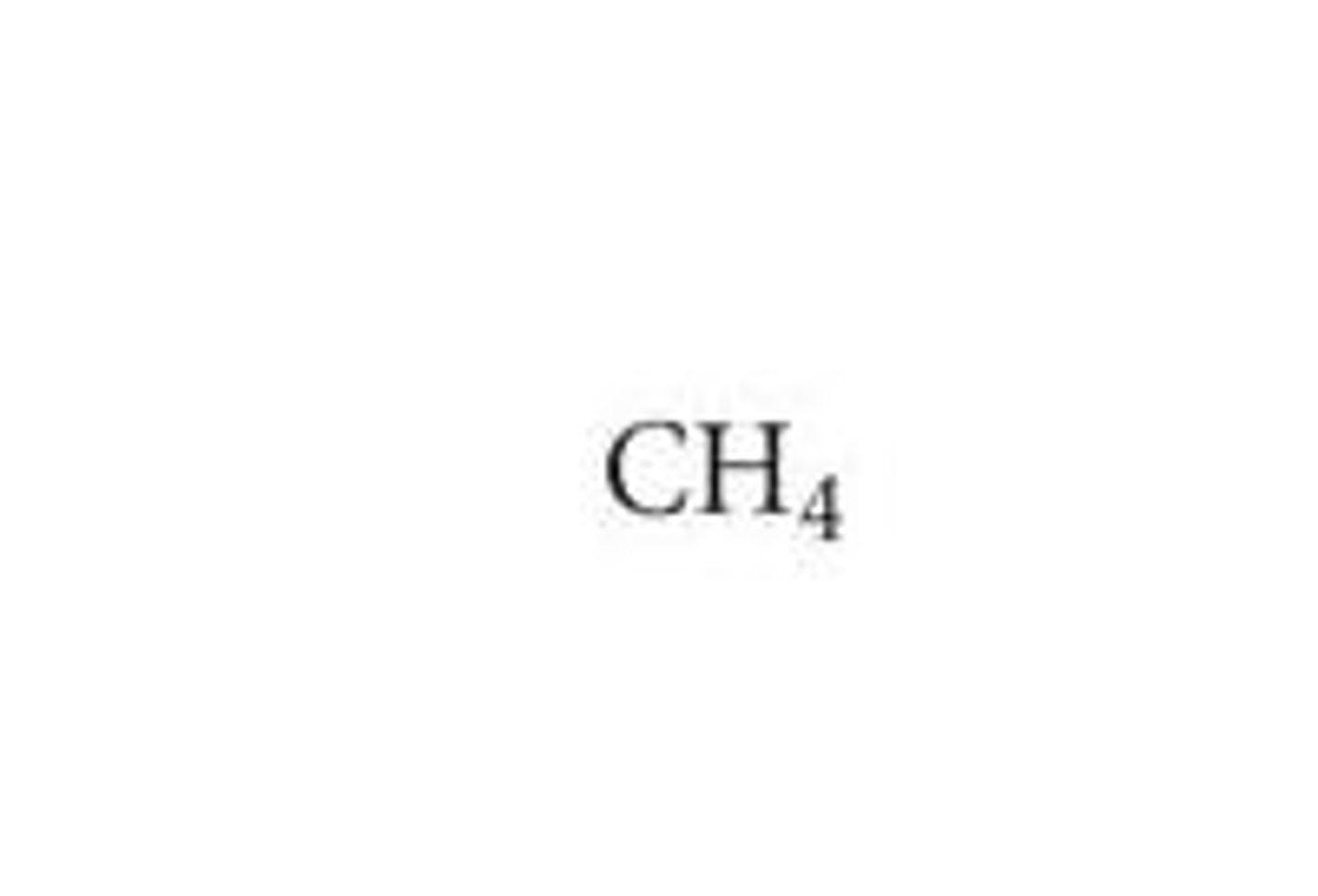
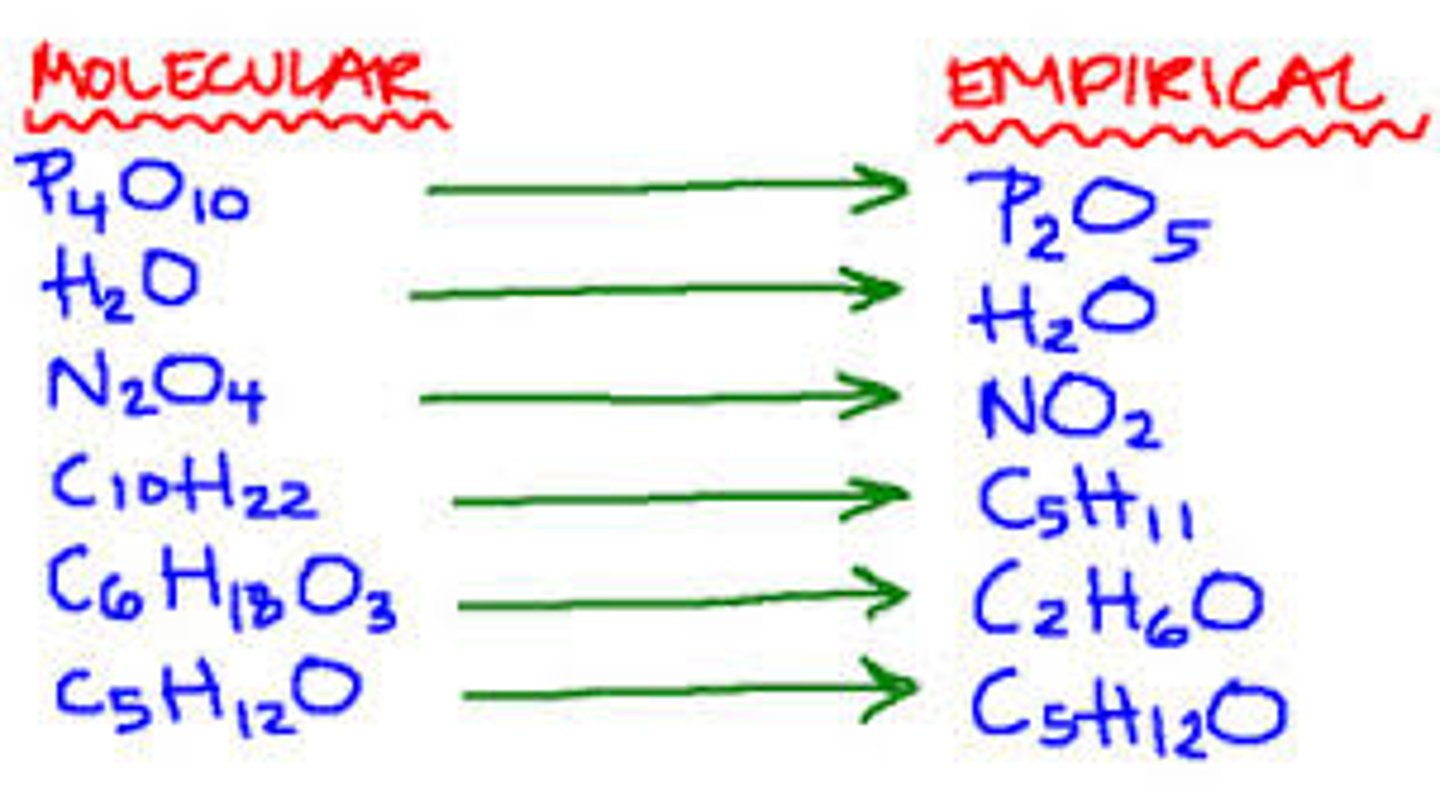
Empirical formula
A chemical formula showing the simplest ratio of elements in a compound rather than the total number of atoms.
