Coaching ( + book week 6)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
What is the working alliance in coaching? What contributes to outcomes of a w-a?
\~ the equivalent to the therapeutic relationship in therapy
\
__three elements of w-a__
i. __goals__ \~ is the goal given by the coachee or by the coach?
ii. __tasks__ \~ actions, activities, tools
iii. __bond__ \~ trust, respect
\
→ scoring higher on w-a correlates w/better outcomes of the coaching
\
__three elements of w-a__
i. __goals__ \~ is the goal given by the coachee or by the coach?
ii. __tasks__ \~ actions, activities, tools
iii. __bond__ \~ trust, respect
\
→ scoring higher on w-a correlates w/better outcomes of the coaching
2
New cards
What are the four elements contributing to successful intervention/effectiveness of coaching/therapy?
i. client variables + extra-therapeutic events (40%)
ii. expectancy and placebo effects (15%)
iii. therapeutic relationship (30%)
iv. models and techniques (15%)
\
→ therapeutic relationship can account for quite a piece of the effectiveness => idea is that it is the same for coaching
ii. expectancy and placebo effects (15%)
iii. therapeutic relationship (30%)
iv. models and techniques (15%)
\
→ therapeutic relationship can account for quite a piece of the effectiveness => idea is that it is the same for coaching
3
New cards
Is it more important what the coach or the coachee think about the working alliance?
__choachee__ \~ when they perceive the w-a as higher/better, their self-efficacy, goal attainment, self-reflection & insight are better
\
→ only their perception is linked to the outcomes (coach needs to know how they perceive it so that they can work w/it)
\
→ only their perception is linked to the outcomes (coach needs to know how they perceive it so that they can work w/it)
4
New cards
What is the WAI-S questionnaire?
\~ questionnaire about how the coachee perceives the working alliance (questions measuring both tasks and bond)
\
→ Working Alliance Inventory - Short
\
→ Working Alliance Inventory - Short
5
New cards
How can working alliance be improved?
not yet so clear in research
\
\~ discuss the goals again, the tasks, &/or what could increase the trust between them
\
\~ discuss the goals again, the tasks, &/or what could increase the trust between them
6
New cards
What is coaching?
\~ many definitions w/some __shared aspects__
i. one-on-one relationship (also possible to do team coaching though)
ii. aimed at non-clinical population
iii. learning and change (behavioural change)
iv. increasing self-awareness
v. improved performance
vi. non-directive (coach is a facilitator, coachee decides)
i. one-on-one relationship (also possible to do team coaching though)
ii. aimed at non-clinical population
iii. learning and change (behavioural change)
iv. increasing self-awareness
v. improved performance
vi. non-directive (coach is a facilitator, coachee decides)
7
New cards
What is coaching not and why?
__**is not**__
i. __advising__ \~ has expertise and knowledge about a topic and gives advice based on that → comes up w/a solution => a coach doesn’t do that
ii. __mentoring__ \~ expertise about a topic that they share w/someone new to it, provides guidance
iii. __therapy__ \~ aimed at more severe psychological problems (sometimes said that therapy is aimed more at the past and coaching at the future → depends on what kind of therapy)
i. __advising__ \~ has expertise and knowledge about a topic and gives advice based on that → comes up w/a solution => a coach doesn’t do that
ii. __mentoring__ \~ expertise about a topic that they share w/someone new to it, provides guidance
iii. __therapy__ \~ aimed at more severe psychological problems (sometimes said that therapy is aimed more at the past and coaching at the future → depends on what kind of therapy)
8
New cards
What are the competencies one needs to become a coach?
i. self-insight
ii. focus on self-development
iii. handling expectations (should be able to explain to the coachee what they can expect from the coaching)
iv. working alliance \~ working on the relationship
v. providing insight so that the coachee can discover the solution themselves
vi. goal and action focused
vii. use (ideally evidence based) methods and techniques
viii. evaluation of their coaching
ii. focus on self-development
iii. handling expectations (should be able to explain to the coachee what they can expect from the coaching)
iv. working alliance \~ working on the relationship
v. providing insight so that the coachee can discover the solution themselves
vi. goal and action focused
vii. use (ideally evidence based) methods and techniques
viii. evaluation of their coaching
9
New cards
How do companies select a coach?
\~ don’t really look at whether or not they are certified, rather on their referrals, recommendations and experience
10
New cards
How do you find/become a coach?
