Psychology test 3 (2nd guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 5:32 AM on 3/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
nomothetic approach
focuses on identifying general principles that apply across people
2
New cards
idiographic approach
focuses on identifying the unique configuration of characteristics and life history experiences within an individual
3
New cards
cardinal trait
single characteristic that directs most of a person's activities
4
New cards
central trait
major characteristic of an individual; accounts for most of our personality
5
New cards
secondary trait
affect behavior in fewer situations
6
New cards
big 5 personality traits
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
7
New cards
imaginative, daring, non-conformative describes which of the following:
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
O (openness to experience)
8
New cards
talkative, outgoing describes which of the following:
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
E (extraversion)
9
New cards
cooperative, trusting, compliant describes which of the following:
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
A (agreeableness)
10
New cards
responsible, purposeful, organized describes which of the following:
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
C (conscientiousness)
11
New cards
anxious, self conscious, moody describes which of the following:
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
O (openness to experience)
C (conscientiousness)
E (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
N (neuroticism)
N (neuroticism)
12
New cards
factor analysis
correlations among many variables are analyzed to identify closely related clusters of intercorrelating traits (traits that go together)
13
New cards
how is factor analysis related to the identification of traits
each cluster (factor) represents an underlying (main) or central trait
14
New cards
6 factor model of personality is shown by:
HEXACO
15
New cards
what does each letter of HEXACO
H (honesty/humility)
E (emotionality)
X (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
C (conscientiousness)
O (openness to experience)
E (emotionality)
X (extraversion)
A (agreeableness)
C (conscientiousness)
O (openness to experience)
16
New cards
do personality traits change over time
yes; typically in ages less than 30
17
New cards
objective personality test:
a test containing direct, unambiguous items relating to the individual being assessed
18
New cards
what are the two types of objective personality tests
clinical interviews and self report inventories
19
New cards
clinical interviews
structured and unstructured; widely used
20
New cards
self report inventories
largest category of objective personality tests
(NEO-PI for big 5; MMPI-2 for abnormal)
(NEO-PI for big 5; MMPI-2 for abnormal)
21
New cards
validity
involves accuracy (personality tests must be accurate in order to have validity)
22
New cards
reliability
refers to the consistency and validity; measure what is intended to measure (have to relate to personality test)
23
New cards
projective personality tests
person is shown an ambigous stimulus and is asked to describe it or tell a story about it; this type of test lacks reliability and validity
24
New cards
roscach test
inkblot test (what do you see is asked); can lack reliability and validity
25
New cards
thematic apperception test
"tell me a story about what is going on in this image"; can lack reliability and validity
26
New cards
barnum effect
tendency people have to accept descriptions of oneself that apply to almost everyone
27
New cards
who created the barnum effect
PT barnum
28
New cards
who founded the psychodynamic approach
Sigmond Freud
29
New cards
what are the 3 core assumptions of the psychodynamic approach
unconscious motivation
psychic determinism
symbolic meaning
psychic determinism
symbolic meaning
30
New cards
unconscious motivation
desires trapped in the unconscious is the primary cause of all behavior
31
New cards
psychic determinism
we are not free to choose our actions
32
New cards
symbolic meaning
all behavior has a symbolic meaning
33
New cards
Id
the primitive, instinctive part of personality that is irrational; includes the pleasure principle (immediate gratification of innate urges)
34
New cards
superego
the moral component of personality that incorporates social standards about what represents right and wrong; includes the conscious and is irrational
35
New cards
ego
mediator; reality principle (delay of gratification for suitable outlets); "executive" of personality
36
New cards
defense mechanism
largely unconscious strategies that people use to reduce anxiety by distorting reality
37
New cards
what do the id, superego, and ego often result in
conflict
38
New cards
list the different types of defense mechanisms
displacement
repression
projection
reaction formation
sublimation
repression
projection
reaction formation
sublimation
39
New cards
displacement
redirecting feelings (often anger) from an original source to a substitute
40
New cards
repression
unpleasent memories or "id' impulses are pushed back into the unconscious
41
New cards
projection
attributing unacceptable feelings of characteristic onto others
42
New cards
reaction formation
changing an unacceptable desire by adopting the opposite stance
43
New cards
what are the stages of freud's physcosexual stage theory IN ORDER
1) oral stage
2) anal stage
3) phalic stage
4) latency stage
5) genital stage
2) anal stage
3) phalic stage
4) latency stage
5) genital stage
44
New cards
what is the sequence, focus, conflict, and consequences of the oral stage (freud's psychosexual stage theory)
sequence: birth to 1.5 years old
focus: sucking, chewing, exploring
conflict: weaning
consequences: abuse alcohol/ drugs
focus: sucking, chewing, exploring
conflict: weaning
consequences: abuse alcohol/ drugs
45
New cards
what is the sequence, focus, conflict, and consequences of the anal stage (freud's psychosexual stage theory)
sequence: ages 1.5 to 3
focus: controlling bodily functions; toilet training
conflict: parents can be too harsh/lenient
consequences: anal retentive (bound and inflexible)
focus: controlling bodily functions; toilet training
conflict: parents can be too harsh/lenient
consequences: anal retentive (bound and inflexible)
46
New cards
what is the sequence, focus, conflict, and consequences of the phalic stage (freud's psychosexual stage theory)
sequence: ages 3 to 6
focus: beginning of sexual feelings (initially directed at parent of opposite sex - known as opedius complex); electra complex
focus: beginning of sexual feelings (initially directed at parent of opposite sex - known as opedius complex); electra complex
47
New cards
what is the sequence, focus, conflict, and consequences of the latency stage
sequence: ages 6 to puberty
focus: developing same sex friendships; grow physically and intellectually
conflict AND consequences: seen as a period of sexual calm and appropriate maturity
focus: developing same sex friendships; grow physically and intellectually
conflict AND consequences: seen as a period of sexual calm and appropriate maturity
48
New cards
what is the sequence, focus, conflict, and consequences of the genital stage
sequence: puberty to death
focus: rebirth of sexuality; focus redirected to appropriate target (others)
conflict: unconscious sexual and aggressive urges
consequences: inability to be successful in work and love
focus: rebirth of sexuality; focus redirected to appropriate target (others)
conflict: unconscious sexual and aggressive urges
consequences: inability to be successful in work and love
49
New cards
Carl Jung's unconscious idea can be described as...