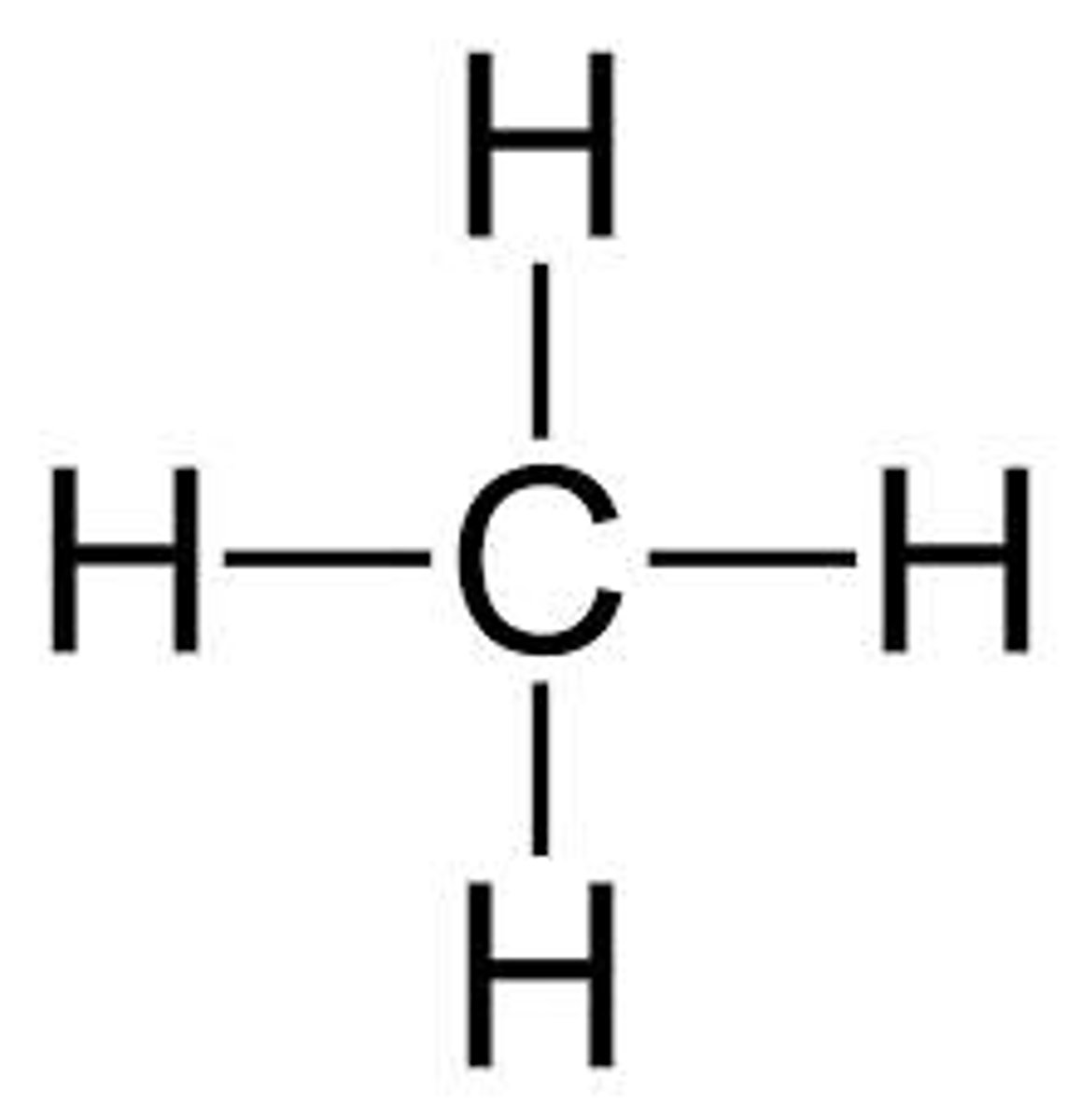
Structural formula
A graphical chemical formula that shows the arrangement of atoms in the molecule of a compound.
Condensed formula
Shows all the atoms in a molecule and places them in sequential order.
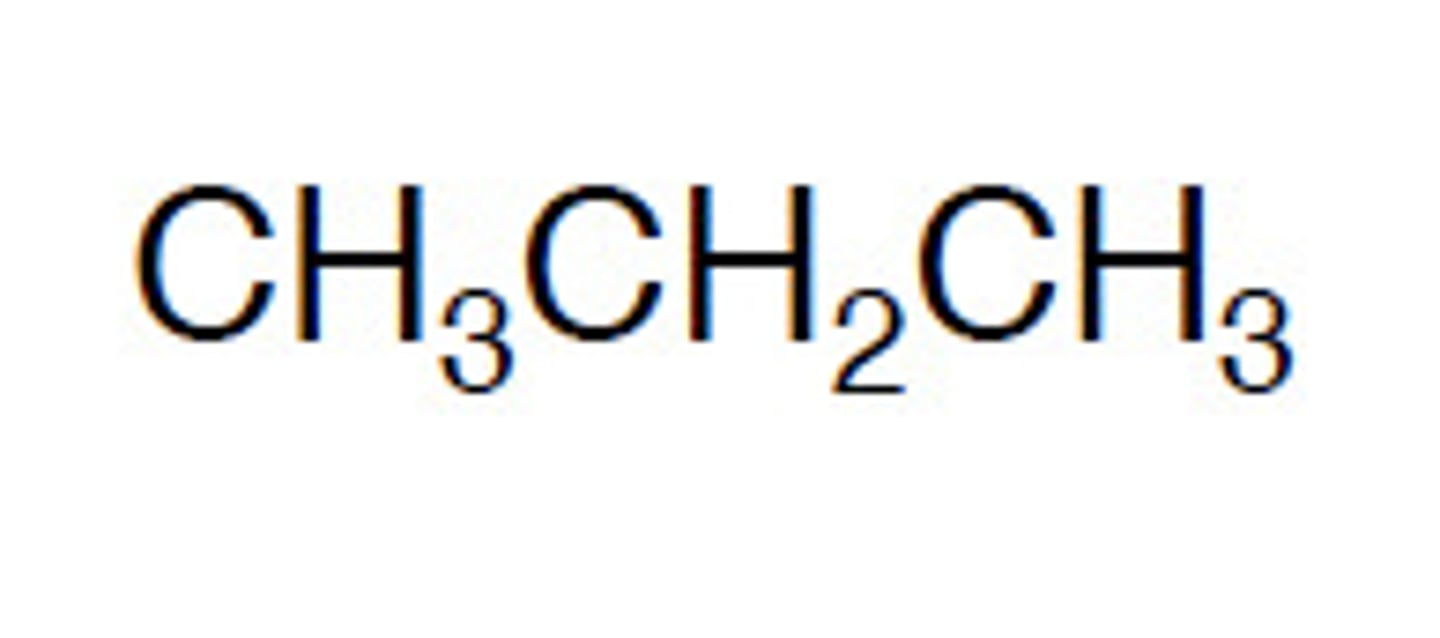
Skeletal formula