__have to have/be__
i. received a coaching training
ii. supervision/intervision sessions
iii. qualification for competencies
iv. bound ethical standards
\
→ professional organisations for coaching (can help you find and/or register a coach)
\
i. received a coaching training
ii. supervision/intervision sessions
iii. qualification for competencies
iv. bound ethical standards
\
→ professional organisations for coaching (can help you find and/or register a coach)
\
11
New cards
What is solution-focused coaching?
\~ rather than focusing on the problem, the focus should be on the solution (focusing on the problem doesn’t make ppl feel better, focusing on small things that are going well/solutions leads to better performance and improvement of the situation)
\
→ derived from solution-focused therapy
\
→ __solution-focused questions__ (what have you already done that has helped you improve, how come this situation is getting worse, etc.) vs __problem-focused questions__ (how long have you had this problem e.g.)
\
→ solution focused que increase self-efficacy and action planning
\
→ derived from solution-focused therapy
\
→ __solution-focused questions__ (what have you already done that has helped you improve, how come this situation is getting worse, etc.) vs __problem-focused questions__ (how long have you had this problem e.g.)
\
→ solution focused que increase self-efficacy and action planning
12
New cards
What is rational emotional behaviour coaching?
\~ thoughts and thinking are important in shaping behaviour (non-constructive thoughts can be replaced by more rational and helpful thoughts to help us get to goals)
\
→ helpful in improving quality of life or health behaviour
\
\
\
→ helpful in improving quality of life or health behaviour
\
\
13
New cards
What is acceptance and commitment training (ACT)?
\~ acceptance of thoughts for what they are (mindfulness and being aware of our values are important aspects)
\
→ can lead to decrease of burnout and stress rates
\
→ can lead to decrease of burnout and stress rates
14
New cards
What is motivational interviewing?
\~ exploring the advantages and disadvantages of a specific behaviour and of the change of that behaviour
\
→ effective esp w/behavioural change esp when the behaviour is not very beneficial for the person but they still do it (e.g. smoking)
\
→ effective esp w/behavioural change esp when the behaviour is not very beneficial for the person but they still do it (e.g. smoking)
15
New cards
Why do organisations coach employees?
a. want for better performance
b. improvement of job satisfaction
c. improvement of leadership and management skills
b. improvement of job satisfaction
c. improvement of leadership and management skills
16
New cards
What are the different types of coachnig?
a. __internal vs external coaching__
- does it happen between people from the company or is there an external party doing the coaching?
\
b. __team coaching__
- coach coaching a group of ppl who share goals
\
c. __peer coaching__
- colleagues coaching each other
\
d. __manager as a coach__
- for their own employees
- can be problematic since they also have to evaluate their employees (which coaches do not do plus there is no such hierarchy in the coaching relationship) → can lead to less disclosure by the employee
- more coaching skills in managers, however, showed to lead to better job satisfaction and higher job commitment
\
e. __coaching culture__
- employees trained to become a coach (usually do not coach a colleague but smb from another department e.g.)
- does it happen between people from the company or is there an external party doing the coaching?
\
b. __team coaching__
- coach coaching a group of ppl who share goals
\
c. __peer coaching__
- colleagues coaching each other
\
d. __manager as a coach__
- for their own employees
- can be problematic since they also have to evaluate their employees (which coaches do not do plus there is no such hierarchy in the coaching relationship) → can lead to less disclosure by the employee
- more coaching skills in managers, however, showed to lead to better job satisfaction and higher job commitment
\
e. __coaching culture__
- employees trained to become a coach (usually do not coach a colleague but smb from another department e.g.)
17
New cards
What is coaching culture?
\~ use of coaching in a more holistic form, making use of all of the different types of coaching not only once in a while but regularly
18
New cards
What is the effectiveness of coaching?
__effectiveness__ → increase in self-efficacy, goal attainment, resilience, well-being, and leadership skills (long-term outcomes)
\
\
\
\
19
New cards
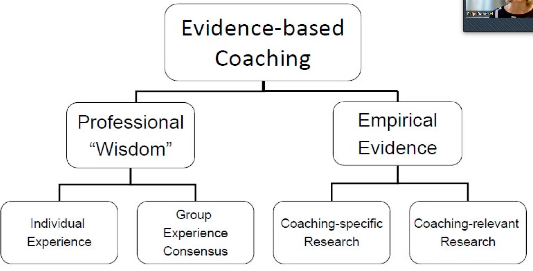
What is evidence-based coaching?