our shared storehouse of memories that ancestors have passed down to us across generations
50
New cards
what are the criticisms of the physcodynamic approach
* not falsifiable
* failed predictions
* overlooked genetics (nature)
* failed predictions
* overlooked genetics (nature)
51
New cards
humanistic approach to personality can be described as...
humans have the compassion for growth and we should focus on these positive growths; focuses on the conscious
52
New cards
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is known as...
a model to understand the motivations of human behavior
53
New cards
what are the stages of Maslow's hierarch of needs IN ORDER
5: physiological needs (food, water, warmth, rest)
4: safety (security and safety)
3: belongingness and love (intimate relationships, friends)
2: esteem needs (prestige, feeling of accomplishment)
1: self actualization (achieving ones full potential)
4: safety (security and safety)
3: belongingness and love (intimate relationships, friends)
2: esteem needs (prestige, feeling of accomplishment)
1: self actualization (achieving ones full potential)
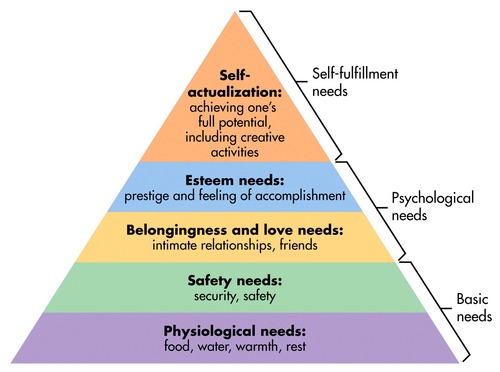
54
New cards
how might ones standing in his/her "hierarchy" impact ones personality
each stage can alter personality
55
New cards
social cognitive approach to personality can be described as...
posits that personality is shaped by interacting social factors, cognitive factors, and behavior
56
New cards
reciprocal determinism can be described as...
the environment influences how a person thinks or feels which influences behavior which impacts the environment; 3 factor model
57
New cards
what are the 3 factors of reciprocal determinism
1) how one thinks and feels
2) environment
3) behavior
2) environment
3) behavior
58
New cards
what was the early biological view of Eysenck:
introverts have a more sensitive arousal system than extroverts
59
New cards
heritability
reports the percent of differences among people due to genetics
60
New cards
a woman is unable to recall that she was raped is \___________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
repression
61
New cards
a brother yells at his younger sister after a teacher gives him a bad grade is \__________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
displacement
62
New cards
a student who goes out drinking the night before a big test rationalizes his behavior by saying the test is not all that important is \_________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
rationalization
63
New cards
a student refuses to believe that he has flunked a course is \_________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
denial
64
New cards
a man who is unfaithful to his wife and feels guilty suspects that his wife is unfaithful is \_________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
projection
65
New cards
a person with strong feelings of aggression becomes a soldier is \__________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
sublimation
66
New cards
a mother who unconsciously resents her child acts in an overly loving way toward the child is \___________
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
(repression, displacement, denial, projection, rationalization, displacement, sublimation, reaction formation)
reaction formation
67
New cards
social psychology
study of how our thoughts and emotions are influenced by others
68
New cards
people are able to judge someone based on a photo in \_______
1/10th of a second
69
New cards
social categorization
grouping according to certain characteristics such as age, race, etc.