A simplified graphical chemical formula that shows the carbon skeleton, omitting C and H symbols, but shows element symbols for all other associated functional groups
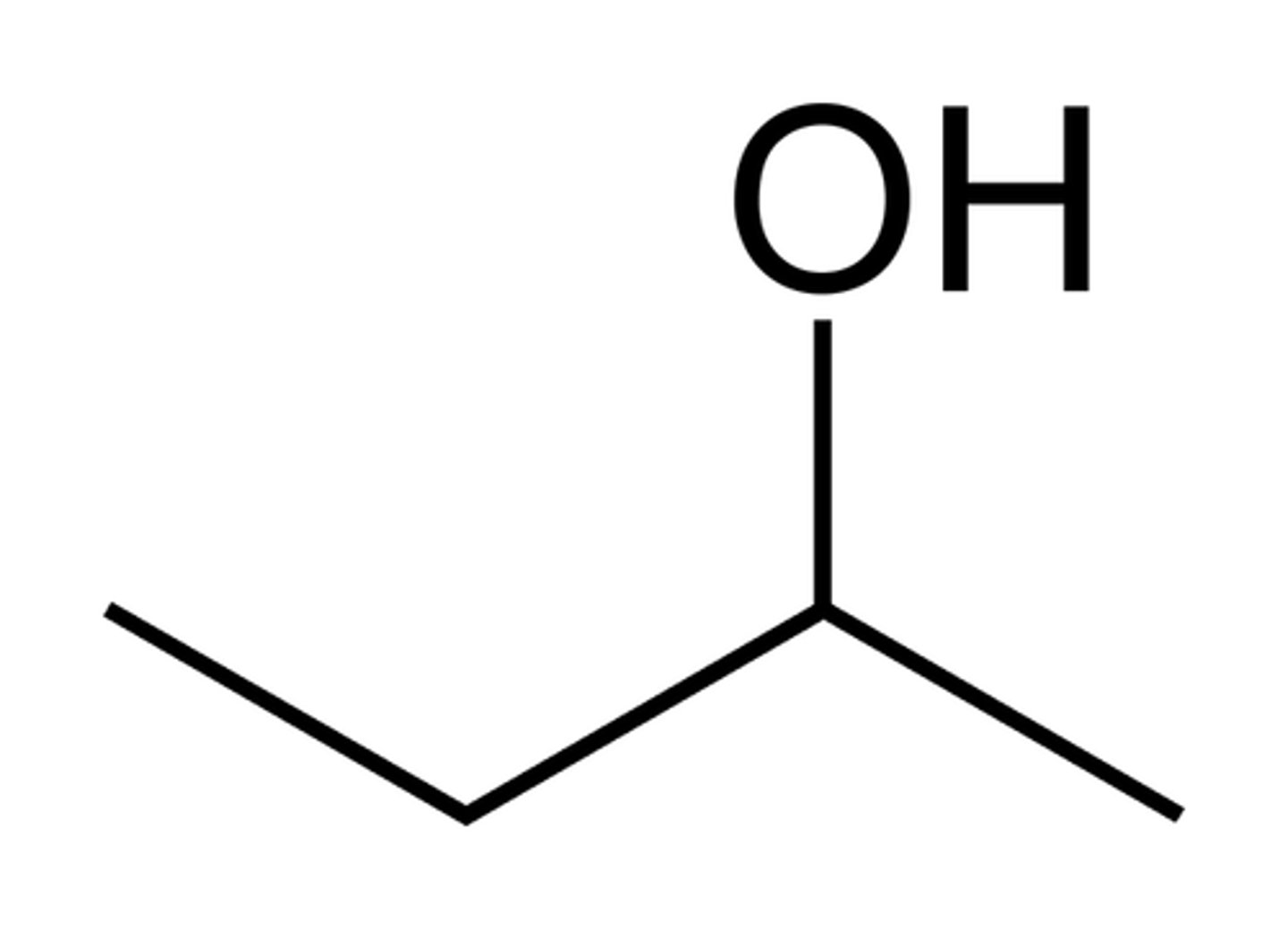
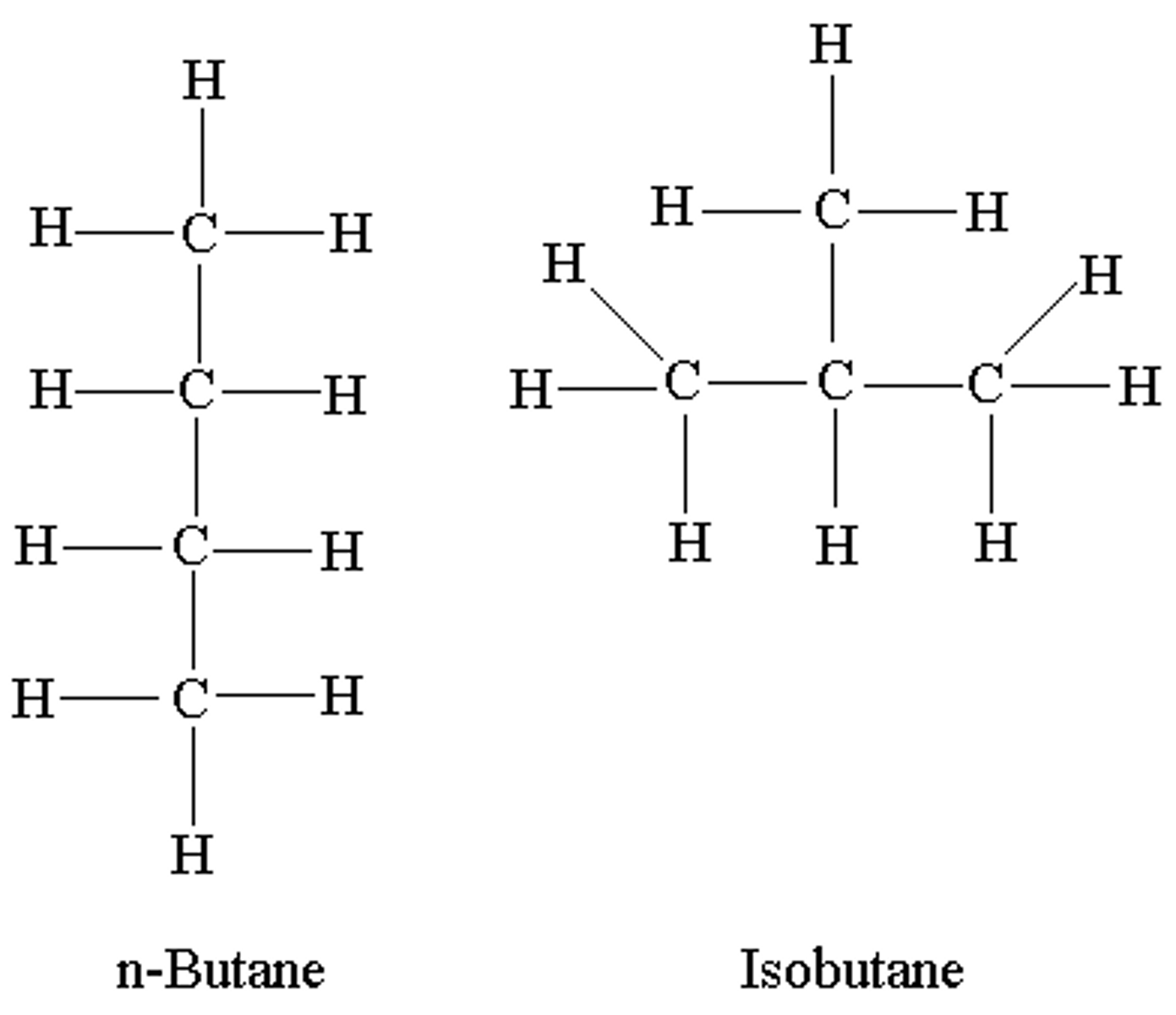
Structural isomer
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangements of their atoms in the molecule.
Alcohol
