physical chemistry
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How is the rate of a reaction calculated?
rate = amount of reactant used / time
OR
amount of product formed / time
Describe how to carry out an experiment to measure the rate of reaction when a precipitate is formed
- Example: Sodium thiosulfate solution and dilute hydrochloric acid react together to form a
precipitate of sulfur
- Place 20 cm3 of sodium thiosulfate solution and 20 cm3 of water in a conical flask
- Add 10 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid to the flask
- Place the flask on a piece of paper marked with a black X
- Time how long it takes before the X can no longer be seen
Describe how to carry out an experiment to measure the rate of reaction when a gas is produced
- Example: The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into H2O and O2
- Place a known mass of H2O2 in a conical flask
- Seal flask with a bung attached to a gas syringe
- Time how long it takes for 100cm3 of oxygen to be collected
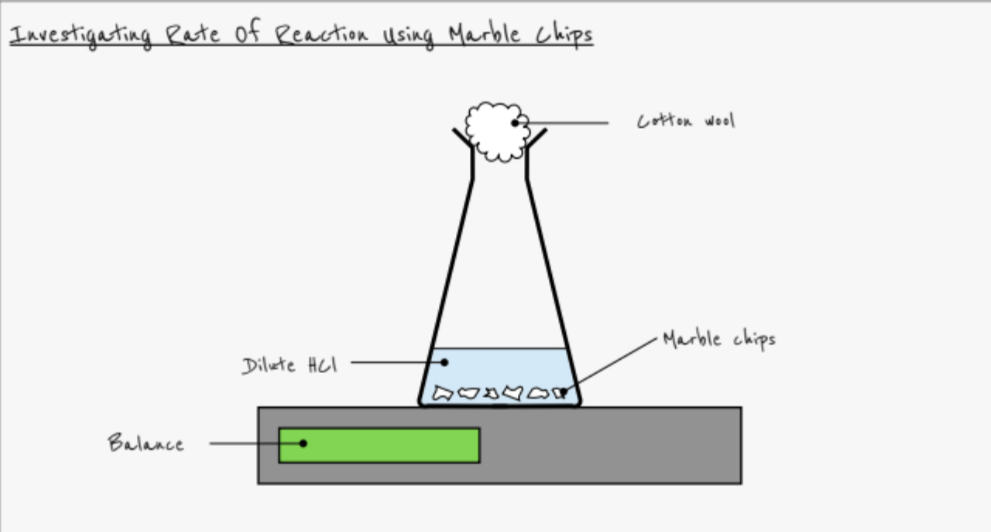
Describe how to carry out an experiment to measure the rate of reaction from the change in mass of a solid
- Example: Reaction of marble chips (CaCO3) with dilute hydrochloric acid
- Place 50cm3 HCl into a conical flask. Place the flask on a balance
- Add marble chips and note the starting mass
- Place cotton wool in the neck of the flask to stop acid spraying out
- Measure the mass of carbon dioxide lost at intervals
- Plot a graph of the results
- Repeat changing one variable only
- e.g. temperature, surface area, concentration of HCl
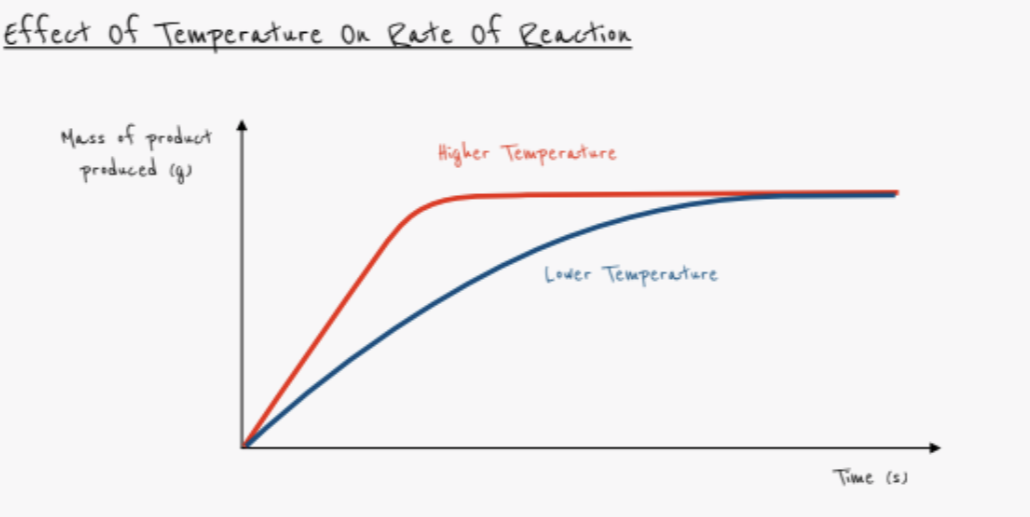
What effect does a higher temperature have on the rate of reaction?