\~ derived from evidence-based medicine, with the idea that coaches make the best possible decisions based on the best available knowledge at that time
\
→ uses evidence from different topics and fields (combines the experience of the coach w/the empirical evidence)
\
→ uses evidence from different topics and fields (combines the experience of the coach w/the empirical evidence)
20
New cards
Is coaching proved to increase performance/decrease stress/increase satisfaction or self-awareness?
\~ no, scientifically there are contradicting findings (e.g. because measuring performance is difficult)
21
New cards
what is a job analysis and what are the different aspects of it?
\~ method used to describe jobs and the personal attributes necessary for doing the job
\
i. systematic procedure \~ specified in advance and stuck to
ii. describing the components of the job rather than it as a whole
iii. leads to a report
\
i. systematic procedure \~ specified in advance and stuck to
ii. describing the components of the job rather than it as a whole
iii. leads to a report
22
New cards
How are job-oriented and person-oriented approaches different?
\~ __job-oriented__ focuses on the nature of the job, describing the tasks and their characteristics while __person-oriented__ approach deals with the KSAOs needed to successfully do the job
\
__five levels of tasks__ (hierarchical from broadest to narrowest)
i. position
ii. duty
iii. tasks
iv. activities
v. elements
\
__five levels of tasks__ (hierarchical from broadest to narrowest)
i. position
ii. duty
iii. tasks
iv. activities
v. elements
23
New cards
What is a competency system?
\~ rewarding emplyoees based on getting the knowledge and skills needed to improve performance and/or to be promoted
24
New cards
How is performance appraised?
\~ criterion(s) are developed (what are the major components of the job that need to be evaluated?) → assessed based on these
\
__critical incidents__ \~ part of the behaviour-focused perf. appraisal → collect instances of specific behaviour representing different levels of job performance
\
__critical incidents__ \~ part of the behaviour-focused perf. appraisal → collect instances of specific behaviour representing different levels of job performance
25
New cards
Who provides information for job analysis? Who is a SME?
\~ job analysts, job incumbents, supervisors, or trained observers
\
SME \~ subject matter expert (incumbent or supervisor)
\
SME \~ subject matter expert (incumbent or supervisor)
26
New cards
What are the methods of job analysis?
a. __Job Components Inventory (JCI)__
- list of KSAOs to tell whether a person is suited for a job and/or if they need additional training
- __five components__ → use of tools and equipment, perceptual and physical requirements, mathematics, communication, decision making and responsibility
\
b. __Occupational Information Network (O*NET)__
- computer-based, lists KSAOs needed to perform the job and characteristics of job tasks
- __six domains__ → experience requirements, worker requirements, worker characteristics, occupation requirements, occupation specific information, and occupation characteristics
\
c. __Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ)__
- used to analyse and compare different jobs on common set of dimensions/KSAOs
- six main domains further divided into subdomains
\
d. __Task Inventory__
- questionnaire listing specific tasks relating to a job w/one or more rating scales for each task
\
e. __Combination Job Analysis Method (C-JAM)__
- makes use of questionnaires and interviews to get a detailed picture of the KSAOs of the job/tasks performed
- list of KSAOs to tell whether a person is suited for a job and/or if they need additional training
- __five components__ → use of tools and equipment, perceptual and physical requirements, mathematics, communication, decision making and responsibility
\
b. __Occupational Information Network (O*NET)__
- computer-based, lists KSAOs needed to perform the job and characteristics of job tasks
- __six domains__ → experience requirements, worker requirements, worker characteristics, occupation requirements, occupation specific information, and occupation characteristics
\
c. __Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ)__
- used to analyse and compare different jobs on common set of dimensions/KSAOs
- six main domains further divided into subdomains
\
d. __Task Inventory__
- questionnaire listing specific tasks relating to a job w/one or more rating scales for each task
\
e. __Combination Job Analysis Method (C-JAM)__
- makes use of questionnaires and interviews to get a detailed picture of the KSAOs of the job/tasks performed
27
New cards
How are job evaluation and job analysis different?