A chemical functional group containing -OH (no need to draw or name in Year 11)
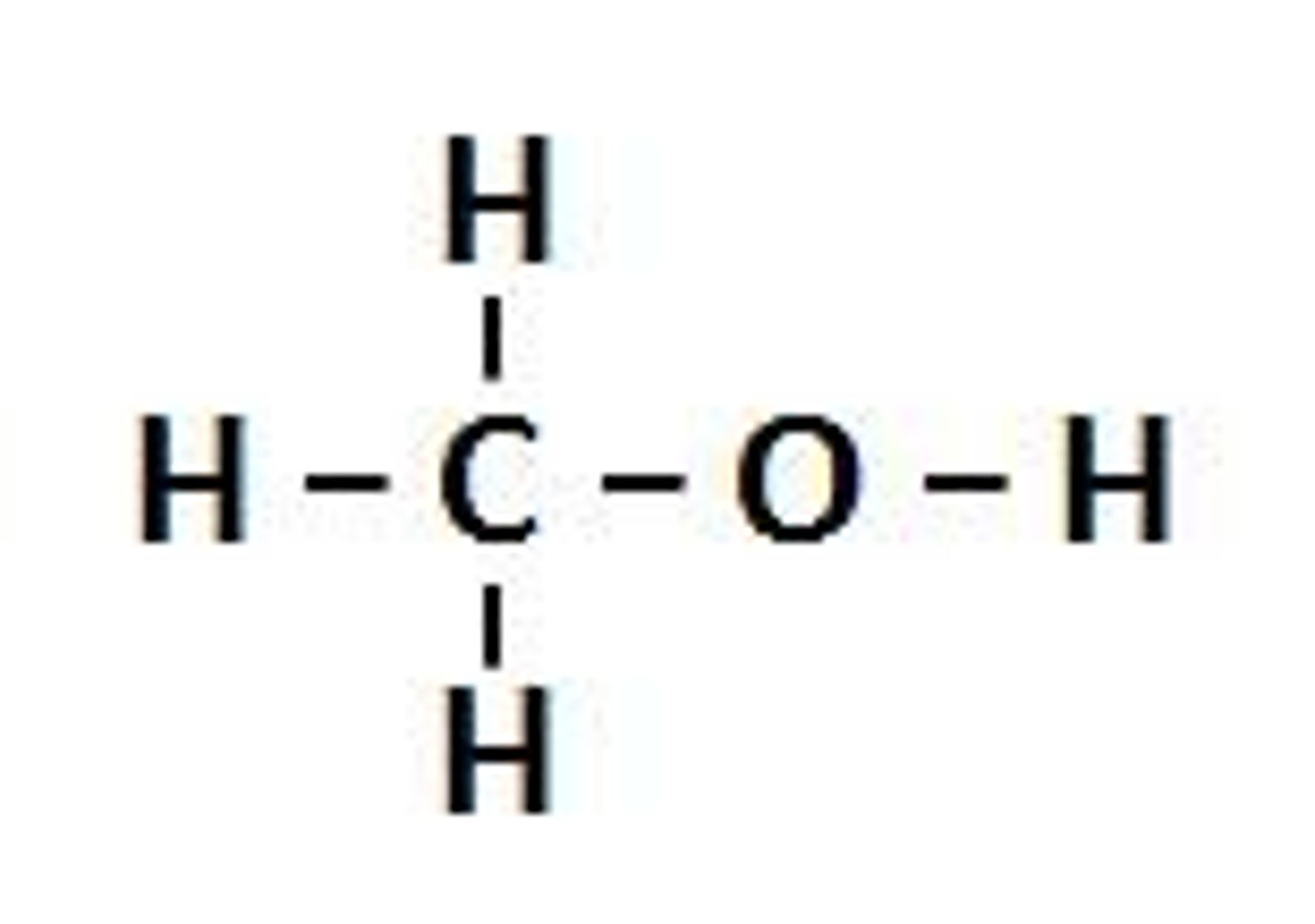
Carboxylic acid
A chemical functional group containing -COOH (no need to draw or name in Year 11)
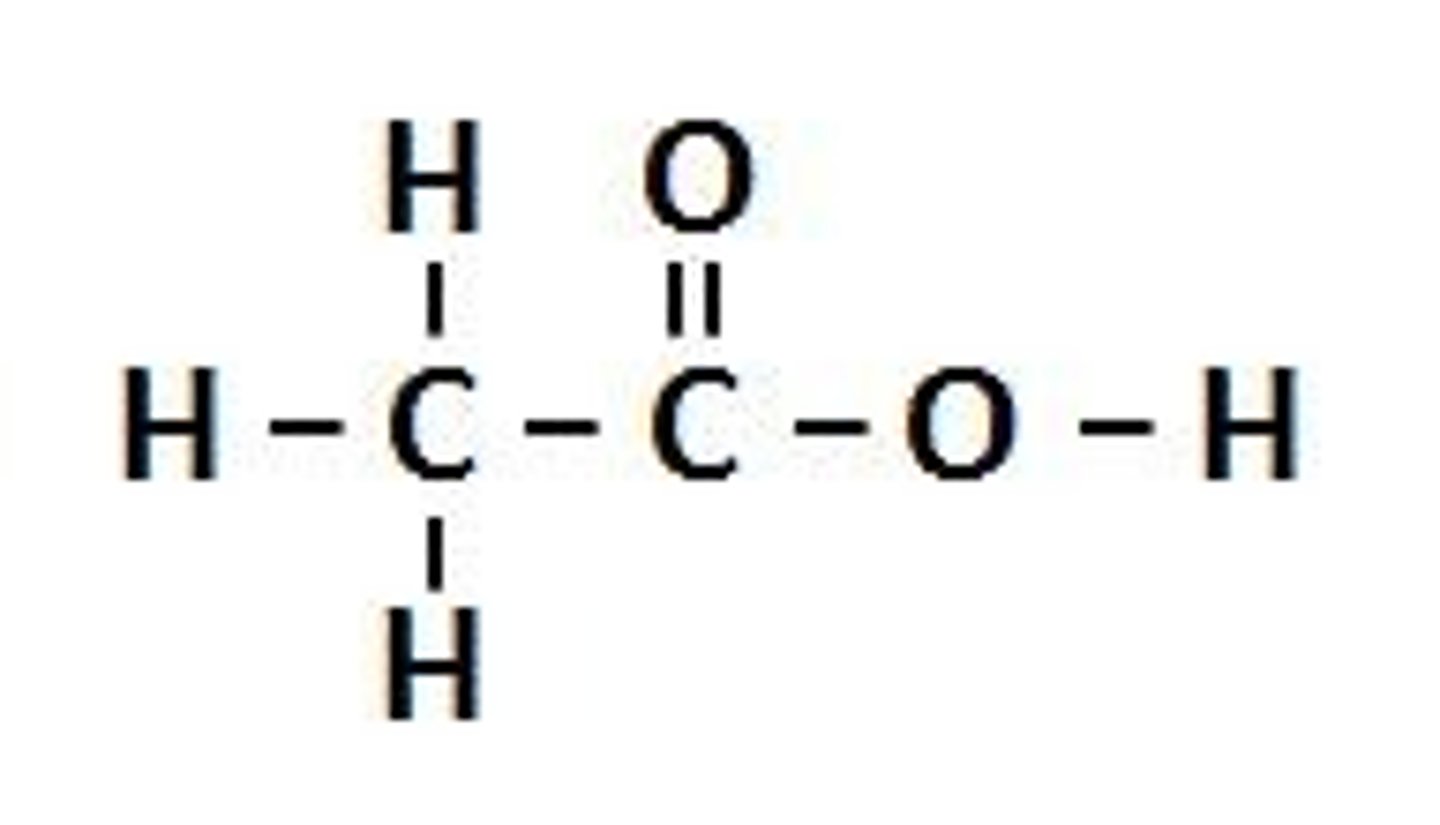
Amine
A chemical functional group containing -NH2 (no need to draw or name in Year 11)