- Rate increases
- Particles have greater kinetic energy
- More collisions have energy greater than activation energy
- More successful collisions occur per second
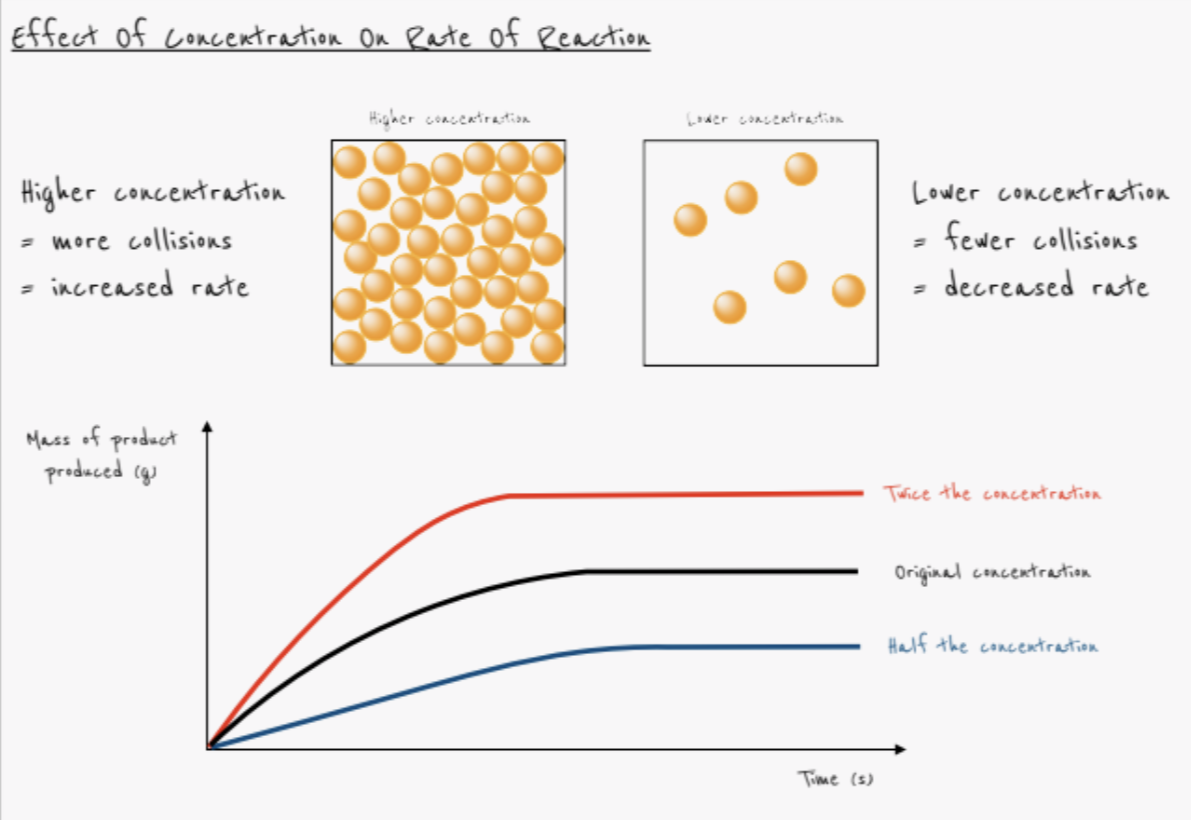
What effect does increasing the concentration have on the rate of reaction?
- Rate increases
- More particles in the same volume
- Collisions occur more frequently
What effect does increasing the pressure of a gas have on the rate of reaction?
