OZ 3: How is Ozone formed in the atmosphere?
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
bond fission
bond breaking
What does bond fission involve?
redistribution of electrons in the covalent bond
What are two methods of bond fission?
heterolytic
homolytic
heterolytic fission
both of the shared electrons go to one of the atoms
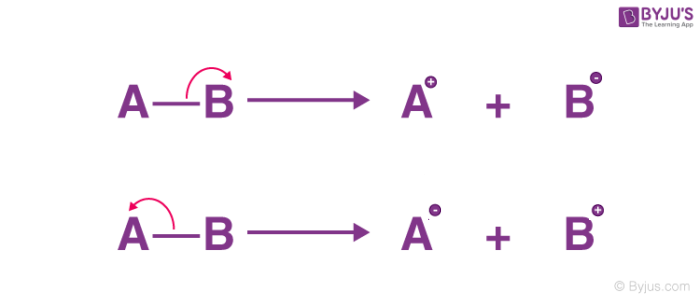
both of the shared electrons go to one of the atoms
heterolytic fission
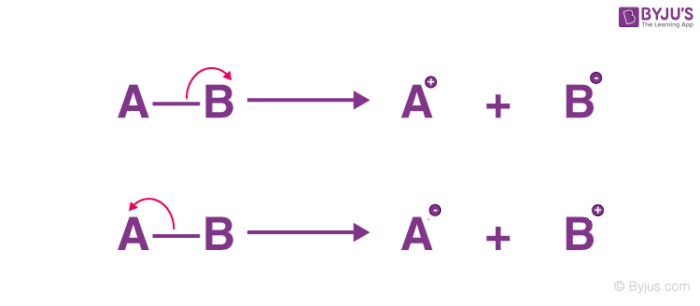
Heterolytic bond fission is common in __________ bonds
polar
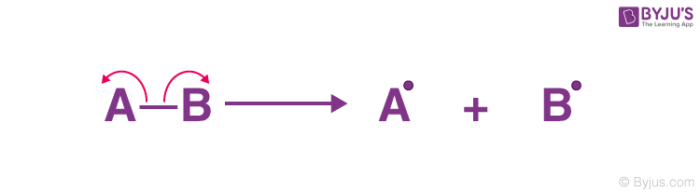
Homolytic fission
shared electrons go to one atom each
shared electrons go to one atom each
Homolytic fission
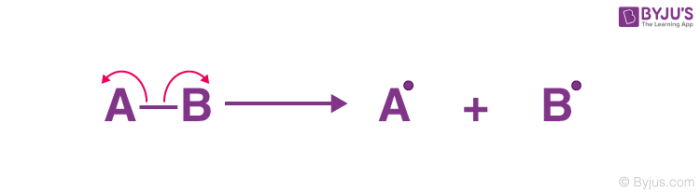
unpaired electrons have a ________ _________ to pair up again with an __________ from another substance
strong tendency
electron
Radicals are commonly formed when bonds are ________ but _________ can also break like this especially in ________ state and presence of _________
non-polar
polar
gas
light
amount of energy taken for bond fission depends on the
bond enthalpy
Equation for formation of ozone
O + O₂ —→ O₃
What is one way to make oxygen atoms?
dissociating dioxygen molecules
Where does the high energy for dissociating oxygen molecules come from?
UV radiation or electric charge
Why can you smell sharp odour of ozone near photocopiers, UV lamps or electric motors?
electric dischargers make dioxygen molecules in the air dissociate
In the troposphere oxygen atoms are produced by the action of _________ on the pollutant gas ____________ ____________
sunlight
nitrogen dioxide
In the stratosphere, oxygen atoms are formed by the ___________ of __________ molecules when _______ radiation of the right _____________ is absorbed
photodissociation
dioxygen
UV
frequency
Reaction for breakdown of dioxygen in the stratosphere
O₂ + hv → O + O
Chain reaction after dioxygen molecules have been dissociated in stratosphere
O + O₂ → O₃
O + O → O₂
O + O₃ → 2O₂
Reaction for the break down of ozone when UV radiation is absorbed
O₃ + hv → O₂ + O
What is radical polymerization?
A process where radicals initiate polymer chain growth
What stops radical polymerization?
Termination reactions or depletion of monomers
What type of reaction is combustion?
A radical chain reaction
What is the role of flame-retardant additives?
They reduce radical propagation to prevent auto-ignition
What effect do radicals have on DNA?
They cause DNA cross-linking, which can lead to cancer
How do radicals affect fats and proteins?
They cause cross-linking, leading to wrinkles
How can radicals contribute to heart disease?
They oxidize low-density lipoproteins, leading to arterial plaques
How do antioxidants help prevent radical damage?
They donate electrons to radicals without becoming unstable
Give an example of an antioxidant.
Vitamin C
Why are radicals reactive?
they have unfilled outer shells
Reaction of Cl with H2
HCl + H
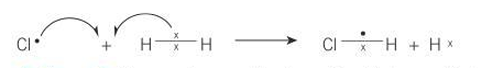
What does a curly electron indicate?
movement of an electron

half-headed curly arrow
one electron

full-headed curly arrow
pair of electrons
tail
where electron starts
head
where electron ends
3 parts of a radical chain reaction
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
Where are radicals found in initiation?
product side
Where are radicals found in propagation?
both sides
Where are radicals found in termination?
reactant side
Alkanes will react with ___________ in the presence of _________
halogens
light