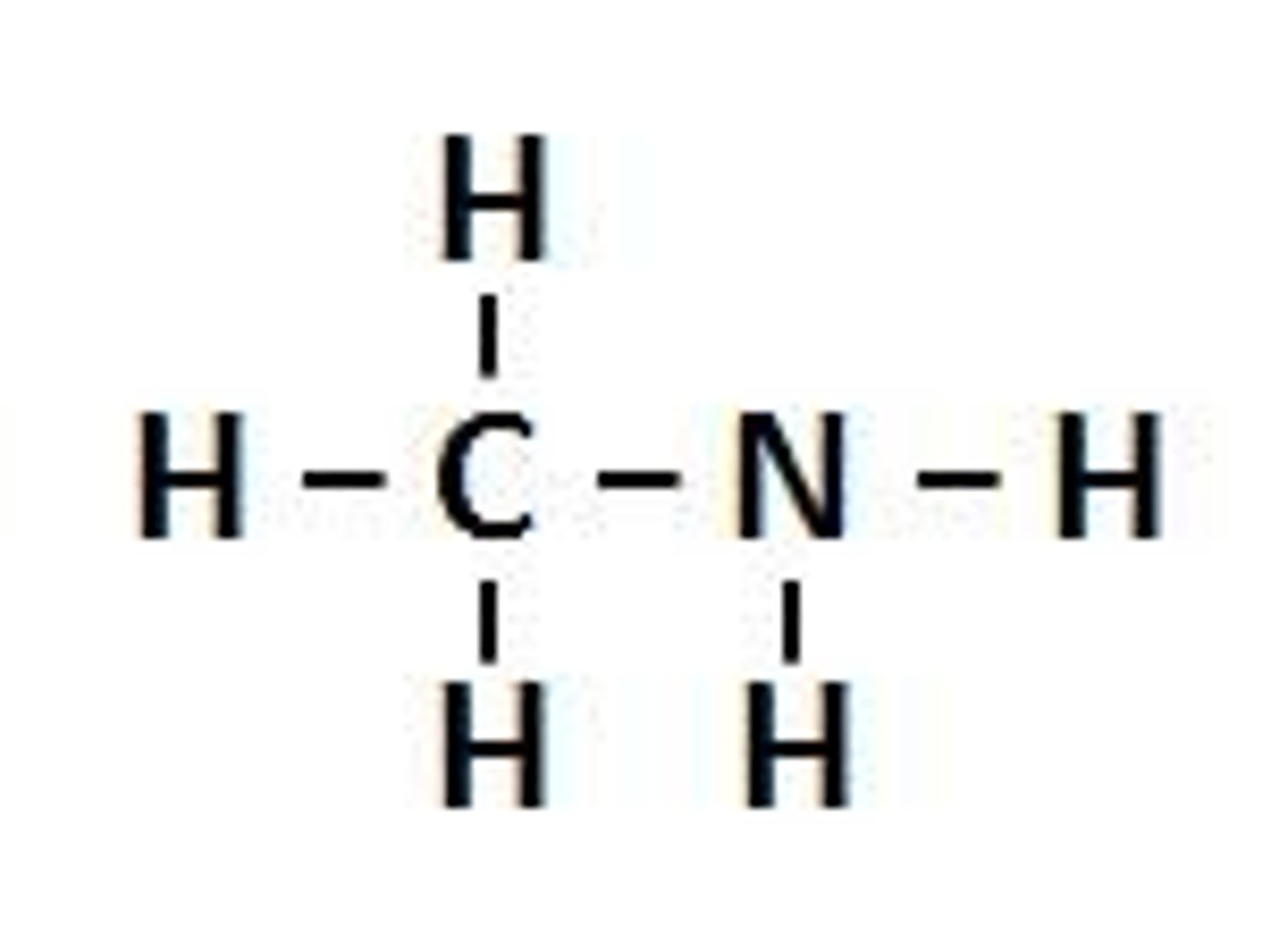
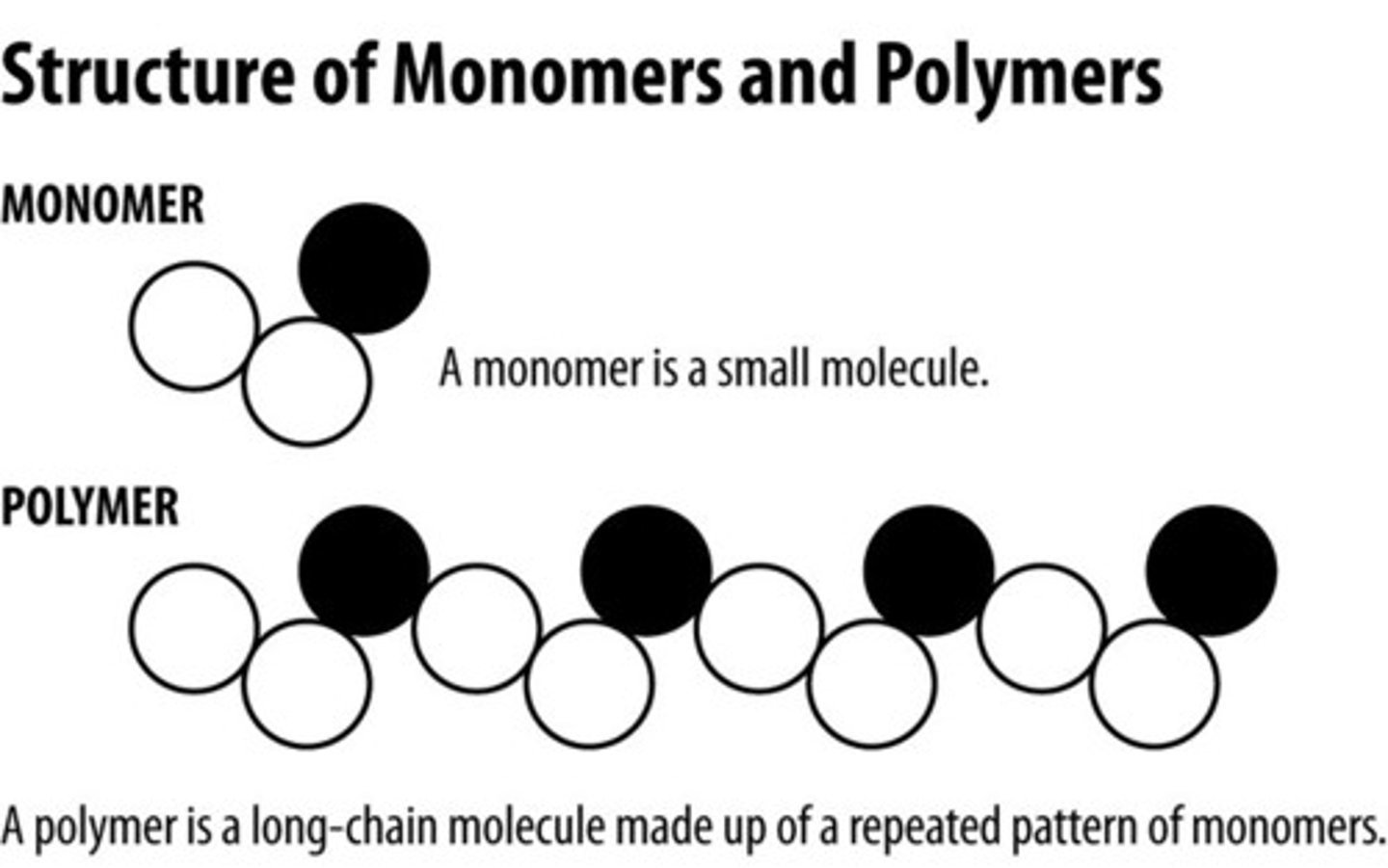
Polymer
Large molecules constructed from smaller repeating units linked together by covalent bonds
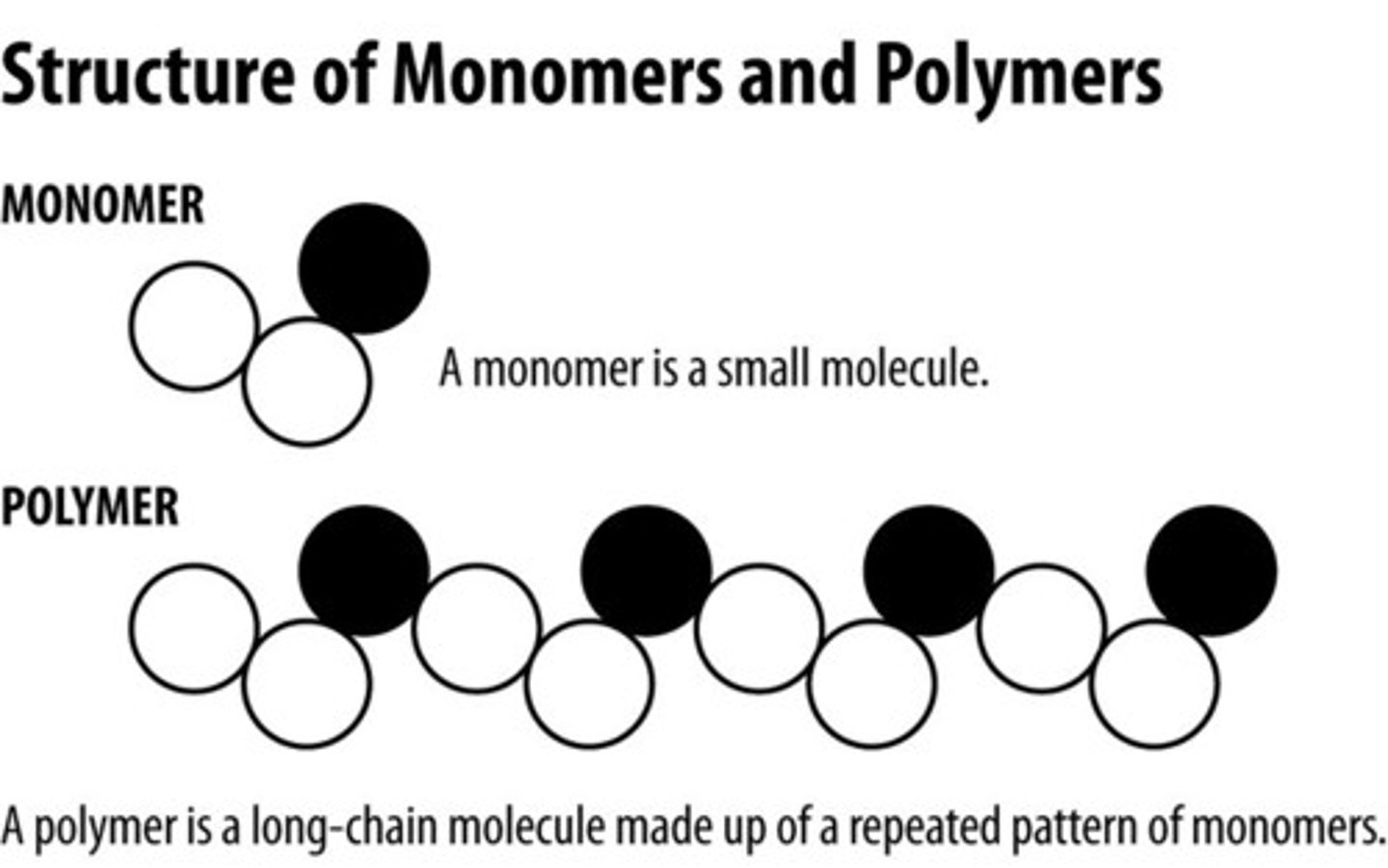
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Repeating unit
A group of atoms derived from a monomer and repeats throughout a polymer.