- Rate increases
- More particles in the same volume
- Collisions occur more frequently
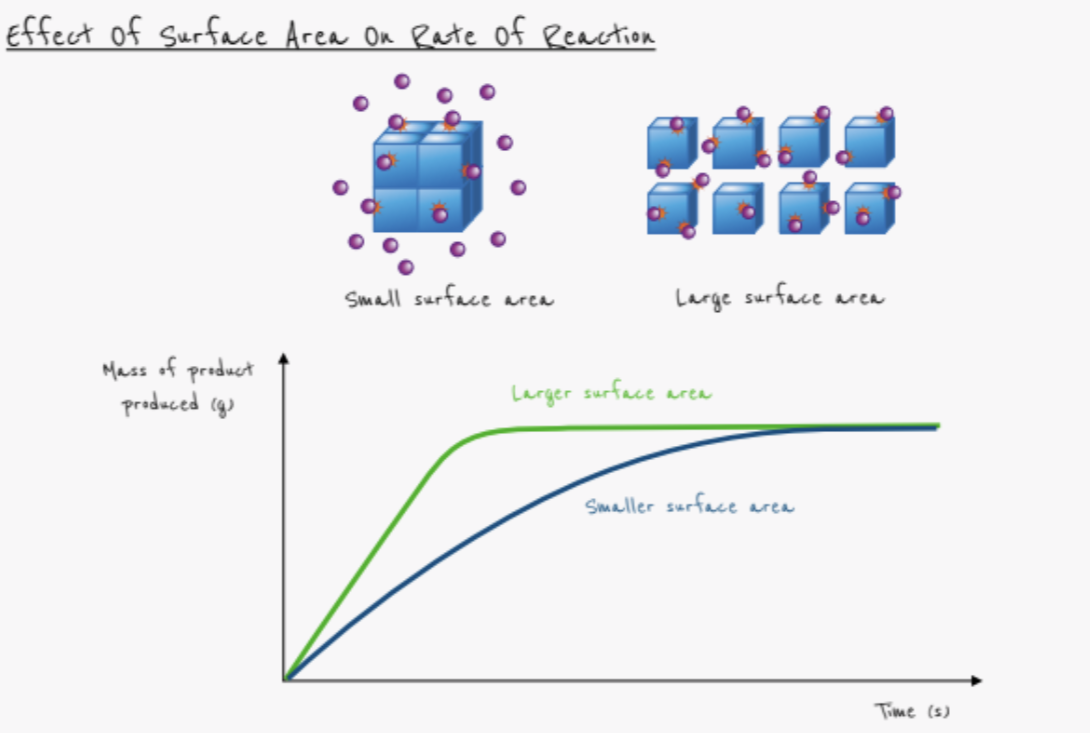
What effect does increasing the surface area have on the rate of reaction?
- Rate increases
- Collisions occur more frequently
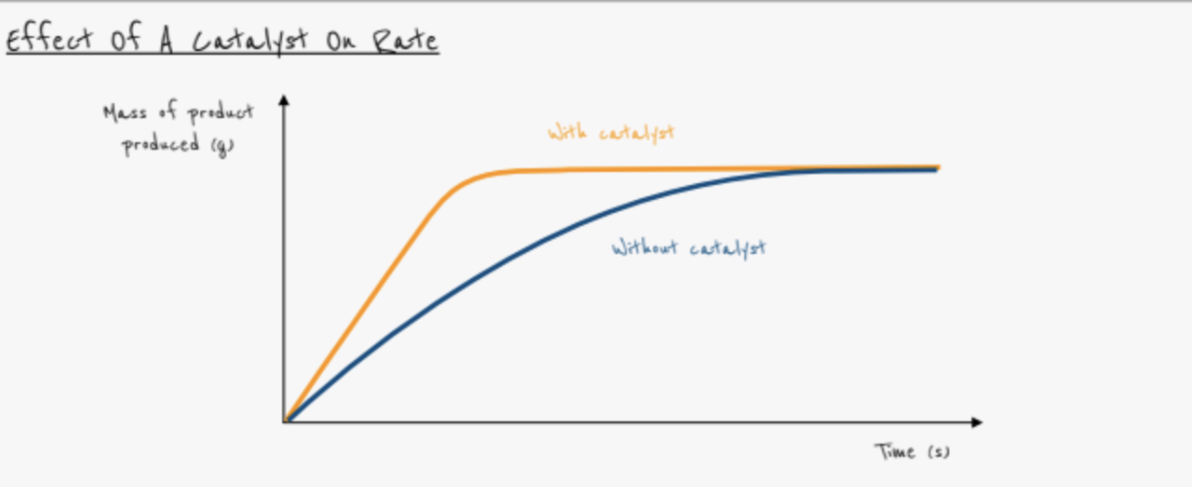
Define catalyst
- A substance that increases the rate of reaction
- Chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
How does a catalyst work?
- Speeds up the rate of reaction without being used up
- Provides alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy
Which variables should be controlled when investigating the effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction?
- Concentration of reactants
- Volume of reactants
- Surface area (if using a solid)
Which variables should be controlled when investigating the effect of concentration on the rate of a reaction?
- Concentration of all reactants other than the one being investigated
- Volume of reactants
- Surface area (if using a solid)
- Temperature
Which variables should be controlled when investigating the effect of surface area on the rate of a reaction?
- Concentration of reactants
- Volume of reactants
- Temperature
Which variables should be controlled when investigating the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction?
- Concentration of reactants
- Volume of reactants
- Temperature
- Surface area
What does this ⇌ arrow represent?
- Reaction is reversible
Describe the dehydration of copper (II) sulfate crystals
- Heat blue (hydrated) copper (II) sulfate crystals
- Blue crystals turn to white powder
- Because water is lost i.e. water of crystallisation is lost
- White anhydrous copper (II) sulfate is formed
- Add water and blue (hydrated) copper (II) sulfate crystals form
- Reaction is reversible
Describe the heating of ammonium chloride
- Place white crystals of ammonium chloride in bottom of boiling tube
- Heat using Bunsen burner
- When ammonium chloride is heated it splits into ammonia and hydrogen chloride
- White crystals disappear from bottom of tube
- Reaction reverses when conditions change from hot to cold higher up tube
- White crystals reform higher up