Perfect Competition
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Deciding factors of Perfect Competition.
Homogenous Products
Low barriers to entry
Many firms in a market
Perfect information
Sellers are price takers
Many small buyers and sellers
Homogenous Products.
All products are perfect substitutes (identical products)
eg: One apple and another apple
No Barries to entry.
Firms are freely able to enter a market and leave a market without constraints and there are no economies of scale, no sunk costs and no patents.
Many firms in a market.
There are many firms in a market instead of a single dominant firm such as a monopoly.
Perfect Information.
Buyers are fully informed and aware of all products.
Buyers know all prices of all firms and producers know how other producers produce their goods
Sellers are price takers.
The sellers set the price.
Many small buyers and sellers.
All sellers have a small market share and are not dominant in the market.
What is a market?
Has many firms.
What if we move the price up?
Demand decreases to 0 as there are many other firms selling at that price and demand is Perfectly Elastic and consumers with their perfection information will be aware of this and go to the other producers.
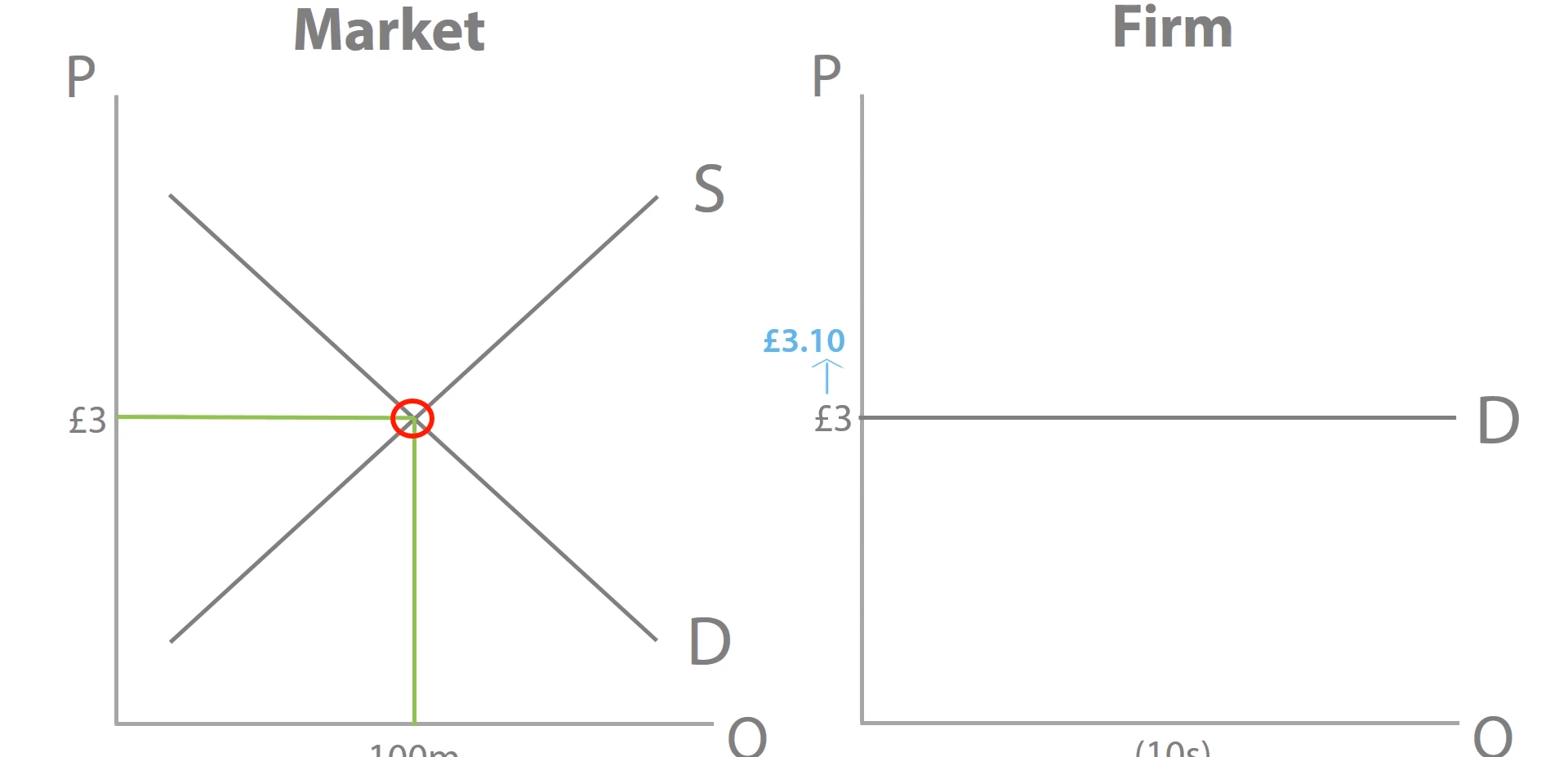
In perfectly competitive markets, firms are price takers, what is this?
They take the market price and sell for that price
Where is profit maximisation?
Where MC = MR
(Marginal Costs are equivalent to Marginal Revenue)
Where is Supernormal profit
Above the AC curve
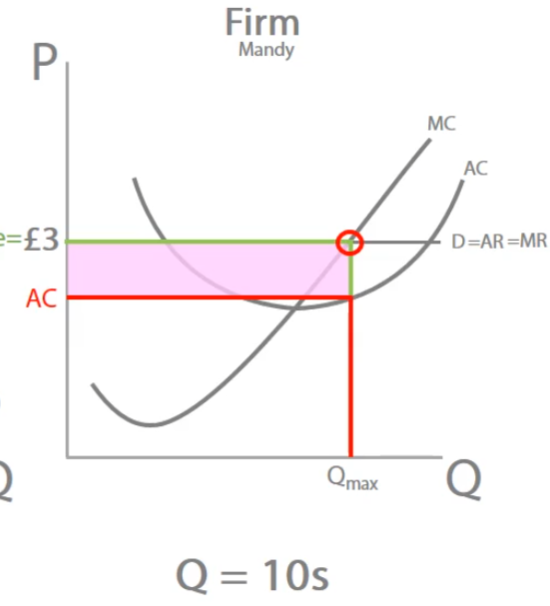
What is Supernormal profit
When the demand is higher than the average costs
Where is Allocative efficiency?
P = MC. When firms are allocating resources according to the consumers demand.
Where is Productive Efficiency?
When the firms operates at the lowest point of the Average Costs curve.