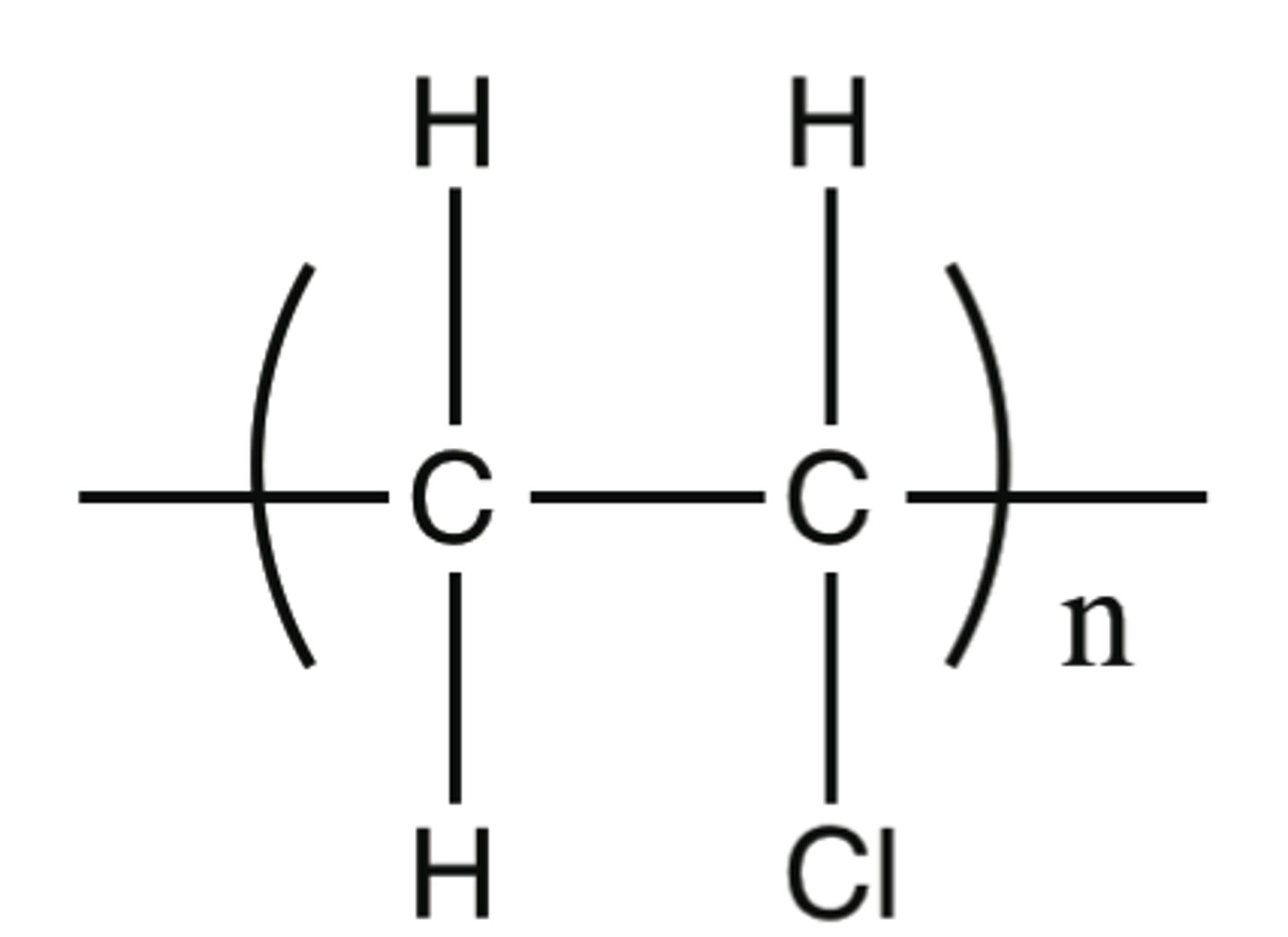
Addition polymerisation
Formation of a very long molecular chain by repeated addition reactions of many unsaturated alkene molecules (monomers).
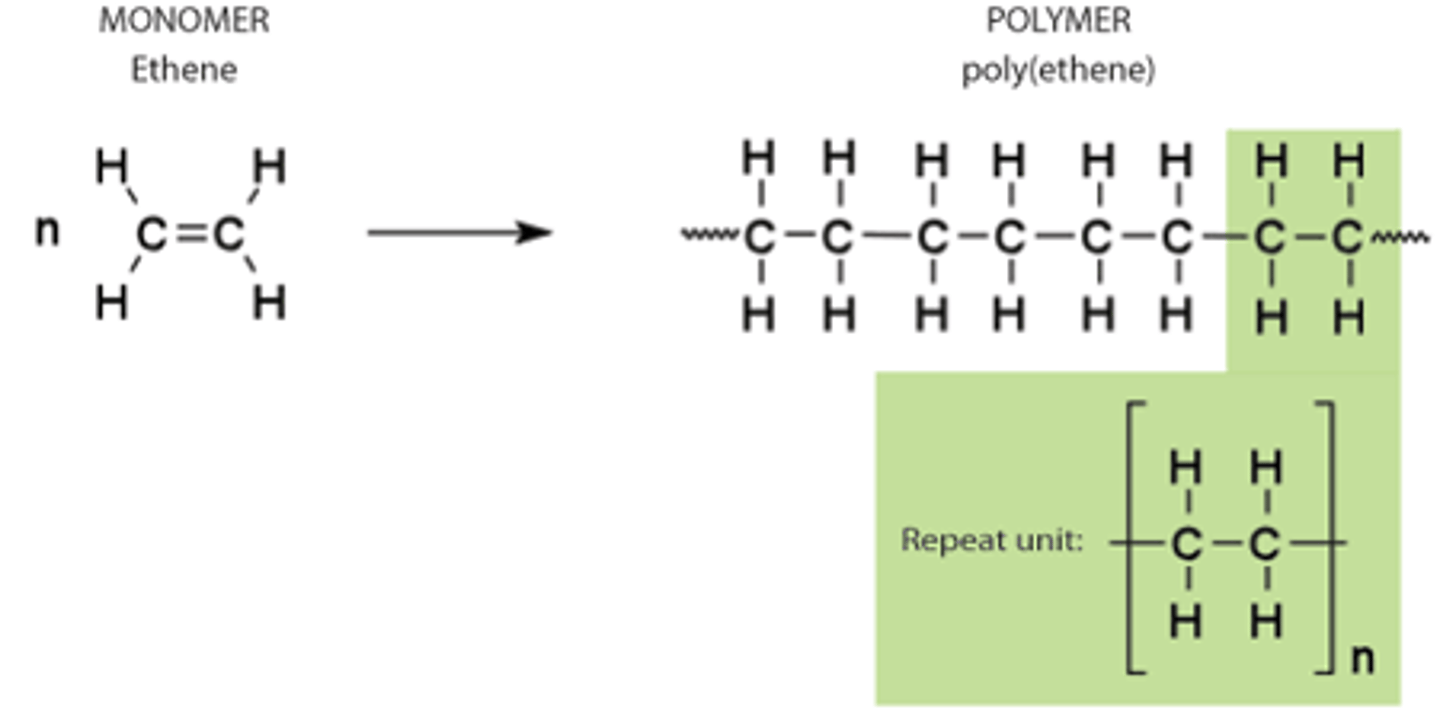
Thermoplastic polymer
Polymers in which the chains cross-link in the solid using dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions or hydrogen bonds and can be recycled by melting and reshaping
Thermoset polymer
Polymers that are chemically cross-linked with covalent bonds, fixing the polymer chains in relation to each other and cannot be melted for recycling

Cross-linking
Linkages between separate polymer chains