70
New cards
implicit personality disorder
people think that certain characteristics go together, when we pick up on we assume the other
71
New cards
attribution
refers to a persons judgement about the cause of someone's behavior
72
New cards
internal attribution
perceived cause based on internal traits
73
New cards
external attribution
perceived cause based on external traits
74
New cards
fundamental attribution error
tendency to overstimulate the influence of dispositional factors and underestimate the role of external situations factors when interpreting other people's behaviors
75
New cards
people (DO/DO NOT) display the fundamental attribution error even when the strength of the situation is obvious
yes
76
New cards
attitude
an evaluative belief or opinion about people, objects, or ideas
77
New cards
explicit attitude
beliefs or opinions that are held consciously and can be reported to others
78
New cards
implicit attitude
beliefs and opinions that are unconscious (involuntary/uncontrollable) often formed through classical conditioning
79
New cards
do attitudes affect behaviors
only in certain instances
80
New cards
La Pierre study
La Pierre went to certain restaurants and hotels and asked if they would serve chinese people and they said no. when the chinese people actually went to the restaurants and hotels they did get served.
81
New cards
theory of planned behavior
attitudes: wether we intend to behave can be dependent on subjective norms
behavioral intentions: best precursor to out behavior is our intention to behave
behavior: when we get a measure of attitudes, subjective norms, and behavior control, we can account for behavior
behavioral intentions: best precursor to out behavior is our intention to behave
behavior: when we get a measure of attitudes, subjective norms, and behavior control, we can account for behavior
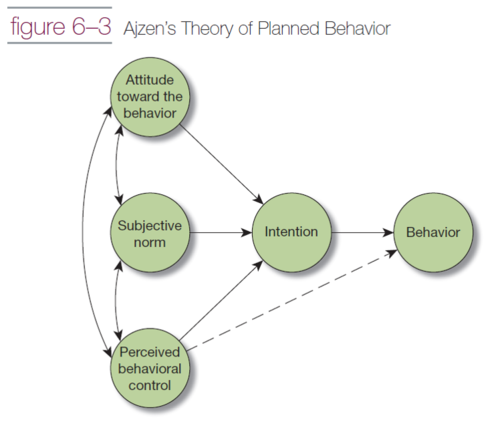
82
New cards
cognitive dissonance theory
a state of psychological tension that develops when a person is faced with a conflicting attitudes and behaviors, we act in a way that generally runs counter to our positive view of ourselves, tension in aroused
83
New cards
how do we reduce dissonance
1: changing behavior to bring it in line with our attitude/cognition
2: justify behavior by changing attitude behavior
3: justify behavior by adding new cognitions
2: justify behavior by changing attitude behavior
3: justify behavior by adding new cognitions
84
New cards
$1 vs. $20 Festinger and Carlsmith study:
Participants completed a task that war boring in order to get either $20 or $1. after completing the task the researcher told the Participants there was a delay because the research assistant was running late and to go tell the participants in other room that the task was fun (encourage participants to lie). the study found that the people given $1 liked the task more because they had no
sufficient justification justification \= dissonance -\> need to reduce dissonance)
sufficient justification justification \= dissonance -\> need to reduce dissonance)
85
New cards
social influence
process by which social groups and individuals exert pressure on an individual either deliberately or unintentionally
86
New cards
conformity
change in behavior or attitudes brought about by a desire to follow the beliefs or standards of other people
87
New cards
what are 2 reasons we conform
to be liked and to be right
88
New cards
what is the takeaway of Asch's study
people will conform no matter if they know they are wrong to be right and liked
89
New cards
factor that reduce conformity the most are...
presence of a fellow dissenter
90
New cards
compliance
change in behavior (submitting) to a person's request
91
New cards
foot-in-the-door technique
small, followed by large requests
92
New cards
door-in-the-face technique
large, followed by smaller requests
93
New cards
why does the foot-in-the-door technique work
works on the principle of consistency;
people prefer not to contradict themselves in both actions and beliefs, meaning that as long as the request is consistent with or similar in nature to the original small request, the technique will work
people prefer not to contradict themselves in both actions and beliefs, meaning that as long as the request is consistent with or similar in nature to the original small request, the technique will work
94
New cards
why does the door-in-the-face technique work
This technique works due to the principle of reciprocity
95
New cards
Milgram's obedience study
a group of social scientists conducted a series of experiments examining the nature of human behaviors and its relationship to social conventions and situations; they shocked people From 0-450 volts in order to understand now the German people could kill Jews so easily. he wanted to know how ordinary people could act so callously and inhumane and to what conditions would a person obey authority that went against their conscious
96
New cards
factors that affect obedience to authority:
agentic state
proximity
location
uniform
legitimate authority
proximity
location
uniform
legitimate authority
97
New cards
social loafing
tendency for individuals to do better on simple tasks in the mere presence of others ; happens when someone puts in less effort when they're judged as part or a group
98
New cards
group polarization
tendency for a generally like minded members to become more extreme in their opinions and positions as a result of being part of the group
99
New cards
when does group polarization happen
occurs when a group of like-minded people reinforce each other's opinions, positive or negative, and these opinions become more extreme as they're discussed.
100
New cards
stereotypes
set of generalized beliefs and expectations about a specific group and its members