\~ job evaluation is different in that it determines the salaries for different jobs in a mathematical way based on the information that is collected in job analysis (kind of, simplified)
\
__point method__ \~ __compensable factors__ given by a panel of ppl → panel judges the degree to which each job has these compensable factors → points are summed (\~ the higher the total score, the higher the salary should be) → plot the actual salaries against these points to see if there is a discrepancy (if it is fair, plot should be straight)
\
__point method__ \~ __compensable factors__ given by a panel of ppl → panel judges the degree to which each job has these compensable factors → points are summed (\~ the higher the total score, the higher the salary should be) → plot the actual salaries against these points to see if there is a discrepancy (if it is fair, plot should be straight)
28
New cards
What is comparable worth?
\~ different but comparable jobs should be paid the same
29
New cards
what is a merit pay system?
\~ raises are tied to the job performance
30
New cards
how are theoretical and actual criterions different?
__theoretical__ \~ theoretical construct of what a good performance is
\
__actual__ \~ how the theoretical construct is assessed, often giving only an estimate due to
i. __criterion contamination__ (part of the actual criterion reflecting smth else)
ii. __criterion deficiency__ (actual criterion inadequately covering the theoretical one \~ content validity)
iii. __criterion relevance__ (to what extent does the actual one assess the theoretical one \~ construct validity)
\
\
\
__actual__ \~ how the theoretical construct is assessed, often giving only an estimate due to
i. __criterion contamination__ (part of the actual criterion reflecting smth else)
ii. __criterion deficiency__ (actual criterion inadequately covering the theoretical one \~ content validity)
iii. __criterion relevance__ (to what extent does the actual one assess the theoretical one \~ construct validity)
\
\
31
New cards
is performance stable over time?
\~no, best performers do not necessarily stay the best over time
32
New cards
what is contextual performance?
\~ extra voluntary things employees do to benefit the organisation/co-workers
33
New cards
How are subjective and objective job performance measures different?
__subjective__ \~ employees job performance is rated by ppl who should be knowledgeable about it
i. *halo effect* → giving the same rating across the dimensions based on the first one(s) even though there are performance discrepancies
ii. *true halo* → when a person actually performs the same across the dimensions
\
__objective__ \~ counts of employee behaviour (absences/accidents/incidents/…) and the results of their behaviour (productivity)
i. *halo effect* → giving the same rating across the dimensions based on the first one(s) even though there are performance discrepancies
ii. *true halo* → when a person actually performs the same across the dimensions
\
__objective__ \~ counts of employee behaviour (absences/accidents/incidents/…) and the results of their behaviour (productivity)
34
New cards
What are the different errors raters (can) make?
i. __distributional errors__ \~ tendency to rate everyone the same
ii. __latency errors__ \~ when everyone is rated at the good end
iii.__severity errors__ \~ everyone rated at the unfavourable end
iv. __central tendency errors__ \~ everyone rated around the middle
\
__RET__ → rater error training (knowing errors & trying to avoid them)
__Frame of reference training__ \~ understanding of the rating task
ii. __latency errors__ \~ when everyone is rated at the good end
iii.__severity errors__ \~ everyone rated at the unfavourable end
iv. __central tendency errors__ \~ everyone rated around the middle
\
__RET__ → rater error training (knowing errors & trying to avoid them)
__Frame of reference training__ \~ understanding of the rating task
35
New cards
what are integrity tests?
\~ predict whether an employee will engage in counterproductive/dishonest behaviour on the job
\
a. __overt integrity test__ → attitudes and behaviour via obvious assessment of honesty and integrity
b. __personality integrity test__ → personality characteristics predictive of counterproductive behaviour w/o disclosing the purpose
\
a. __overt integrity test__ → attitudes and behaviour via obvious assessment of honesty and integrity
b. __personality integrity test__ → personality characteristics predictive of counterproductive behaviour w/o disclosing the purpose
36
New cards
What is a self-directed search test?
\~ associates six personality types (realistic, investigative, artistic, social, enterprising, and conventional) to a particular family of occupations
37
New cards
What is a work sample?
\~ assessment requiring ppl to show how well they can perform a task under standardised conditions
38
New cards
How are in-basket exercise and leaderless group exercise different?
\~__in-basket__ requires the individual to pretend the situation is real and deal w/it appropriately while in __leaderless group__, people are given a problem to solve (either competitive or cooperative)
39
New cards
what are the four factors that attract people to jobs?
i. perceived fit between the job and the person
ii. anticipated treatment by the organisation
iii. anticipated quality of relationships w/coworkers
iv. prestige and reputation of the organisation
ii. anticipated treatment by the organisation
iii. anticipated quality of relationships w/coworkers
iv. prestige and reputation of the organisation