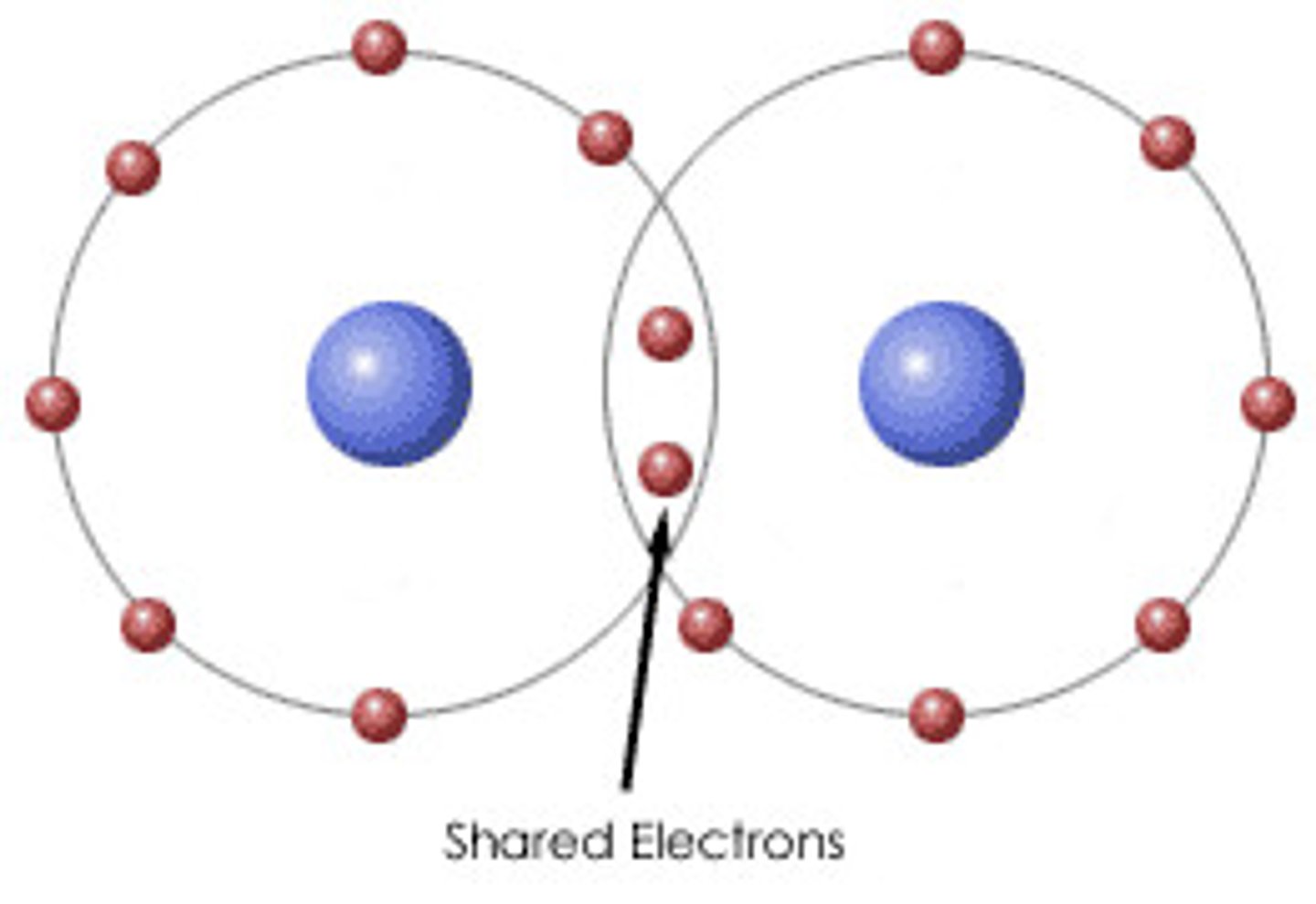
Covalent bond
A chemical bond formed when two non-metal atoms share electrons
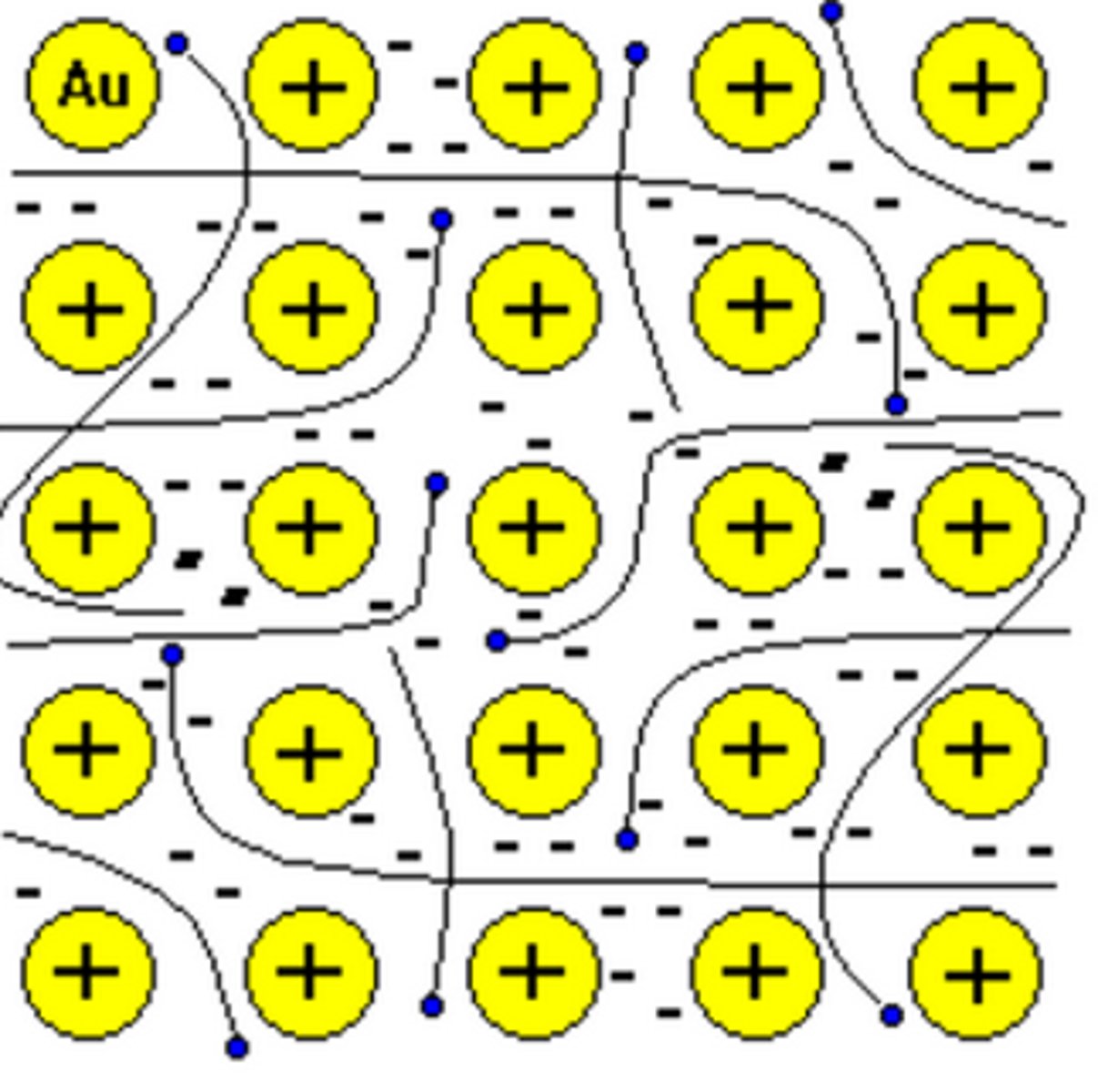
Metallic bond
A chemical bond formed by the attraction between positively charged metal ions and delocalised electrons
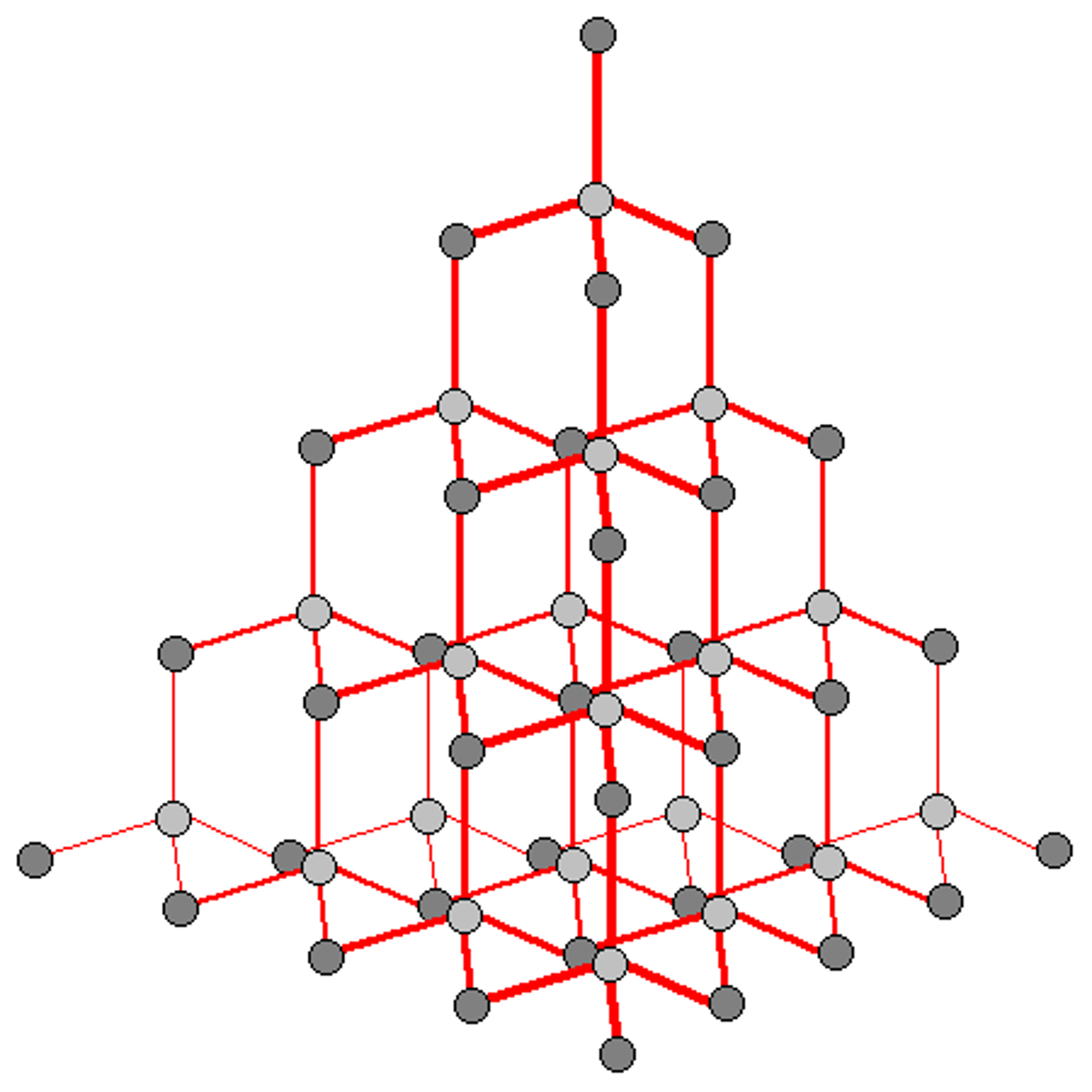
Continuous covalent network/lattice
Atoms are bonded by covalent bonds in a continuous network extending throughout the material - High melting point and not conductive
Covalent molecular
Atoms are bonded by covalent bonds into discrete molecules. Molecules are held together by weak secondary forces of attraction, not bonds - Low melting point and not conductive
Metallic materials
Atoms are bonded by metallic bonds in a continuous network extending throughout the material - High melting point and conductive
Polarity
Molecules having uneven distribution of charges due to polar bonds for which the centres of the partial +ve and -ve charges are in different positions
Bond through dipole-dipole interactions or H-bonds
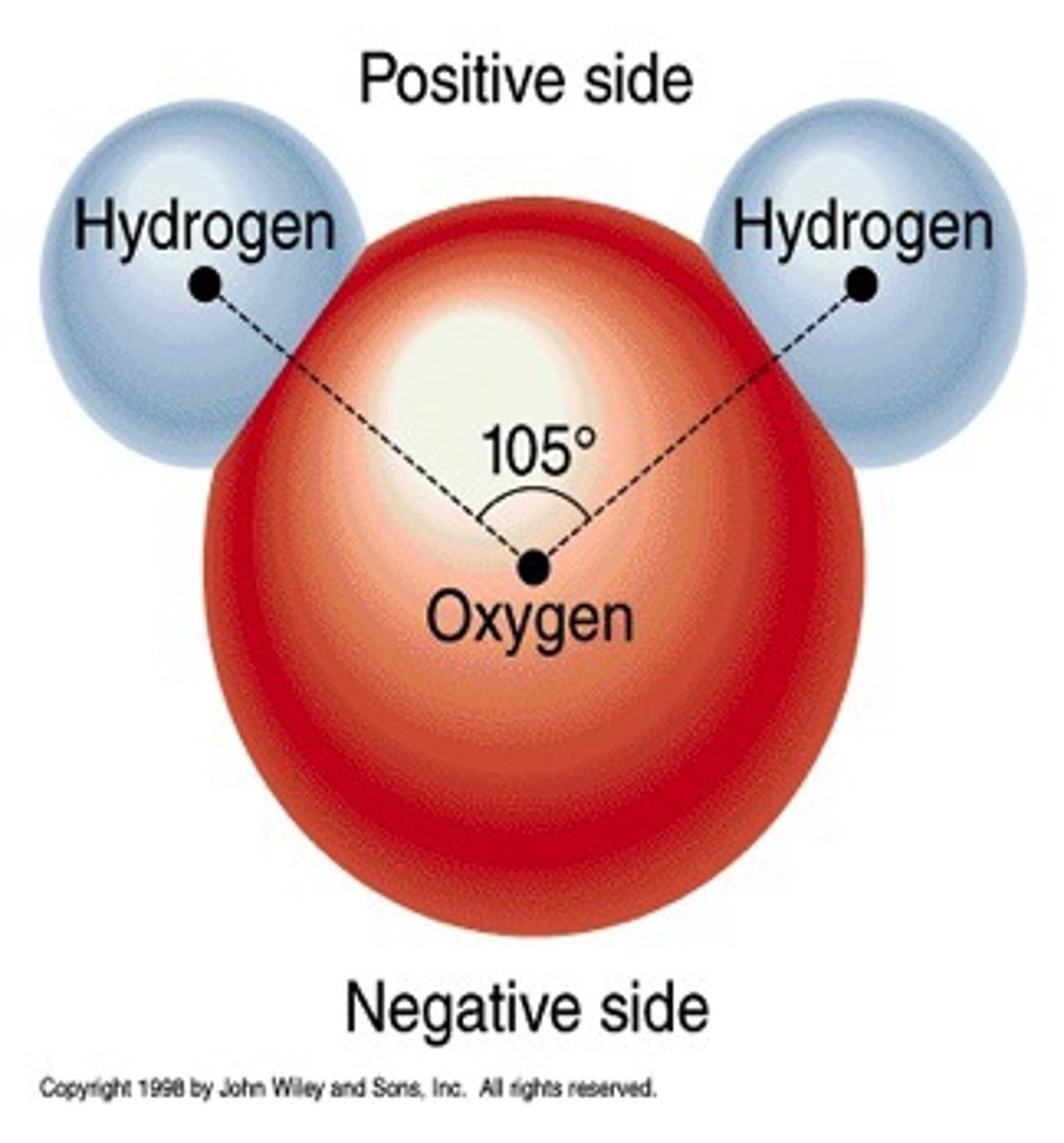
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract the bonding electrons
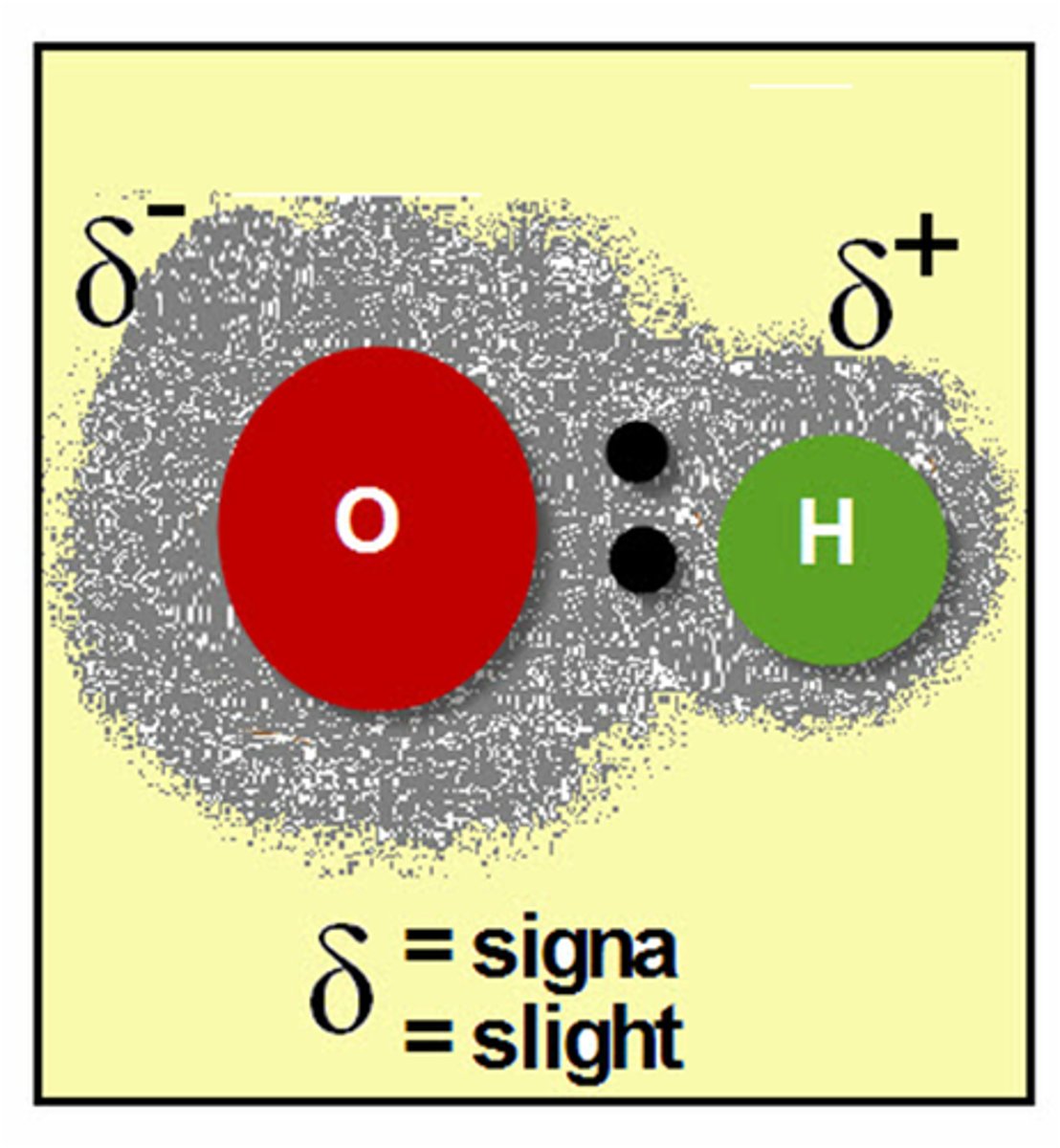
Non-polar
a molecule in which all atoms have similar or the same electronegativity and the electron distribution is equal
Bond through weak dispersion forces